Digestive System
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Assimilation
The process by which nutrients from foods are taken into the cells of the body after the food has been digested and absorbed.
Absorption
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood
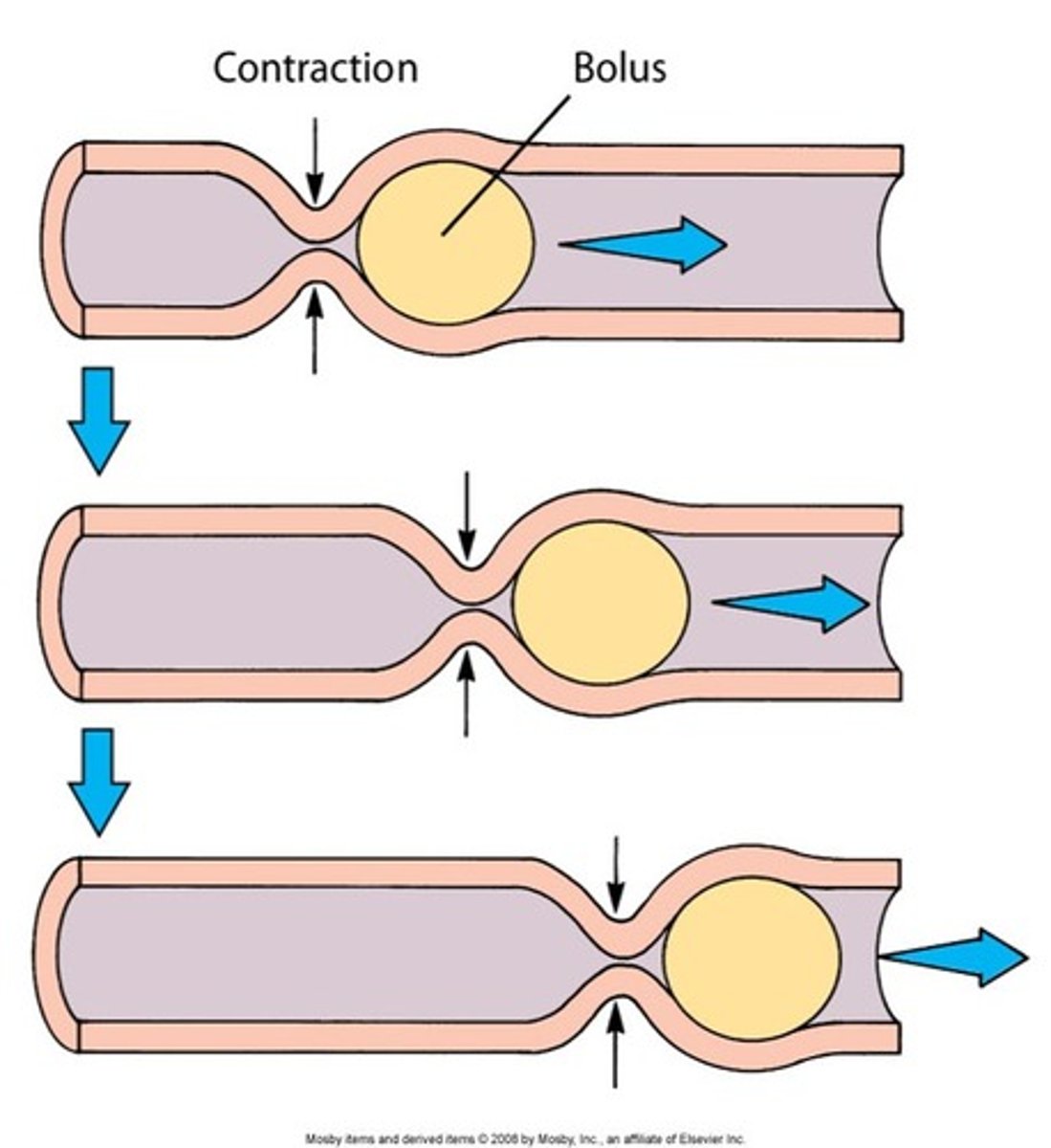
Bolus
A term used to describe food after it has been chewed and mixed with saliva
Chyme
Partially digested, semiliquid food mixed with digestive enzymes and acids in the stomach.
Digestion
Breakdown of food substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used. There are two kinds.
Defecation
Elimination of feces
Ingestion
The intake of food from the environment into the alimentary canal
Mechanical Digestion
Physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces (chewing and intestinal compression)
Chemical Digestion
Process by which enzymes break down food into small molecules that the body can use (Stomach acid and saliva)
Digestive System
Extends from mouth to anus and consists of:
Alimentary Canal and Accessory Organs
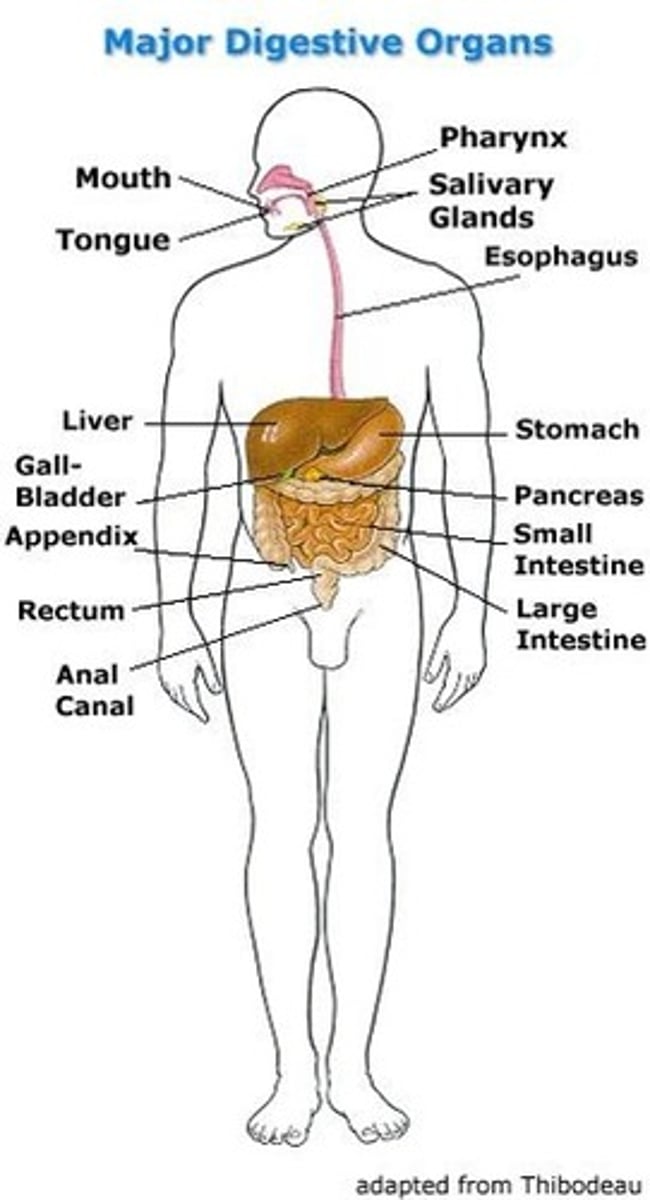
Alimentary Canal
Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestines, Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus.
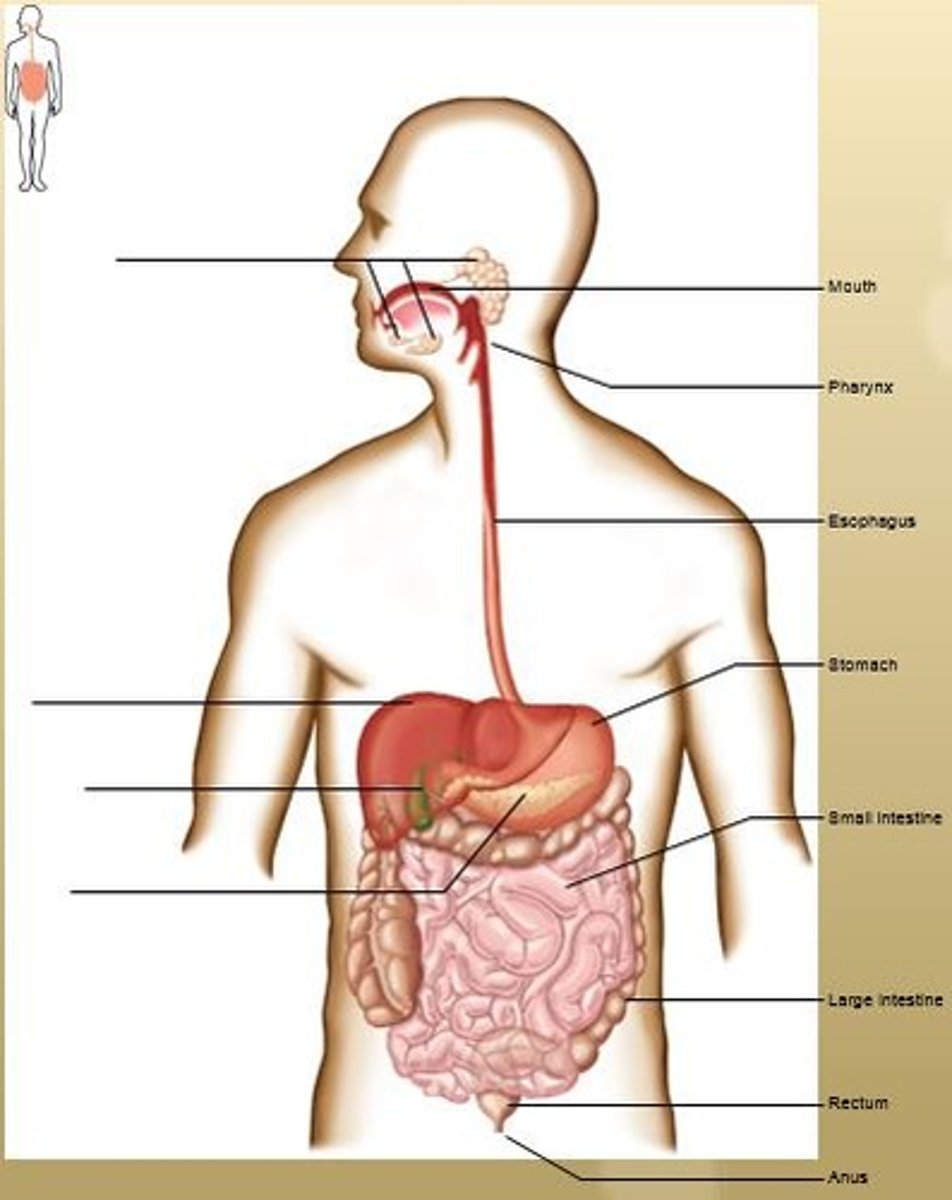
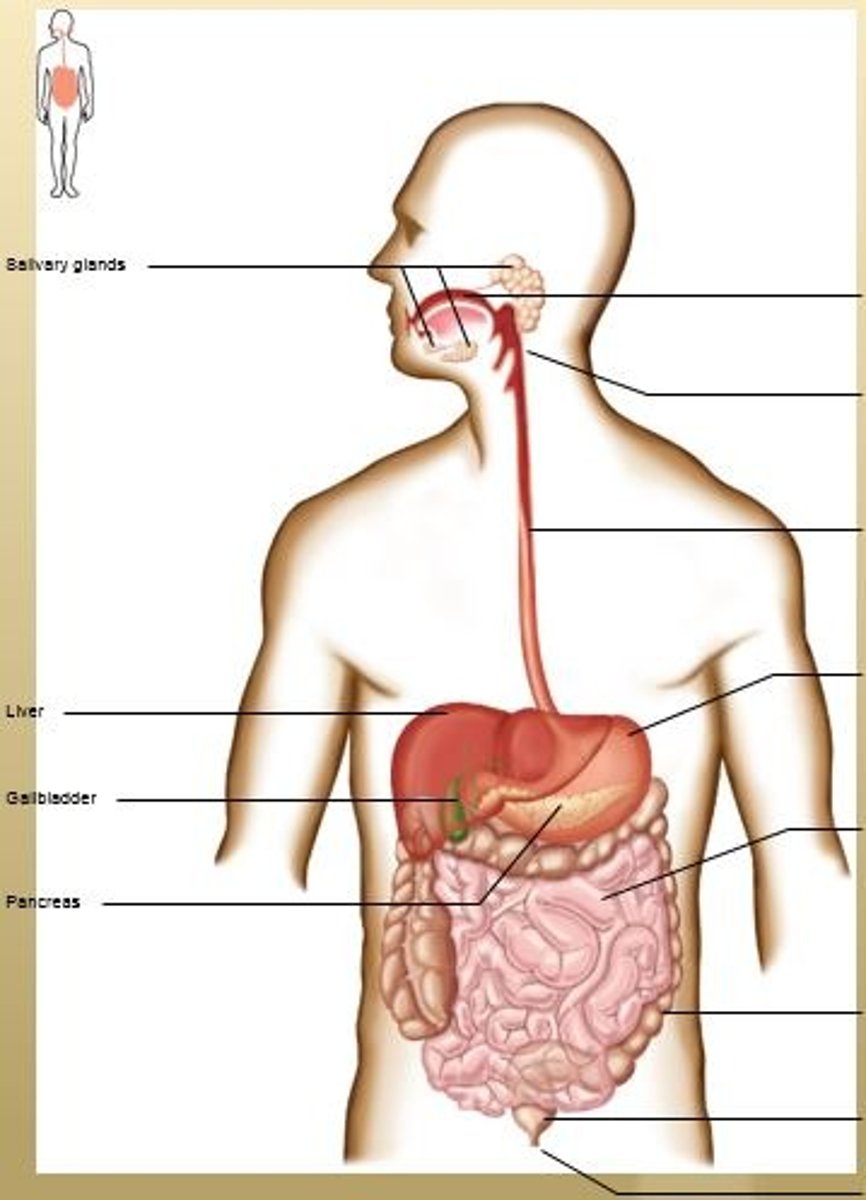
Accessory Organs
Salivary Glands, Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas.
