AP World: Modern - Unit 2: Networks of Exchange
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
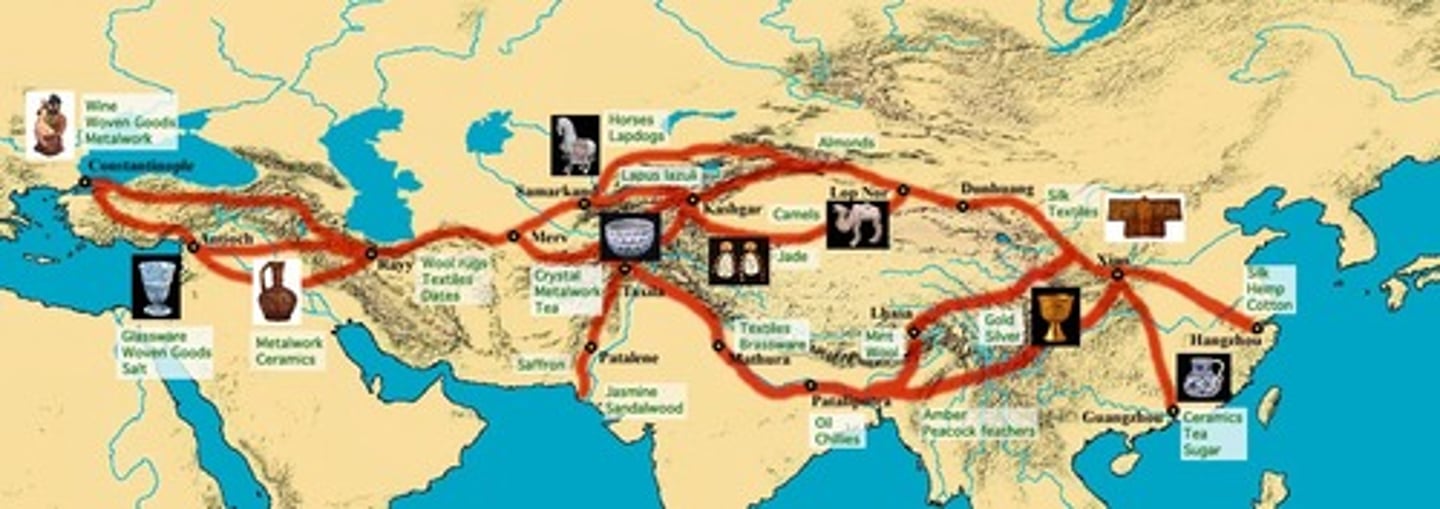
Silk Road Trade
The most famous of the trading routes established by pastoral nomads connecting the Chinese, Indian, Persian, and Mediterranean civilizations; transmitted goods and ideas among civilizations.
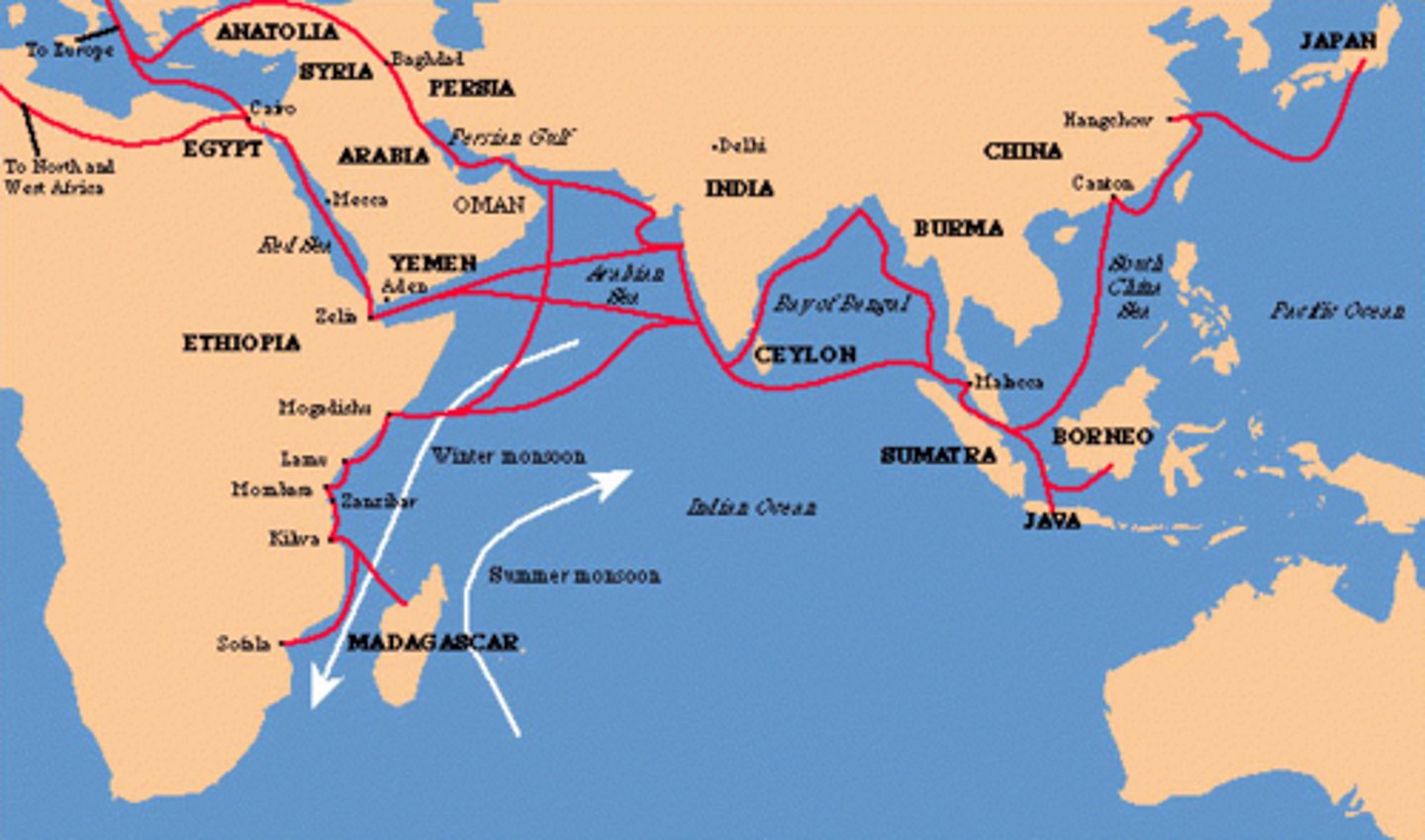
Indian Ocean Trade Route
linked East Asia with Arabian Peninsula and Africa; traded gold, spices, and slaves; spread Islam and Buddhism; sea trade
Silk Road technology
Stirrups, saddles, caravanserai
Kashgar
a central trading point where the Eastern and Western Silk Roads met.
Samarkand
During the rule of Timur Lane was the most influential capital city, a wealthy trading center along the Silk Roads known for decorated mosques and tombs.
New forms of credit
Bills of exchange, banking houses, paper money - these made trade safer and more efficient over long distances

