Sci Rev, Enlightenment, American Revolution
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Scientific Revolution
A major change in European thought, starting in the mid-1500s, in which the study of the natural world began to be characterized by careful observation and the questioning of accepted beliefs.

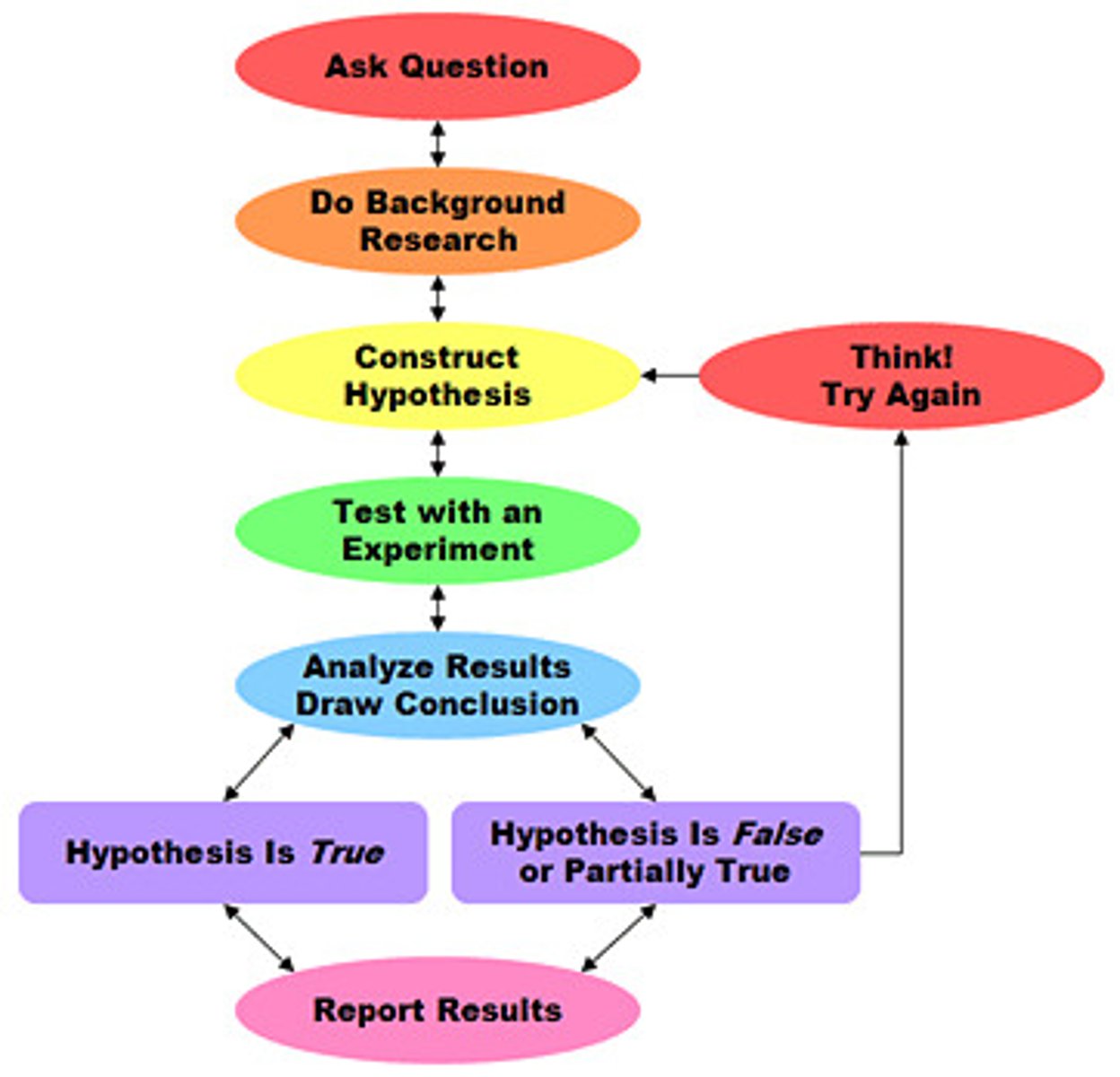
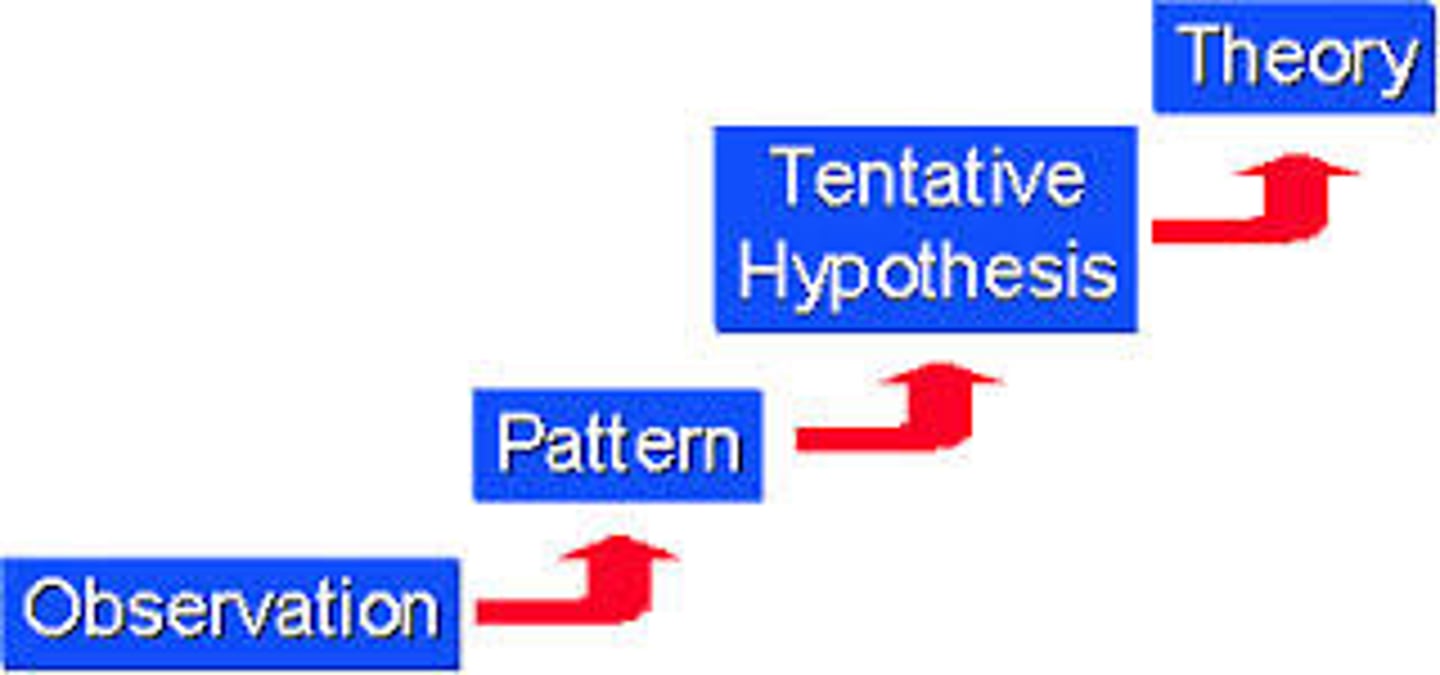
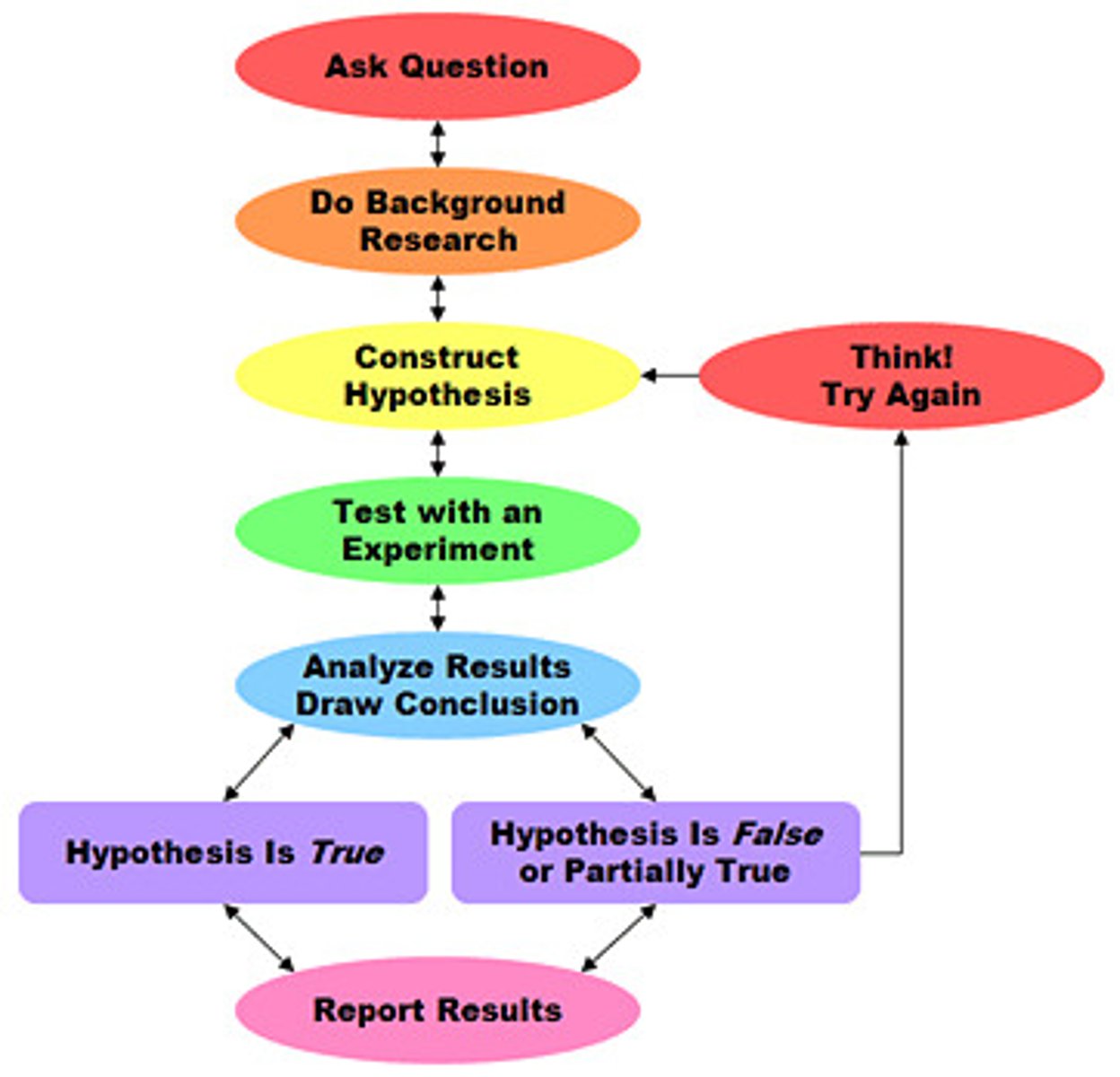
scientific method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions.
