Unit 5A.5: EYES Assessment | Eyes, Ears, Nose & Sinuses, Mouth & Pharynx, Neck
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Credit to original flashcards made by @maledine
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Orbicularis Oculi
muscle that allows you to close your eyes, squint, blink and wink
the lens bulges to focus on close objects and flattens to focus on far objects, possible due to the refractive ability of the lens.
snellen or snellen E chart
hand-held snellen card or near vision screener (eg Rosenbaum)
ishihara plates
penlight, opaque cards, ophthalmoscope
cotton pedget, disposable gloves
Equipment for eye and vision assessment:
Position and alignment of eyeball in eye socket
Inspect eyelids and eyelashes
Assess ability of eyelids to close
Note position of eyelids compared to eyeballs
Observe redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
Inspect bulbar conjunctiva and sclera
Inspect palpebral conjunctiva
Inspect lacrimal apparatus
Palpate lacrimal apparatus
Inspect cornea and lens
Inspect iris and pupil
Pupillary reaction to light
Accommodation of pupils
Corneal light reflex test
Cover test
Positions tes/Cardinal gaze test
Color vision
Distant visual acuity
Near visual acuity
Gross peripheral vision
20 Steps for the Eye Assessment
Position and alignment of the eyeball in the eye socket
First Step of the Eye Assessment
Eyeballs are symmetrically aligned in sockets s̅ protruding or sinking
Normal sample documentation for 1. Position and alignment of the eyeball in the eye socket
Difference of more than 2 cm
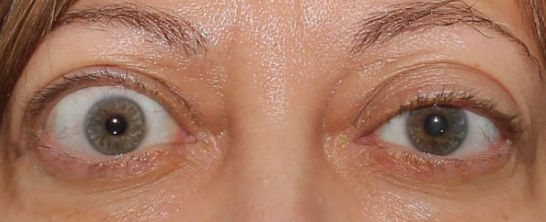
Exophthalmos
Sunken eyeballs
Abnormal findings for 1. Position and alignment of the eyeball in the eye socket
2 cm
Abnormal findings for 1. Position and alignment of the eyeball in the eye socket
A difference in distance greater than ___ is abnormal
Exophthalmos
Abnormal findings for 1. Position and alignment of the eyeball in the eye socket
Bulging eyes
could be a sign of thyroid gland problems; it can be treated but it needs to be checked quickly as your vision can be affected