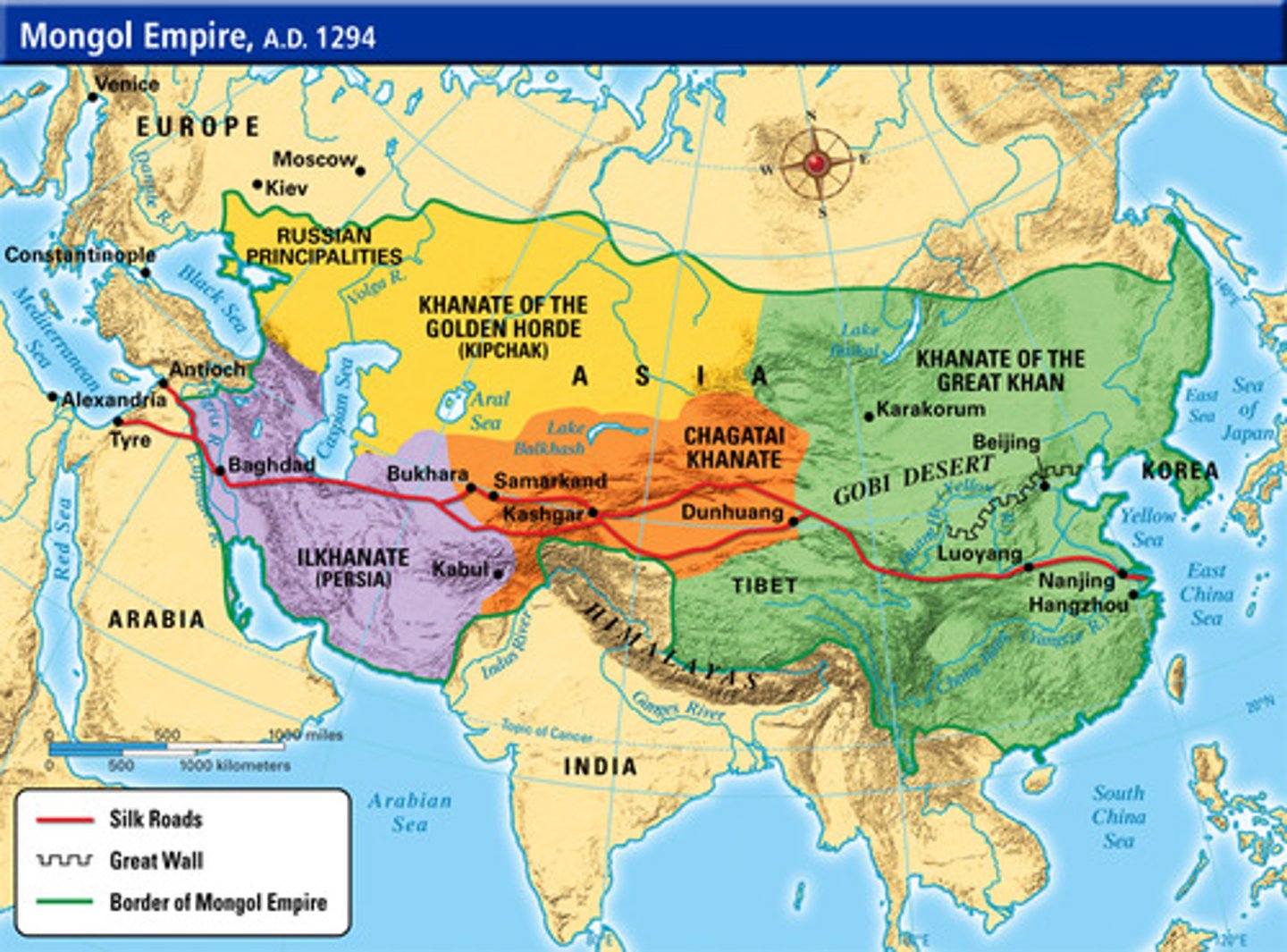
Mongols
People from Central Asia who created the largest single land empire in history.