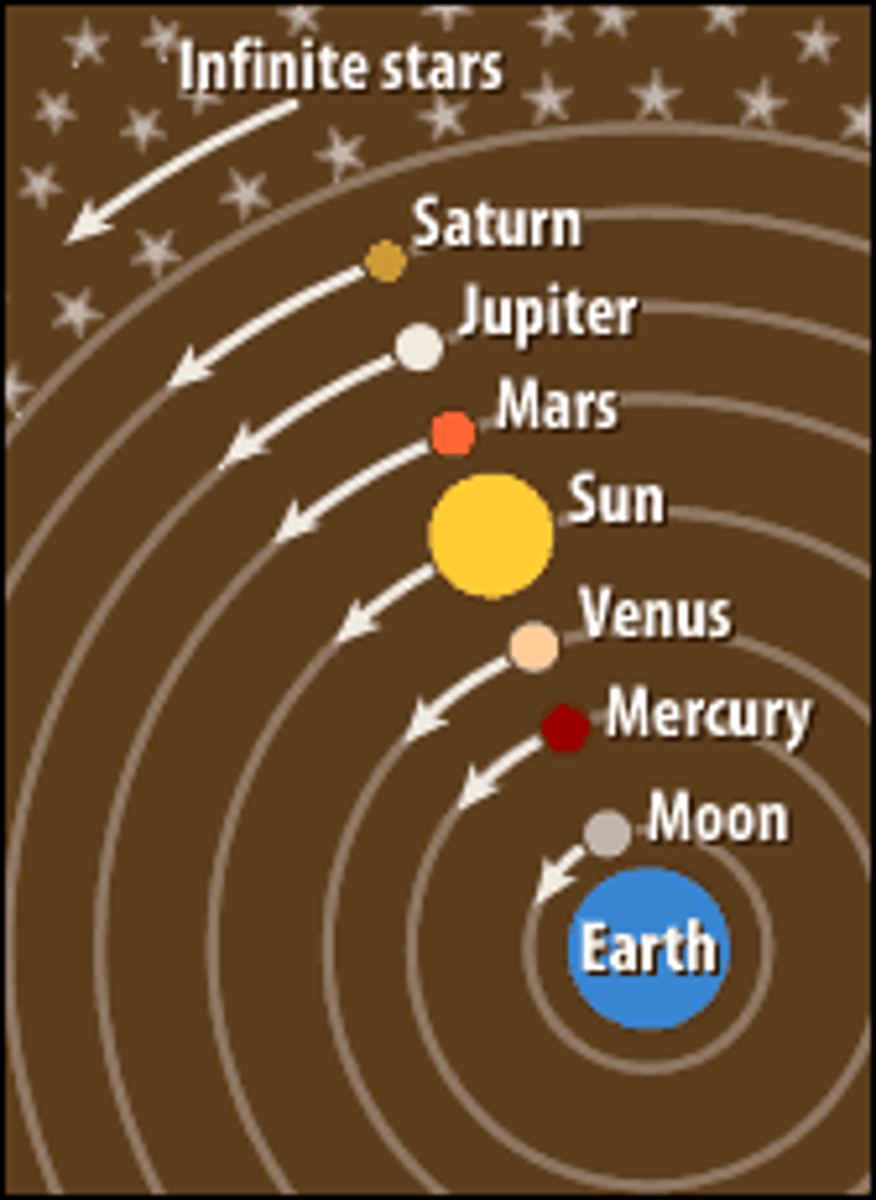
heliocentric model
Model that was proposed by Copernicus that put the Sun at the center of the universe.
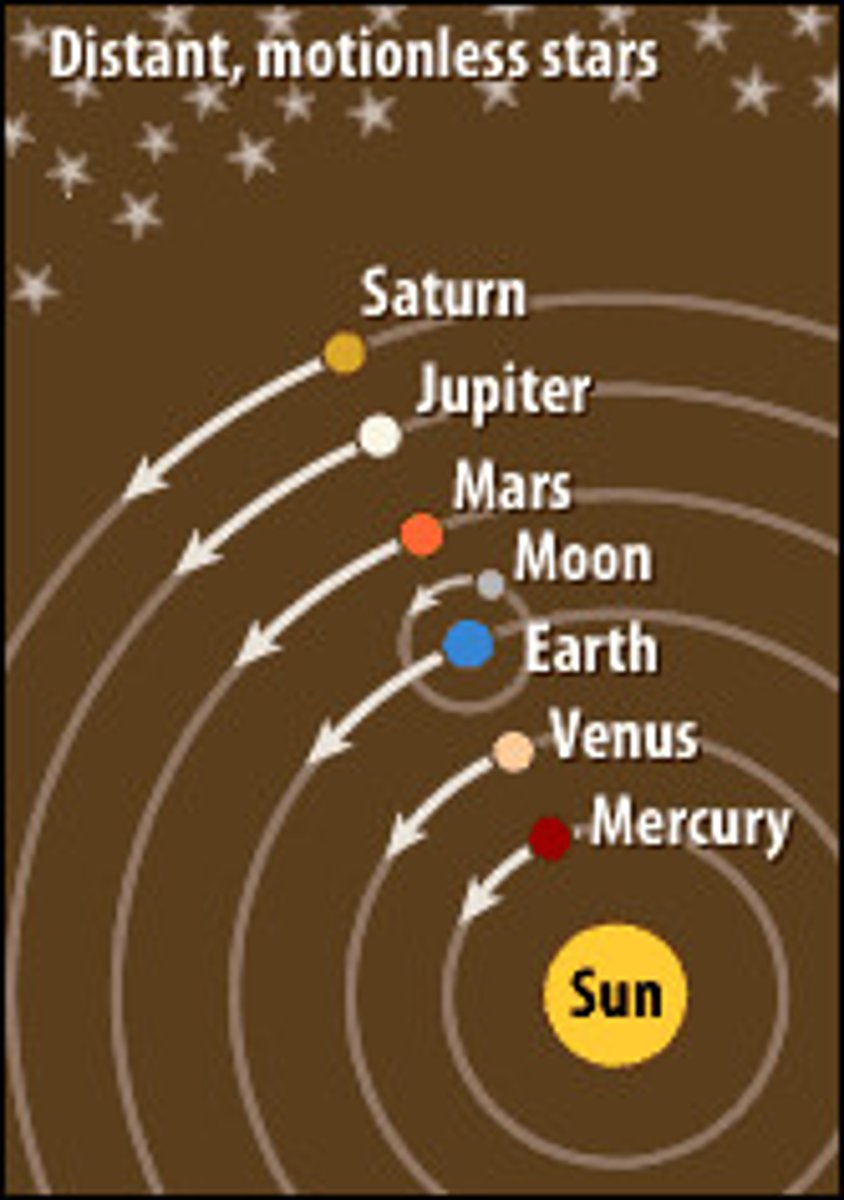
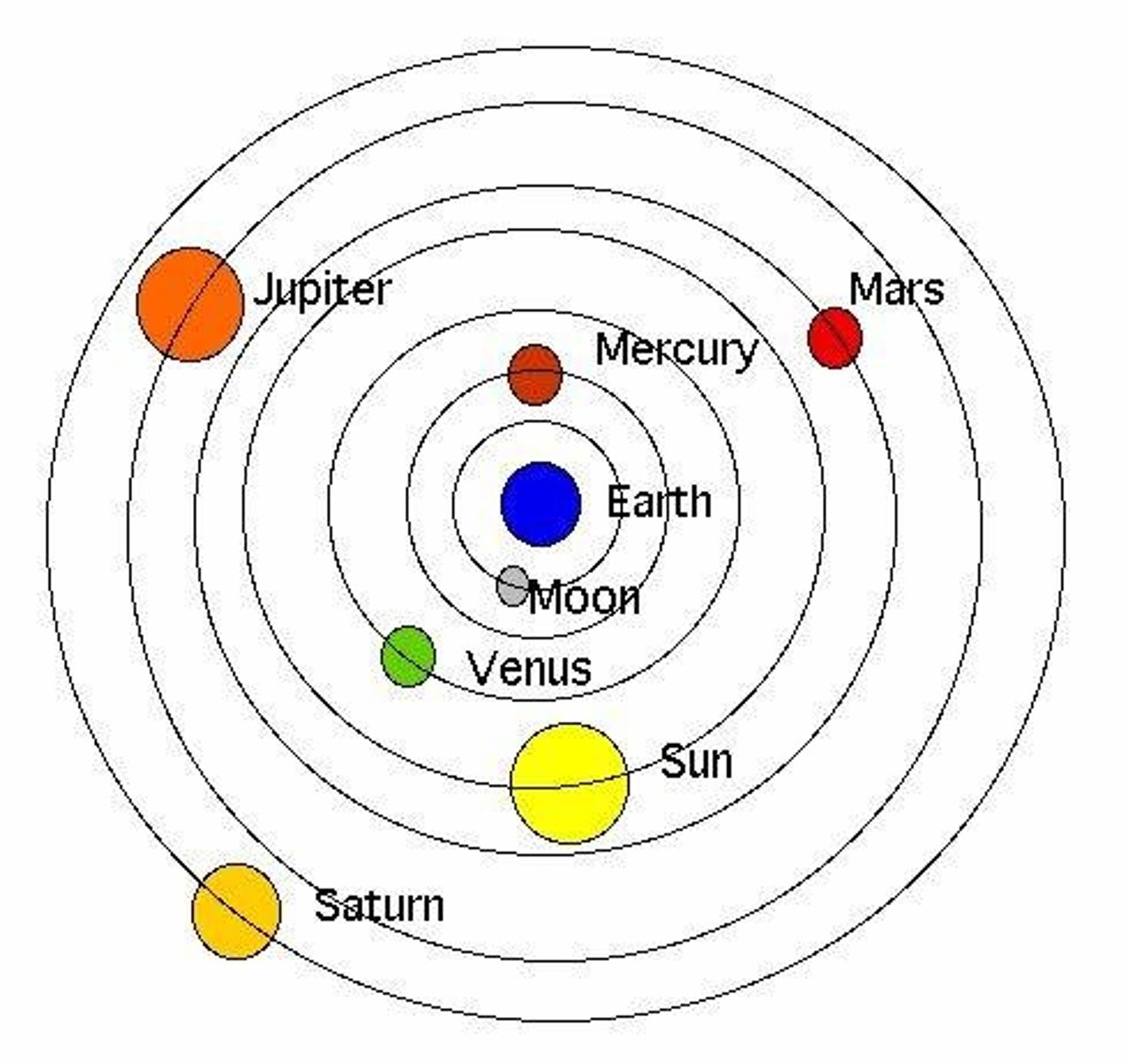
geocentric model
Model proposed by Ptolemy that places the Earth at the center of the universe.
absolute monarchy
A system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power given by God or another diety; this person, in theory, controls everything.

