Wk 7: Pharmacology of Histamines
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what is histamine? what group is it part of?
- endogenous mediator
- autocoid group
what are key aspects of histamine?
1. bioactive amine synthesized from histdine
2. released to produce local effects (in the CNS and PNS)
3. role of histamine
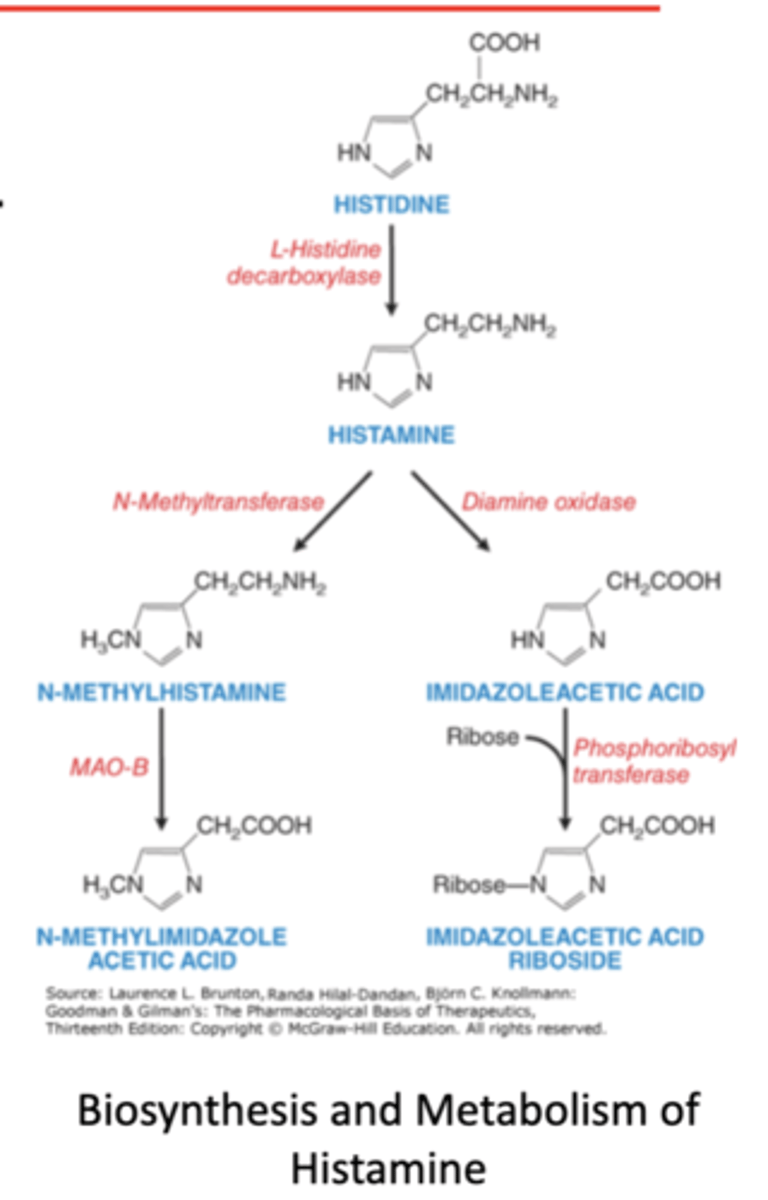
what are the 3 roles of histamine
- immediate allergic response
- regulation of basal acid secretion in the stomach
- neurotransmitter and modulator of neurotransmitter release
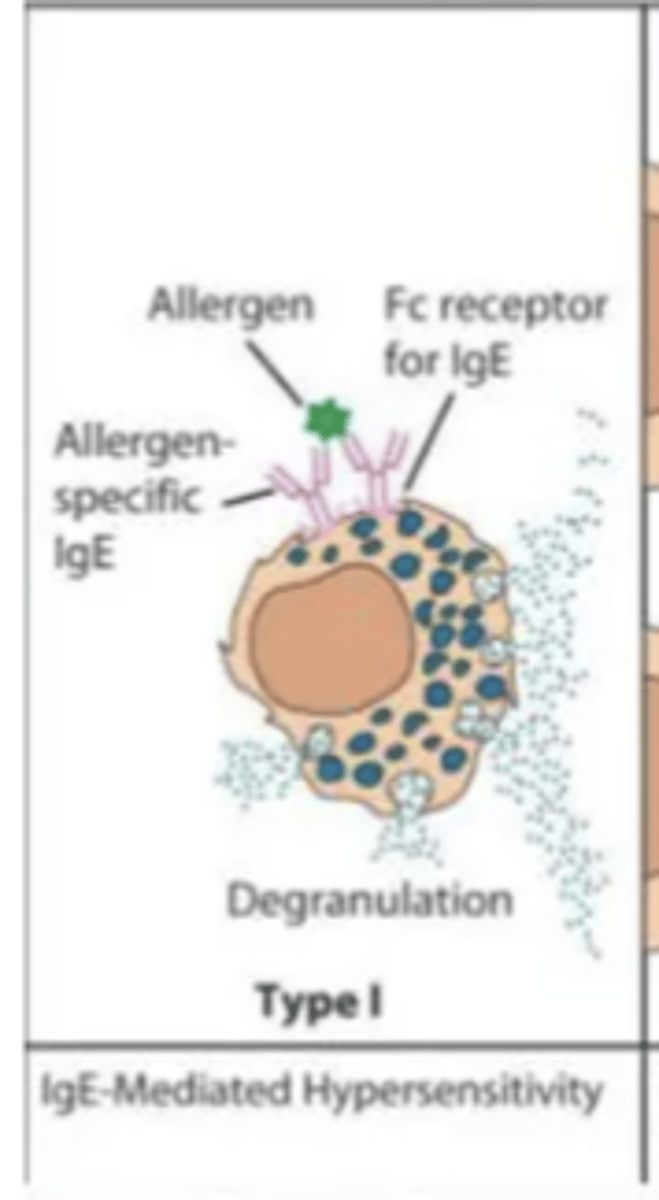
Describe gell-coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions (type I moa, clinical manifestations and timing of reaction)