Pax Mongolica
The period of approximately 150 years of relative peace and stability created by the Mongol Empire. Trade and culture thrived.
Khanate
Four regional Mongol kingdoms that arose following the death of Chinggis Khan.
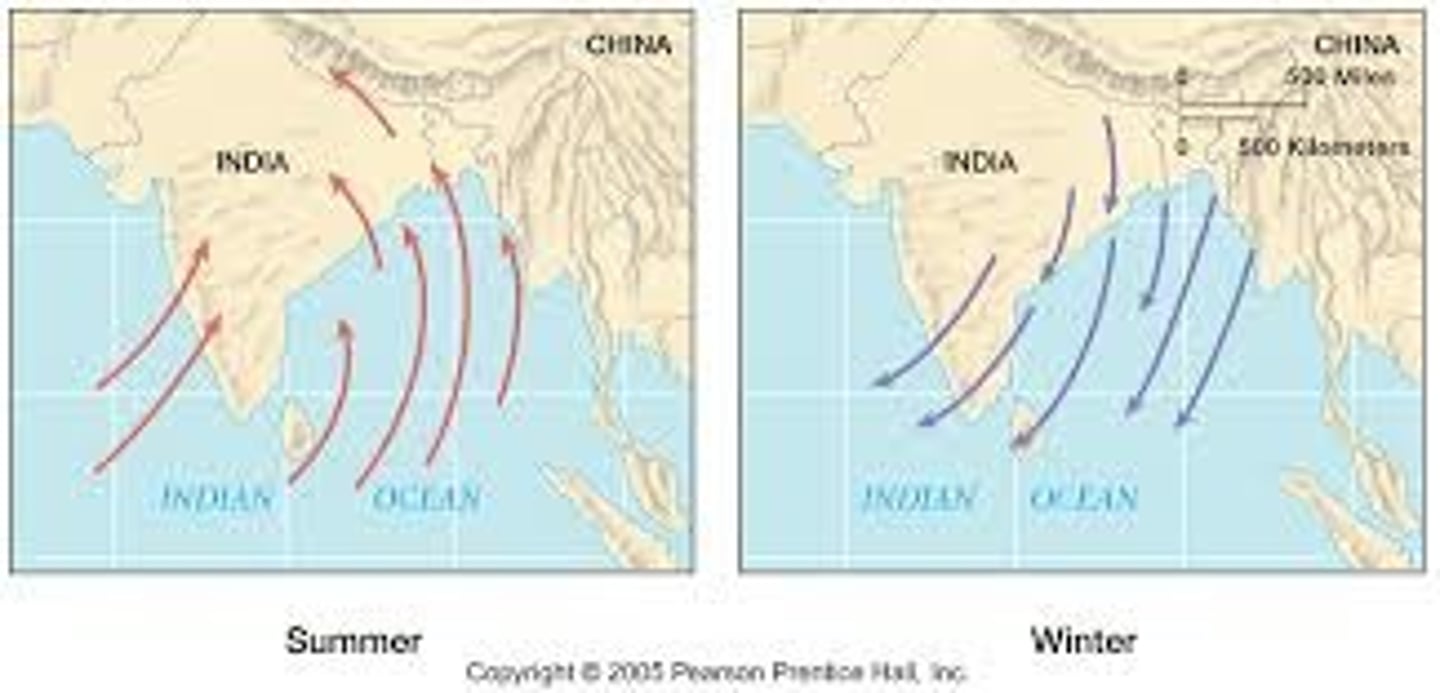
Monsoons
Seasonal wind patterns that cause wet and dry seasons; better understanding was key to Indian Ocean trade routes.
Indian Ocean technology
compass, astrolabe, larger ships (dhow, junks), lateen sails
Junk Ships
A very large flat-bottom sailing ship produced in China specially designed for long-distance commercial travel.
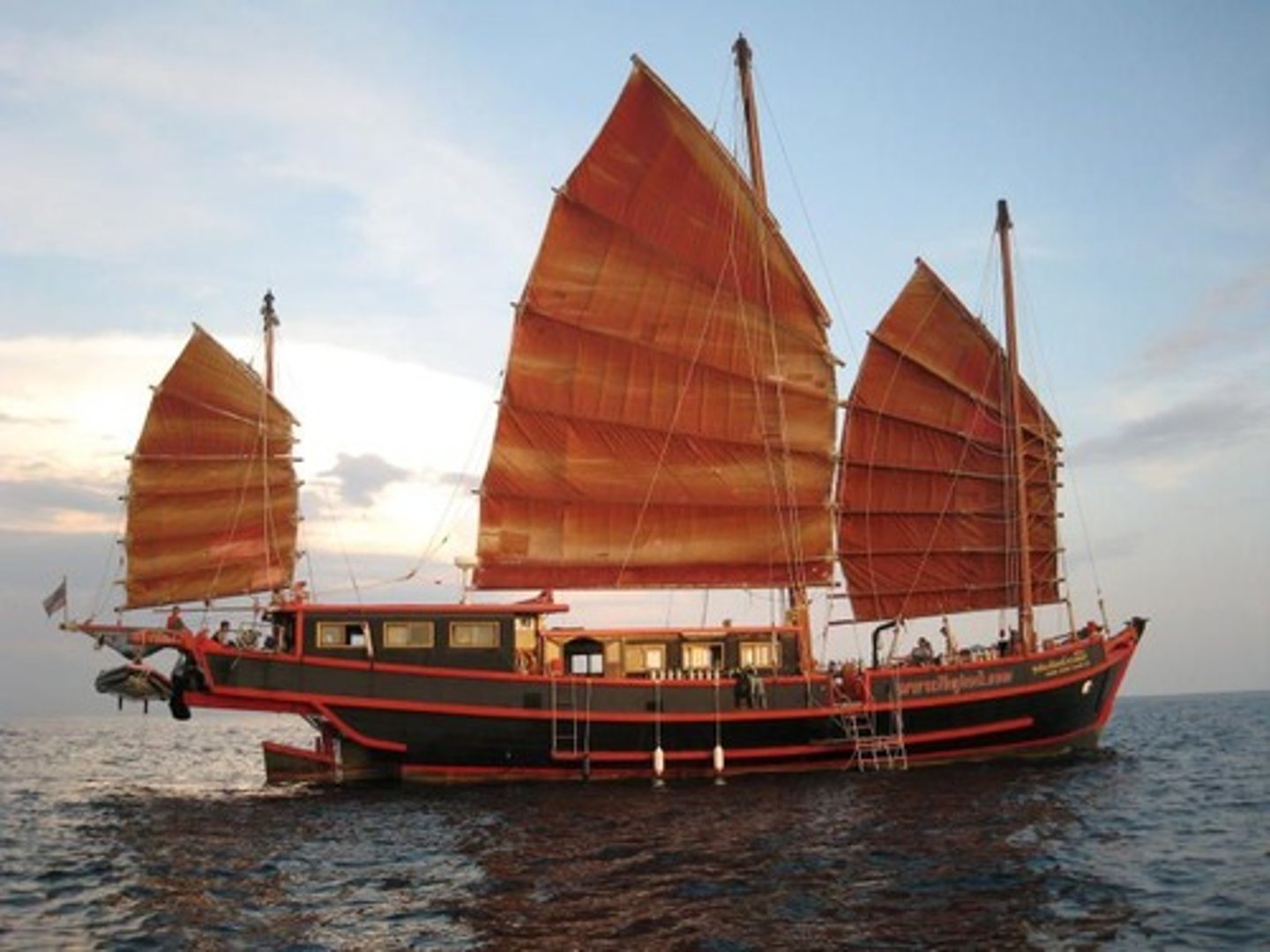

Dhow
Sailboat using wind-catching, triangular sails; used by Arab traders
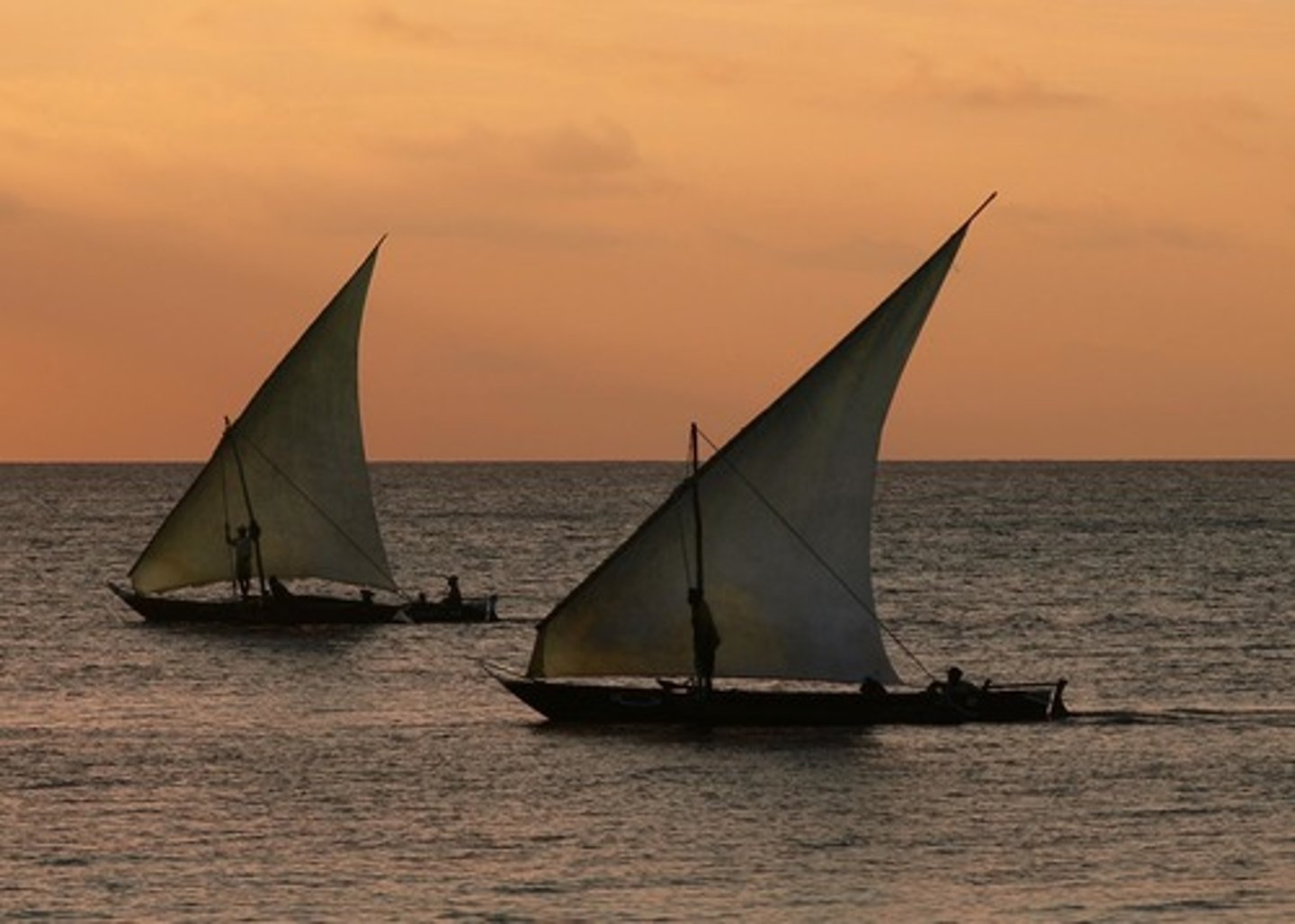