Enlightenment
A philosophical movement which started in Europe in the 1700's. It emphasized reason and the scientific method. Writers of the enlightenment tended to focus on government, ethics, and science, rather than on imagination, emotions, or religion. Many members of the Enlightenment rejected traditional religious beliefs which holds that the world is run by natural laws without the direct intervention of God.

rationalism
belief that knowledge is gained by thinking things through using reason

inductive reasoning
A method of reasoning in which a number of specific facts or examples are used to make a generalization.
heliocentric theory
the idea that the earth and the other planets revolve around the sun.
geocentric theory
Earth is the center of the Universe
natural rights
Life, Liberty, and Property

tolerance
allowing other to hold beliefs that are different from one's own

Scientific revolution led to
new efforts to use reason to improve human life

Enlightenment thinkers had
new ideas about natural right and government

Philosophers of enlightenment wanted
to improve social and economic life
Enlightenment is also called the…
Age of Reason

Legacy of Scientific Revolution
Development of new tools and instruments to make the precise observations that the scientific method required. Improvements in medicine and the study of the human body. Discoveries in chemistry and other fields of science that helped improve the quality of life.
Legacy of the Enlightenment
Challenged the beliefs and ideas of society. Examined the divine rights of monarchs, the union of church and state, and the unequal social classes and realised they needed reform. Influenced progress and the growth of knowledge. Urged the end of slavery and argued for greater social equality. The importance of the individual and their rights became important.
Scientific Revolution
discoveries by astronomers, physicists and mathematicians changed the way that the Europeans viewed the world

Scientific Method
direct observation
Isaac Newton
Gravity
Calculus
Optics

Copernicus
Heliocentric theory

Galileo
Laws of motion
Inertia
Proved Copernicus right using the telescope

Enlightenment
Age of Reason - intellectual movement

Voltaire
Strong advocate for personal freedoms - especially freedom of speech. Used satire and wit to make his points. "I do not agree with what you are saying; but will fight to the death for your right to say it."

