AP Psych Unit 1B Test
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
Active consciousness
planning and decision making
Passive consciousness
daydreaming and sleeping
naturally occurring altered states of consciousness
sleeping, dreaming, and daydreaming
naturally induced altered states of consciousness
hypnosis, meditation, and drug-altered consciousness
Cognitive neuroscience
relationship between the brain and cognitive processes
Duel processing
two neural pathways- conscious and unconscious
Parallel processing
the brain’s ability to process multiple pieces of information at the same time
Sequential processing
information is processed in a step by step order
Sleep
we are unconscious, but our brain is still active
Circadian rhythm
24 hour cycle of biological functioning
Jet lag
disorientation from traveling across different time zones, which disrupts your circadian rhythm
EEG patterns
Brain wave patterns categorized by frequency
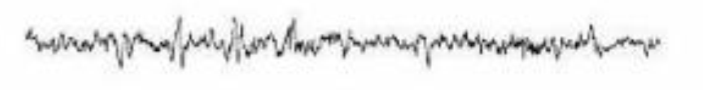
Alpha waves
Sleep stage 1- awake and sleepy
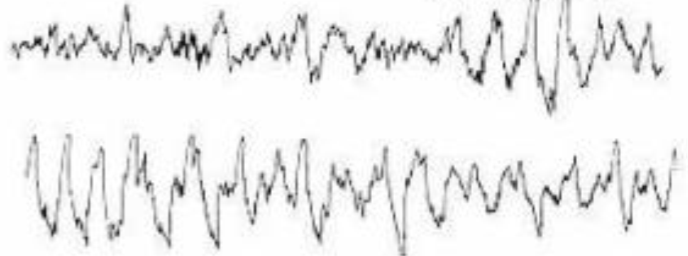
Delta waves
Stages 3+4- deep sleep
NREM
nonREM, anything that is not the REM sleep stage
Sleep deprivation studies
William Dement and Randy Gardner
Effects of sleep loss
difficulty concentrating, fatigue, irritibilty, unhappiness, obesity, high blood pressure, poor motor performance
Ghrelin
stimulates hunger
Cortisol
hormone that plays a role in the body’s stress response
Disrupting gene expression
altering the process of creating a protein from a gene
Limbic system dominance w/food
the limbic system controls the emotional aspect of food
Microsleep
when there are sudden shifts between wakefulness and sleep
Hallucinations
the perception of something not present, can happen from lack of sleep
Hypnagogic sensations
vivid dream like experiences that happen in the transition from wakefulness to sleep. Can include any of the 5 senses

REM
Beta waves, dreams and full body paralysis (except eyes) happen
REM rebound
when the body compensates for sleep loss with longer periods of REM sleep
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
the brain’s internal clock
Why do we sleep?
safety, restorative value, memory, creativity, growth
Dream
involuntary sequences of mental imagery that happen during REM sleep
What we dream
depends on our waking experiences
Why we dream
Wish fulfillment, information processing, psychological function
physiological function of dreaming
helps the brain process emotions, consolidate memories, and maintain healthy brain function
activation synthesis theory
dreams are the brain’s attempt to make sense of random neural activity while we sleep
consolidation (information processing theory)
dreams help store and organize information from the day into long term memory
cognitive development theory
dreams reflect the dreamer’s level of cognitive and emotional development
insomnia
difficulty falling or staying asleep
narcolepsy
a sleep disorder causing sudden, uncontrollable sleep attacks
REM sleep behavior disorder
acting out dreams due to lack of normal muscle paralysis during REM sleep
Sleep apnea
repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep
somnambulism (sleepwalking)
walking or performing activities while sleeping
Sensation
the process of detecting physical energy through sensory organs
perception
the brain’s organization and interpretation of sensory information
sensory receptor
specialized cells that detect sensory stimuli (like light, sound, touch)
bottom up processing
perception starting from sensory input and building up to recognition
top down processing
perception guided by experience, expectations, or prior knowledge
psychophysics
study of how physical energy relates to psychological experience
absolute threshold
the smallest stimulus detected 50% of the time
signal detection theory
predicts when we will detect weak signals amid background noise
subliminal
below the level of conscious awareness
difference threshold (just noticeable difference)
the smallest change in a stimulus that can be detected
weber’s law
to notice a difference, stimuli must differ by a constant proportion
vision wavelengths
distance between light waves- determines color (hue)
hue
the color we see, determined by wavelength
intensity
brightness, determined by wave amplitude
cornea
outer covering that blends light into the eye
pupil
opening in the eye that lets light enter
iris
colored muscle controlling the size of the pupil
retina
light sensitive layer at the back of the eye where images form
blind spot
area with no receptors where the optic nerve leaves the eye
visual (optic) nerve
carries visual information from retina to brain
Lens
focuses light on the retina by changing shape
Accommodation
process by which the lens shape changes to focus on near/far objects
nearsightedness
can see only near objects clearly
farsightedness
can see only far objects clearly
Fovea
central part of the retina with sharpest vision
photoreceptors
light detecting cells
transduction
converting sensory energy into neural impulses
rods
detect dim light, black, and white
cones
detect color and fine detail
Young-Helmholz trichromatic theory
we see color using three cone types: red, green, blue
opponent process theory
We see colors in opposing pairs
feature detectors
neurons responding to specific features
Afterimages
Visual impressions that remain the same after the stimulus is gone
Ganglion cells
neurons in the retina that form the optic nerve
dichromatism
color blindness where only two cone types function
monochromatism
complete color blindness
prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces
blindsight
ability to respond to visual stimuli without conscious seeing
parallel processing
processing multiple aspects of vision at once
hearing wavelengths
distance between sound waves
frequency
number of waves per second
Pitch
How high or low a sound is
Amplitude
Height of sound waves; determines loudness
Middle ear
amplifies sound
cochlea
fluid filled inner ear structure where sound waves trigger neural impulses
Inner ear
contains cochlea and canals for hearing and balance
Place theory
different pitches stimulate different places on a cochlea’s membrane
Volley theory
neurons fire in rapid alternation to match high frequencies
Frequency theory
pitch is determined by the frequency of neural impulses
conduction deafness
hearing loss from damage to outer or middle ear
Sensorineural deafness
hearing loss from damage to inner ear or auditory nerve
cochlear implant
device that converts sounds to electrical signals to stimulate the auditory nerve
sound localization
ability to locate a sound
olfactory system
sense of smell
thalamus
brain’s sensory relay (smell bypasses)
Pheromones
chemical signals affecting behavior in other members of the species
Gustation
sense of taste
Taste receptors
cells on the taste buds that detect flavor
umami
savory taste