Alimentary Canal: Mouth
Hollow chamber with roof, floor, and walls.
Receives the food (ingestion) and begins mechanical (chewing) and chemical (saliva) digestion (chemical digestion of carbohydrates)
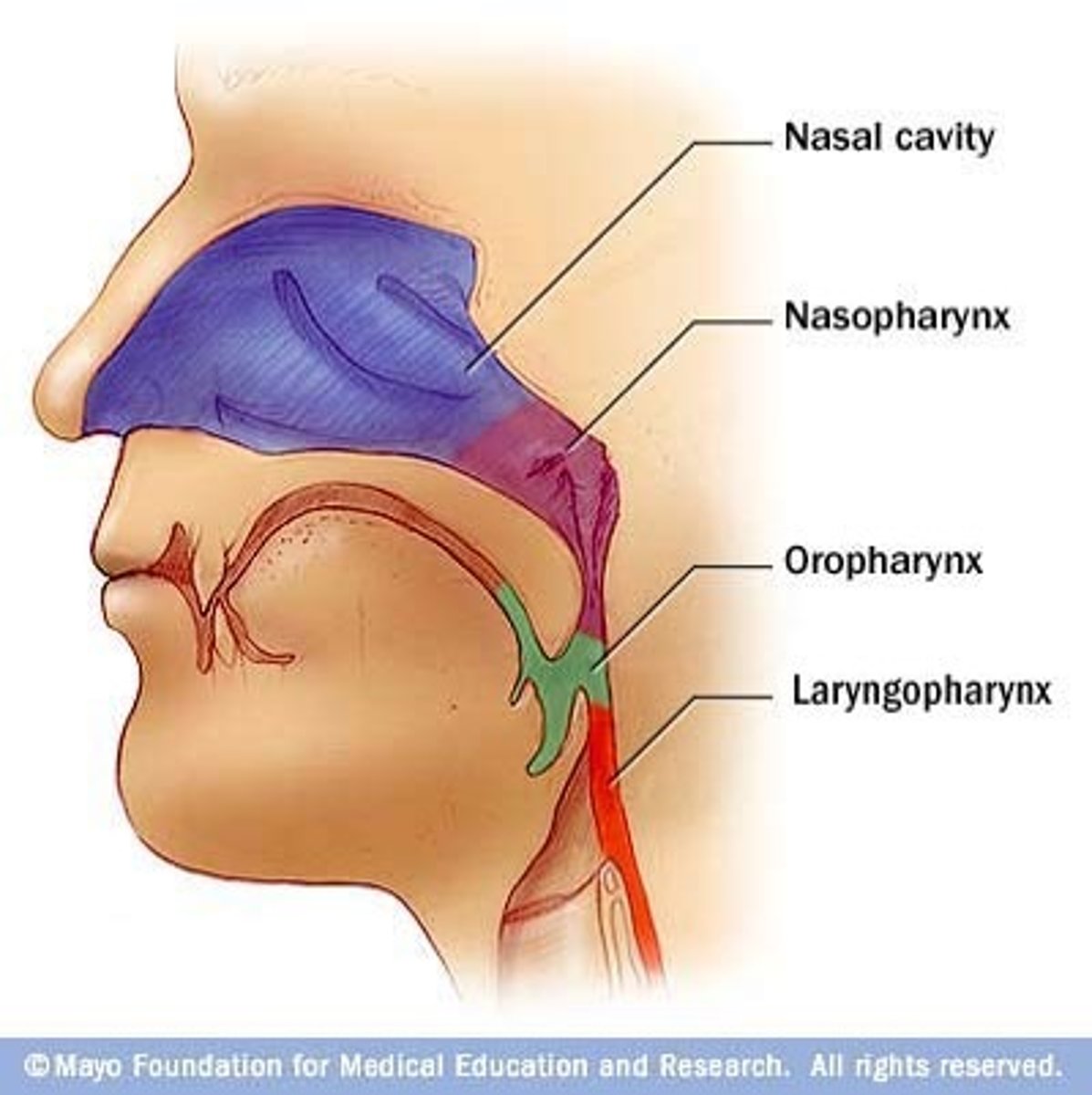
Alimentary Canal: Pharynx
Tube-like structure made of muscle and lined with mucous membranes
Connects nasal/oral cavities with larynx/ esophagus.
Three parts: Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, and Laryngopharynx
Alimentary Canal: Esophagus
Peristalsis pushes food to stomach.
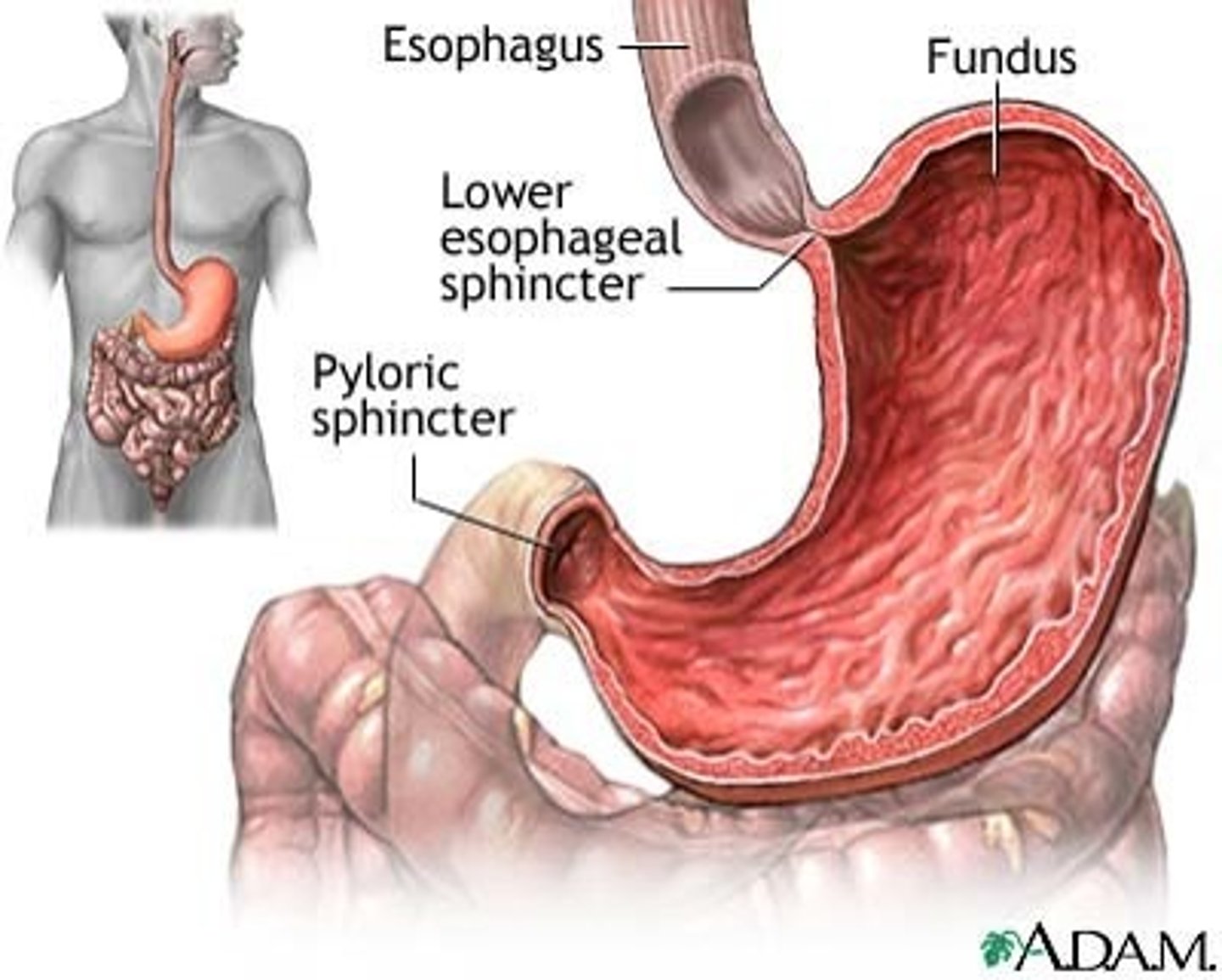
Alimentary Canal: Stomach
Secretes acid and enzymes. Mixes food with secretions to begin enzymatic digestion of proteins
Alimentary Canal: Small Intestines
Mixes food with bile and pancreatic juice.