Descartes
I think; therefore, I am.
Rationalism

Locke
Felt men should overthrow governments that do not protect their natural rights. Felt that all power of government derives from the consent of those being governed.

Hobbes
Felt man is "nasty and brutish" and should be controlled by an absolute leader

Rousseau
One of only a few of the philosophes who had respect for the common man.
Published Emile and The Social Contract saying that human nature is essentially good and moral. He said institutions like governments, churches and schools corrupted the goodness. General Will! He felt men should have control to create govts. that would protect human rights.

Adam Smith
wrote A Wealth of Nations which promoted capitalism

Diderot
compiled an Encyclopedia of knowledge

Enlightened Despots
Monarchs who were influenced by the natural rights of the Enlightenment
Joseph II of Austria
Made many reforms to lesson the power and prestige of the nobles and established church.

Frederick the Great of Prussia
Enlightened Despot - called himself the First Citizen of Prussia

Catherine the Great of Russia
Enlightened Despot who had dictionary of Russian language written
But after Pugachev Rebellion did not free the serfs

Tabula Rasa
our mind is a blank slate at birth and our experiences build our knowledge base

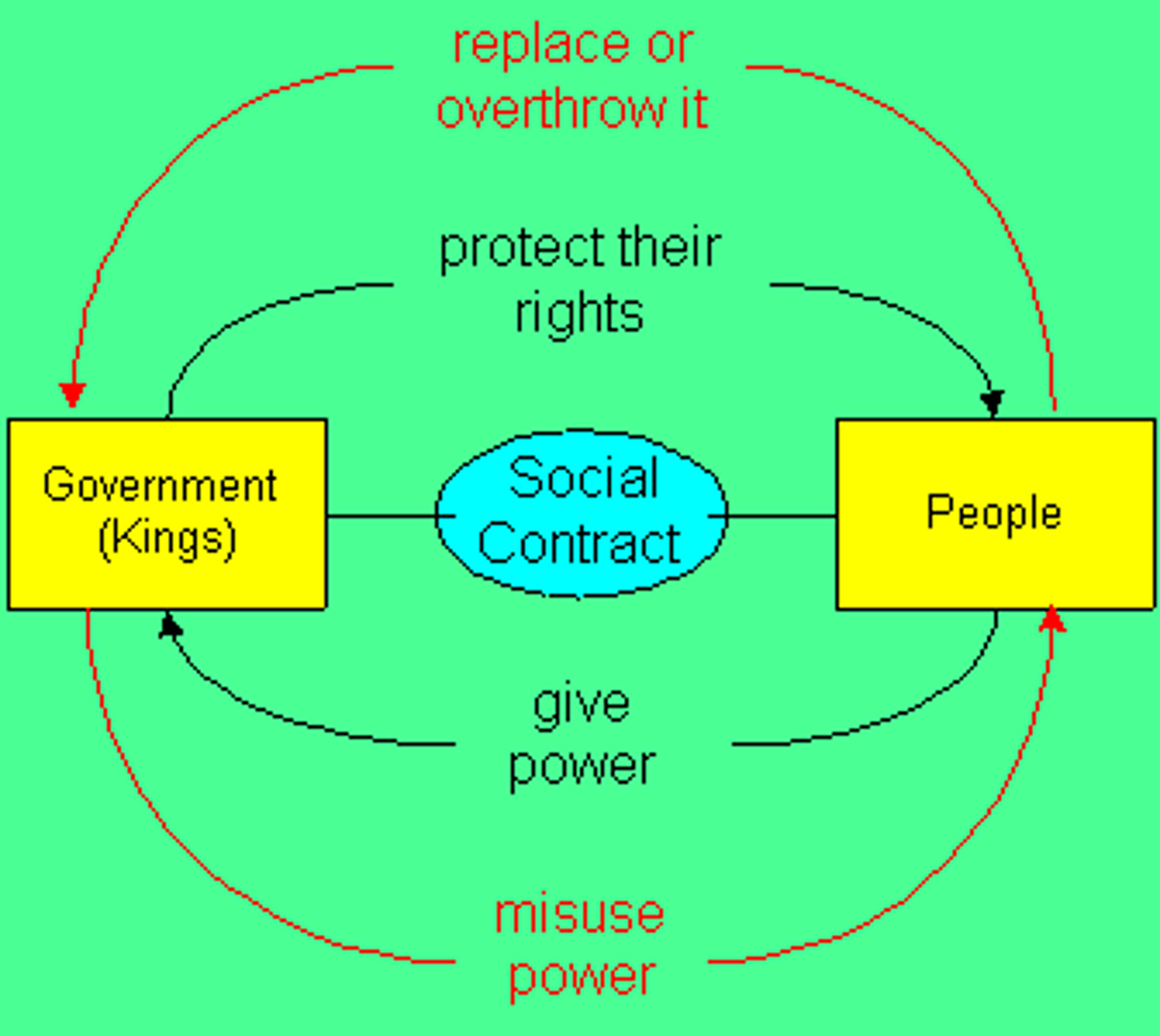
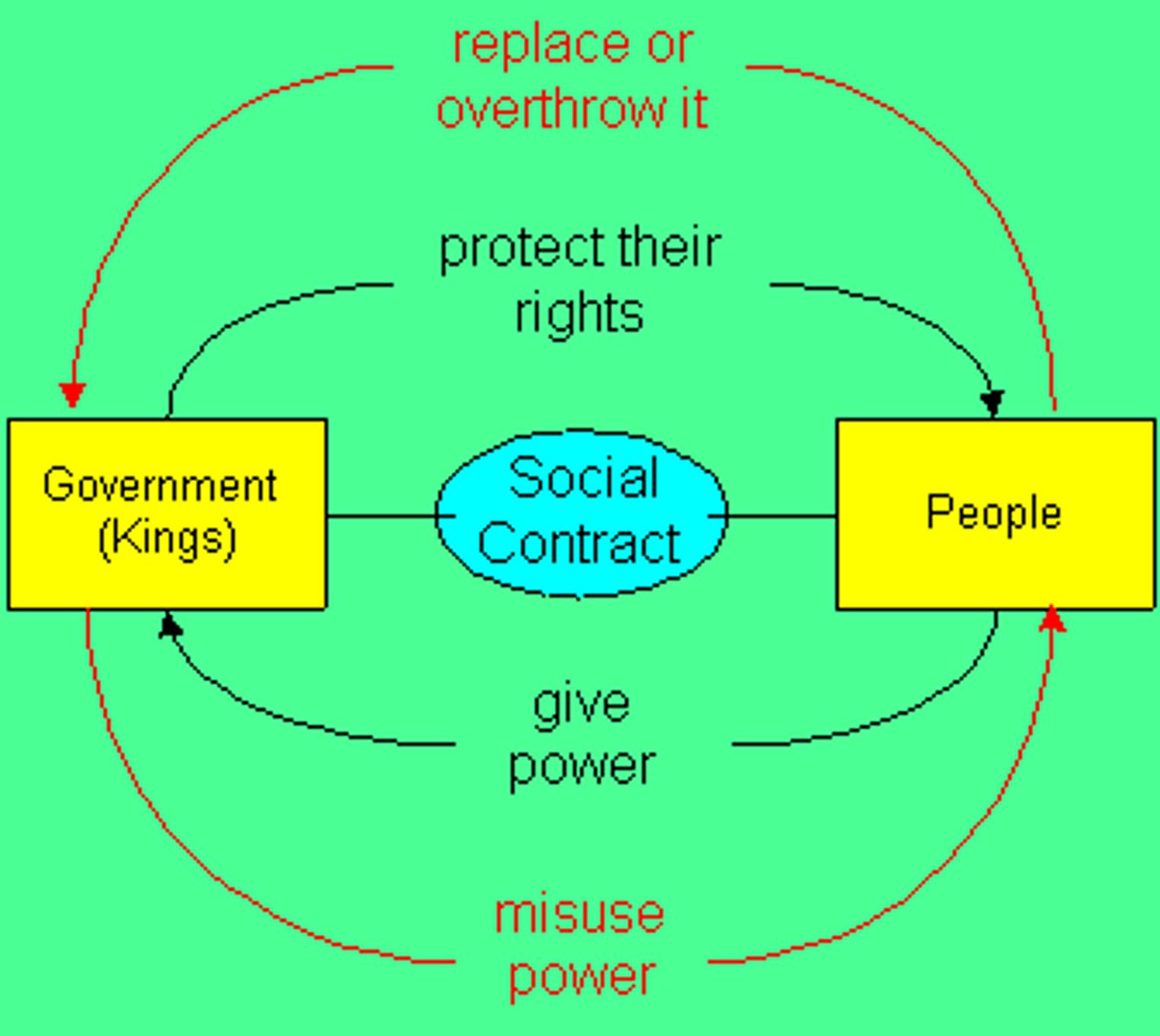
Social Contract
Rousseau's argument that inequality among people can be ended by the citizens coming together and agreeing to a general will
Montesquieu
Believed in separation of powers in governmental structure and checks and balances