Diasporic communities
merchant communities that introduced their own cultures into other areas
Swahili city-states
Dominated trade along the east African coast; an illustrative example of states growing due to Indian Ocean trade.
Malacca
Flourishing trading city in Malaya; established a trading empire after the fall of Srivijaya. An illustrative example of states growing due to Indian Ocean trade.
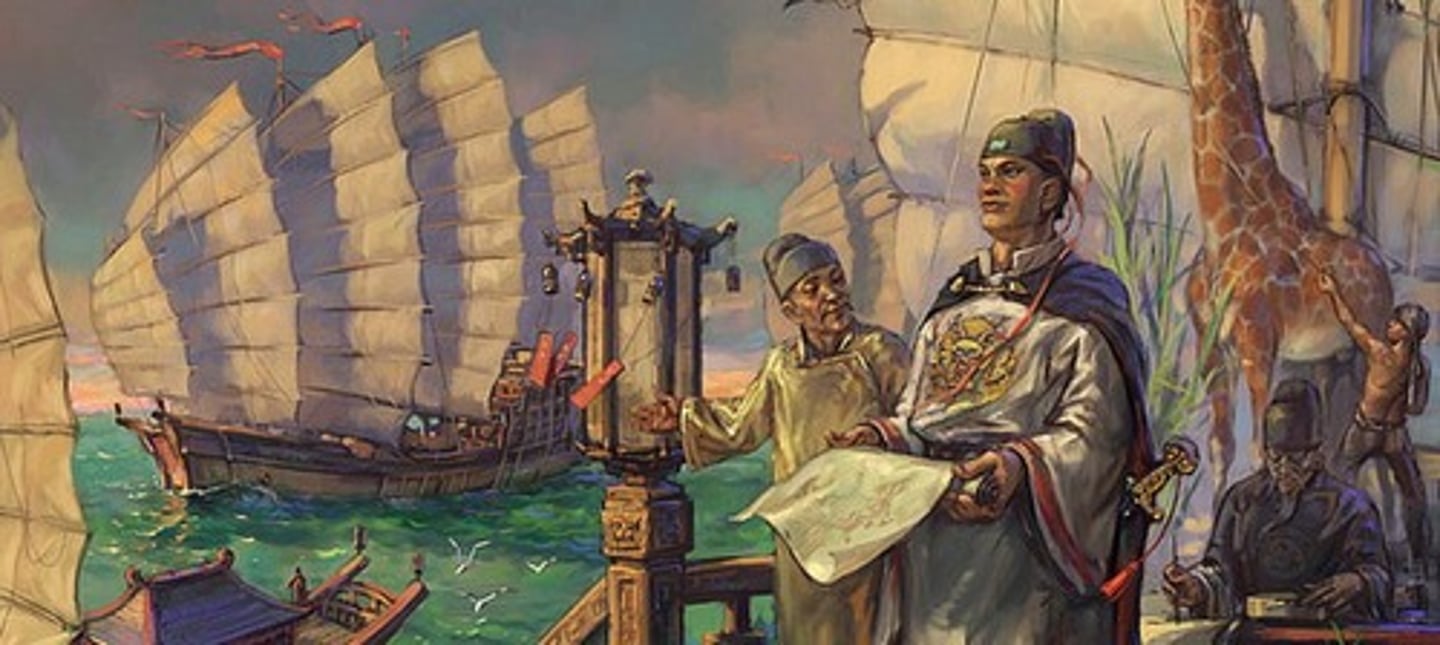
Zheng He
An imperial eunuch and Muslim, entrusted by the Ming emperor Yongle with a series of state voyages that took his gigantic ships through the Indian Ocean, from Southeast Asia to Africa.