Final enzymatic breakdown of food molecules; main site of nutrient absorption
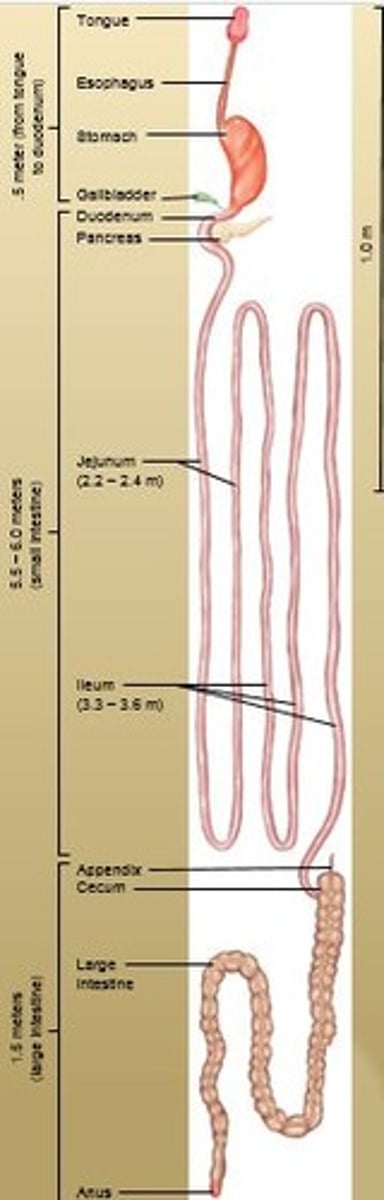
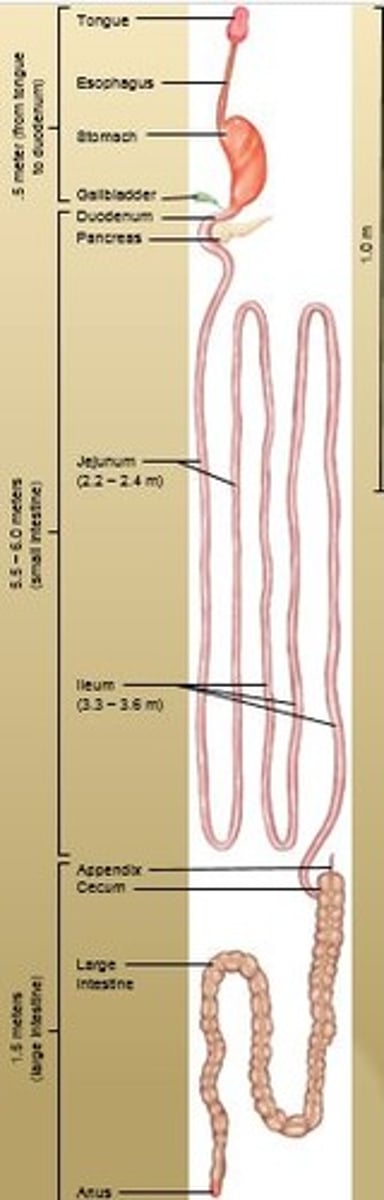
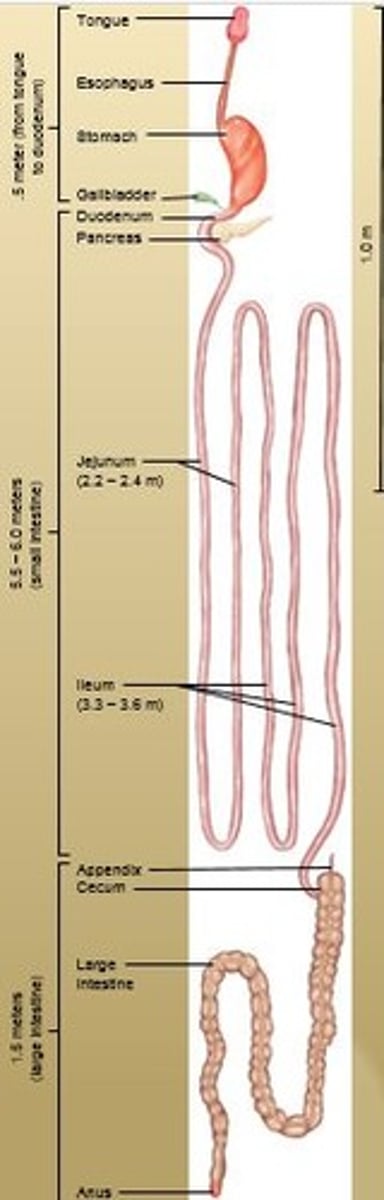
Tubular organ, about 7 meters (20 feet) long that completes digestion and facilitates absorption.
Transports remaining residue to the large intestine which takes 3 - 10 hrs.
Alimentary Canal: Large Intestines
Absorbs water and electrolytes to form feces. Consists of ascending, traverse, descending, and sigmoid colons.
Alimentary Canal: Rectum
Regulates elimination of feces. Temporary storage site for undigested material before defecation.
Alimentary Canal: Anus
Opening at the end of the alimentary canal through which solid waste matter leaves the body
Accessory Organs: Salivary Glands
Secretes about 1 liter per day to help moisten and bind food particles.
Amylase begins chemical digestion of carbohydrates. Stimulated by sight, smell, taste or thought of food.
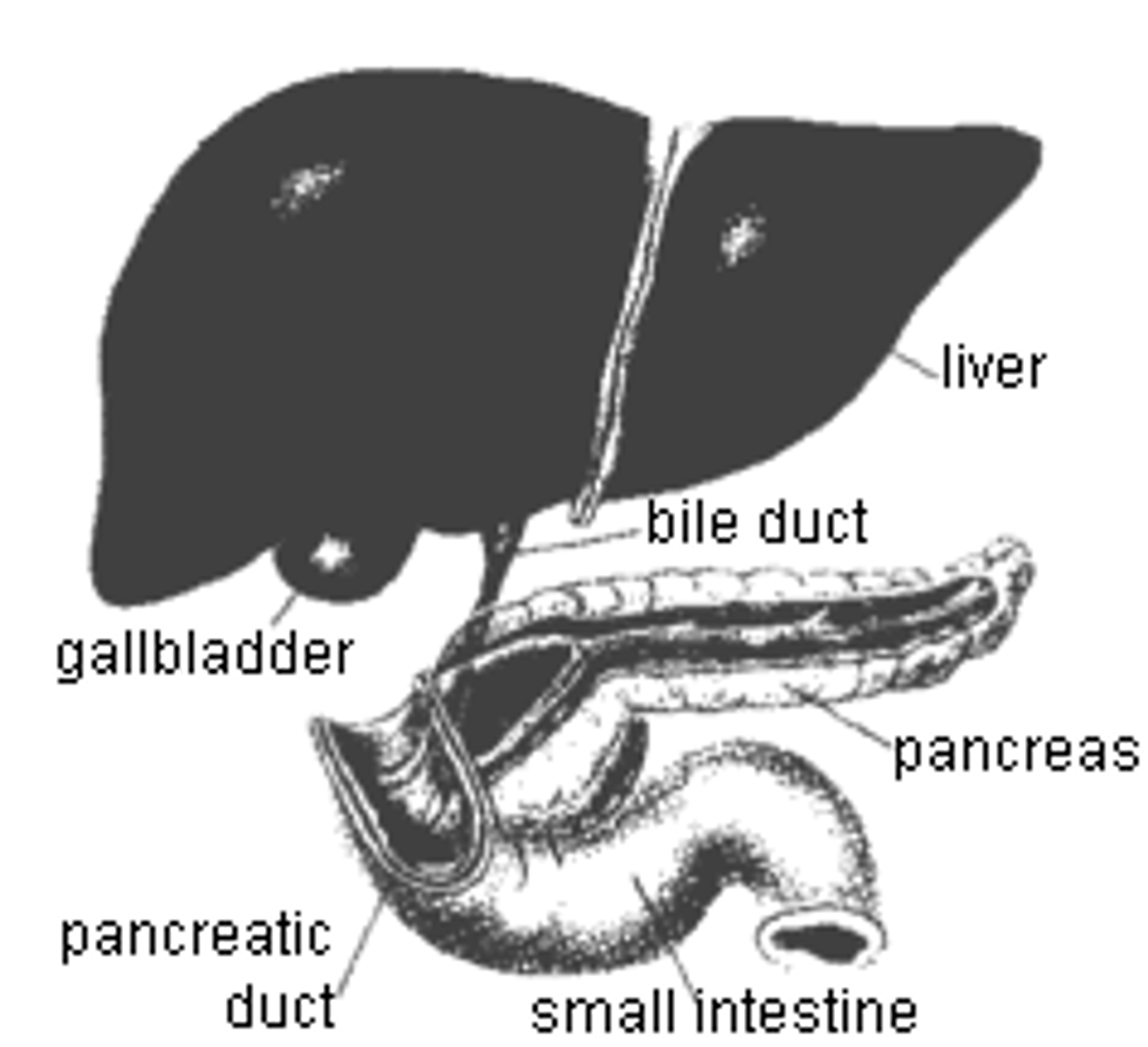
Accessory Organs: Liver
Produces bile, which emulsifies fat
Accessory Organs: Gallbladder
Stores bile and introduces it into small intestine
Accessory Organs: Pancreas
Produces and secretes
pancreatic juice, containing
digestive enzymes and
bicarbonate ions,
into small intestine
Tongue
Mainly consists of skeletal muscle and help move the food to the back of the oral cavity. Contains taste buds.
Esophagus
A muscular, mucous-lined tube about 25cm (10 in.) long which serves as a passageway for food.
It connects the pharynx with the stomach and descends posterior to the trachea. Peristalsis pushes food to stomach. Contains the esophageal hiatus.
Stomach
A hollow, muscular organ that serves as a pouch which can hold about one liter.
Divided into three areas: Fundus, Body, and Pylorus. It connects to the duodenum and controls the emptying of chyme.
Gallbladder
A pear-shaped sac whose main function is to
store bile. Fats in chyme "trigger" release of Cholecystokinin or CCK which stimulates contractions. Cystic duct + common hepatic duct = common bile duct.
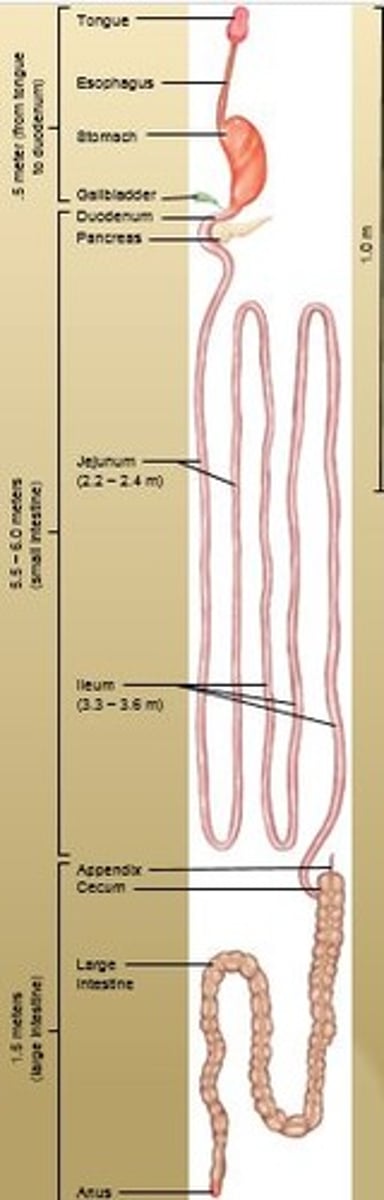
Duodenum
C-shaped section where most chemical digestion occurs
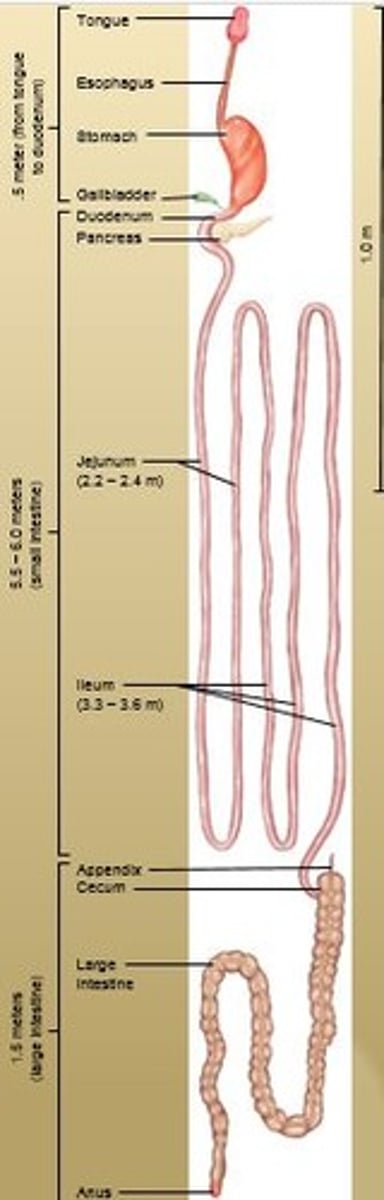
Jejunum
The middle section of the small intestine; connects the duodenum and ileum
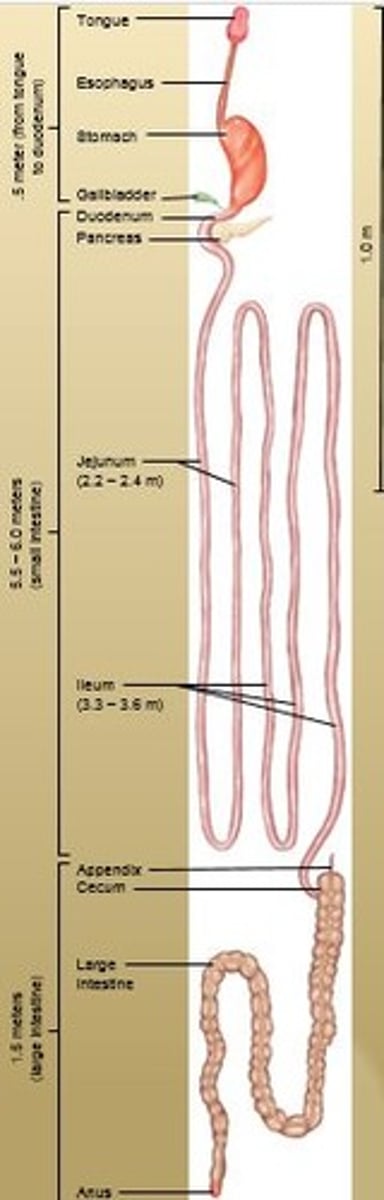
Ileum
Joins the large intestine at the ileocecal valve.