Protrusion of eyeballs accompanied by retracted eyelid margins
Characteristic of Grave's’ disease (type of hyperthyroidism)
Sunken Eyeballs/Enopthalmos
Abnormal findings for 1. Position and alignment of the eyeball in the eye socket
“eyebags”, sunk in your face. Family history, dehydration and lack of sleep.
usual to severely dehydrated px
Seen with severe dehydration or chronic wasting illness

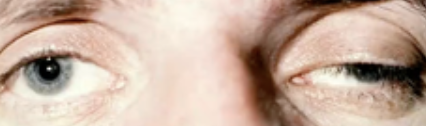
Ptosis
Ectoprion
Conjunctivitis
Exophthalmos
Chalazion
Hordeolum (Stye)
Entropion
Blepharitis
Diffuse Episcleritis
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Ptosis
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Drooping eye
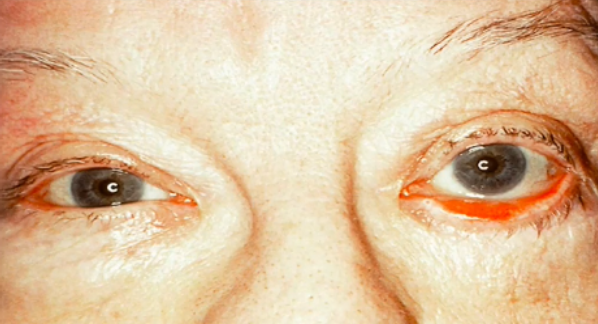
Ectropion
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Outwardly turned lower lid
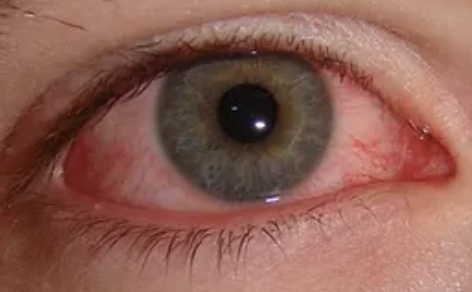
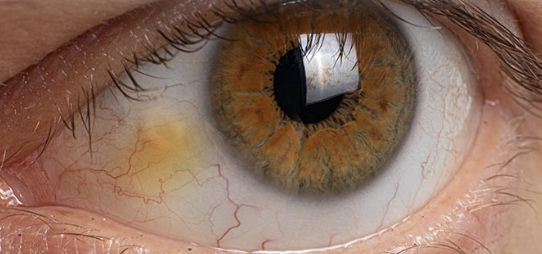
Conjunctivitis
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Generalized inflammation of the conjunctiva
Commonly known as pink eye
Exophthalmos
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Protruding eyeballs and retracted eyelids
Chalazion
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Infected meibomian gland

Hordeolum
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Stye
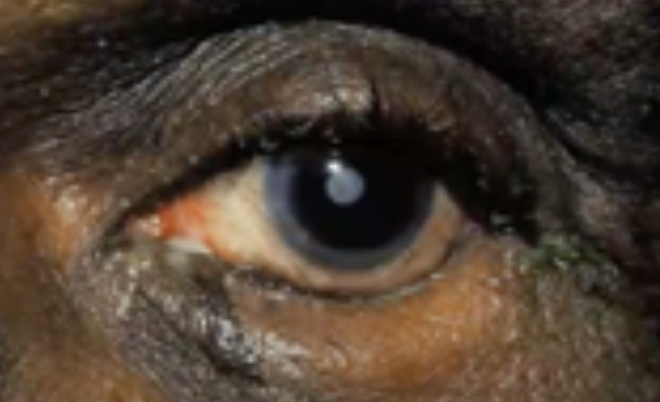
Entropion
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Inwardly turned lower lid
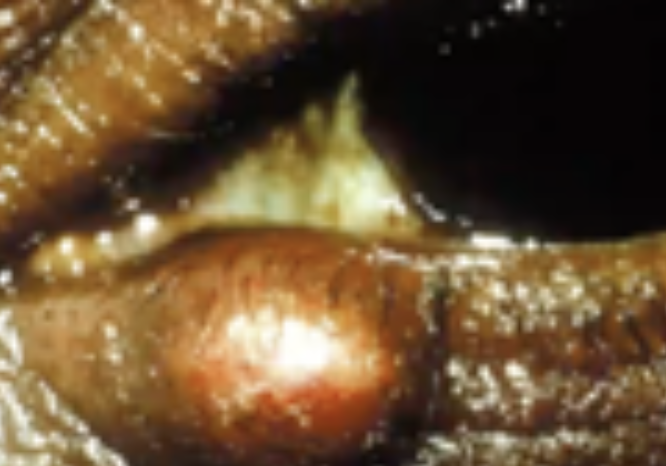
Blepharitis
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Staphylococcal infection of the eyelid
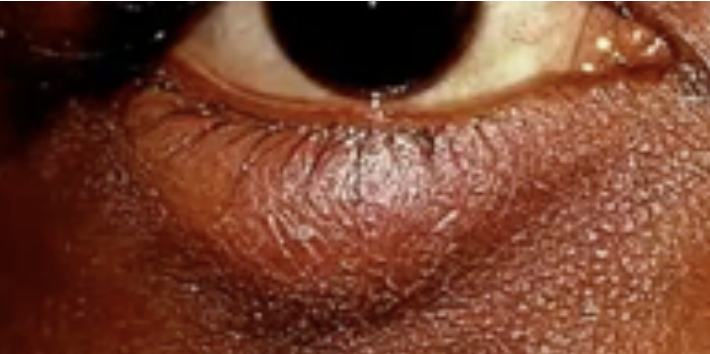
Diffuse Episcleritis
Abnormalities of the External Eye
Inflammation of the sclera
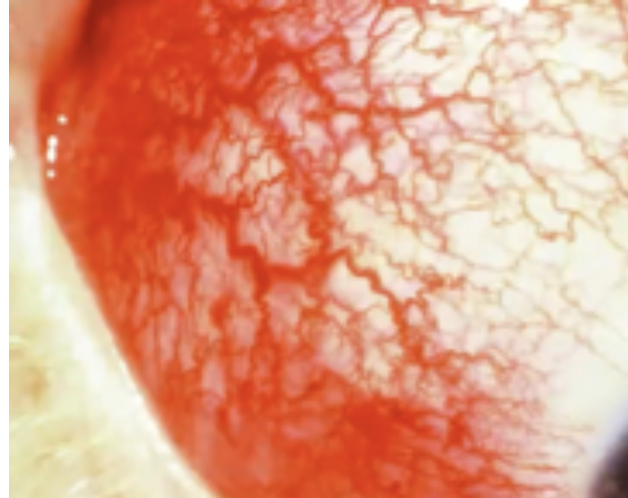
Inspect Eyelids & Eyelashes
Second Step of the Eye Assessment
Upper lid margin should be between the upper margin of the iris and upper margin of the pupil
Lower lid margin rests on the lower border of the iris. No white sclera is seen above or below the iris. Palpebral fissures may be horizontal.