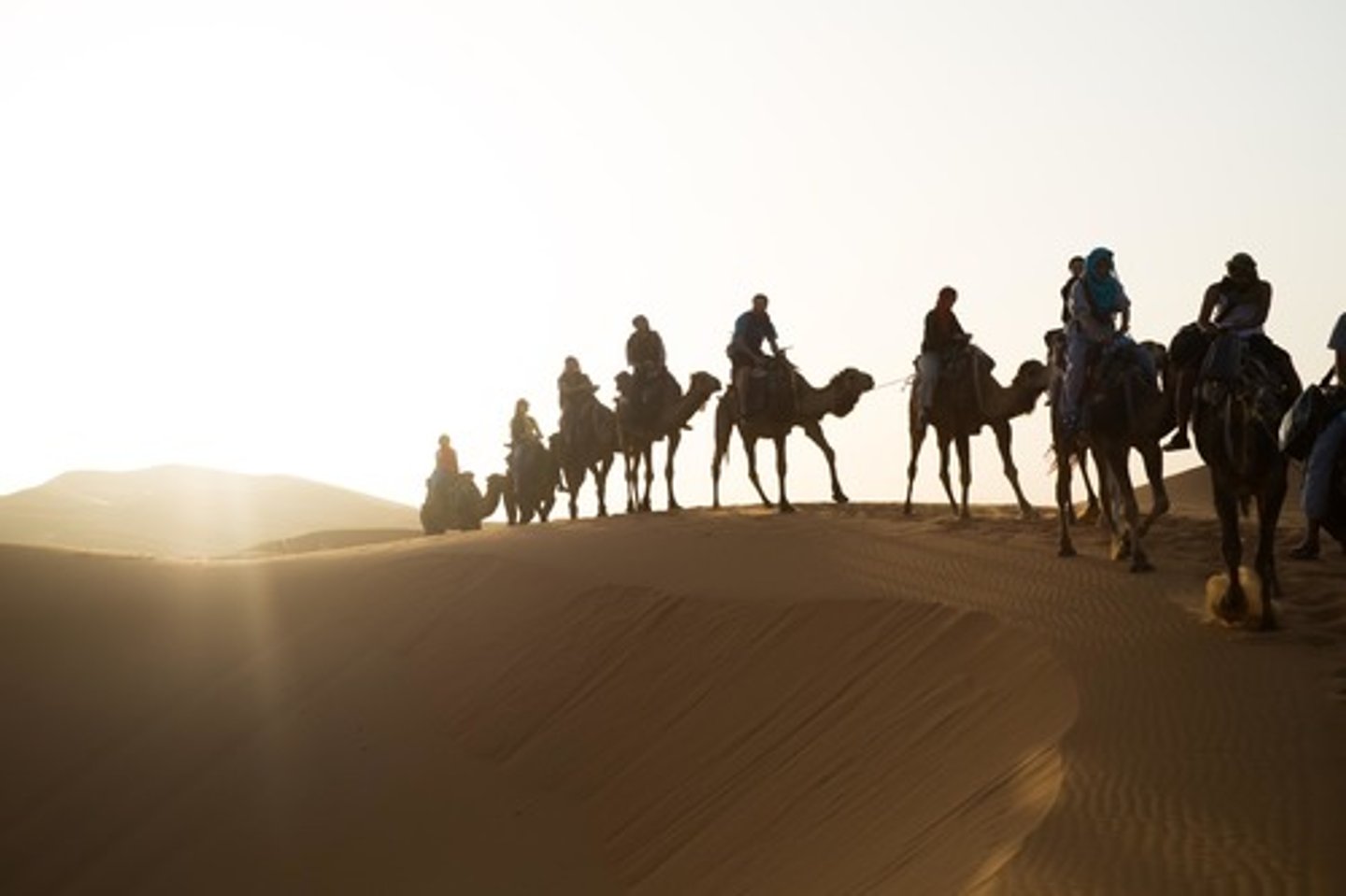
Trans-Saharan Trade
Major trade route that traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling dessert, camels played a huge role in the trading
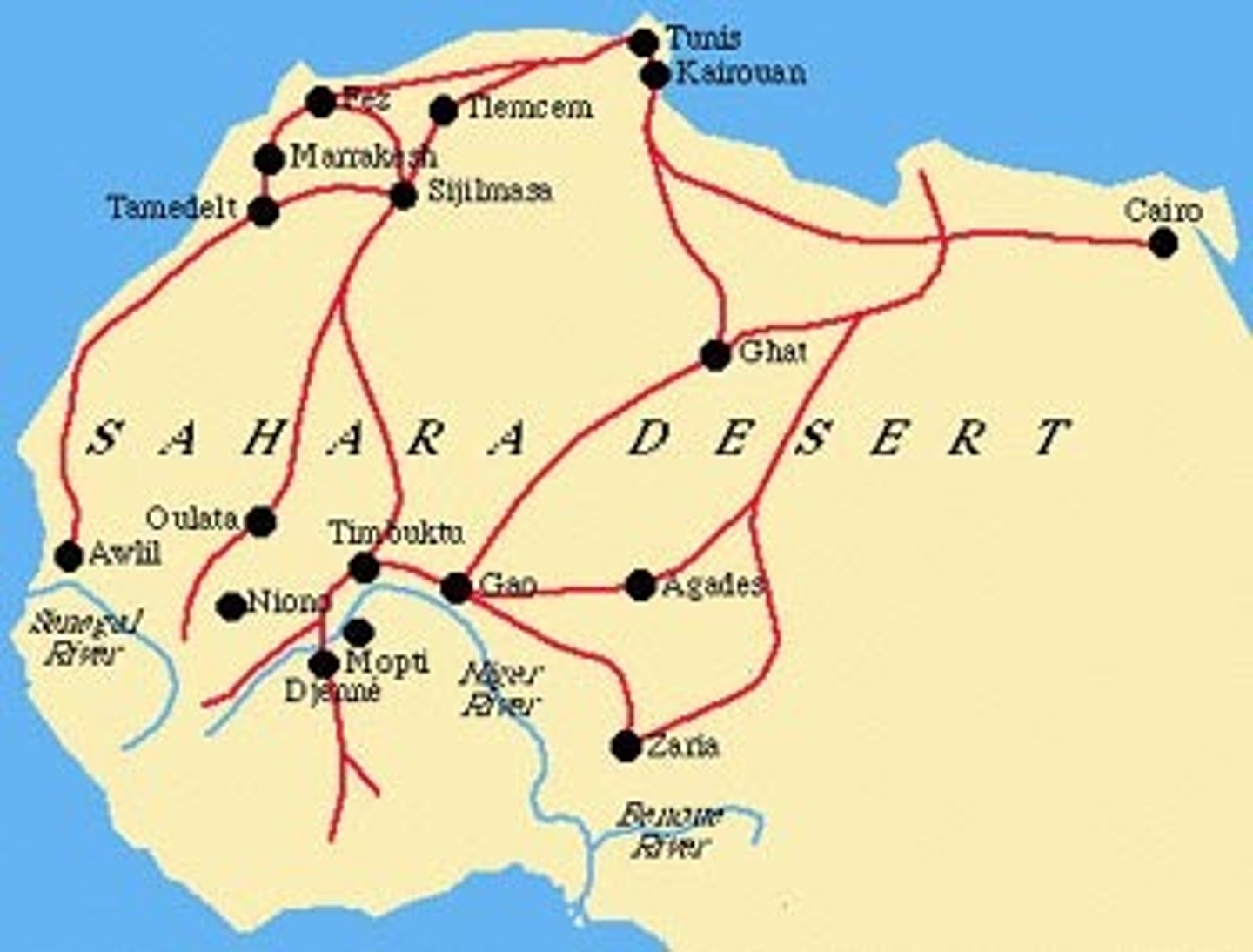
Caravanserai
a roadside inn where travelers (caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey
Gold-Salt Trade
The economic system of north Africa and across the Sahara Desert; controlled by African kingdoms like Ghana, Mali and Songhai.