Philosophes
Enlightened thinkers who wanted to use reason and logic to figure out the natural laws of the universe

Salons
place where the philosophes met to debate

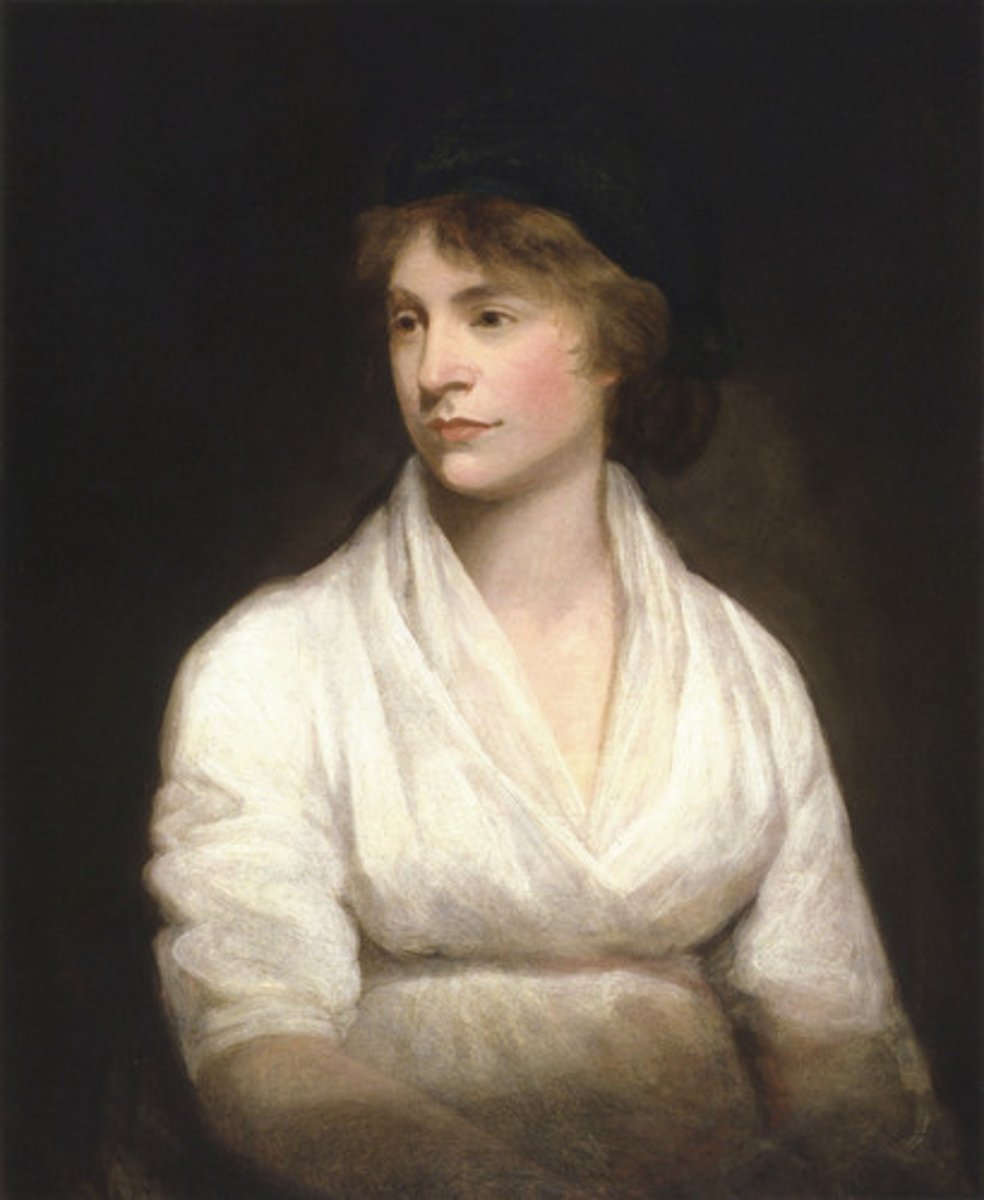
Mary Wollstonecraft
Challenged Enlightened thinkers to expand concepts of liberties to women. Felt women needed to have better educational opportunities.

How did Enlightenment influence the American Revolution?
Used Locke's concept of the social contract to protest against unfair laws and taxes.

How did Enlightenment influence Declaration of Independence?
Sought to justify the breaking from the Mother Country. Declaration of Independence is the best example of the Enlightenment put into action. "All men are born..with unalienable rights..."

How is US Constitution different than European constitutions?
Most importantly a lack of a monarch. President now served as head of state.