MOA:
- IgE-drug complex binds mast cells with release of histamine (inflammatory mediators)
clinical manifestations
- uticaria
- angioedema
- bronchospasm
- itching
- vomiting/diarrhea, anaphylaxis
timing
- min-hours after drug exposure
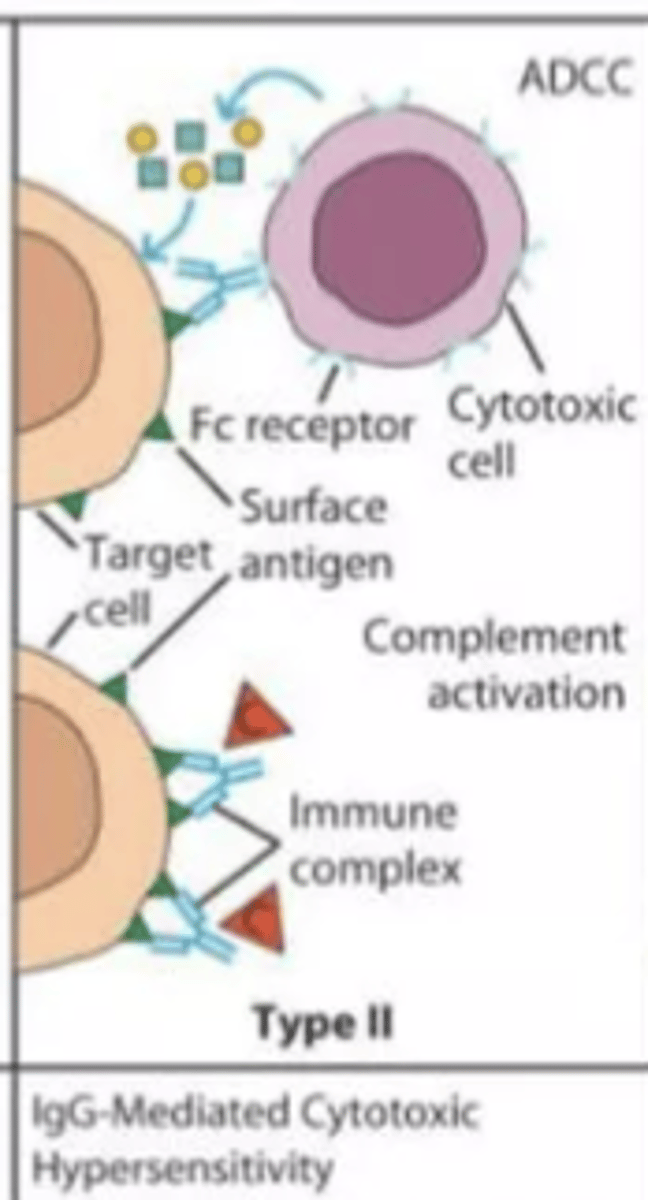
Describe gell-coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions (type II moa, clinical manifestations and timing of reaction)
MOA
- IgG or IgM antibodies directed at drug hapten coated cells
clinical manifestations
- hemolytic anemia
- neutropenia
- thrombocytopenia
timing
- variable
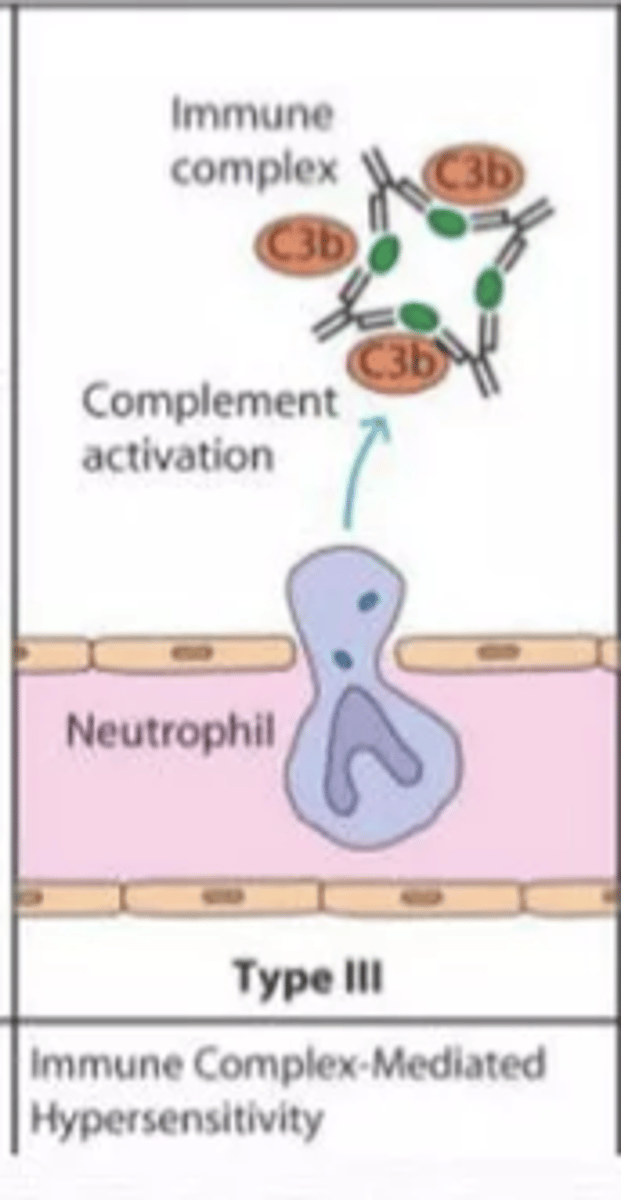
