Apes Study Guide 10
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Infectious disease
Pathogen invades the body, and multiplies
some are NOT transmissible
transmissible disease
contagious diseases that are transmissible by people (Covid, the Flu, etc.)
Bacteria
rapid reproduction, easily spread (R- selected species)
use anti-biotics
the plague, TB, Cholera
Virus
smaller than bacteria, infectious agent
needs a host cell
prevent/treat w/ vaccine
HIV/AIDS, Flu
Parasite
treat w/ anti parasitic
Malaria, tapeworms, etc
Toxicity
the measure of how toxic something is to a substance, and its ability to cause injury, illness, or death to a living organism
Mutagen
Chemicals, or radiation that cause mutations to DNA , or increase their frequency (cancer?)
could be passed onto offspring
Teratogen
Chemicals that cause harm, or birth defects to unborn babies/fetus
Carcinogen
Type of chemical that can cause, or promote cancer
10-40 year delay?
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease in organisms (bacteria, us, parasite, protozoa, fungi)
Endocrine Disruptor
Substances that can interfere with the body’s hormone system
Dose
Basic toxicology principle
Anything can be toxic if large enough dose
Dose-response curve
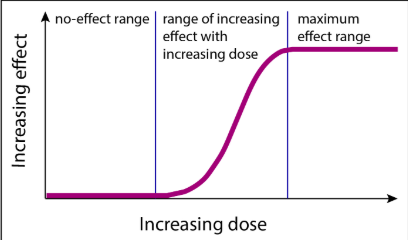
LD-50
Lethal Dose 50
How much of a chemical is lethal to 50% of testing
Threshold Concentration
The concentration of a substance that initiates a response
Dioxin
Toxic chemical pollutants from industrial process
Found in: soil, air, water, food
Causes: Cancer, teratogen, immune system damage, hormone interference
bioaccumulates in animal fat, builds up in the food chain
Endocrine system
A gland that releases hormones to regulate bodily systems
Immune system
protects the body from disease
network of cells, tissues, and organs that protect the body
Primary pollutant
emitted DIRECTLY into the air
Carbon Monoxide, PB, SOx, NOx
Secondary pollutants
formed by ractions of primary pollutants w/ other chemicals
ozone, acid deposition/rain, certain PM, smog
SOx
Sulfur Oxides (SO2, SO3)
air pollutants from fossil fuels (coal power plants, Oil refineries, volcanoes)
Environmental: Acid rain
Health: irritates lungs, worsens asthma, respiratory issues
regulation/reduction: low-sulfur fuels, emission laws
NOx
NO, NO2
Burning fuel
vehicle emissions, power plants, industrial process
Respiratory issues, worsens asthma/lung disease
Regulation/reduction: Catalytic converters, cleaner fuels, emission controls
VOCs (volatile organic compounds)
organic chemicals easily evaporating into the air
Vehicle exhaust, industrial process, paints, solvents, household products
Smog, ground level ozone formation
headache, dizzy, liver/kidney damage (some carcinogenic)
low VOC products, improve ventalation
Aldehydes
type of VOC
Vehicle exhaust, cig smoke, industrial emissions, paints, adhesives
ENT irritation, likely carcinogenic
Improve ventilation, low emission products
Particulate Matter
tiny solid/liquid particles in the air
Vehicle emissions, industrial pollution, WILDFIRE, DUST, CONSTRUCTION
increase Haze, settle in water/soil → harm ecosystem
lung/heart problems, asthma, premature death
use air filters, dust control, clean energy sources
Ozone
secondary pollutant
NOx + VOCs + sunlight
Vehicle emissions, industrial pollution, chemical solvents
Damage crops, forests, reduce air quality
Lung irritation, worse asthma, reduce lung function
Reduce vehicle emissions, clean energy resources
Radon
primary
color-less, odorless radioactive gas
from uranium decay in solid rock
naturally seeps into homes, poorly ventilated areas
Accumulates indoors (esp. poor ventilation)
leading cause of lung cancer
improve ventilation, seal cracks, test homes
Photochemical smog
sun + NOx + VOCs
vehicle emissions, industrial pollution, fossil fuel combustion
reduces visibility, damage crops, harm ecosystems
lung irritation, asthma, reduce lung function
reduce vehicle use/emission, cleaner energy
Temperature inversion
when warmer air sits on top of cooler air (not supposed to happen)
usually caused by radiative cooling of the earth at night
dry acid deposition
when SOx/NOx settles directly into surfaces, causing acidic rocks/ surfaces
Wet acid deposition
acid rain/snow/hail, etc
respiratory system
take in oxygen, put out CO2
nose/mouth/trachea/lungs
air pollution damages lung tissue
asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer results of smoking
Catalytic converter
exhaust emission that reduces toxic gas in vehicle exhaust
Clean air act
federal law (1970) that regulate air emissions from stationary/mobile sources
Buffer
substance that resists change in PH by neutralizing acid/base
absorbs excess acid or base to keep a stable PH
protect bodies of water from wet acid deposition