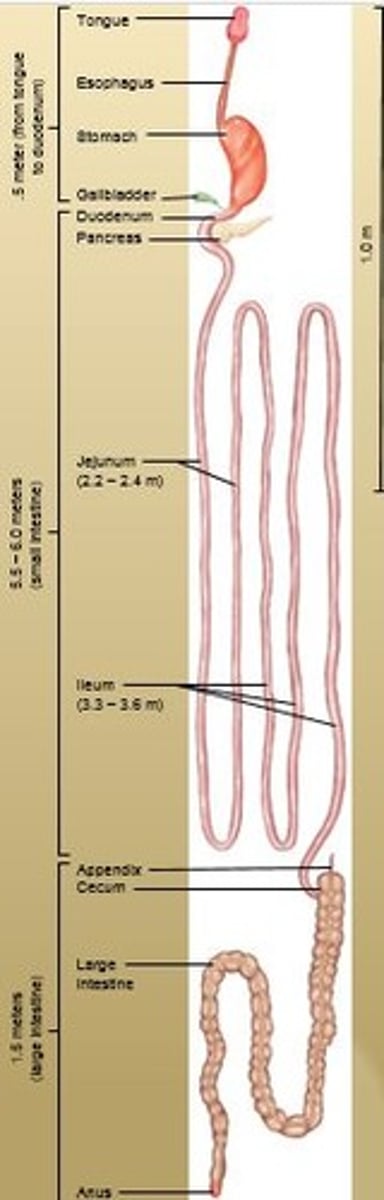
Appendix
A small, fingerlike extension of the vertebrate cecum; contains a mass of white blood cells that contribute to immunity.
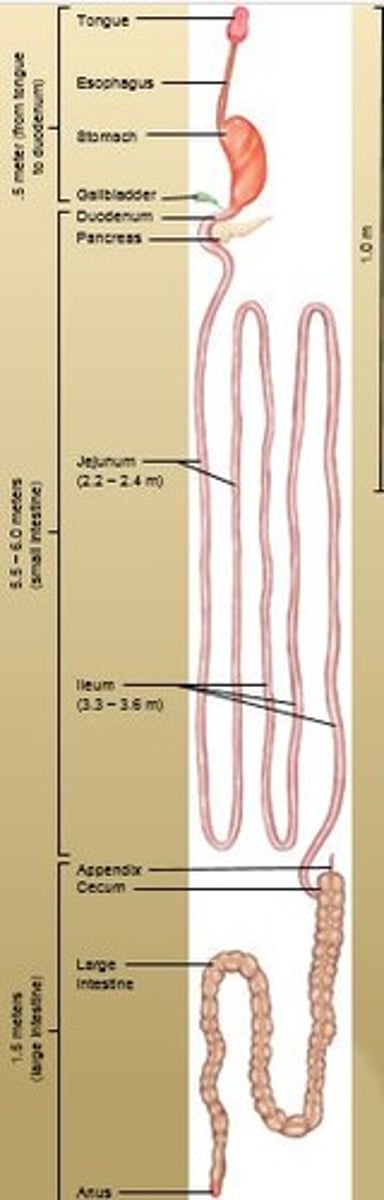
Cecum
First part of large intestine which is pouch-like. Contains the Vermiform appendix which serves no important digestive function in humans but contains lymphatic tissue.
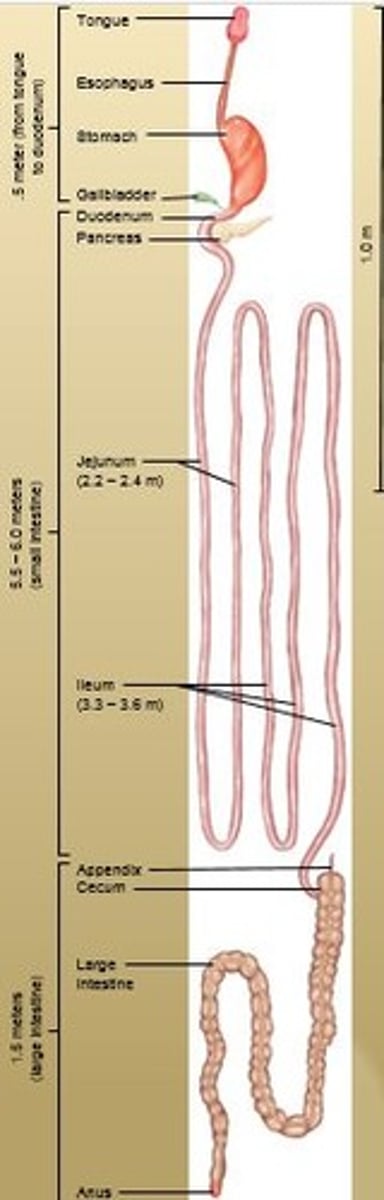
Large Intestine
1.5 meters (5 feet) long. Takes care of undigested and unabsorbed food.
Absorbs some water and electrolytes.
Forms and stores feces.
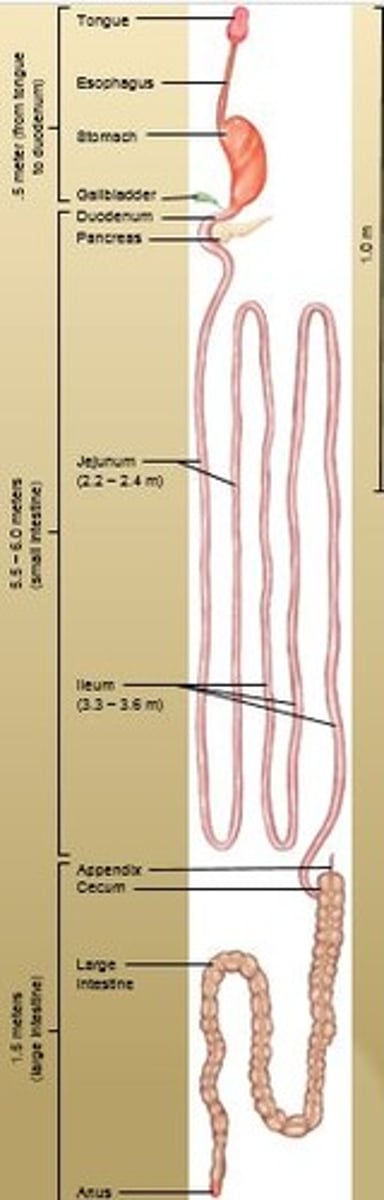
Anus
Opening of the anal canal to the outside which is guarded by two sphincter muscles:
Internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle under involuntary control) and External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle under voluntary control).
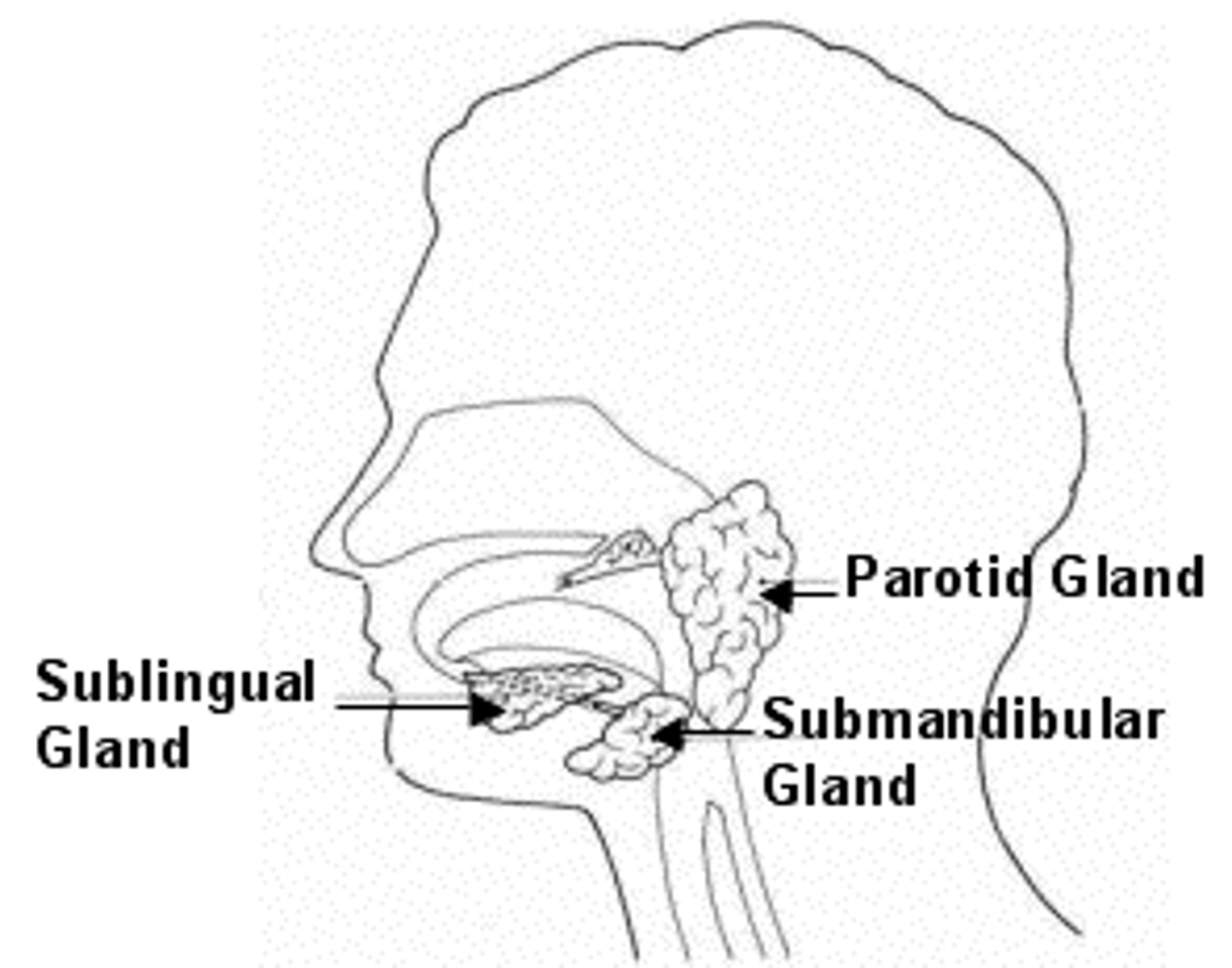