Describe gell-coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions (type III moa, clinical manifestations and timing of reaction)
MOA
- tissue deposition of drug antibody complex that activates complement and inflammation
clinical manifestations
- serum sickness
- fever
- rash
- vasculitis
- glomerulonephritis
timing
- 1-3 weeks after drug exposure
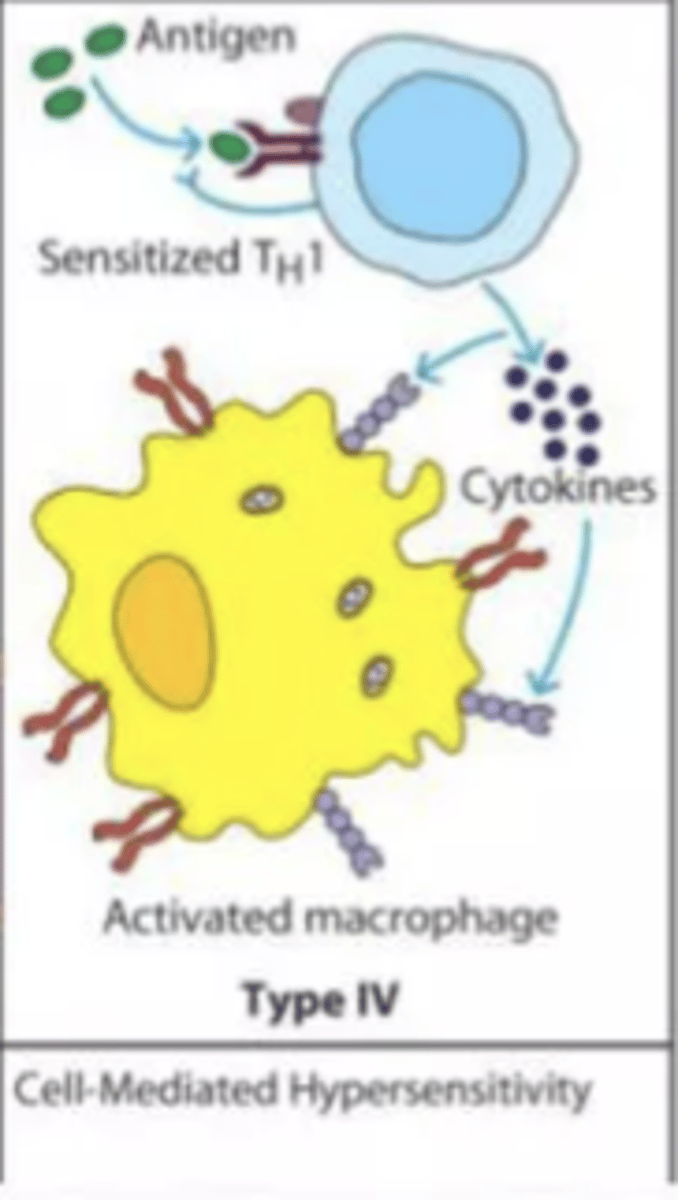
Describe gell-coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions (type IV moa, clinical manifestations and timing of reaction)
MOA
- MHC presentation of drug molecules to t cells with cytokine and inflammatory mediator release