Normal documentation for 2. Inspect Eyelids & Eyelashes
Width & position of palpebral fissures
What to note in 2. Inspect Eyelids & Eyelashes
Ptosis
Exophthalmos
Abnormal findings of 2. Inspect Eyelids & Eyelashes
Ptosis
Abnormal findings of 2. Inspect Eyelids & Eyelashes
Drooping of the upper lid
Attributed to oculomotor nerve damage, myasthenia gravis, weakened muscle or tissue, or a congenital disorder
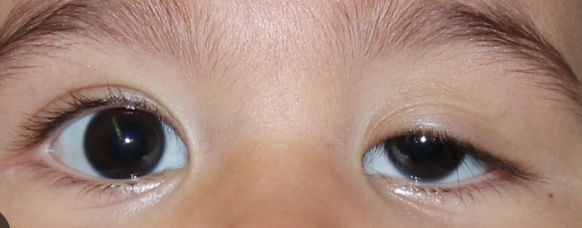
Exophthalmos
Abnormal findings of 2. Inspect Eyelids & Eyelashes
Retracted lid margins
Viewing of sclera when eyes are open
Suggest hyperthyroidism
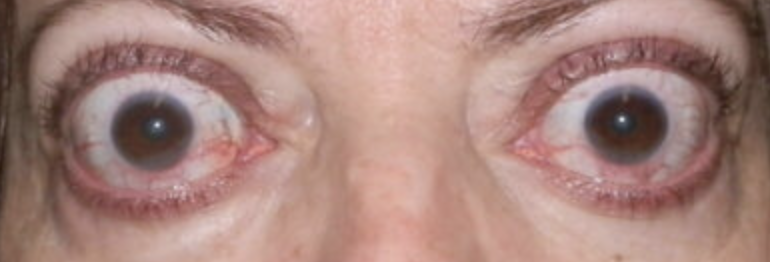
Assess ability of eyelids to close
Third Step of Eye Assessment
Upper and lower lids close easily and meet completely when closed.
Normal finding for 3. Assess Ability of Eyelids to Close
Failure of lids to close completely puts client at risk for corneal damage
Abnormal finding for 3. Assess Ability of Eyelids to Close
Position of the eyelids in comparison with the eyeballs
Fourth Step of Eye Assessment
Lower eyelid is upright with no inward or outward turning
Eyelashes are evenly distributed and curve outward along the lid margins
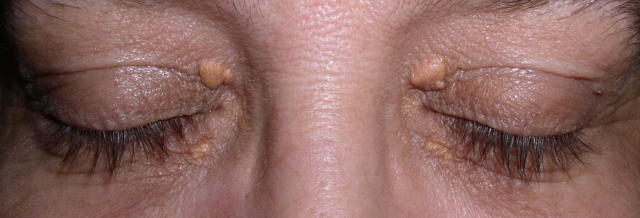
Xanthelasma
Normal Findings in 4. Position of the eyelids in comparison with the eyeballs
Xanthelasma
One of the normal findings in 4. Position of the eyelids in comparison with the eyeballs
Raised yellow plaques located most often near the inner canthus
Normal variation associated with increasing age and high lipid levels
Entropion
Ectropion
Abnormal Findings in 4. Position of the eyelids in comparison with the eyeballs
Entropion
Abnormal Findings in 4. Position of the eyelids in comparison with the eyeballs
Inverted lower lid
May cause pain and injure the cornea as the eyelash brushes against the conjunctiva and cornea
Ectropion
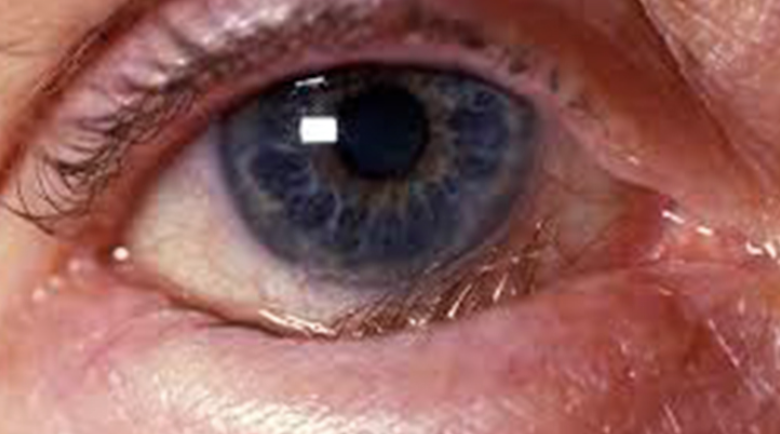
Abnormal Findings in 4. Position of the eyelids in comparison with the eyeballs
Everted lower eyelid
Results in exposure and drying of the conjunctiva
Redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