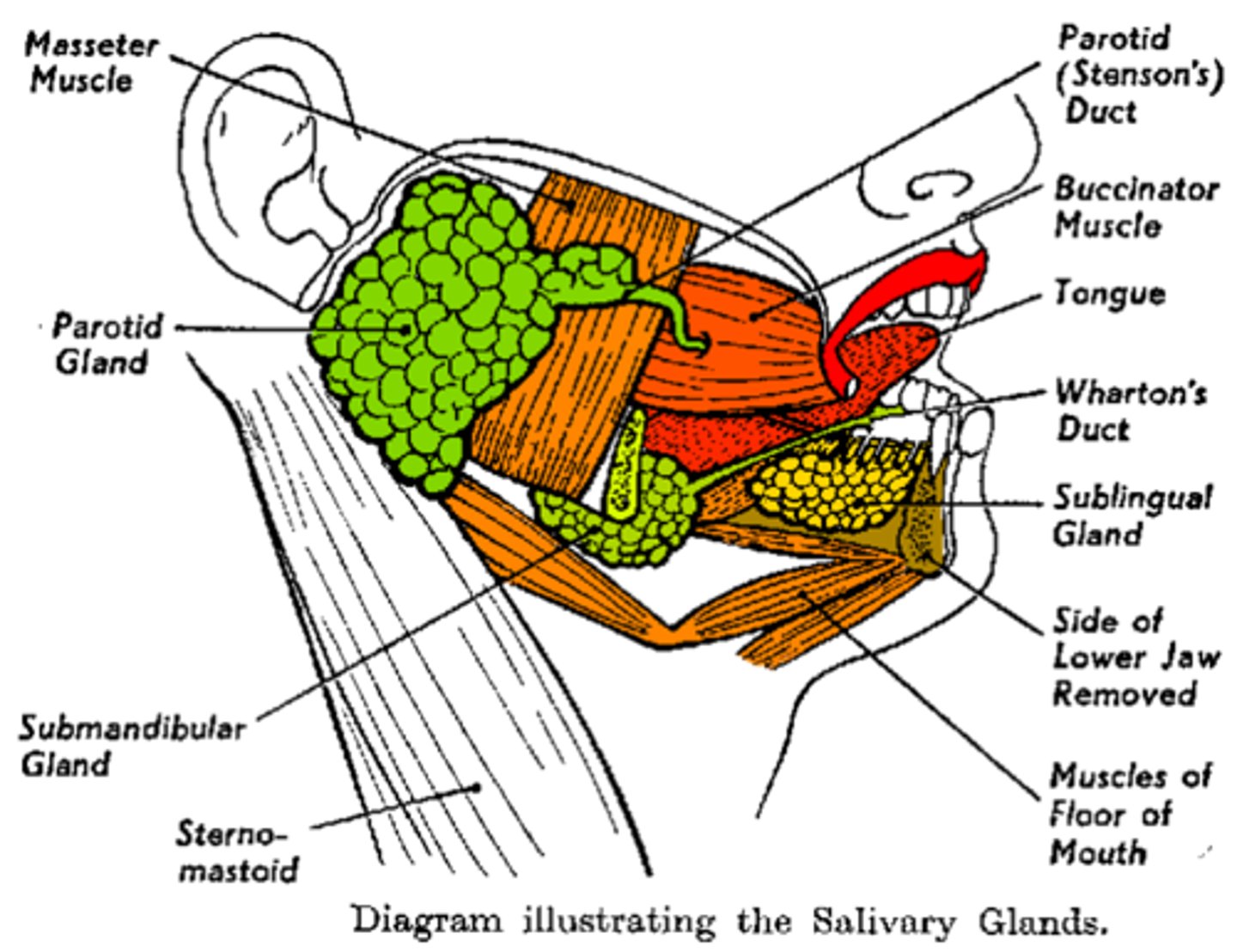
Salivary Gland: Parotid
The largest of the salivary glands which lie inferior to each ear
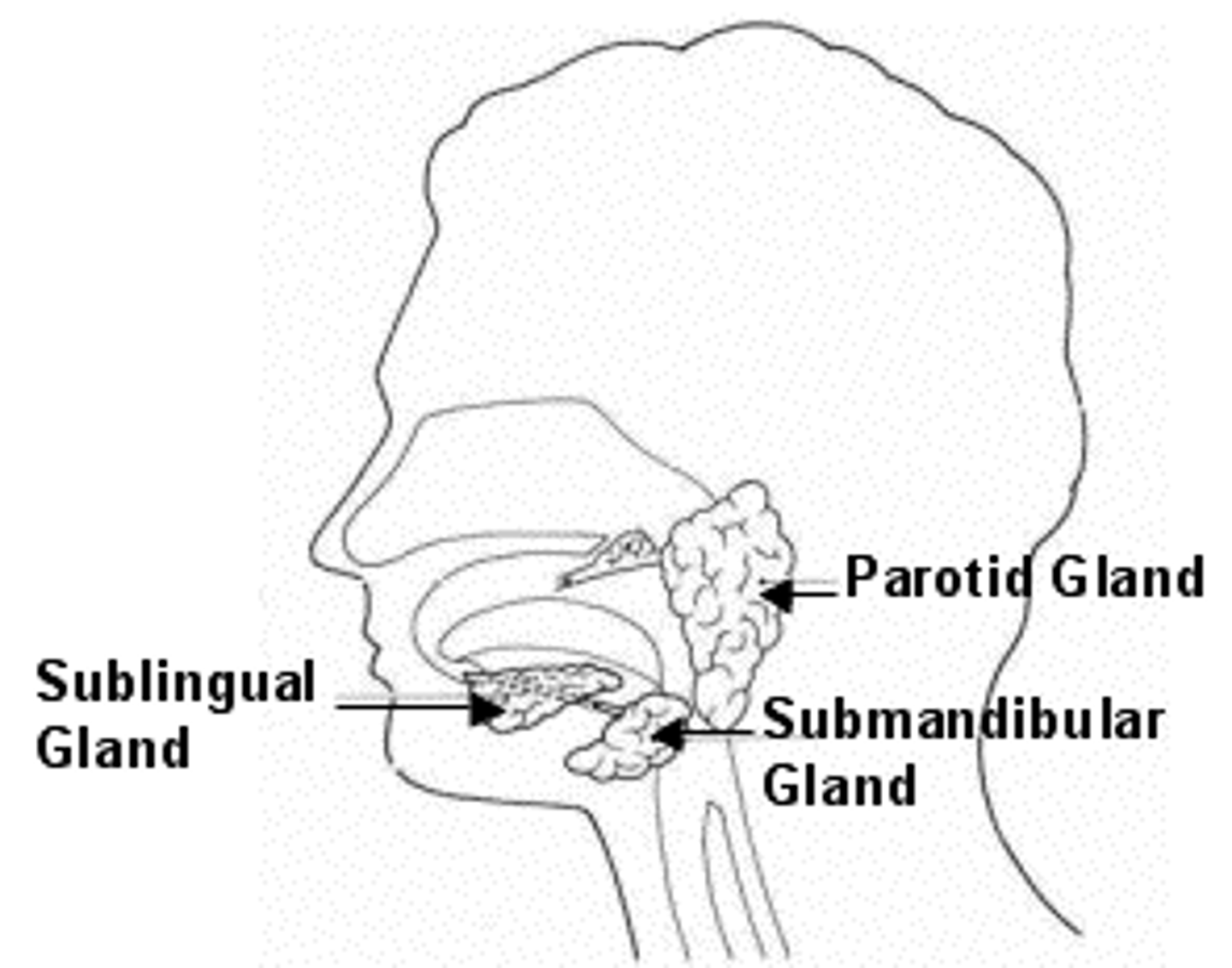
Salivary Gland: Submandibular
These open into the mouth on either side of the lingual frenulum
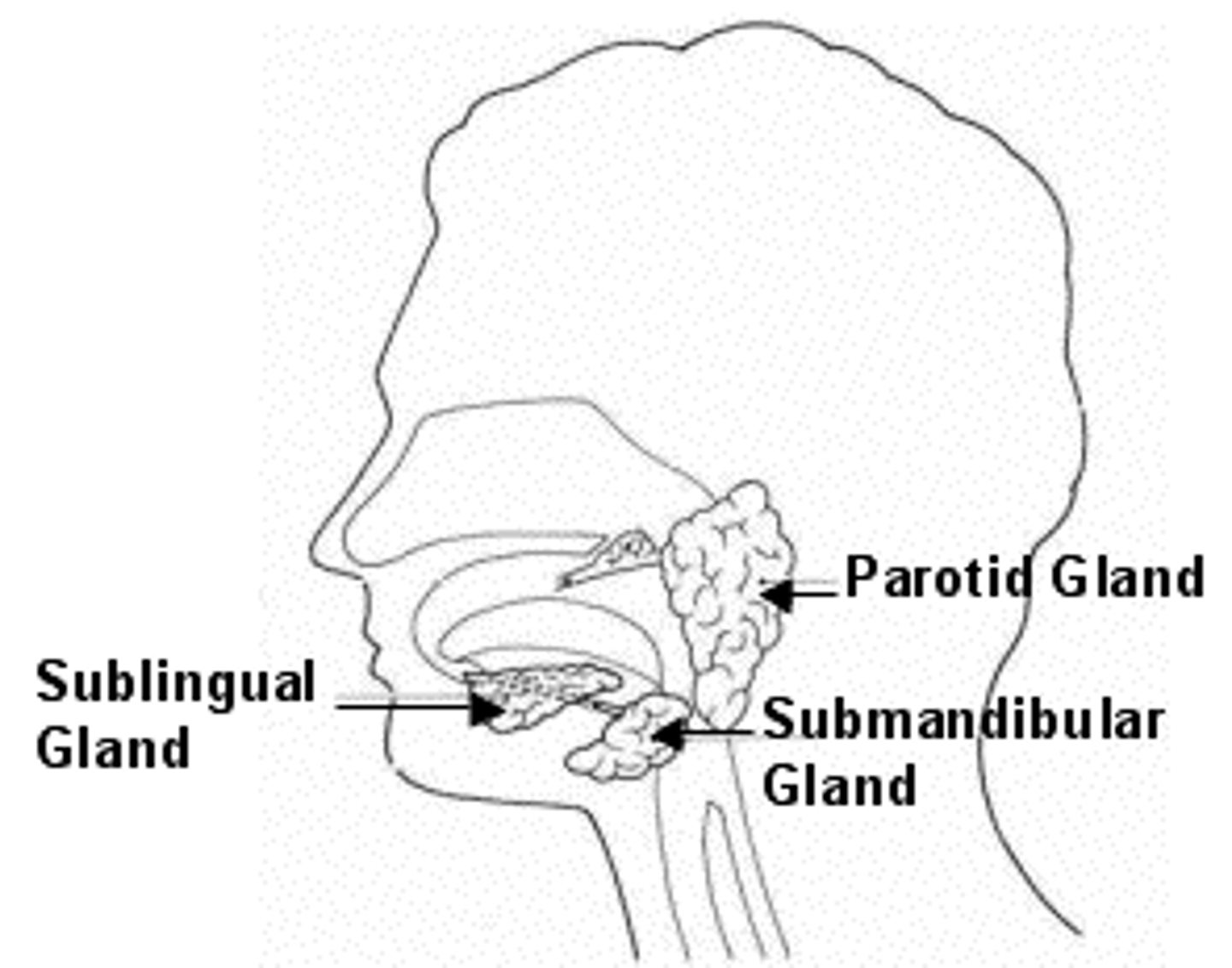
Salivary Gland: Sublingual
The smallest of the salivary glands. These open into the floor of the mouth
Bile Duct
A tube that carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the intestine
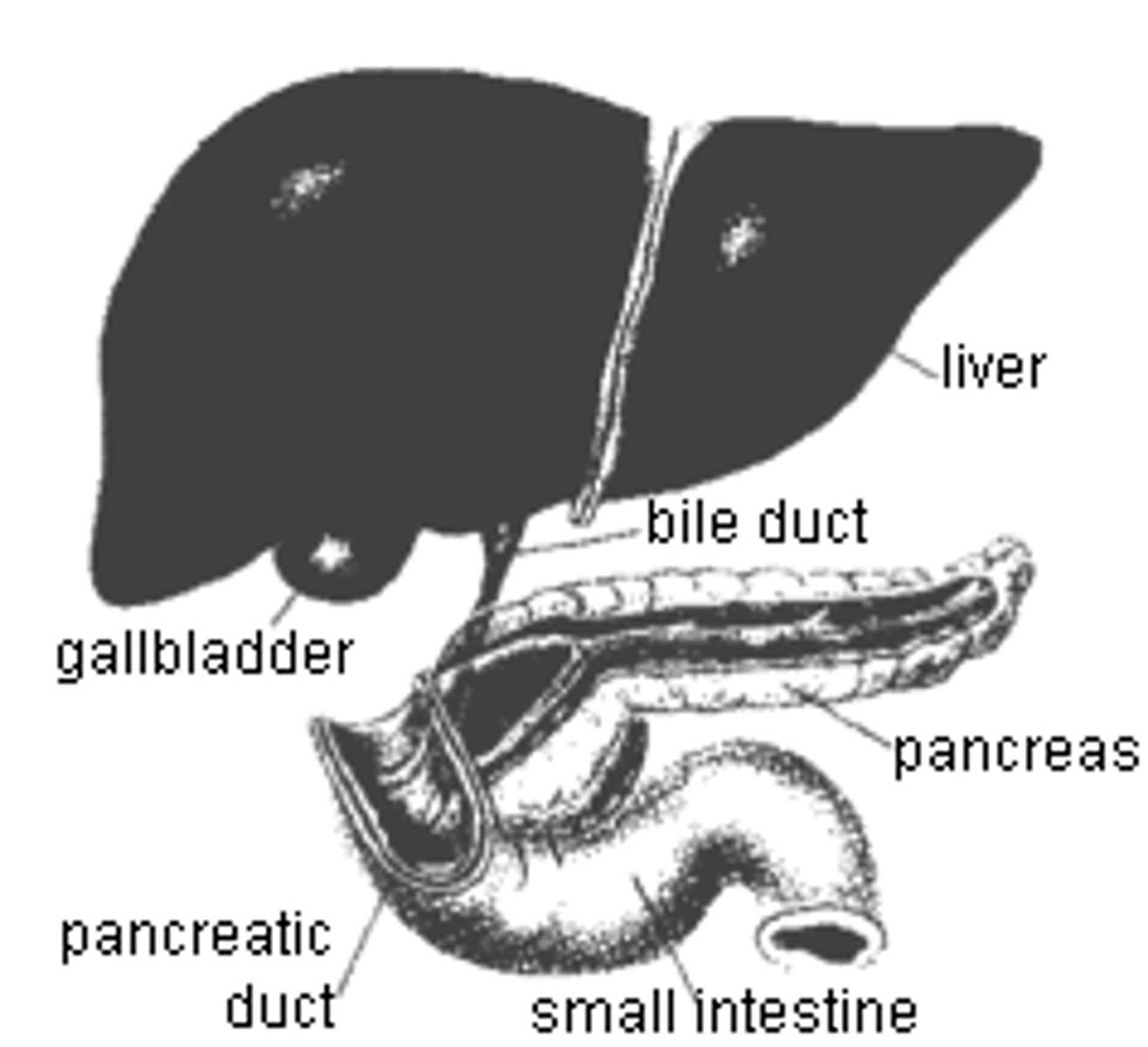
Pancreatic Duct
Extends the length of the pancreas
connects with duodenum at major duodenal papillae
General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
About 8 meters long (27ft), Muscular / irregular tube, Open at both ends, Passes through the ventral cavity. Different areas have particular functions, however, the structure of its walls, innervation (nerve structure), and how it moves food is the same throughout.