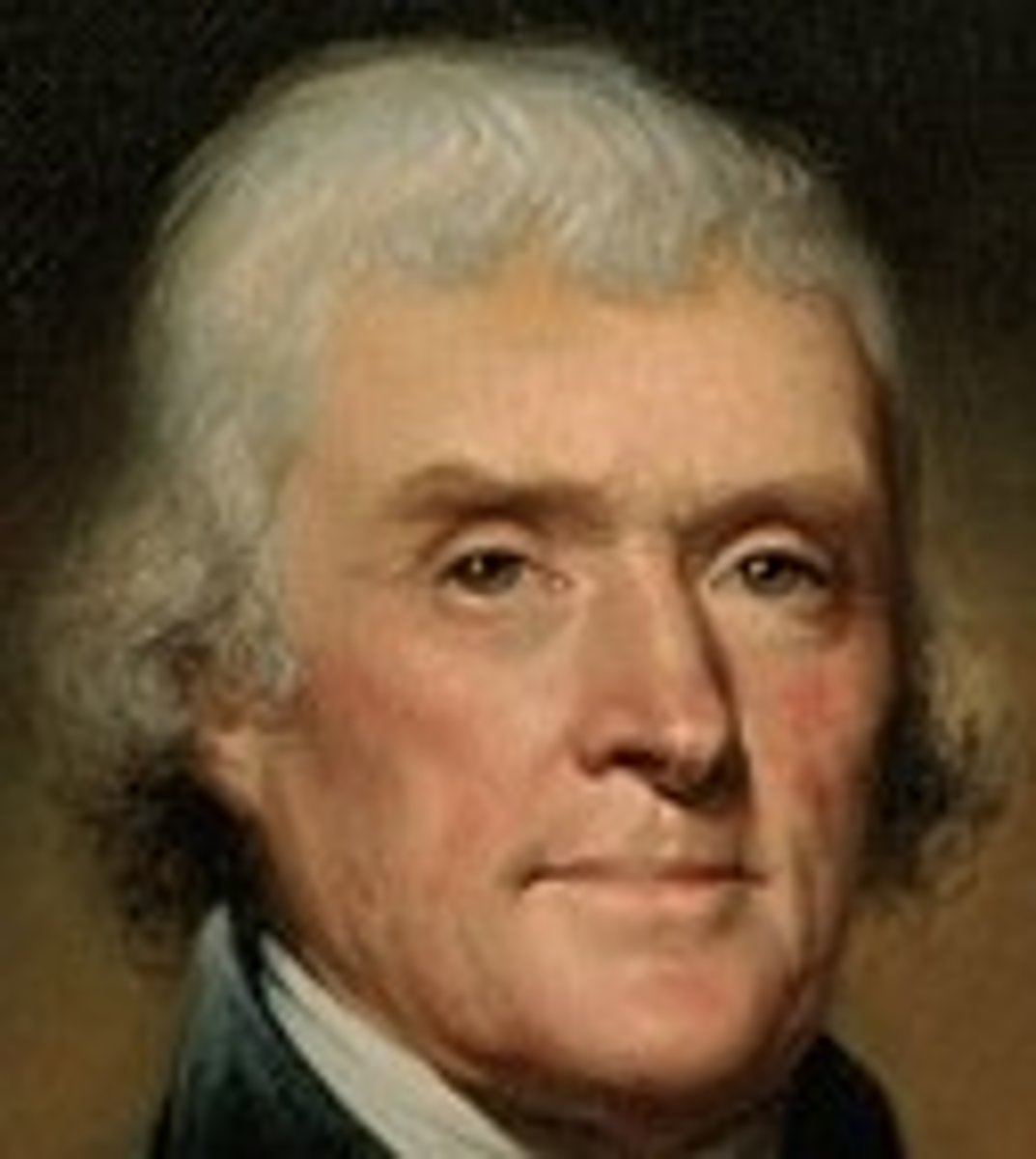
Summarize Thomas Jefferson's place among Enlightened thinkers.
Used Enlightened principles to justify the colonies breaking from Mother Country of England

Articles of Confederation
Failed first government of United States due to it giving too much power to the states.

Thomas Paine
Writer who justified that no monarch was needed in the American and the French revolutions

Popular Sovereignty
power from the people
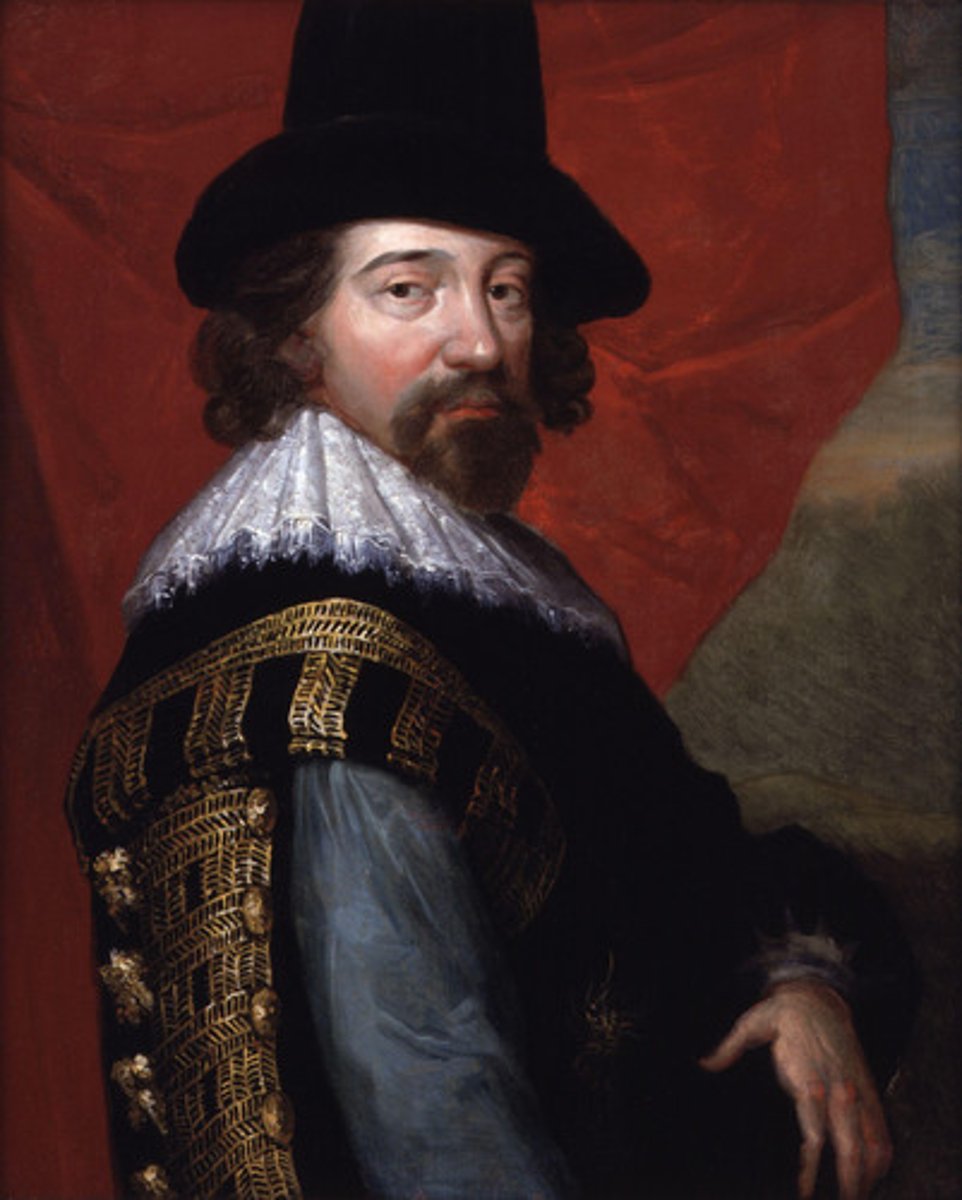
Francis Bacon
Inductive thinking - make observations and then draw conclusions from them

Skepticism
unwillingness to accept explanations for events unless such explanations were based on empirical evidence or logic

The Social Contract
directly challenged the theory of the divine right of kings
Agreement between people and government
Whose ideas had the most impact on the American and French revolutions?
Montesquieu, Locke and Rousseau
Deism
Denied the occurrences of miracles in that they did not believe God interfered with daily life. Felt God had created everything and then back away.

Enlightened Despot who abolished punitive laws against the Jews, imposed limits on the Catholic Church, and granted toleration to all Christian denominations?
Joseph II of Austria

"Men are by nature all free, equal and independent...no one can be subjected to the political power of another without his own consent...to join and unite into a community for the comfortable, safe, and peaceable living..."
John Locke

Noble Savage
Rousseau's concept of the simple man - enamored with the exotic
General Will
Rousseau's thought that what is good for the most should be what is guaranteed by a government
Pugachev Rebellion
this uprising of peasants in Russia led to Catherine the Great NOT freeing the serfs

Isaac Newton
developed three important laws of motion which laid the foundations for new inventions

Leeuwenhoek
used the microscope to study life forms too small to see with the naked eye

Harvey
studied the circulatory system
Immanuel Kant
tried to bridge the gap between rationalism [of Descartes - emphasized reason] and empiricism [of Bacon - emphasized experience]
![<p>tried to bridge the gap between rationalism [of Descartes - emphasized reason] and empiricism [of Bacon - emphasized experience]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b41013aa-0bd3-451d-9280-dc53013d8277.jpg)
limitations of the Enlightenment
a movement by men concerning the political rights of men - more specifically, wealthy, well- educated, white men
Bossuet
advocated royal absolutism - said kings were chosen by God