Fifth Step of Eye Assessment
Skin on both eyelids is without redness, swelling, or lesions
Normal Finding for 5. Redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
Seborrhea or Blepharitis
Hordeolum (Stye)
Chalazion
Abnormal Findings for 5. Redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
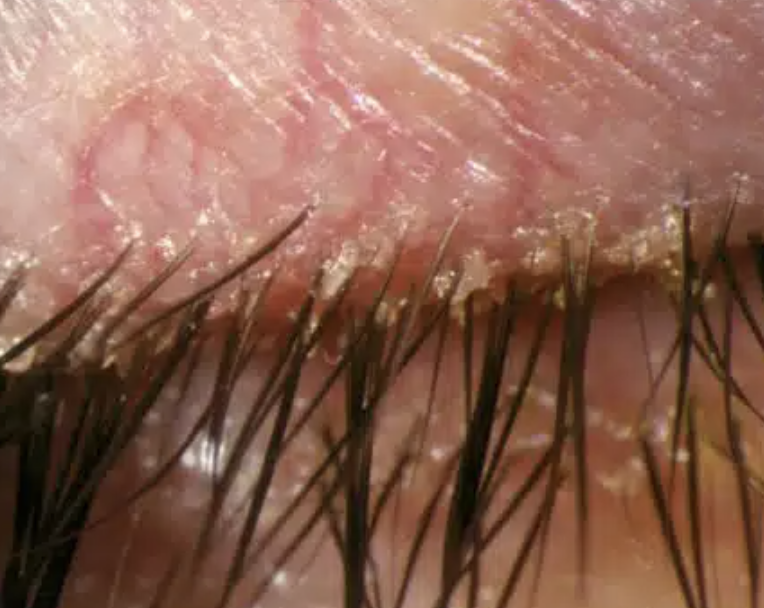
Seborrhea or Blepharitis
Abnormal Findings for 5. Redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
Redness and crusting along the lid margins
Infection caused by Staphylococcus Aureus
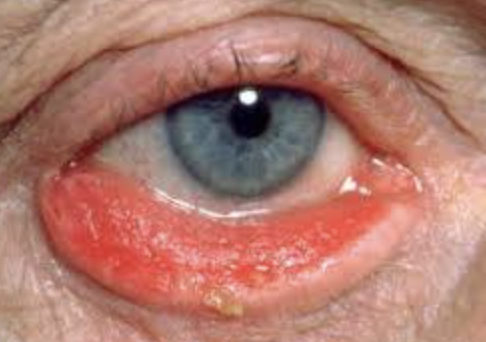
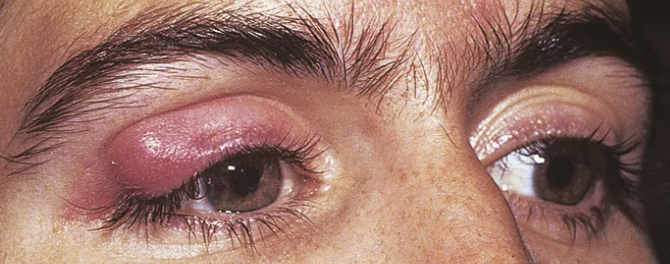
Hordeolum (Stye)
Abnormal Findings for 5. Redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
Hair follicle infection, causes local redness, swelling, and pain
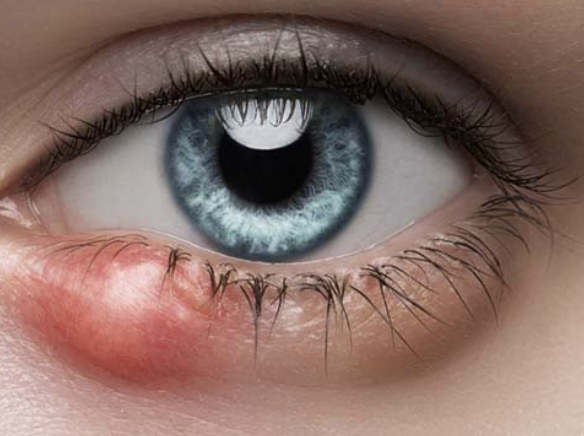
Chalazion
Abnormal Findings for 5. Redness, swelling, discharge, or lesions
Infection of the meibomian gland (located in the eyelid)
May produce extreme swelling of the lid, moderate redness, but minimal pain
Inspect bulbar conjunctiva and sclera
Sixth Step for Eye Assessment
Bulbar conjunctiva is clear, moist and smooth
Sclera is white
Pinguecula
Normal Findings for 6. Inspect bulbar conjunctiva and sclera
Pinguecula
One of the Normal Findings for 6. Inspect bulbar conjunctiva and sclera
Yellowish nodules on the bulbar conjunctiva
Harmless nodules common in older clients
Appear first on the medial side of the iris and then on the lateral side
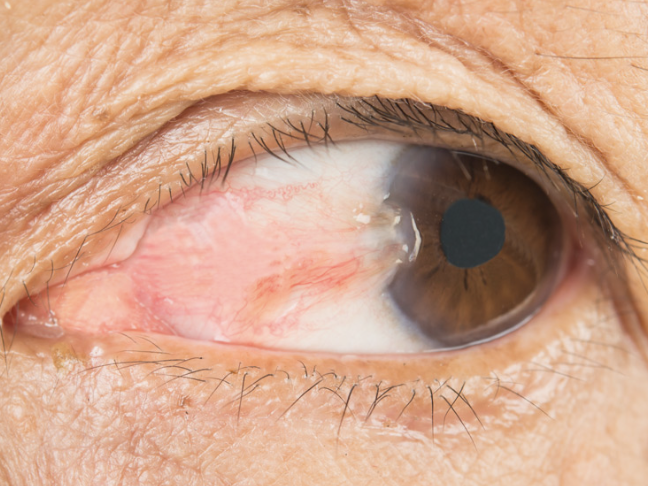
Conjunctivitis
Episcleritis
Abnormal Findings of 6. Inspect bulbar conjunctiva and sclera
Inspect palpebral conjunctiva
Seventh Step for Eye Assessment
Lower and upper palpebral conjunctivae are clear and free of swelling or lesions
Normal Finding for 7. Inspect palpebral conjunctiva
Cyanosis
Foreign body or lesion
Abnormal Findings for 7. Inspect palpebral conjunctiva
Cyanosis
Abnormal Finding for 7. Inspect palpebral conjunctiva
Heart or lung disorder
Inspect lacrimal apparatus
Eighth Step of Eye Assessment
Lacrimal Glands
Puncta
What is assessed in 8. Inspect lacrimal apparatus?