Four Distinct Layers of the Alimentary Canal Walls
Mucosa, Submucosa, Muscularis, and Serosa.
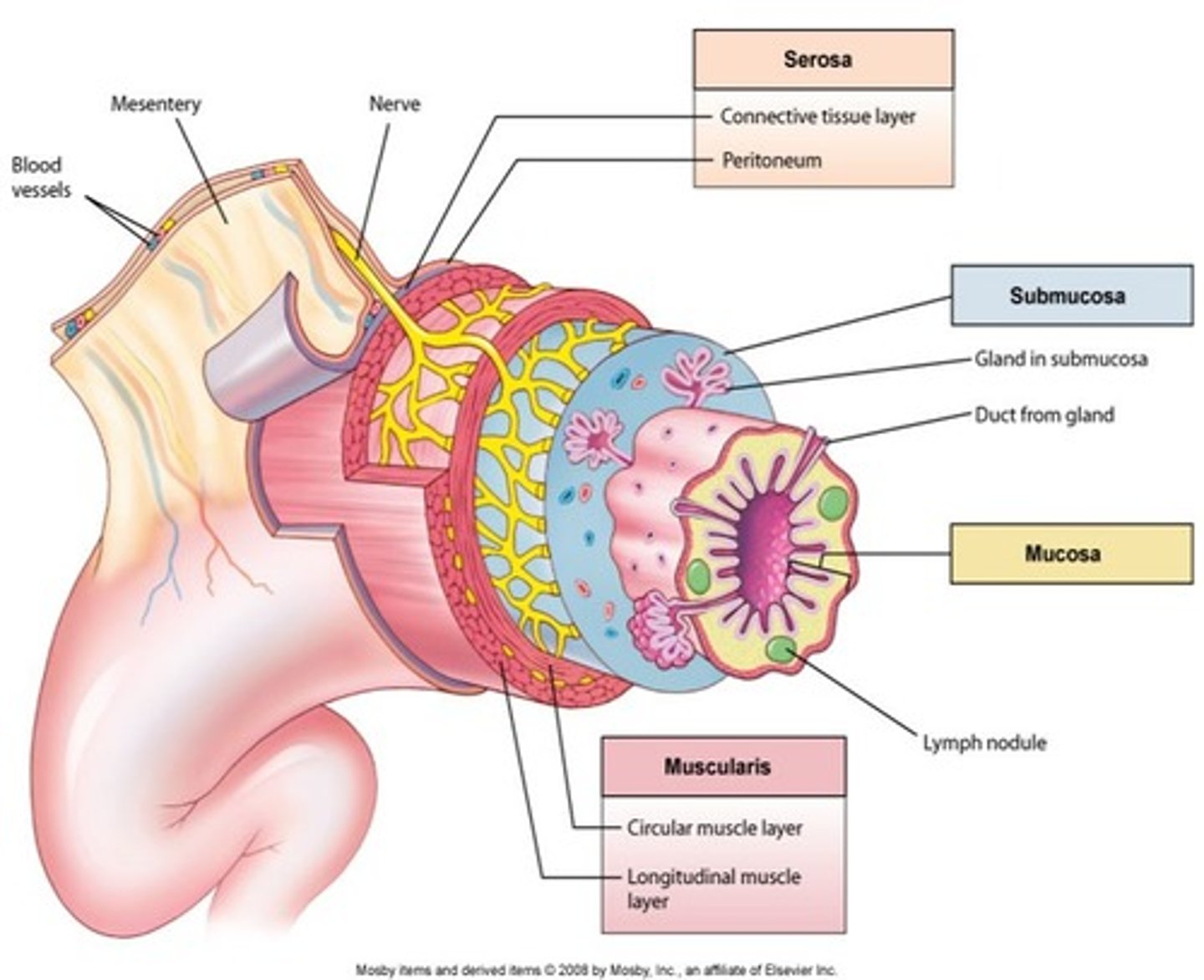
Mucosa
(The mucous membrane) 1st layer from inside out.
Lines the lumen (open inside area) of the GI tract.
Simple columnar epithelium designed for absorption, secretion, protection.
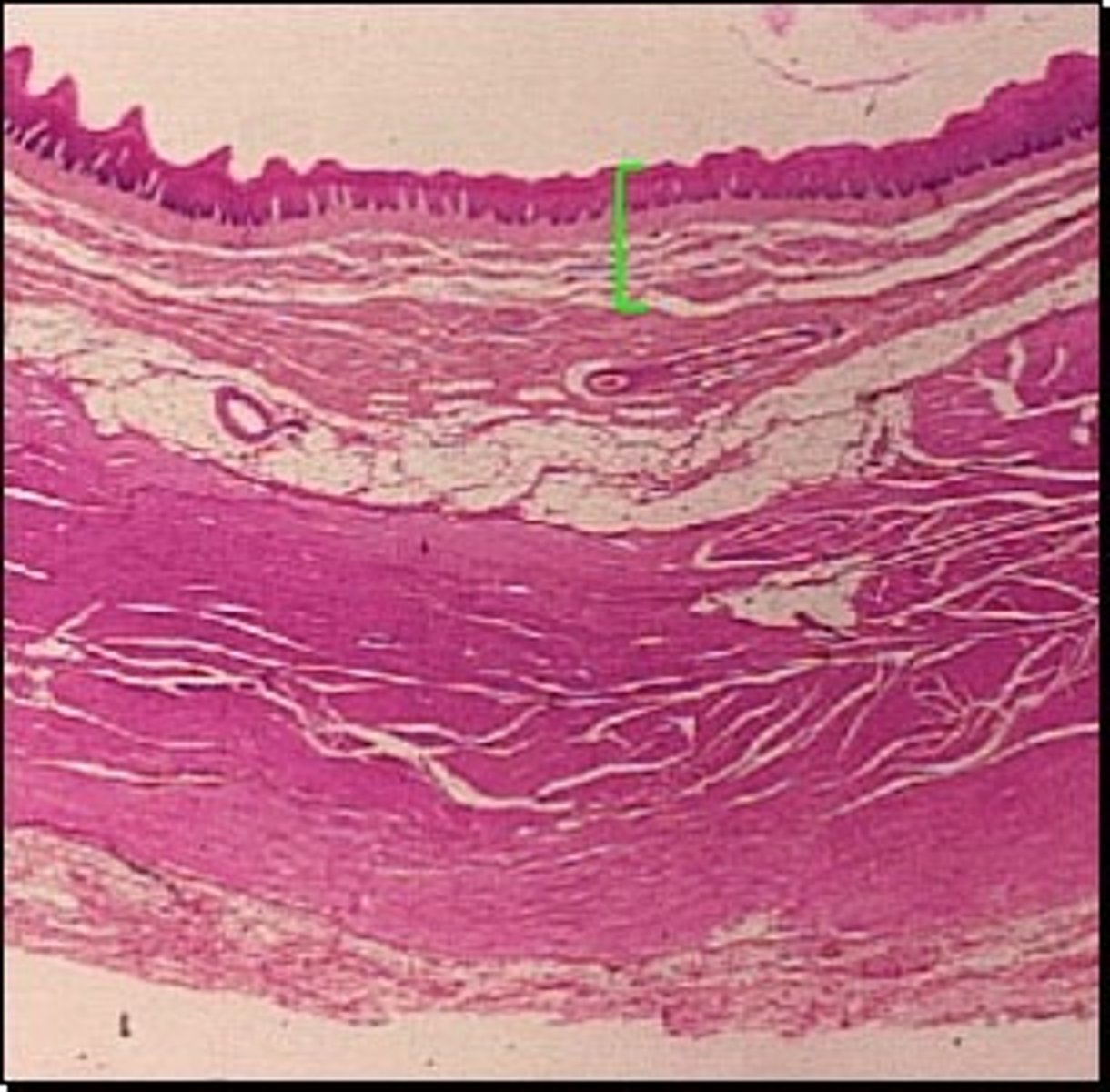
Submucosa
2nd layer from inside out.
Connective tissue layer which contains many blood vessels and nerves.