clinical manifestations
- allergic contact dermatitis
- drug rash
timing
- 2-7 days after continuous exposure
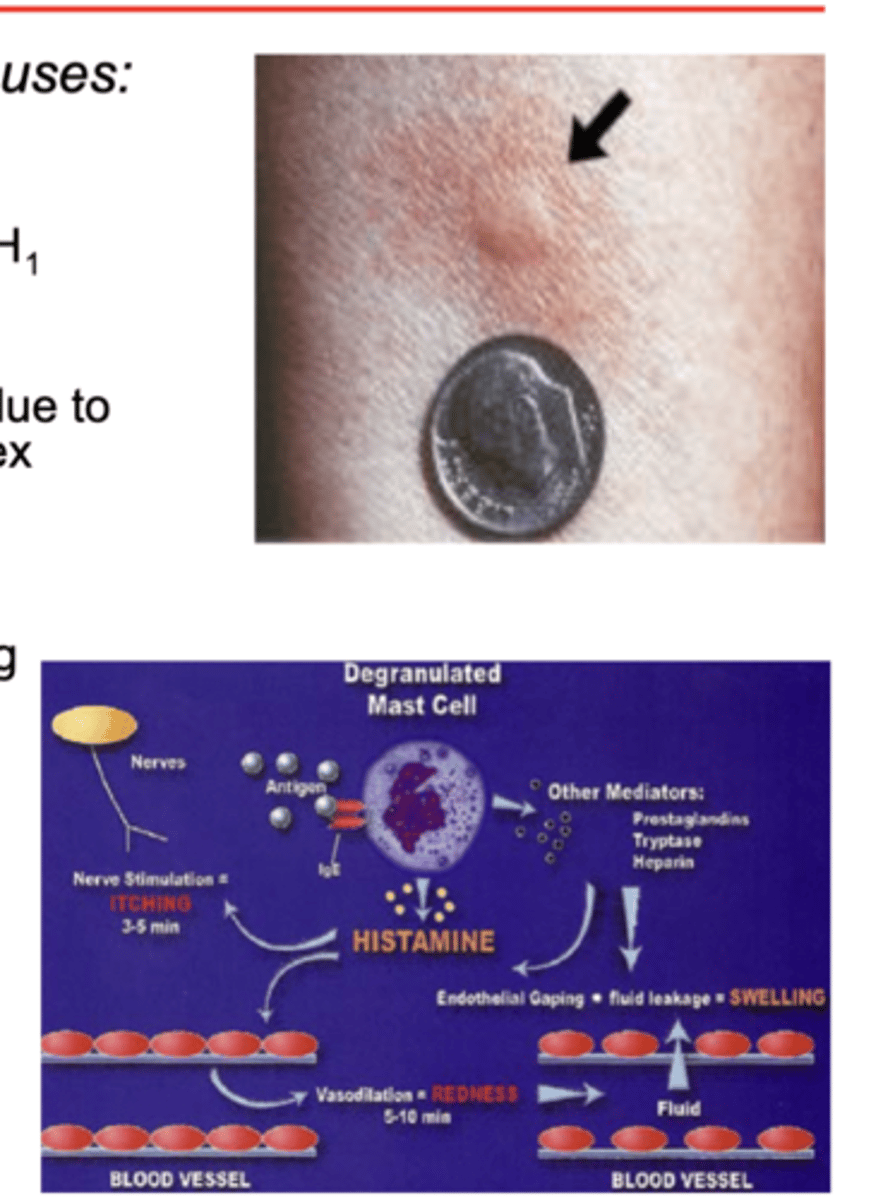
describe histamines triple response of lewis
A: red spot
- appears within seconds (max 1 min)
- due to direct vasodilator effect of H1
- mediated by NO production
B: Flare or red flush
- develops slowly due to induced stimulation of neuronal reflex causing vasodilation (indirect effect)
C: wheal
- swelling 1-2 min at injection site
- due to histamine effect on capillaries increasing permeability
what are clinical symptoms associated with histamine release (mild,mild to moderate, and severe)
mild/cutaneous
- erythema