No swelling or redness should appear over areas of the lacrimal gland
Puncta is visible without swelling or redness and is turned slightly toward the eye
Normal Finding for 8. Inspect lacrimal apparatus
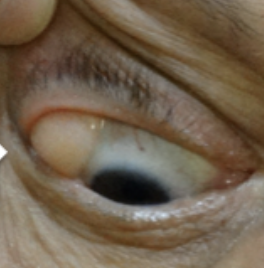
Swelling of lacrimal gland
Redness or swelling around puncta
Excessive tearing
Abnormal Findings for 8. Inspect lacrimal apparatus
Swelling of the lacrimal gland
Abnormal Finding for 8. Inspect lacrimal apparatus
May be visible in the lateral aspect of the upper eyelid
Caused by blockage, infection, or an inflammatory condition
Redness or swelling around the puncta
Abnormal Finding for 8. Inspect lacrimal apparatus
Indicate infectious or inflammatory condition
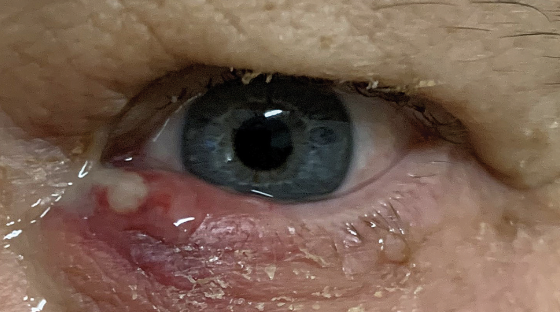
Excessive tearing
Abnormal Finding for 8. Inspect lacrimal apparatus
Indicate nasolacrimal sac obstruction
Palpate the lacrimal apparatus
Ninth Step of the Eye Assessment
No drainage should be noted from the puncta when palpating the nasolacrimal duct
Normal finding for 9. Palpate the lacrimal apparatus
Expressed drainage from the puncta on palpation occurs with duct blockage
Abnormal finding for 9. Palpate the lacrimal apparatus
Inspect the cornea and lens
Tenth Step of the Eye Assessment
Shine a light side of the eye for an oblique view
Look through the pupil to inspect the lens
How do you 10. Inspect the cornea and lens?
Cornea is transparent, with no opacities
Oblique view shows a smooth and overall moist surface
Lens is free of opacities
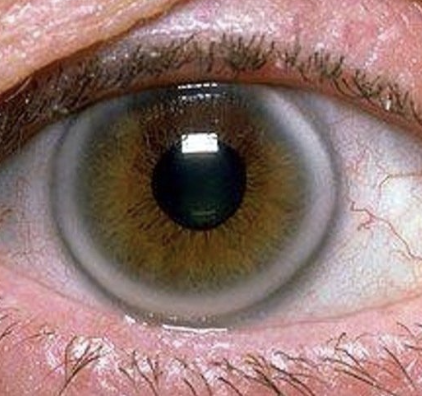
Areus senilis
Normal Findings for 10. Inspect the cornea and lens
Areus Senilis
One of the Normal Findings for 10. Inspect the cornea and lens
Normal condition in older clients
White arc around the limbus
Has no effect on vision
Roughness or dryness of cornea
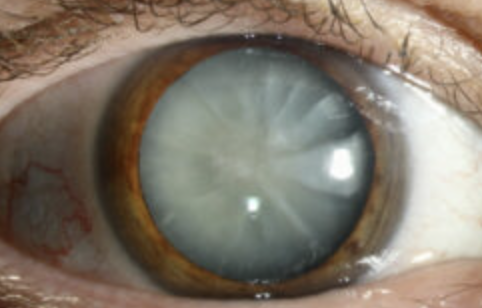
Cataracts
Abnormal Finding for 10. Inspect the cornea and lens
Roughness or dryness on cornea
Abnormal Finding for 10. Inspect the cornea and lens
Often associated with injury or allergic responses
Cataracts
Abnormal Finding for 10. Inspect the cornea and lens
Opacities of the lens
Corneal Scar
Early Pterygium
Keratitis
Corneal Ulcer
Keratoconus
Corneal Dystrophies
6 Corneal Abnormalities
Corneal Scar