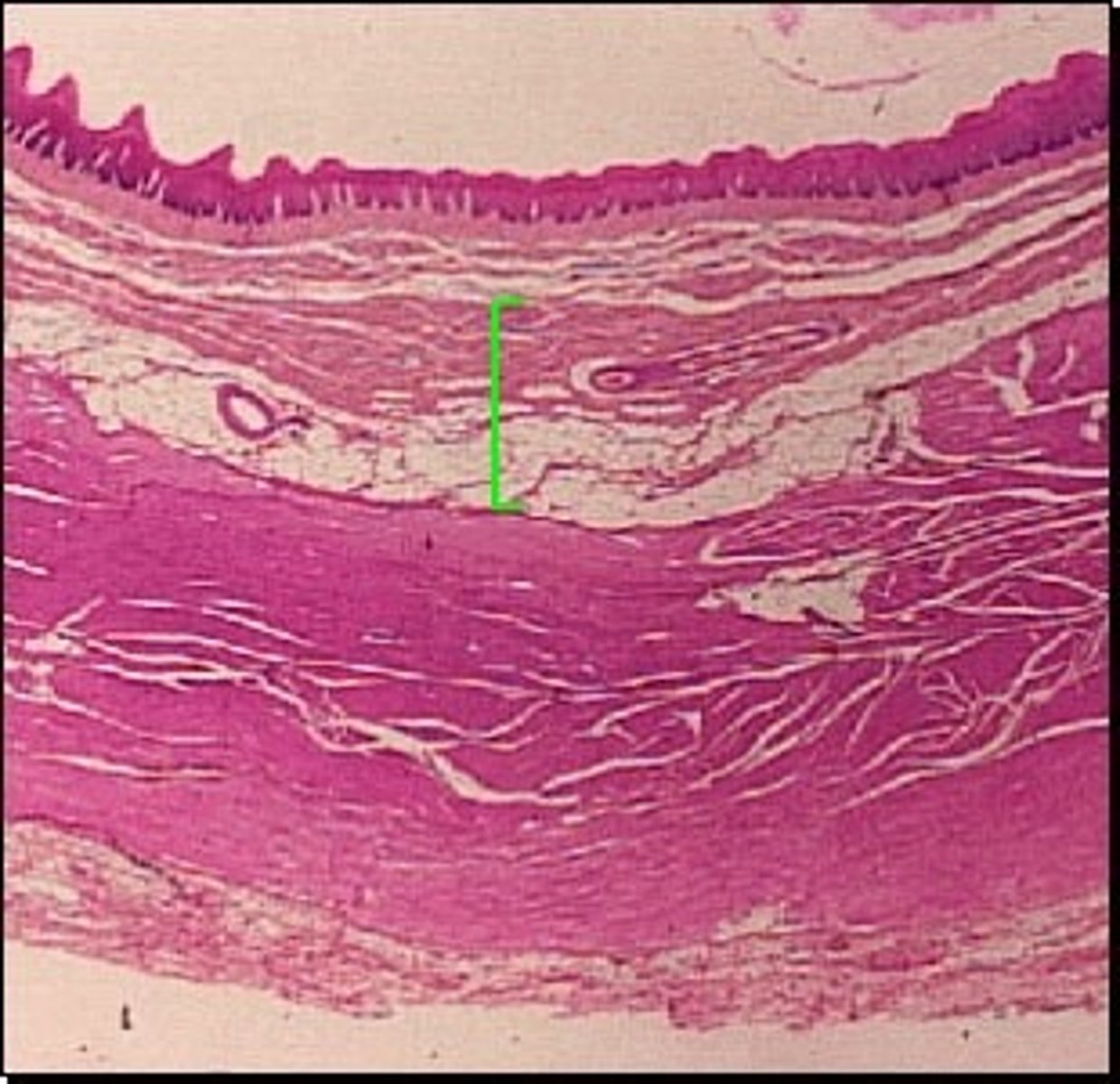
Muscularis
Third layer from the inside out.
2 layers: outer longitudinal and inner circular.
Peristalsis within the tube ( involuntary waves which produce movement).
Mixing and mechanical breakdown of larger food particles.
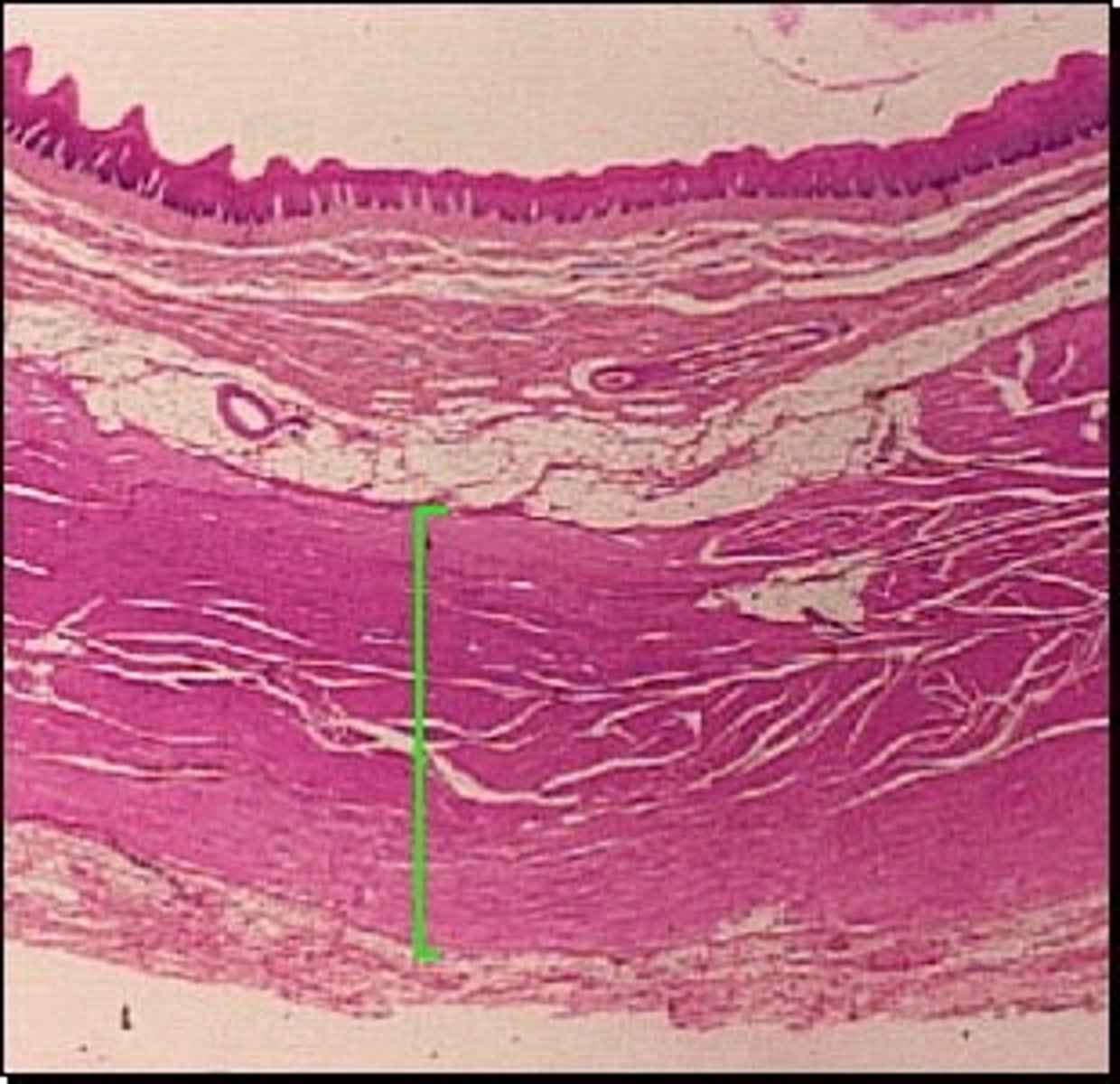
Serosa
Outermost layer from inside out.
Cells produce serous fluid which provides moisture and lubrication and allows organs within the abdominal cavity to slide freely against one another.
Peristalsis
Propelling movements created by a ring of muscle that contracts then relaxes
Serous Fluid
Fluid having a thin and watery appearance
Palate
Forms the roof of the mouth and is divided into the hard and soft portions. Helps to prevent choking.
Uvula
Prevents food or liquids from entering the nasal cavities.
Teeth
Responsible for the initial mechanical digestion. 20 Deciduous and 32 Permanent.
Deciduous begin erupting around 6 months of age. Permanent begin erupting around 6 years of age.
Amylase
An enzyme that digests starch into disaccharides. Secreted by salivary glands and by the pancreas.
Lingual Frenulum
Fold of mucous membrane that connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth
Three Major Pairs of Salivary Glands
Parotid, Submandibular, and Sublingual glands
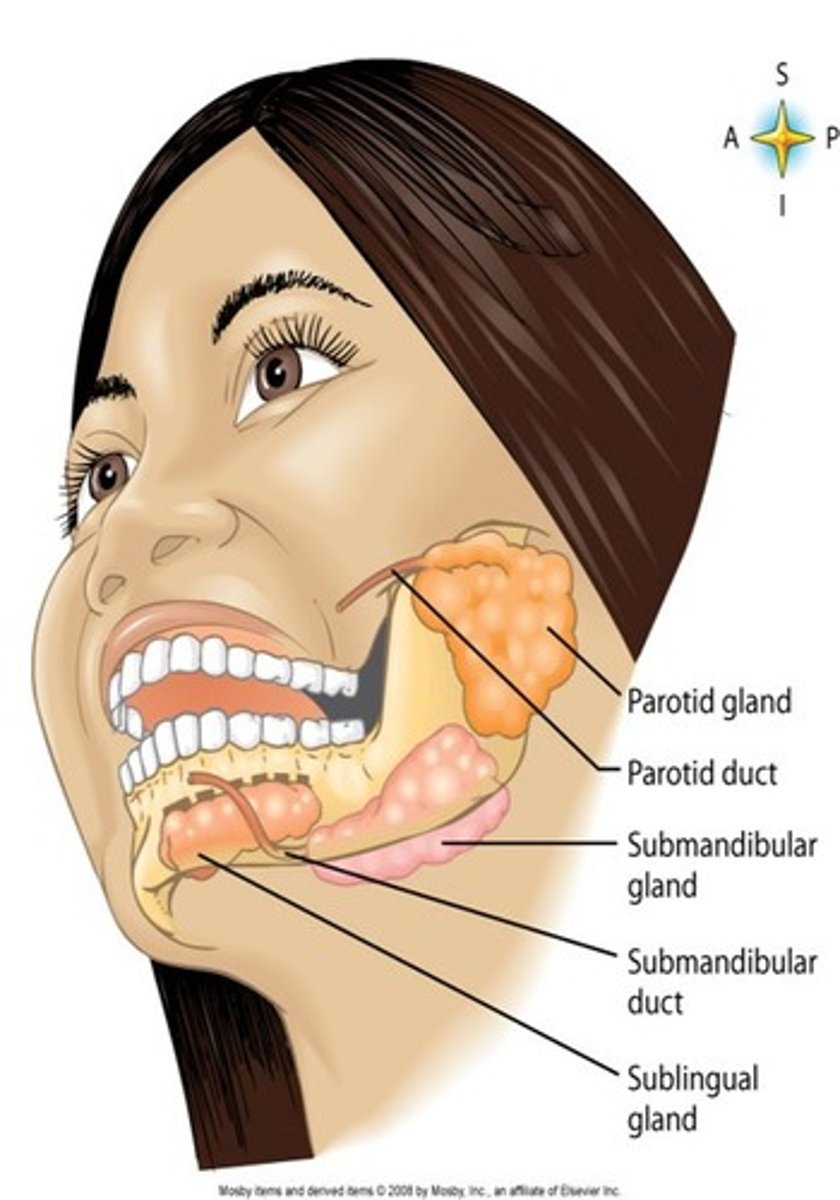
Wharton's Duct
The excretory duct of the submandibular gland
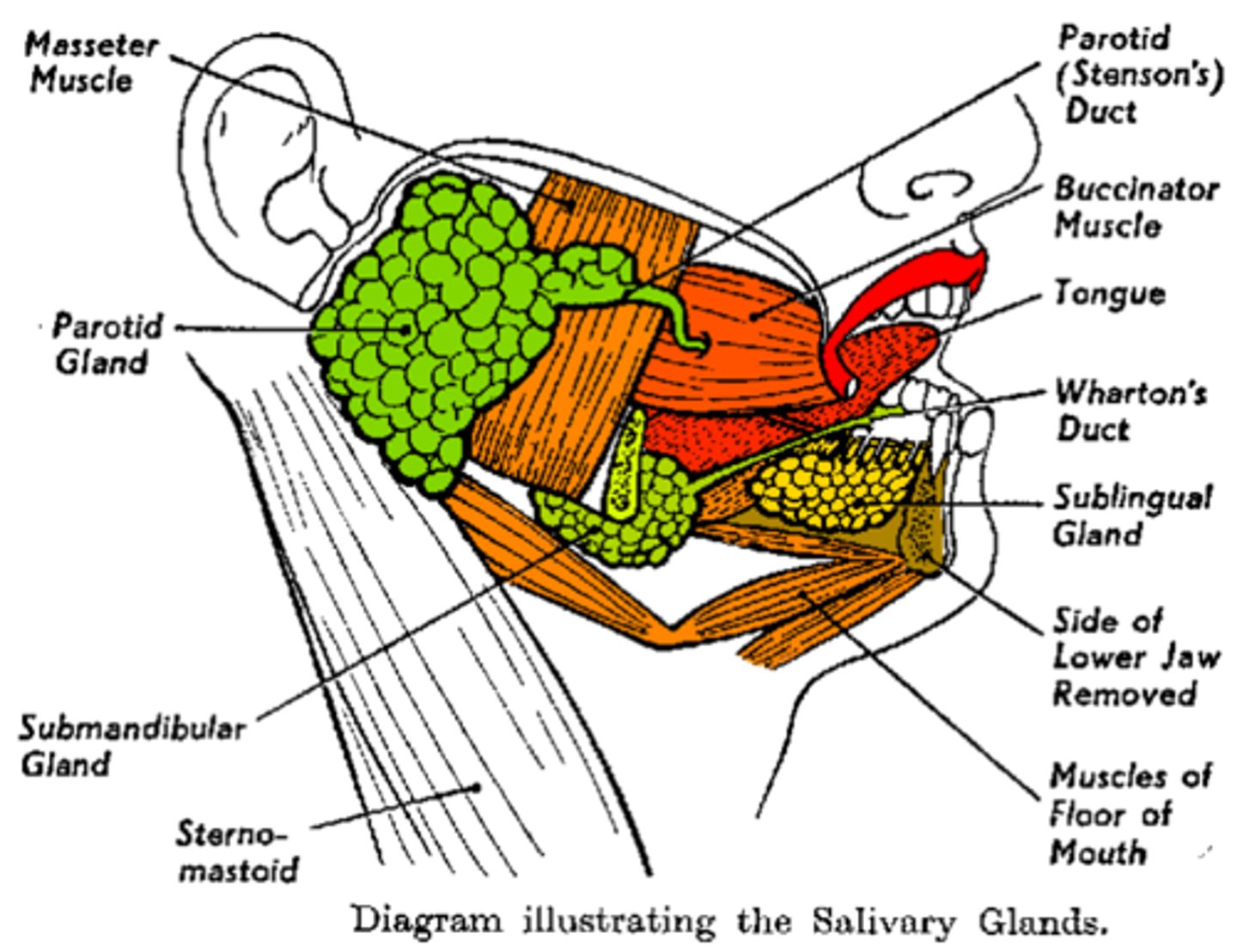
Stenson's Duct
The excretory duct of the parotid gland
Nasopharynx
Located above the soft palate and is the passageway for air.