Ghana
Kingdom in sub-Saharan West Africa between the sixth and thirteenth centuries C.E. Their location allowed them to profit from the gold-salt trade.
Mali Empire
Formed in 1240 when Sundiata took control of Ghana Empire. It controlled trade across Sahara, the South and the Niger River.
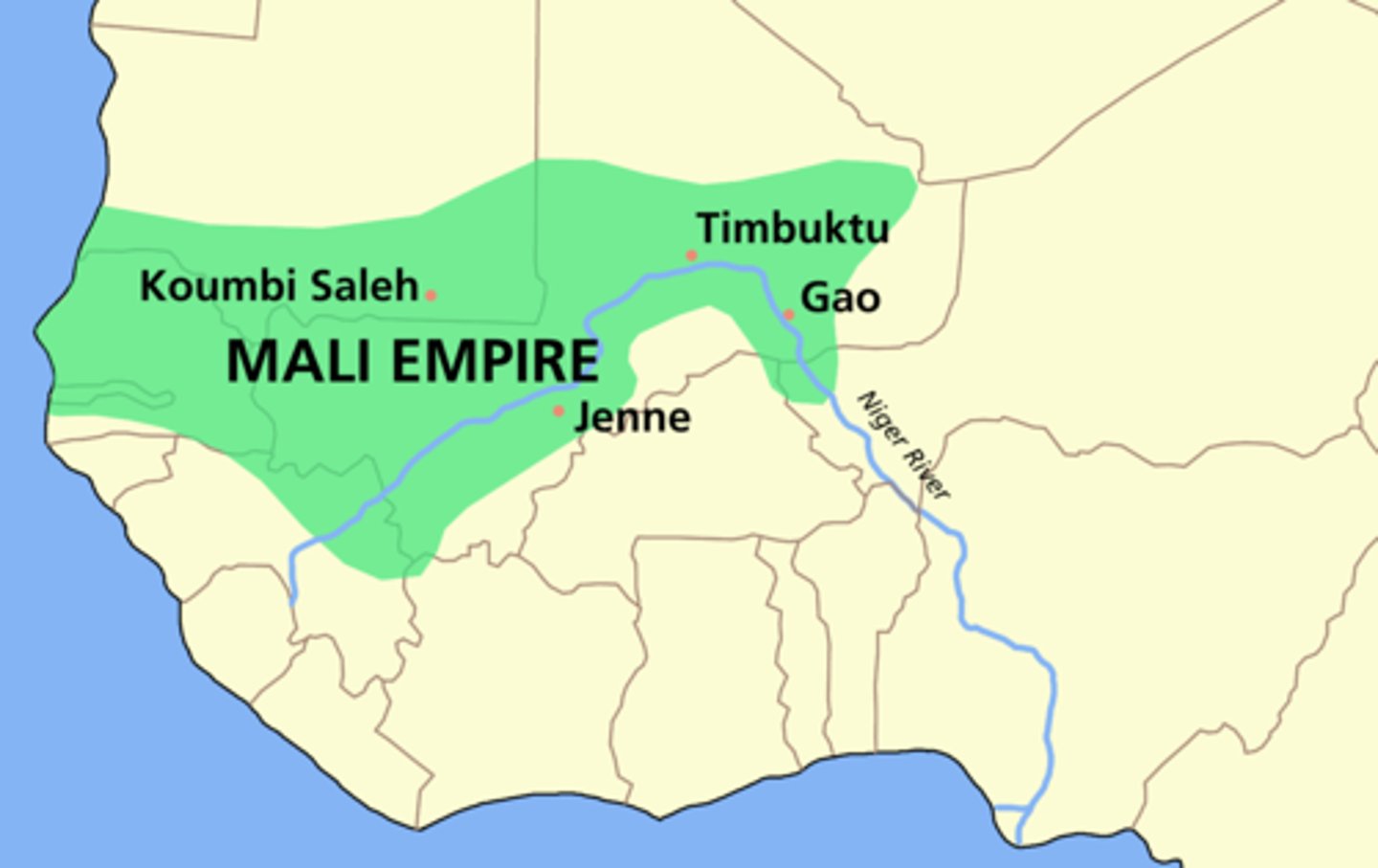
Songhai
a West African empire that conquered Mali and controlled trade from the 1400s to 1591
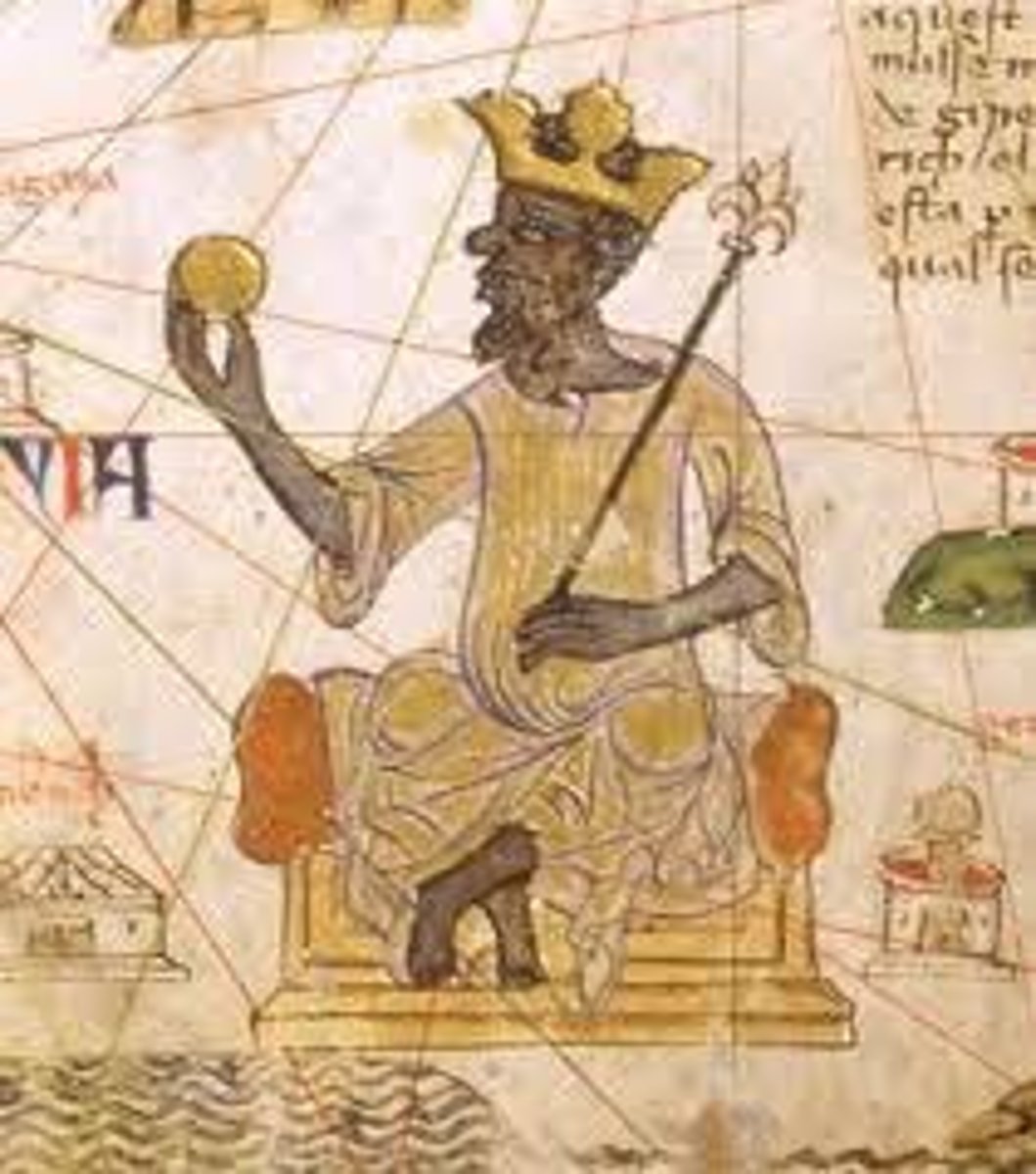
Mansa Musa
Emperor of the kingdom of Mali in Africa. He made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca and established trade routes to the Middle East.