One of the 6 Corneal Abnormalities
Appears grayish white
Usually due to an old injury or inflammation
Early Pterygium
One of the 6 Corneal Abnormalities
Thickening of the bulbar conjunctiva that extends across the nasal side
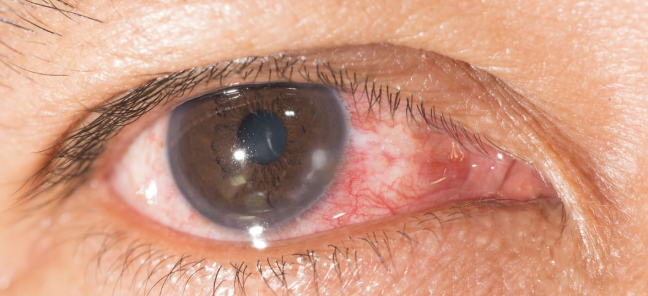
Keratitis
One of the 6 Corneal Abnormalities
Inflammation of the cornea, which can be infectious (bacterial, viral, fungal) or non-infectious (due to trauma, dry eyes, or improper use of contact lenses)
Accompanied by eye redness, pain, decreased vision, discharge, and photophobia
Corneal Ulcer
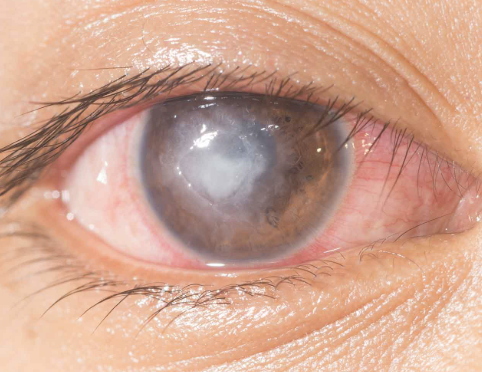
One of the 6 Corneal Abnormalities
An open sore on the cornea, often resulting from untreated keratitis or corneal abrasions
Can lead to permanent scarring and vision loss if not promptly treated
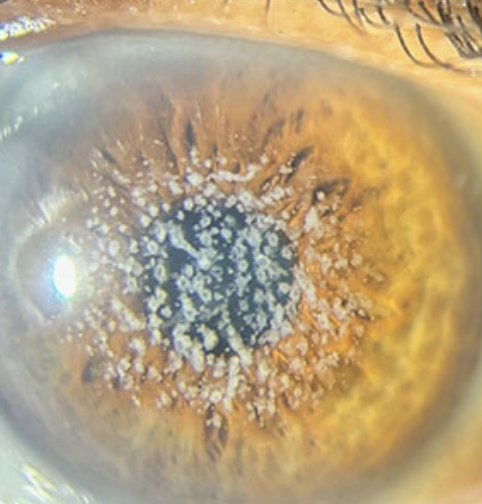
Keratoconus
One of the 6 Corneal Abnormalities
A progressive, degenerative disorder where the cornea thins and bulges into a cone shape, leading to distorted vision

Corneal Dystrophies
One of the 6 Corneal Abnormalities
Group of inherited disorders that cause abnormal deposits or growths in the corneal tissue
Examples include Fuchs’ dystrophy and lattice dystrophy
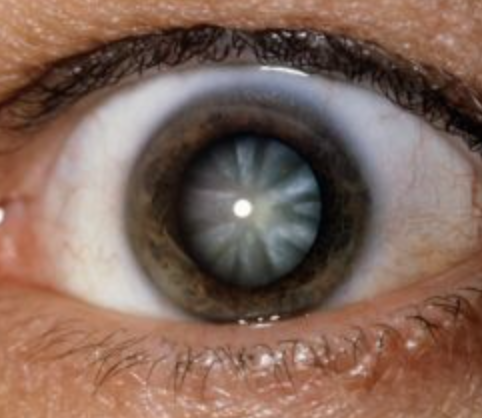
Nuclear Cataract
Peripheral Cataract
Ectopia Lentis
Spherophakia
4 Lens Abnormalities
Nuclear Cataract
One of the 4 Lens Abnormalities
Appear gray when seen with a flashlight
Appear as a black spot against the red reflex when seen through an opthalmoscope
Peripheral Cataract
One of the 4 Lens Abnormalities
Looks like gray spokes that point inward when seen with a flashlight
Look like black spokes that point inward against the red reflex when seen through an opthalmoscope
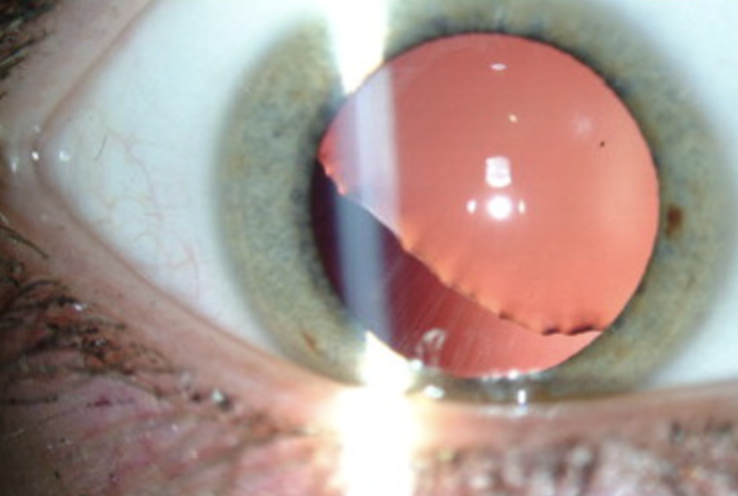
Ectopia Lentis
One of the 4 Lens Abnormalities
Condition where the lens becomes displaced from its normal position due to trauma, genetic disorders (like Marfan syndrome), or conditions like homocystinuria
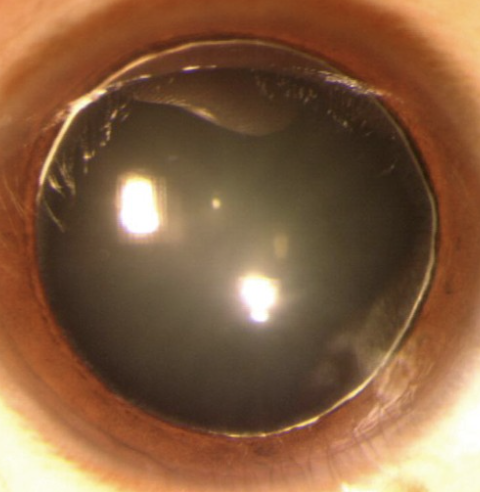
Spherophakia
One of the 4 Lens Abnormalities
Rare congenital lens abnormality where the lens is abnormally small and spherical, leading to refractive errors susch as myopia or lens dislocation
Inspect iris and pupil
Eleventh Step of Eye Assessment