How did Newton's laws change the world?
People began to see the world as driven by natural laws rather than by the will of God

Explain how chemists radically altered human interpretation of matter.
Applied scientific method to analyze the essence of matter and how it changes...in doing so, they disproved many traditional teachings
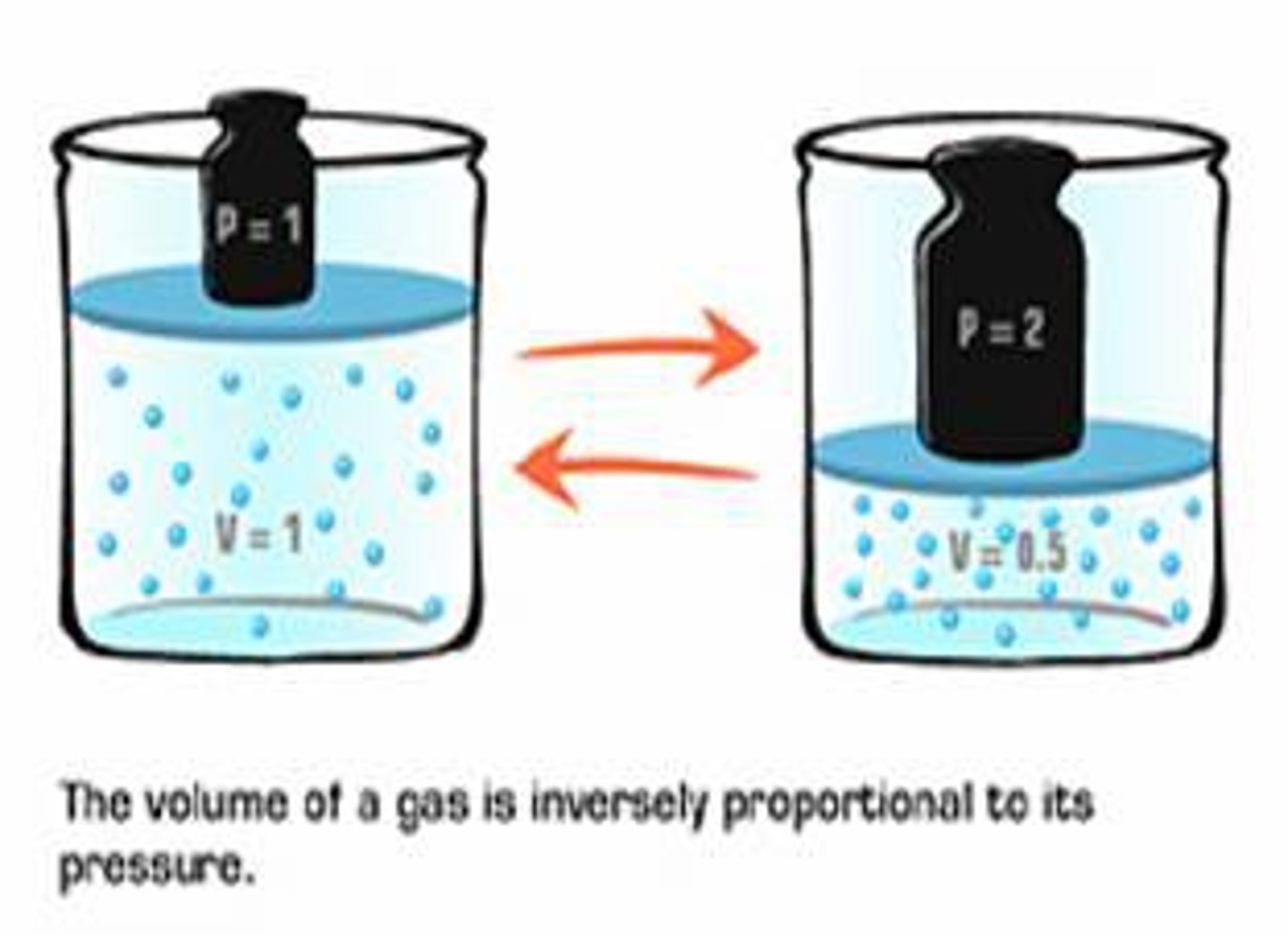
Boyle
proved that temperature and pressure affect the space that a gas occupies
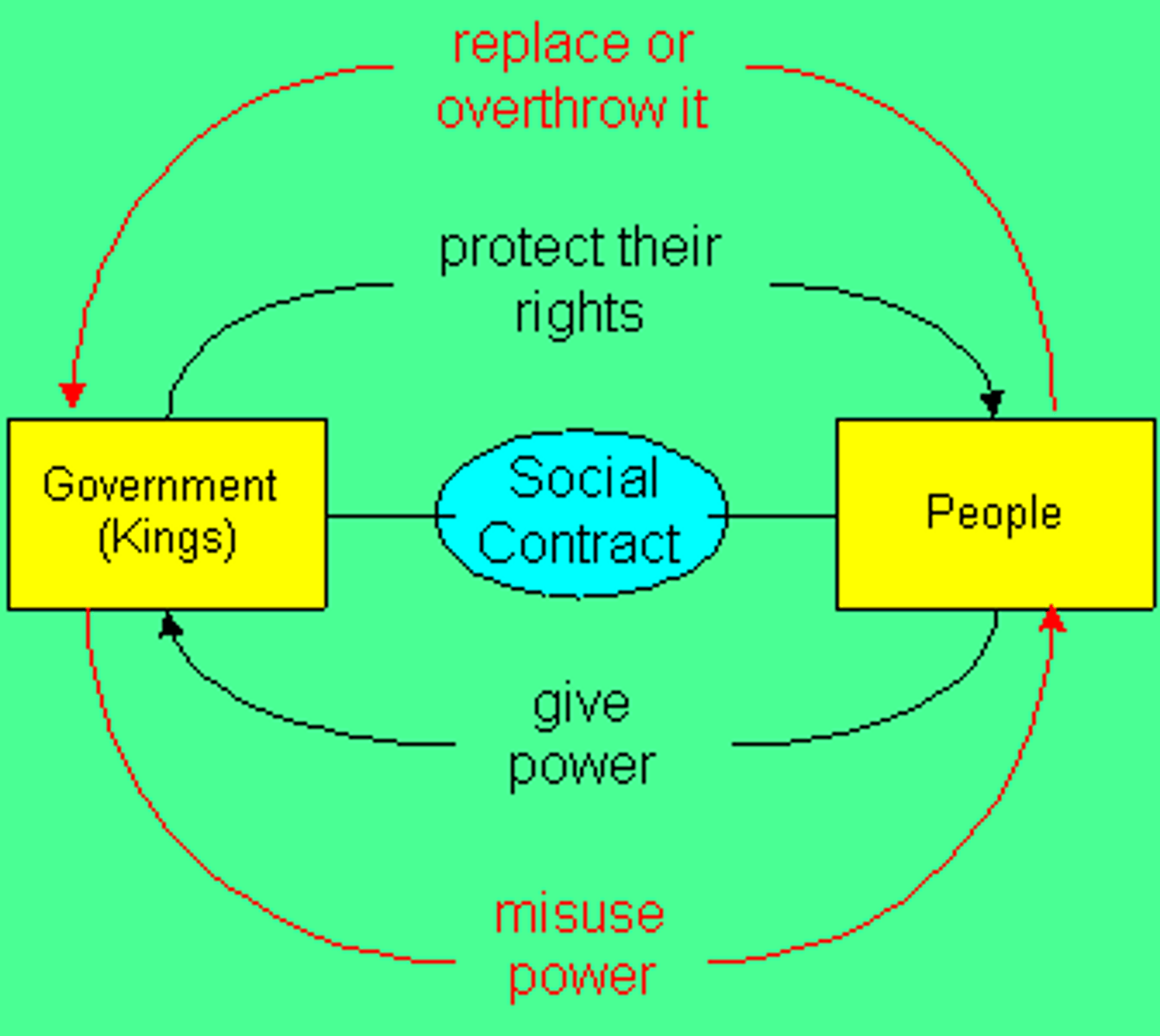
Hobbes
Felt that people should enter into a social contract with a strong king to end violence and chaos

Locke
Became a critic of Hobbes' theories - Locke accepted the social contract but interpreted it differently. Felt humans had natural rights and if a ruler tried to oppress these; the people had a right to overthrow that govt.