Oropharynx
Located behind the mouth and is a passageway for food and air.
Laryngopharynx
The passageway to the esophagus.
Esophageal Hiatus
The opening where the esophagus pass through the diaphragm
Fundus
Enlarged portion to the left and above esophagus.
The region of the stomach most associated with secretion of acid and enzymes.
Body
Central or main part of the stomach and lies between the fundic and the pyloric region.
Pylorus
Lower narrow section that ends with the Pyloric sphincter
Three Areas Of The Stomach
Fundus, Body, and Pylorus
Main Functions of the Stomach
Stores swallowed food. Mixes the food with acids.
Begins the second phase of digestion: breakdown of proteins. Sends the formed chyme to the small intestine.
Gastric Juices
Contain hydrochloric acid and enzymes.
Constantly being produced though the rate varies.
Seeing, smelling, or tasting appetizing food stimulates increased production.
Digestive enzymes:
-Pepsinogen
-Activated by HCl (Hydrochloric Acid)
-Forms Pepsin
--begins protein digestion in stomach
--turns bolus into chyme
Pepsinogen
The inactive form of pepsin that is first secreted by specialized cells located in gastric pits of the stomach.
Pepsin
Enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller polypeptide fragments
HCl
Hydrochloric Acid (Stomach Acid)
Digestive Enzymes
Proteins found in digestive juices that act on food substances, causing them to break down into simpler compounds. Secreted by the Pancreas.
-Pepsinogen
-Activated by HCl (Hydrochloric Acid)
-Forms Pepsin
--begins protein digestion in stomach
--turns bolus into chyme
Pancreas
Lies behind the stomach in C shape of duodenum.
Has both and endocrine and exocrine functions:
Exocrine - secretion of the digestive juice
Endocrine - secretion of insulin.
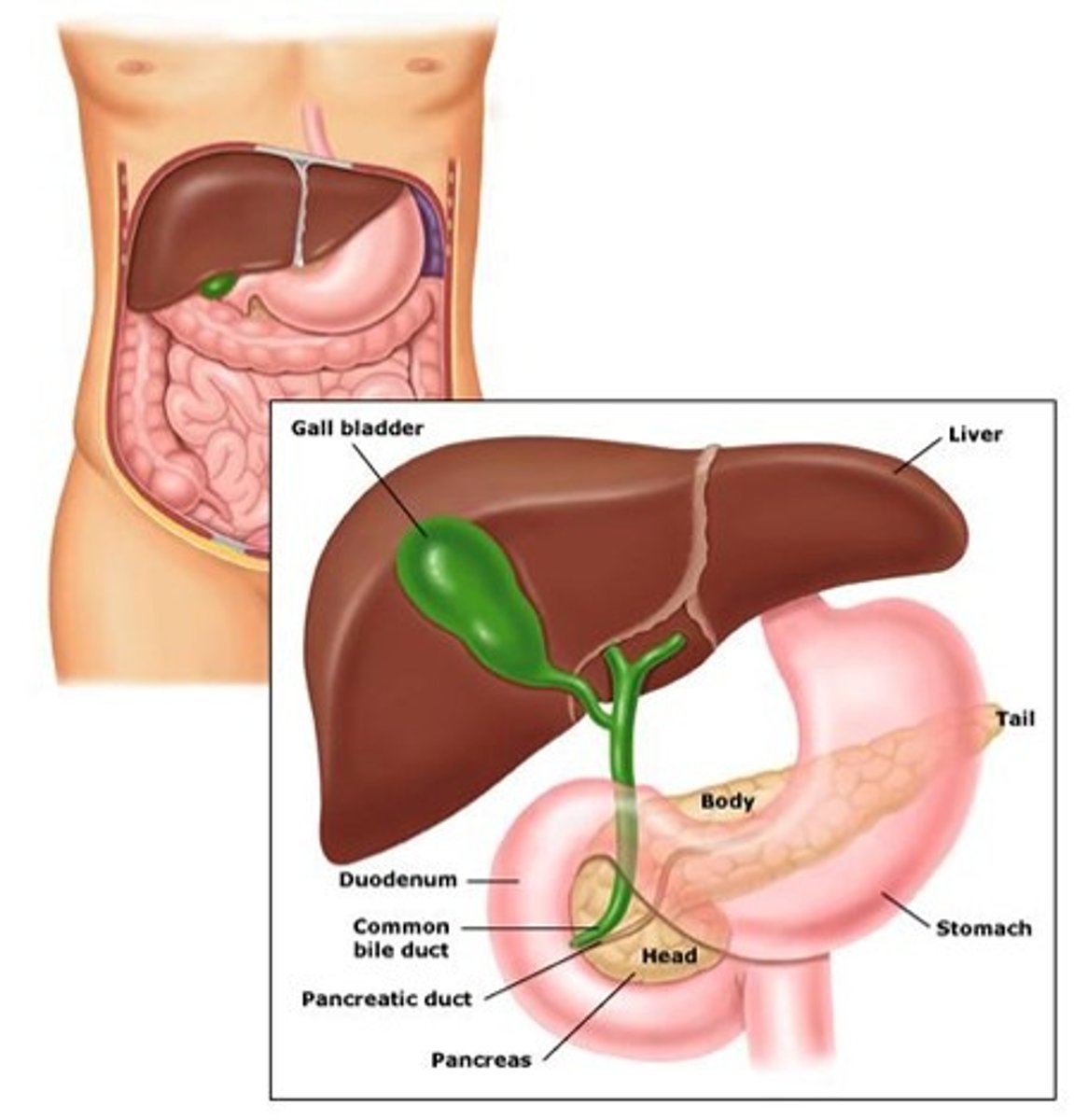
Duodenal Papillae
Opening through which bile and enzymes from the pancreas enter the duodenum
Pancreatic Juice
The most important digestive juice.
Contains enzymes:
Pancreatic amylase - breaks down carbohydrates.
Pancreatic lipase - breaks down fats.
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin and Carboxypeptidase - act on proteins.
Contains sodium bicarbonate, an alkaline substance, that neutralizes HCl in gastric juice that enters the intestines.
Pancreatic Amylase
Breaks down carbohydrates.
Pancreatic Lipase
Breaks down fats.
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin and Carboxypeptidase
Act on proteins.
Liver
Fills entire upper right section of abdominal cavity and
sits just below diaphragm. It is and exocrine gland and the largest gland in the body. Divided into two lobes.
Each lobe has its own hepatic duct. Hepatic ducts merge to form the common hepatic duct.
Liver Functions
Responsible for: The metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Excretion of bilirubin, cholesterol, hormones, and drugs. Enzyme activation. Storage of glycogen, vitamins, and minerals. Synthesis of plasma proteins, such as albumin, and clotting factors. Blood detoxification and purification. Bile production and secretion.
Common Hepatic Duct
Name of the duct where all Liver ducts merge.
Bile
Contains cholesterol and bile salts. Allows for emulsification of fats and elimination of cholesterol from the body.
Enhances the absorption of fatty acids, cholesterol and the fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K.
Lack of = poor lipid absorption, vitamin deficiencies. Stored in the Gallbladder.
Mesentery
Suspends the small intestines from the posterior abdominal wall. Is a double layered peritoneal membrane.
Plicae
Deep circular folds of the mucosa and submucosa that extend completely or partially around the circumference of the small intestine
Villi
Millions of fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption. Each contains: blood capillaries, lymphatic vessel (lacteal), and nerve fibers.
Microvilli
Brush-like border or the villi which further increases surface area
Vermiform Appendix
Worm-like projection of lymphatic tissue hanging off the cecum with no digestive function; may help to resist infection.
Ascending Colon
Begins at Cecum and travels upward. Becomes hepatic flexure.
Transverse Colon
Extends across front of abdomen. Becomes the splenic flexure.
Hepatic
Pertaining to the liver
Splenic
Pertaining to the spleen
Descending Colon
Down the left side of the abdomen
Sigmoid Colon
S-shaped segment. Terminates at the rectum
Anal Canal
The last 2.5 to 4 centimeters of the large intestine with its proximal end attached to the rectum
Functions of the Large Intestines
Receives undigested and unabsorbed food material. Some reabsorption of water and electrolytes. Little or no digestive function. Housing bacteria (called intestinal flora) inside. Synthesize certain vitamins such as K, B12, thiamine and riboflavin. Produce intestinal gas (flatus). Responsible for pungent odor.
Movements of Large Intestines
Peristalsis much slower. Normal passage is 3 - 5 days. Medical conditions (i.e. colitis or inflamed colon) can initiate more peristaltic waves.