Diffusion of technology
Gunpowder and paper making from China
Ibn Battuta
Moroccan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan.
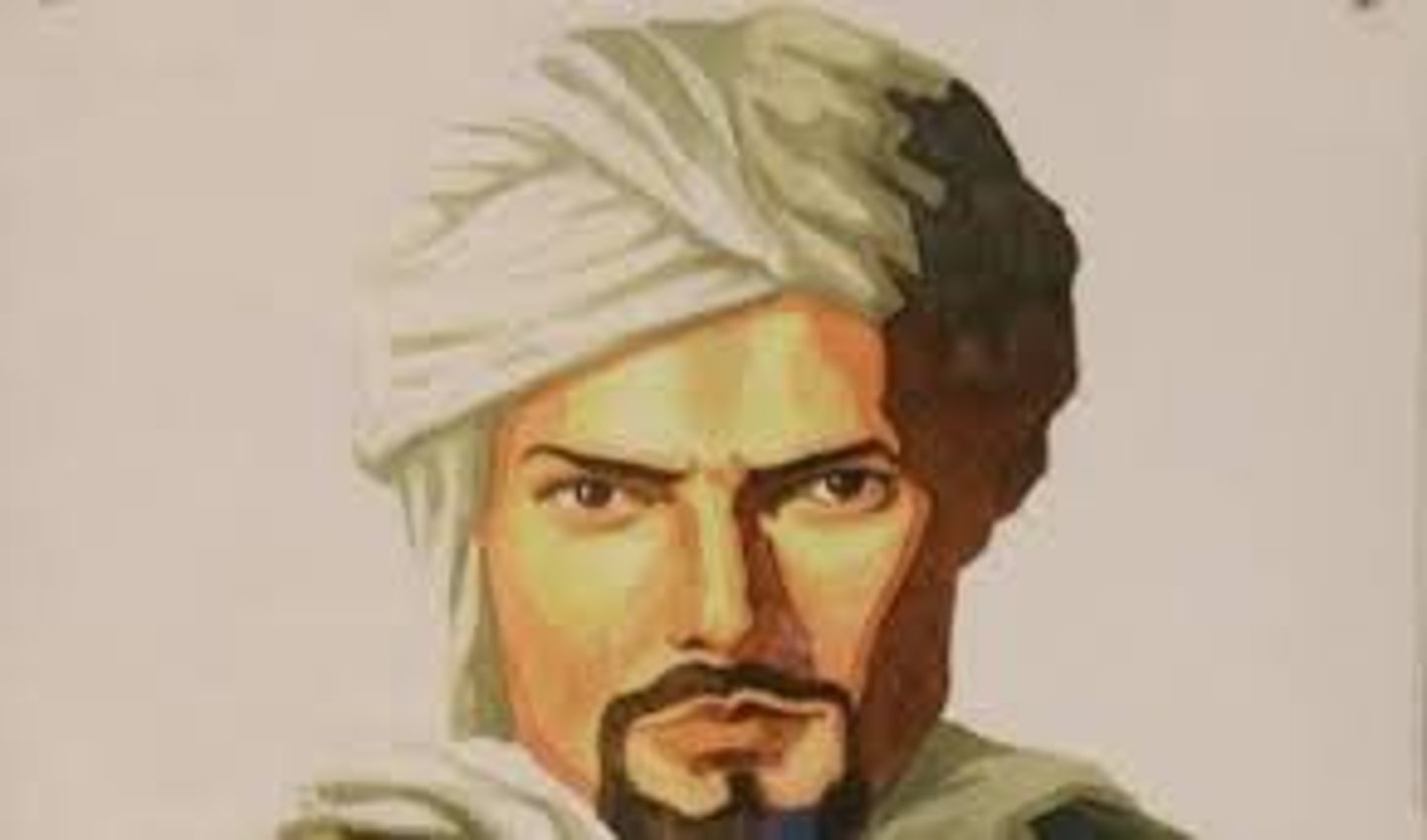

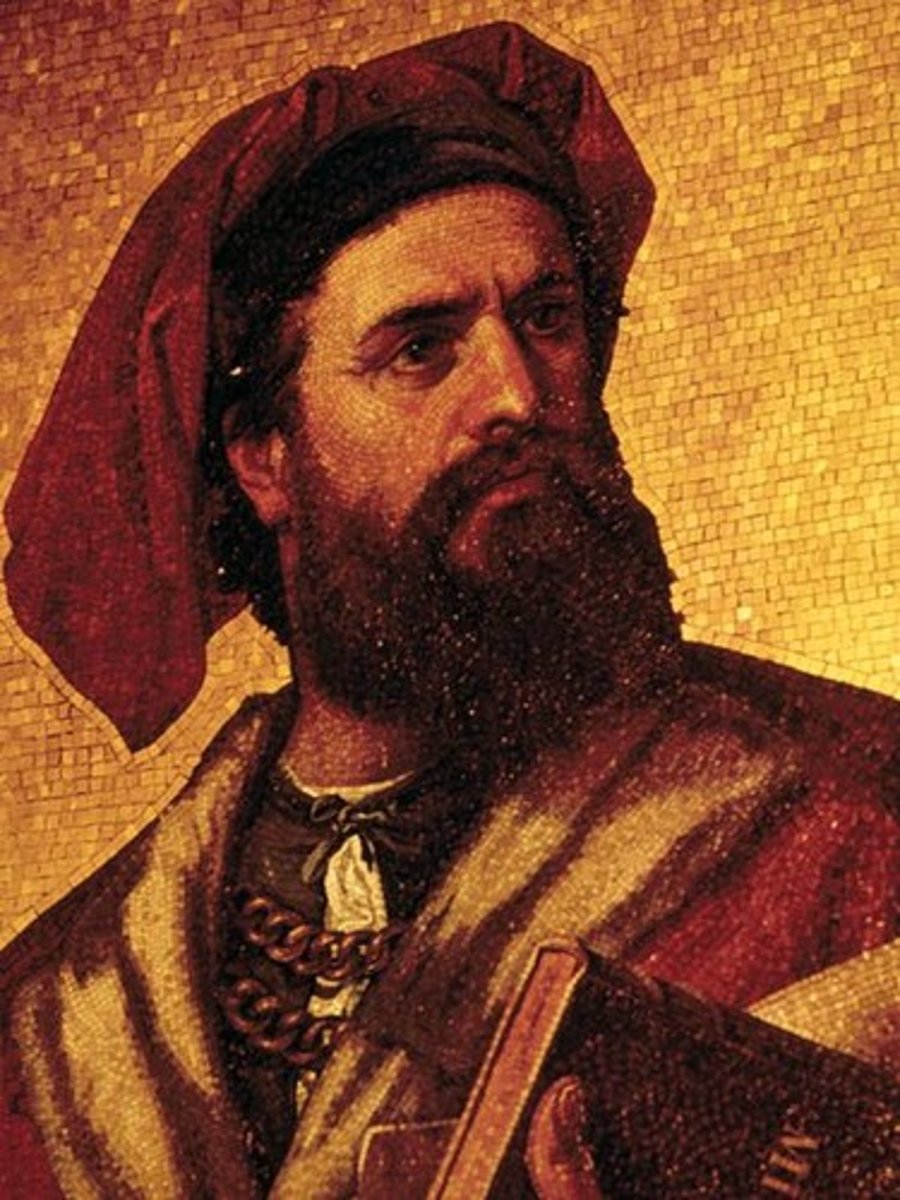
Marco Polo
Italian explorer and author. He made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys. He is responsible for much of the knowledge exchanged between Europe and China during this time period.

Margery Kempe
Wrote the first autobiography in the English language. Chronicles her pilgrimages to holy sites in Europe and Asia. Claimed to have vision that called her to leave the vanities of the world (saw vision of Christ). Her writings provide insight into the middle class female experience in the Middle Ages.
Diffusion of crops
Bananas in Africa, new rice varieties in East Asia, citrus throughout Dar al-Islam and the Mediterranean basin
Bubonic Plague
Disease brought to Europe from the Mongols during the Middle Ages. It killed 1/3 of the population and helps end Feudalism. Rats, fleas.
luxury goods
goods that have special qualities that make them more expensive than alternative goods
porcelain
a thin, beautiful pottery invented in China

Textiles
a type of cloth or woven fabric often sold on trade routes

silk
a valuable cloth, originally made only in China from threads spun by caterpillars called silkworms

Monopoly
A market in which there are many buyers but only one seller. Ex: China had a monopoly on silk

stirrup
device for securing a horseman's feet, enabling him to wield weapons more effectively.