- uricaria
- itching
mild to moderate
- skin reactions
- tachycardia
- dysrhythmias
- moderate hypotension
- mild respiratory distress
severe/anaphylactic
- severe hypotension
- V fib
- cardiac arrest
- bronchospasm
- respiratory arrest
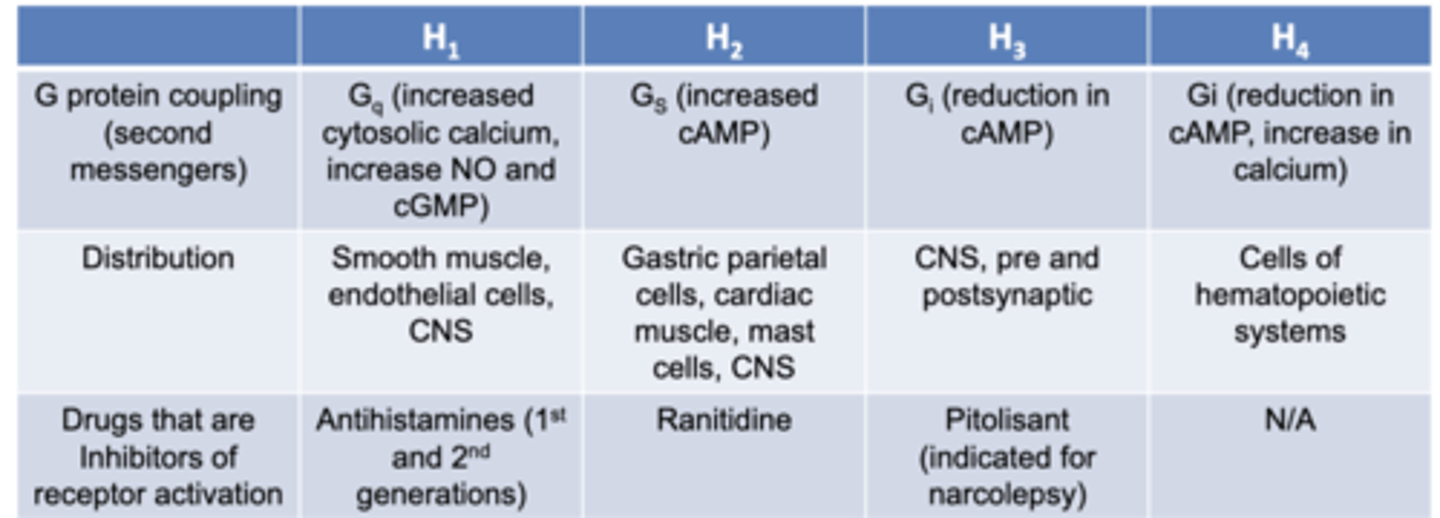
what are the 4 histamine receptors? they are all ____ protein couples receptors
H1, H2, H3, H4
- G protein coupled receptors
what does activation of H1 receptors cause?
- itching
- stimulation of nasal mucosa secretion
- contraction of bronchial smooth muscles
-CNS: inhibits appetite and increased wakefulness
- vascular capillary dilation
- increased vascular permeability