Rene Descartes
mechanistic worldview emphasizing the separation of the physical realm from human perception

"Principia Mathematica"
Isaac Newton's work

"Spirit of the Laws"
Montesquieu - separation of powers

"The Social Contract"
Rousseau - man allows govt. to rule - based on the "general will" - freedom is achieved by being forced to follow the "general will" or what is best for all
Diderot
compiled the "Encyclopedia"

Thomas Paine
He wrote Common Sense, published on January 1, 1776, to encourage the colonies to seek independence. It spoke out against the unfair treatment of the colonies by the British government and was instrumental in turning public opinion in favor of the Revolution.

Despot
A ruler who exercised absolute power.

Enlightened Despot
Monarchs who embraced the new ideas to rule justly and made reforms that reflected the Enlightenment spirit.
Why is Catherine called the GREAT?
She was successful in defeating the Turks and taking warm water ports.

Galileo
his observations with the telescope showed that the planets in our universe are made of materials similar to those found on Earth

Descartes believed the world could be understood through?
mathematical thinking
French philosophes
Enlightenment began in France - they were literate intellectuals who sought to change the world based on reason and rationality

Secularization
search to find natural laws governing man and nature
Deism
based on Newton's concept of a rational universe following scientific laws

American Revolution effects on Europeans
Demonstrating that the ideas of the Enlightenment could be realized politically
Deist beliefs
-There was a GOD
-but there were no miracles, superstitions, or prophecies
-did not believe in organizes religion and the Bible
Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
Versailles Palace
Royal palace built during the reign of Louis XIV that became the most impressive palace in all of Europe. It was the quintessential embodiment of absolutism and baroque architecture.
Peter the Great
(1672-1725) Russian tsar (r. 1689-1725). He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg.
Stuart Dynasty
After Queen Elizabeth Tudor's death in 1603, the Stuart Line of rulers came. Started with James I, King of Scotland. (Cousin of Elizabeth.) Then came Charles I, his son. Oliver Cromwell- not a Stuart. Charles II. Then James II. Then William of Orange.
James I of England
Divine right of kings, absolutist
Charles I of England
King of England, numerous conflicts with Parliament; fought wars with France, Spain, and Scotland; eventually provoked Civil War, convicted of treason, and beheaded
Oliver Cromwell
English military, political, and religious figure who led the Parliamentarian victory in the English Civil War (1642-1649) and called for the execution of Charles I. As lord protector of England (1653-1658) he ruled as a virtual dictator.
English Civil War (1642-1649)
Armed conflict between royalists and parliamentarians, resulting in the victory of pro-Parliament forces and the execution of Charles I.
Petition of Right (1628)
A document drawn up by Parliament's House of Commons listing grievances against King Charles I and extending Parliament's powers while limiting the king's. It gave Parliament authority over taxation, declared that free citizens could not be arrested without cause, declared that soldiers could not be quartered in private homes without compensation, and said that martial law cannot be declared during peacetime.
Charles II of England
Restoration King (Monarch) restores the English monarchy after Oliver Cromwell's death
James II of England
Catholic King after Charles II who is ousted by Parliament
Glorious Revolution (1688)
The bloodless coup in 1688 in England when James II (a Catholic) gave up the throne and his daughter Mary and her husband William of Orange (of the Netherlands) - both Protestants - replaced James II to reign jointly. No Catholic monarch has reigned in England since.
Two Treatises of Government
John Locke
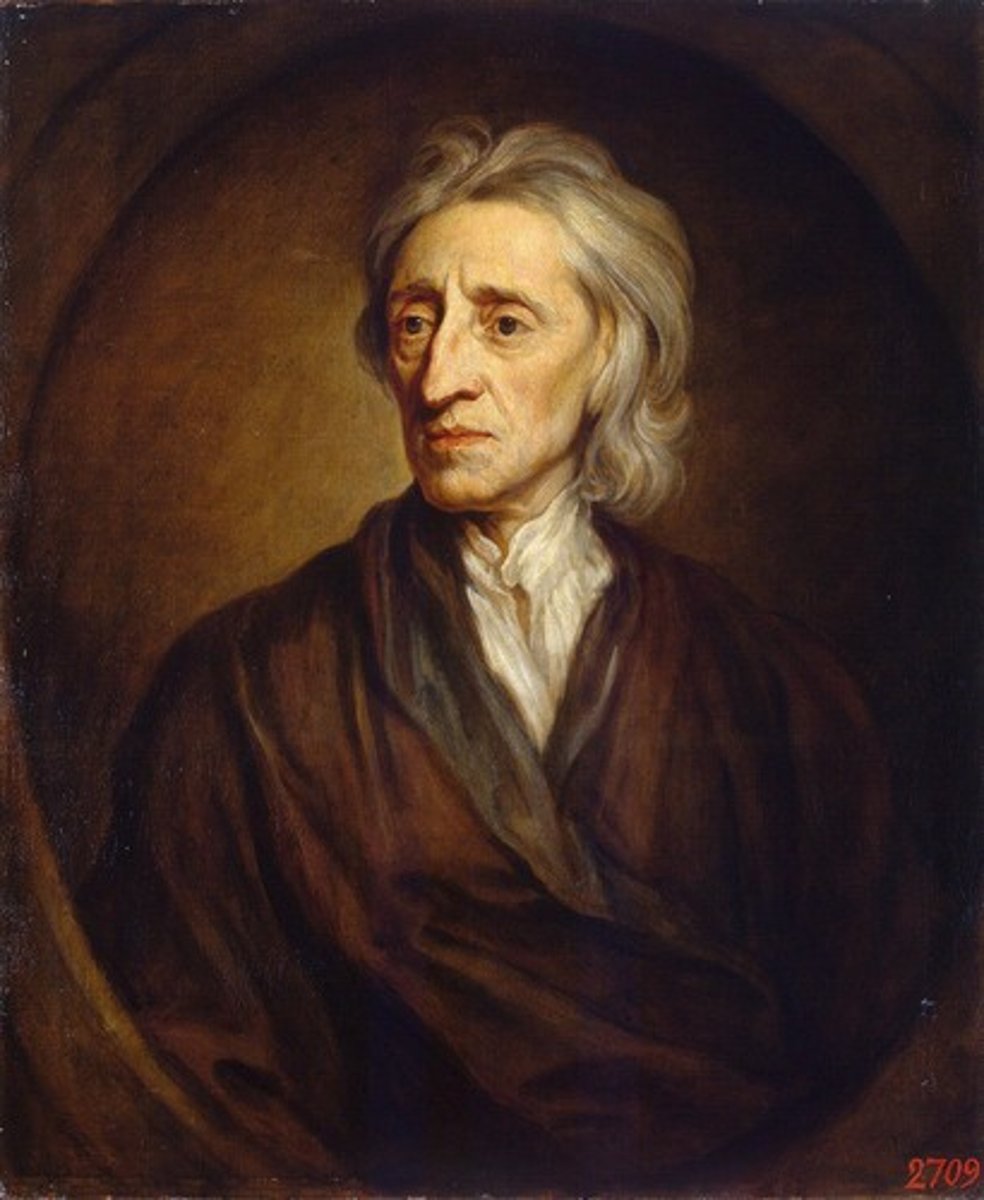
John Locke
17th century English philosopher who opposed the Divine Right of Kings and who asserted that people have a natural right to life, liberty, and property.
English Bill of Rights
King William and Queen Mary accepted this document in 1689. It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.