Inpect shape and color of iris and size and shape of pupil
If pupil is larger, smaller, or different sizes, measure pupils against a gauge
How to conduct 11. Inspect iris and pupil?
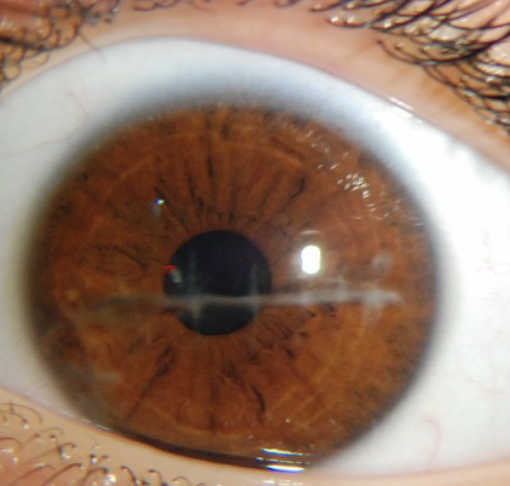
Iris is round, flat, and evenly colored
Pupil is round with a regular border, and is centered in the iris
Pupils are normally equal in size (3-5 mm)
Normal finding for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Inequality in pupil size less than 0.5 mm
Normal variation for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Irregularly shaped irises
Miosis
Mydriasis
Anisocoria
4 Abnormal Findings for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Irregularly Shaped Iris
4 Abnormal Findings for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Causes a shallow anterior chamber, which may increase the risk for narrow-angle (closed-angle) glaucoma
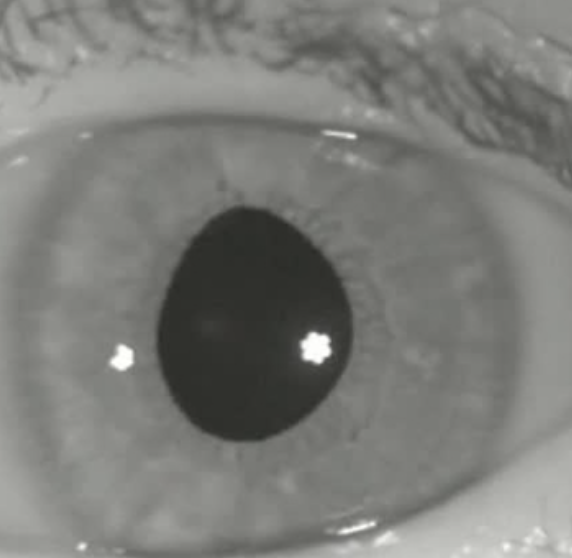
Miosis
4 Abnormal Findings for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Aka pinpoint pupils
Characterized by constricted and fixed pupils
Possibly a result of narcotic drugs or brain damage

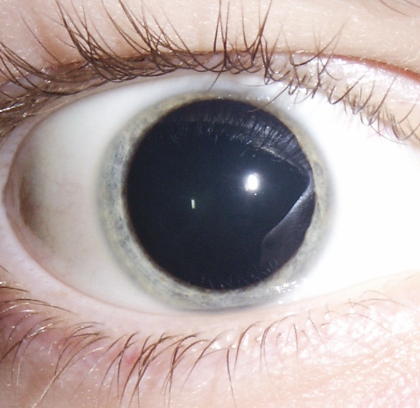
Anisocoria
4 Abnormal Findings for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Pupils of unequal size
If greater in bright light compared with dim light, the caused may be trauma, tonic pupil (caused by impaired parasympathetic nerve supply to iris), and oculomotor nerve paralysis
If greater in dim light compared with bright light, the cause may be Horner’s syndrome (caused by paralysis of the cervical sympathetic nerves and characterized by ptosis, sunken eyeball, flushing of the affected side off the face, and narrowing of the palpebral fissure)
Mydriasis
4 Abnormal Findings for 11. Inspect iris and pupil
Dilated and fixed pupils, typically resulting from CNS injury, circulatory collapse, or deep anesthesia
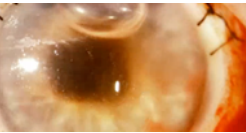
Hyphema
Abnormal findings for iris
Collection of blood inside anterior chamber of eye (space between cornea and iris)
Pooling or collection of blood inside the anterior chamber of the eye (the space between the cornea and the iris); trauma
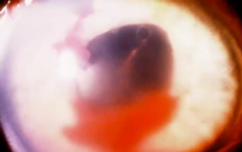
Hypopyon