what does activation of H2 receptors cause?
- induce vascular capillary dilation with H1
what does activation of H3 receptors cause?
-act as autoreceptors for histamainergic neurons
- promote wakefullness
what does activation of H4 receptors cause?
- chemotaxis of immune cells and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines
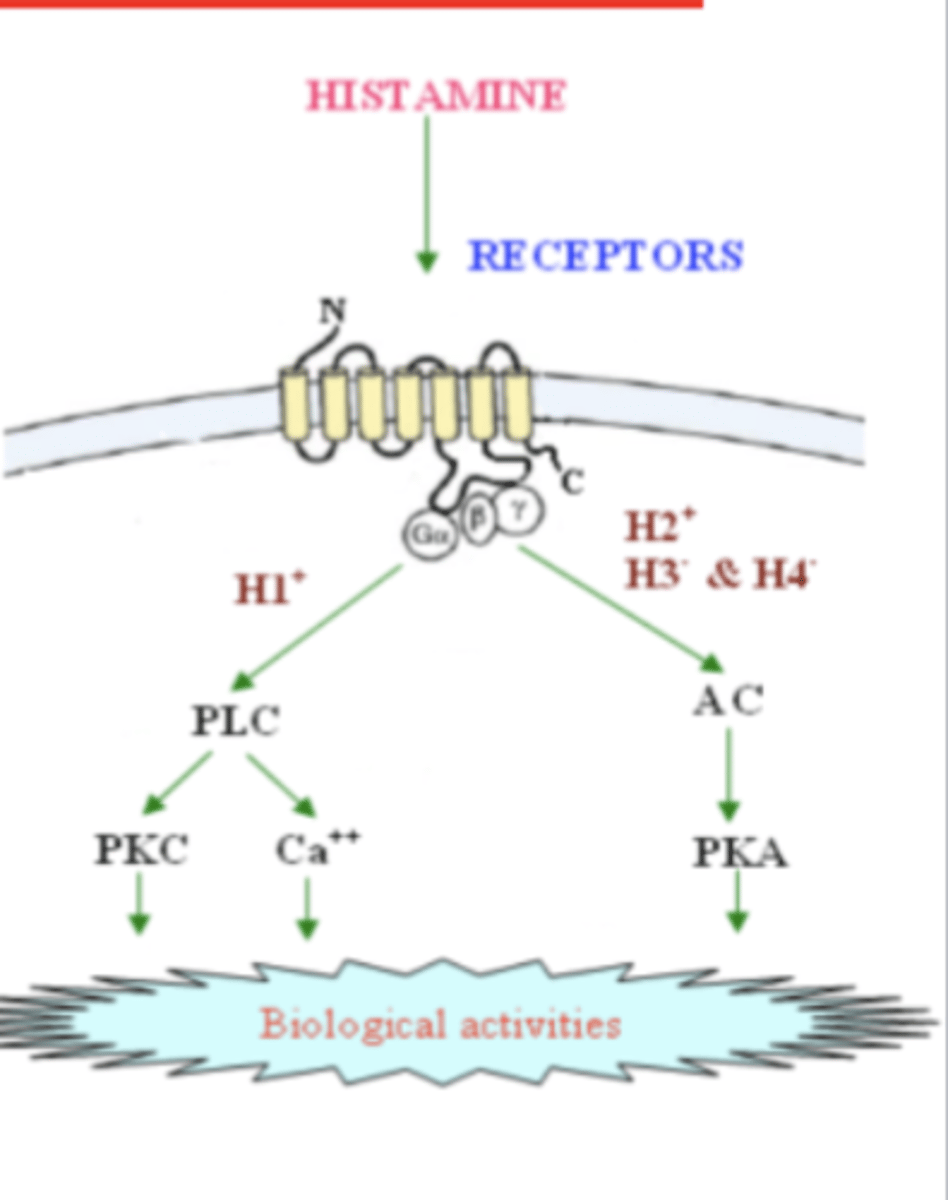
Histamine receptors
memorize
describe epinephrine as a antihistamine
MOA:
1. antagonizes H1's: reduces bronchial smooth muscle contraction
2. A1 receptor agonism: vasocontricts leading to SVR and reduced mucosal edema
3. B1 receptor agonism: incrases inotropy and HR (increasing CO)