Gunpowder
The formula, brought to China in the 400s or 500s. In later centuries it was used to make explosives and grenades and to propel cannonballs, shot, and bullets.

Zoroastrianism
system of religion founded in Persia in the 6th century BC. This religion blocked the further spread of Buddhism to the west.

Smallpox
a disease that causes a high fever and often death. Devastaed populations in Rome and Han China and led to their decline.
barter economy
system in which one set of goods or services is exchanged for another.

money economies
an economic system based on money rather than barter. The growth of trade increased the development of this type of economy, as bartering became too difficult.

Pastoral People
mobile shepharding, herders, with a need for lots of grazing areas that follow seasonal changes. The Mongols were pastoral people.

Genghis Khan (Temujin)
A Mongolian general and emperor of the late twelfth and early thirteenth centuries, known for his military leadership and great cruelty. He conquered vast portions of northern China and southwestern Asia.

Mandate of Heaven
in Chinese history, the divine approval thought to be the basis of royal authority. The Chinese believed Mongols had the Mandate of Heaven upon their conquest.

Yuan Dynasty
Dynasty in China set up by the Mongols under the leadership of Kublai Khan, replaced the Song (1279-1368). Mongol rule was harsh. They used Chinese administrative practice and improved infrastructure, but the Chinese people were more repressed.
Khubilai Khan
Reigned in China after establishing the Yuan Dynasty; he actively promoted Buddhism; descendant of Chinggis Khan.
Khanate of the Golden Horde
the Mongol empire, that, after the fall of Kiev in Russia, ruled all of southern Russia for 200 years with heavy taxes on Russians. Mongols didn't 'occupy' Russia like they did to China, but primarily receded in steppe lands outside of Russian cities
Ilkhanate - Persia and the Mongols
Huge slaughter of Persians by Mongols, The Persians were very peaceful, Mongols weren't into changing Persia, did not change their government or religion, Converted to Islam, Turned to farming, Married local people, Eventually the Mongols were having difficulty, society absorbed them
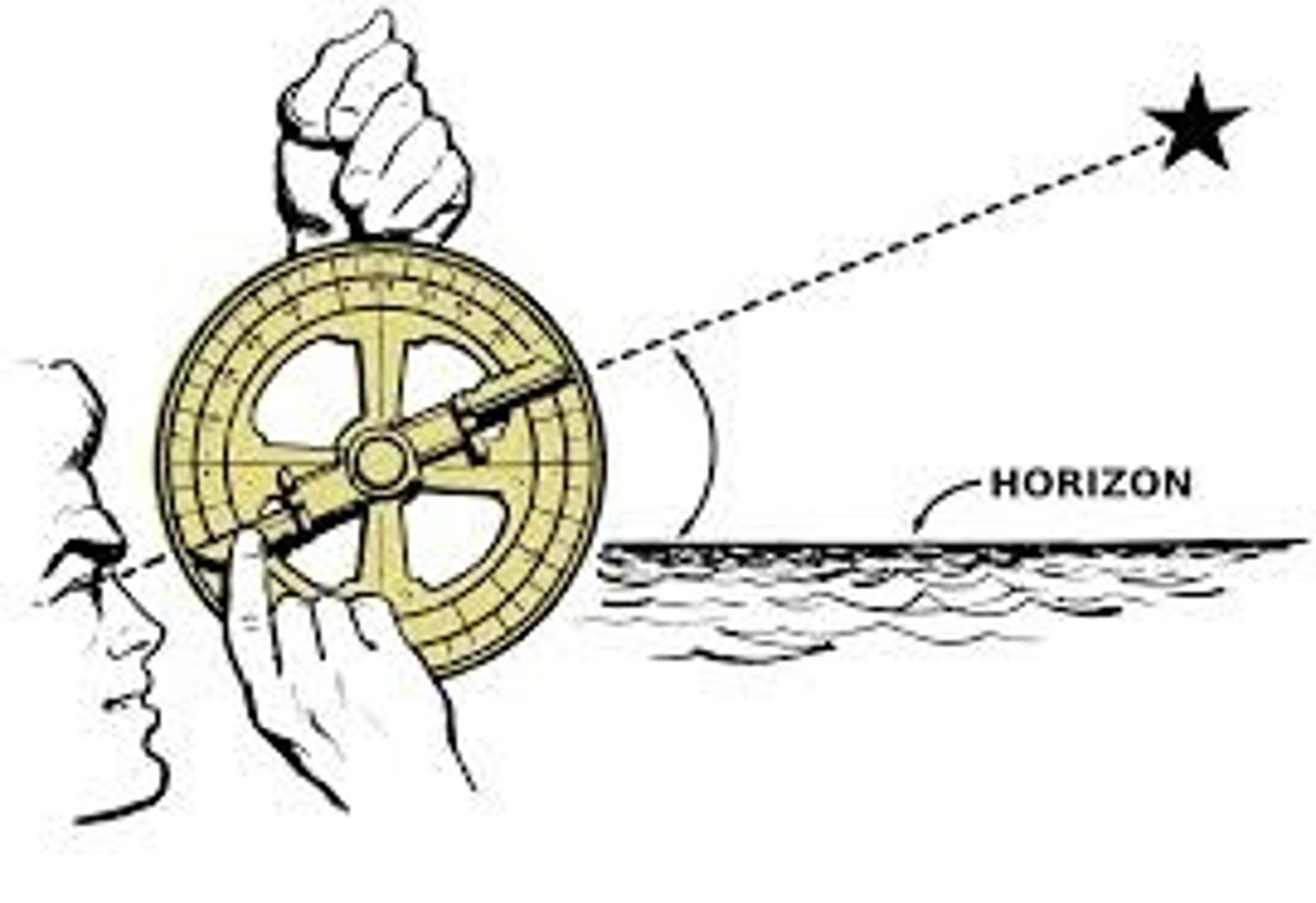
Astrolabe
An instrument used by sailors to determine their location by observing the position of the stars and planets
compass
an instrument containing a magnetized pointer that shows the direction of magnetic north and bearings from it.

Chinese Tribute System
Rulers of other countries presented tribute, and preformed required rituals of submission, and received in return abundant gifts, title and trading opportunities with China.
Srivijaya
A Malay kingdom that dominated the spice trade in the Straits of Malacca between 670 and 1025 C.E.; they were attracted to Buddhism
Uyghur script
script adopted by the mongolians

How did Islam spread to West Africa and Southeast Asia?
Trade Routes
Muslim Merchants
Sufi Missionaries
Places Islam spread via Conquest
Spain
Persia
North Africa
Arabian Peninsula
New crops introduced to the Middle East that created an "Islamic Green Revolution"
Rice, Sugarcane, sorghum, hard wheat, bananas, lemons, limes, watermelons, coconut palms, spinach, artichokes, and cotton