Abnormal findings for Iris
Condition involving inflammatory cells in anterior chamber of eyes
Accumulation of white blood cells that form a whitish layer of fluid in the lower portion of the eye’s anterior chamber (front part); infection of internal eye.
P-E-R-R-L-A (Pupils Equally Round, Reactive to Light Accommodation)
testing pupillary reaction to light (direct and consensual)
testing accommodation of pupils
3 procedures for assessing the pupil:
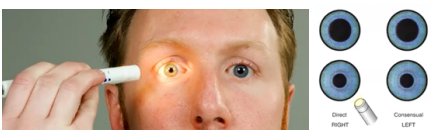
in checking the pupils - the pupils will constrict when there is light, the pupil will dilate when it is dark
(3 procedures for assessing the pupil)
testing pupillary reaction to light (direct and consensual)
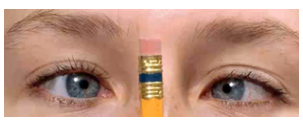
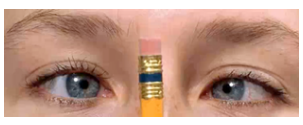
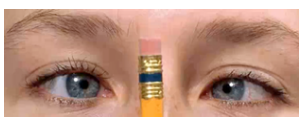
equally round about 3 mm in size; illuminated pupil constricts and pupil opposite the one illuminated constricts simultaneously; pupils converge and constricts as object moves in toward nose; pupil responses uniform
(3 procedures for assessing the pupil)
sample documentation for testing accommodation of pupils
Pupillary reaction to light
Twelfth Step of Eye Assessment
Darken the room and ask client to focus on a distant object
Shine a light obliquely into one eye and observe the pupillary reaction
How to test 12. Pupillary reaction to light?
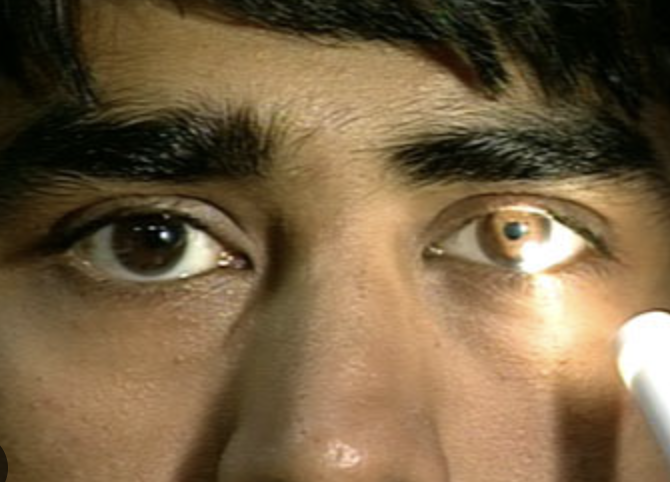

Left Eye (Oculus Sinister)
3 - Pupil’s eye at rest
2 - Constricted size
How to interpret result of O.S. 3/2 in 12. Pupillary reaction to light?
Constriction of the pupils
Normal Finding for 12. Pupillary reaction to light
Monocular Blindness
Both pupils constrict
Abnormal Findings for 12. Pupillary reaction to light
Monocular Blindness
Abnormal Findings for 12. Pupillary reaction to light
Light directed to the blind eye results in no response in either pupil
Accommodation of pupils
Thirteenth Step of the Eye Assessment
Hold finger 12-15 in from client
Ask client to focus on finger and to remain focused on it as it is moved closer
How to test 13. Accommodation of pupils?
Constriction of the pupils and convergence of the eyes when focusing on a near object (accommodation and convergence)
Normal finding for 13. Accommodation of pupils