4. B2 receptor agonism: bronchodilation and inhibition of further mediatory release from mast cells
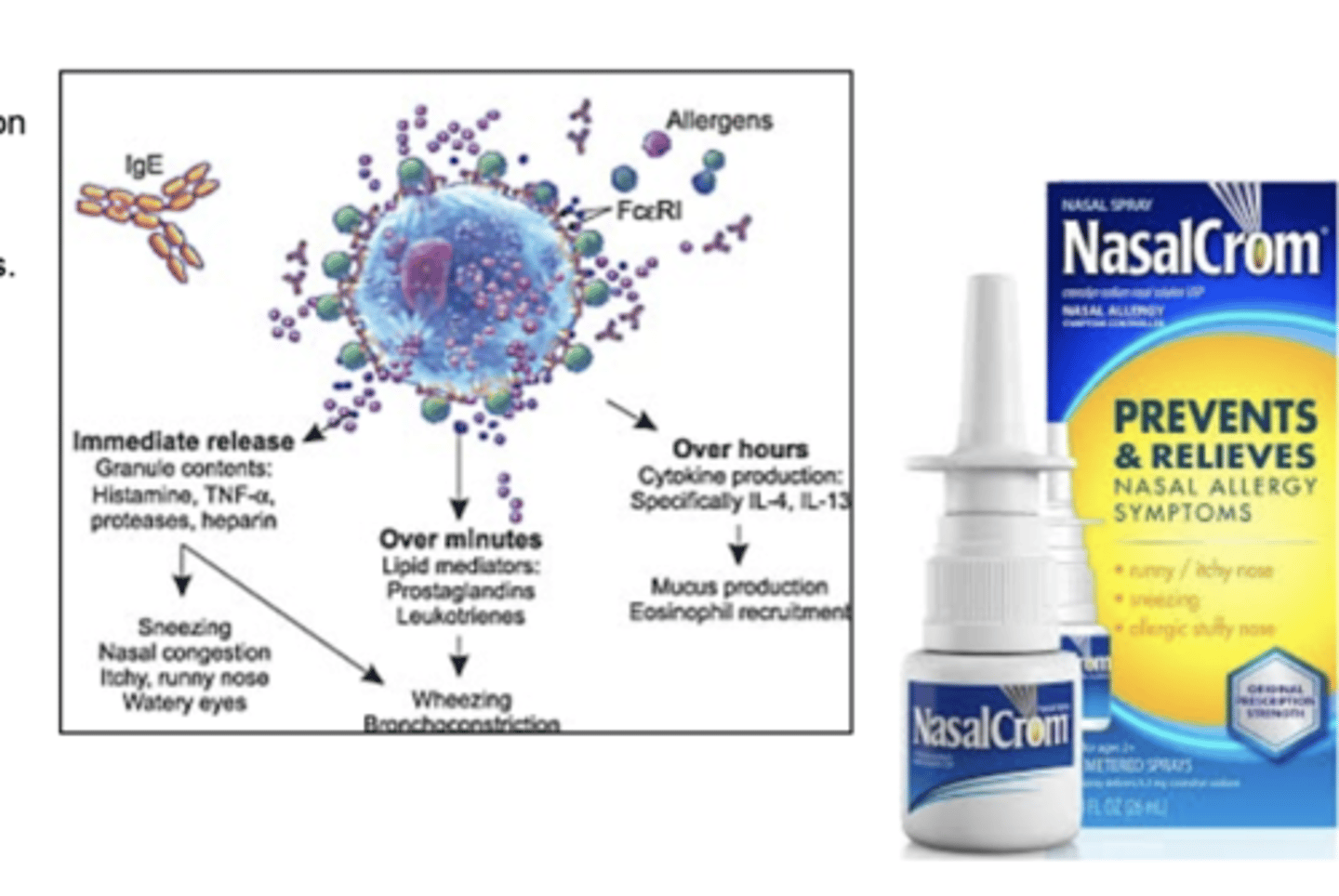
describe MOA and uses for mast cell stabilizers
MOA
- prevents mast cell degranulation and release of histamine/other mediators
USES
- allergic rhinitis
- allergic eye conditions
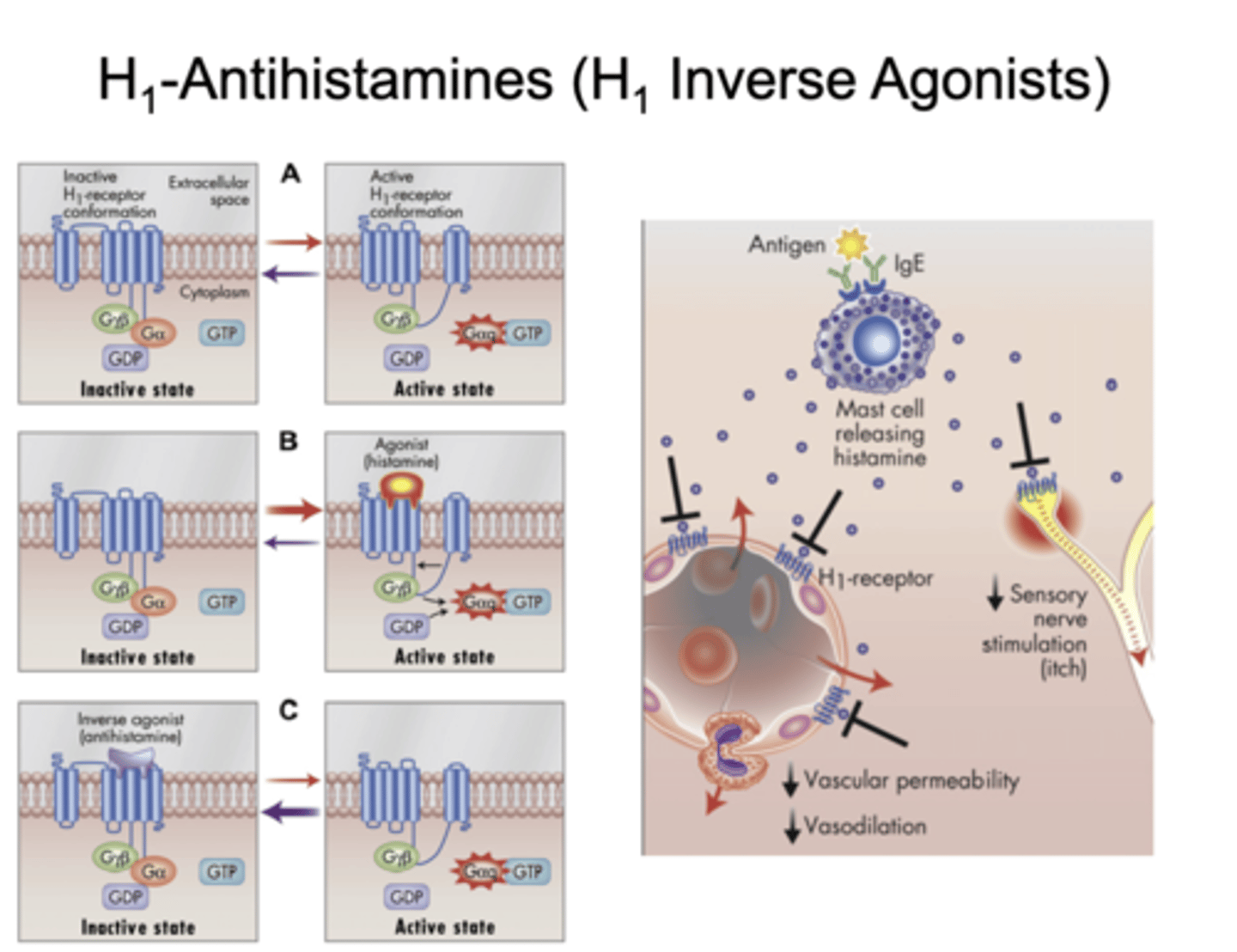
describe H1 inverse agonists
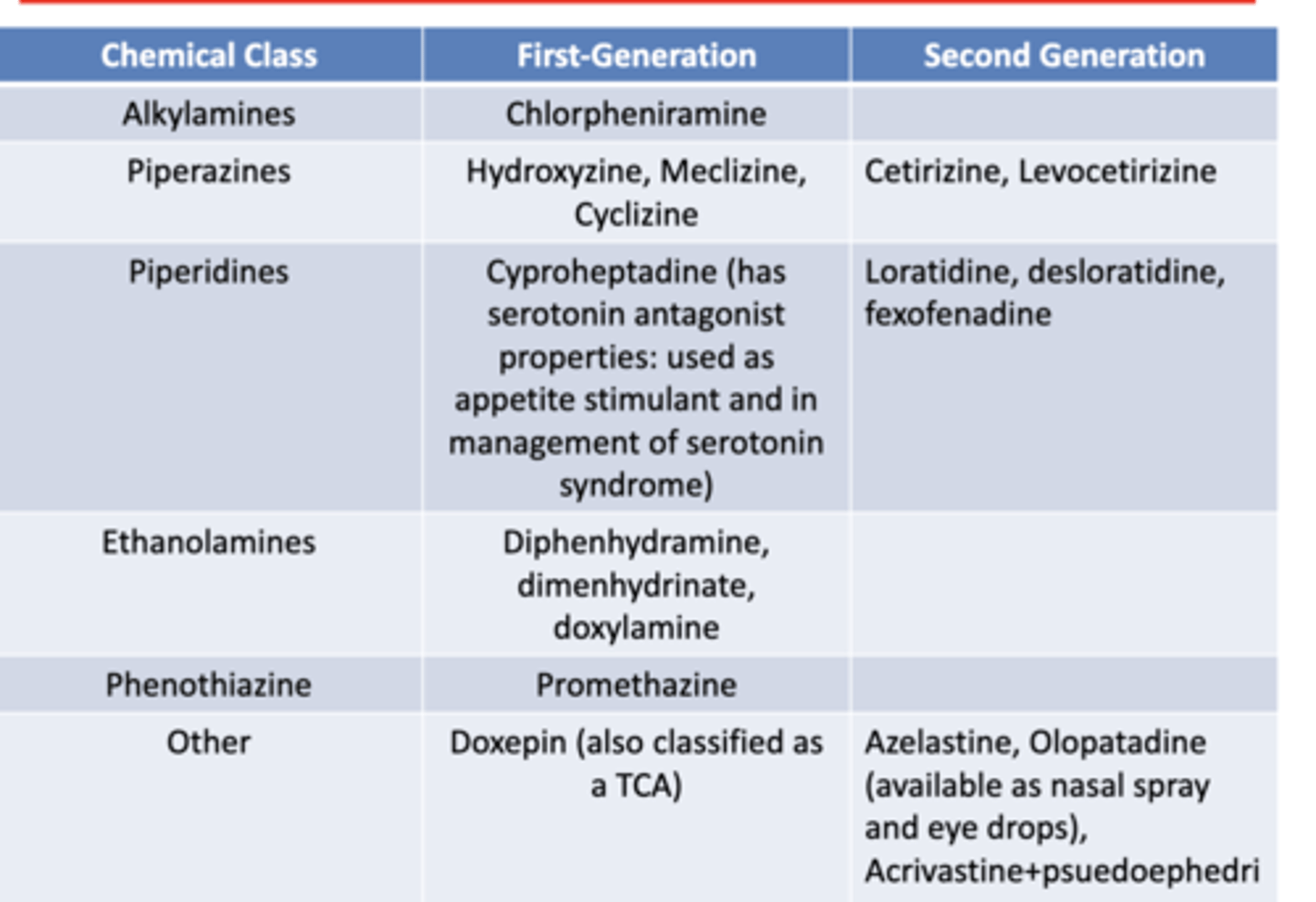
1st and 2nd generation antihistamines
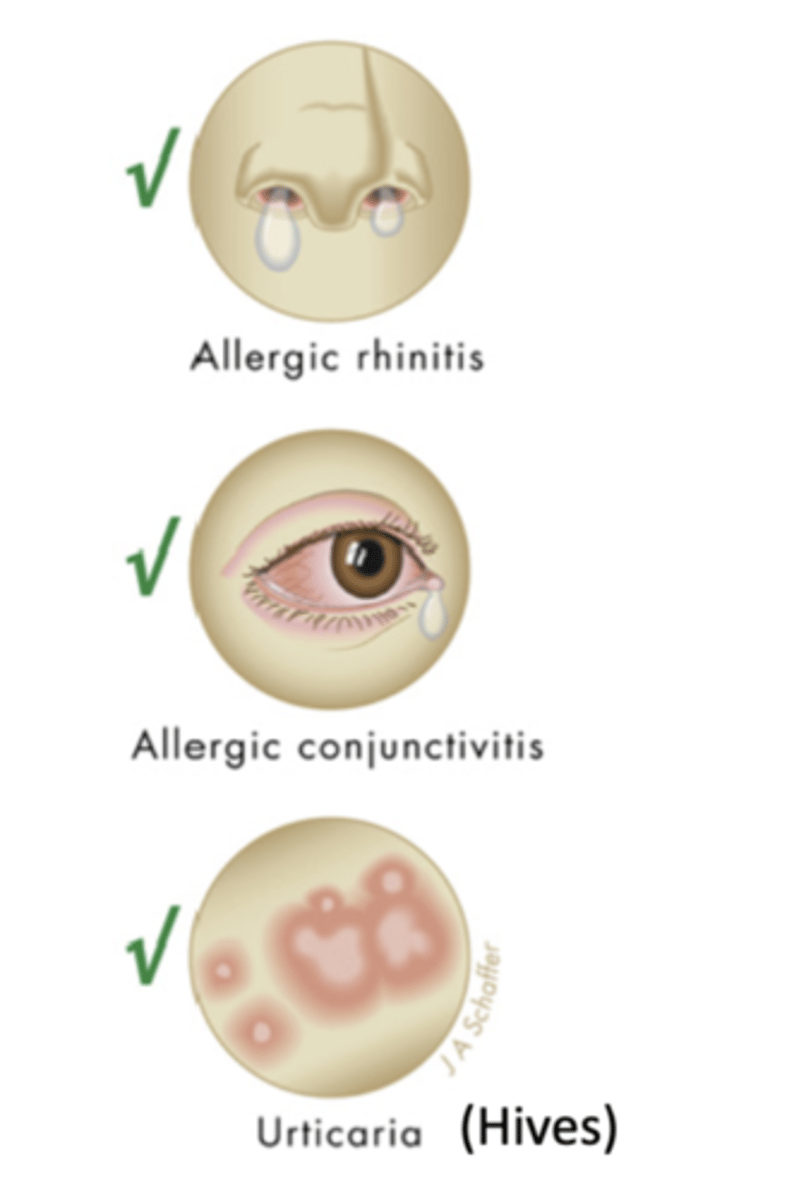
what are pharmacological and other uses for antihistamines
pharmacological
- allergic rhinitis
- allergic conjunctivitis
- hives (urticaria)
other uses
- manage cold symptoms
- eczema
-itching from atopic dermatitis
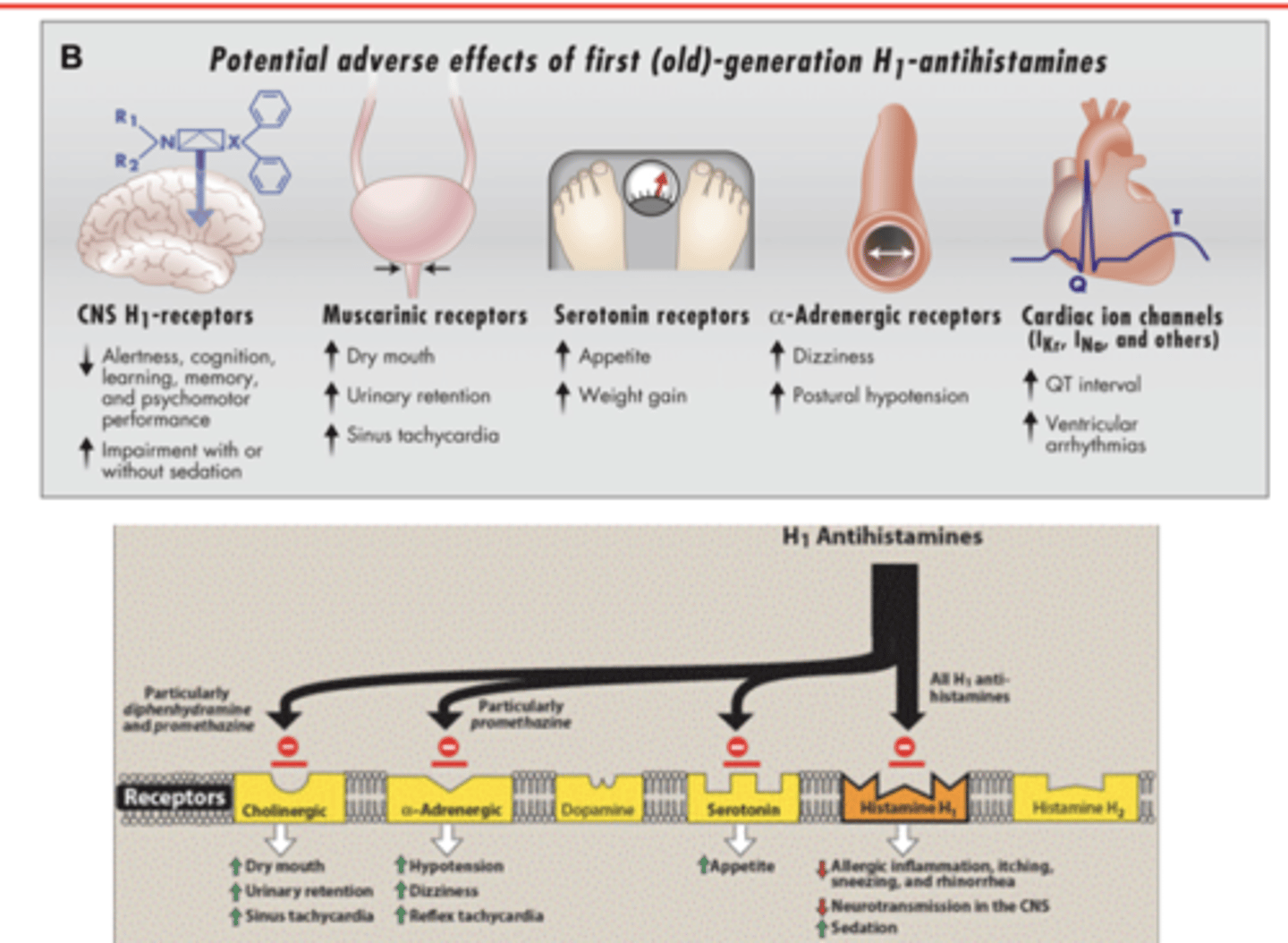
describe side effects of 1st generation antihistamines
- ANTISLUD
- hypotension
- dizziness
- reflex tachycardia
- weight gain
what are other uses for 1st gen antihistamines
- motion sickness
- acute dystonia associated with D2 receptor blockade (diphenhydramine)
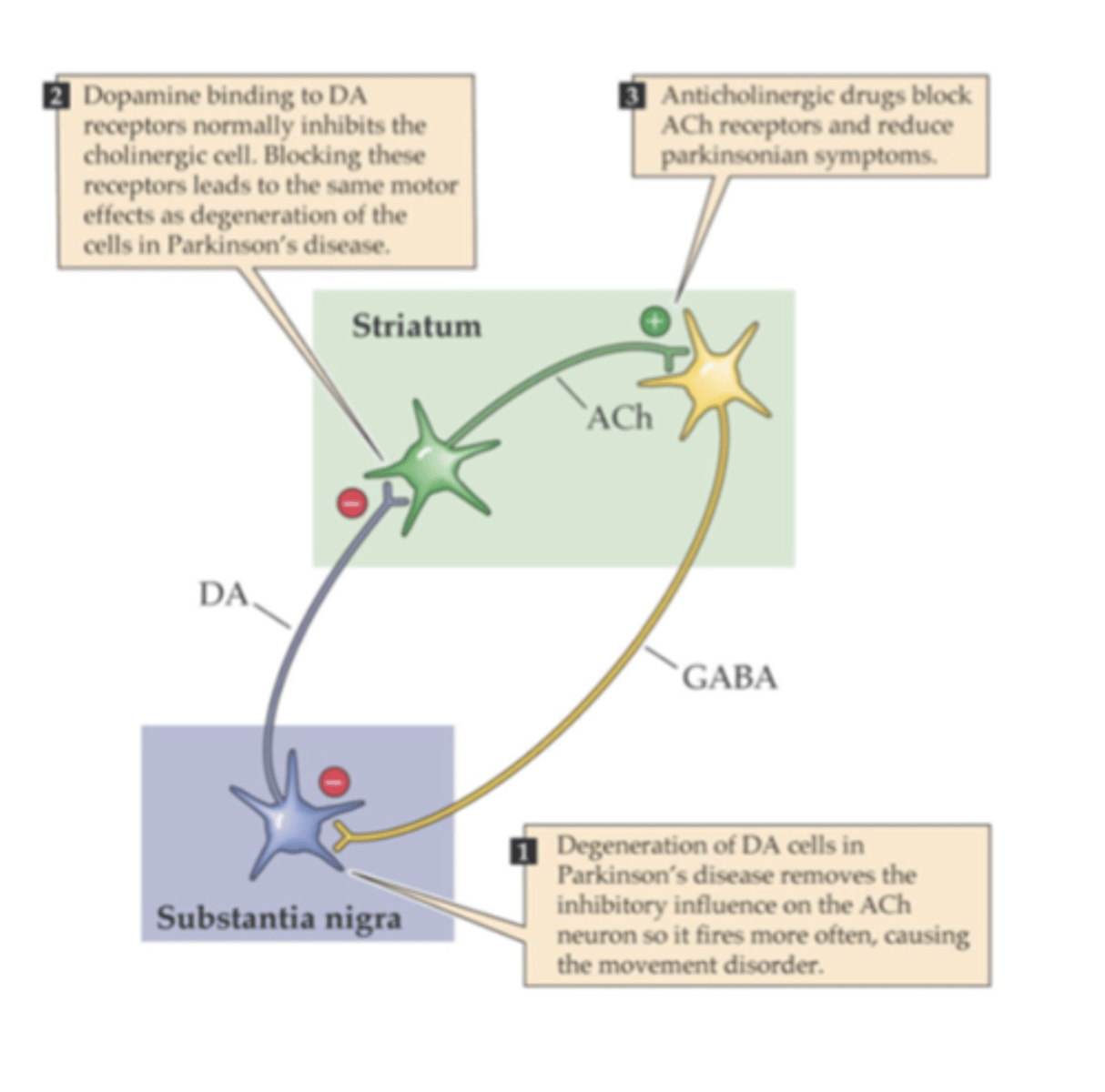
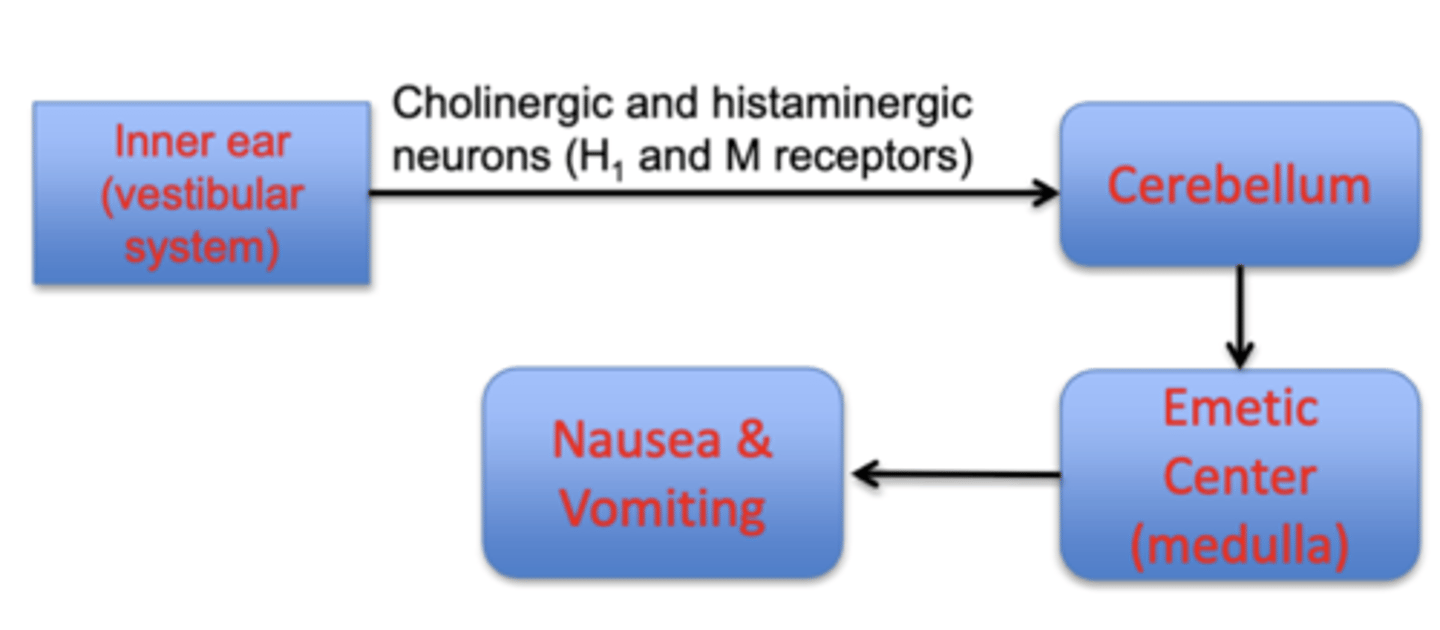
describe the pathophysiology of motion sickness
-mediated by the inner ear and increased cholinergic/histaminergic neurotransmission
drugs
- scopolamine (muscarinic receptor antagonist)
- meclizine, dimenhydrinate