Lecture 15 Glycogen
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Cellular respiration
the biochemical process by which cells turn nutrients into energy
Glycolysis -> TCA Cycle -> ETC and oxidative phosphorylation
3 steps of Cellular respiration
Glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the electron transport chain (ETC)
what step occurs in the cytoplasm
glycolysis turns glucose to pyruvate
What step occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
Pyruvate fuels the KC which passes electrons to electron carrier molecules
What step occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Electron carriers power the proton gradient in the ETC to make ATP
Glycogenolysis
the process of breaking down glycogen
-monomers are released from glycogen by a phosphorolysis reaction that creates phosphorylated glucose molecules
skeletal muscle cells require
stores of glycogen to supply energy for bursts of activity
where can the phosphate on glycogen be removed?
In the liver and kidneys.
-allowing free glucose to be transported out of the cell to the blood for use in the brain and other tissues when dietary glucose is not sufficient
-performed by glucose 6-phosphatase
-Muscle cells lack this enzyme, so glucose from glycogenolysis cannot leave the muscles
Glycogenesis
glycogen synthesis
-requires a protein primer and an activated glucose precursor
-Individual glucose molecules (activated as sugar nucleotides) are added to the nonreducing end of growing linear chains of the glycogen β-granule
-When storing glucose as glycogen, a branching enzyme periodically adds branches to the glycogen polymer chains.
regulating glycogen formation and breakdown
critical for organism homeostasis
-This balance is ultimately controlled by hormones (e.g., epinephrine, glucagon, and insulin) and achieved through allosteric regulation and phosphorylation of enzymes
-These enzymes and the regulatory proteins that act on them are integral parts of the glycogen granule
GLUT transporters
a family of membrane proteins that allow glucose to pass through the cell membrane lipid bilayer
GLUT-1
RBCs ad the blood-brain barrier
-Provides basal glucose uptake, especially under low glucose conditions
GLUT-2
Liver, pancreas, and kidneys
-A bidirectional transporter
-Particularly important in the liver for glucose storage and release
GLUT-3
Primarily in neurons
-High affinity for glucose
-Ensures a steady glucose supply to the brain, even at low blood glucose levels
GLUT-4
Muscle and adipose tissue
-is inuslin-dependent
-Stored in vesicles inside the cell
-When insulin binds, a intracellular signaling cascade moves GLUT-4 to the surface, allowing glucose to enter the cells
Phosphorylases
add inorganic phosphate (Pi)
Kinases
add phosphate rom a high energy molecule (e.g., ATP)
Phosphatases
remove phosphate groups
where is glycogen primarily found?
in muscle and liver
-Glycogen stored in the liver provides a reservoir that maintains blood glucose homeostasis when blood sugar levels drop
How long does glycogen breakdown take in muscle?
within seconds
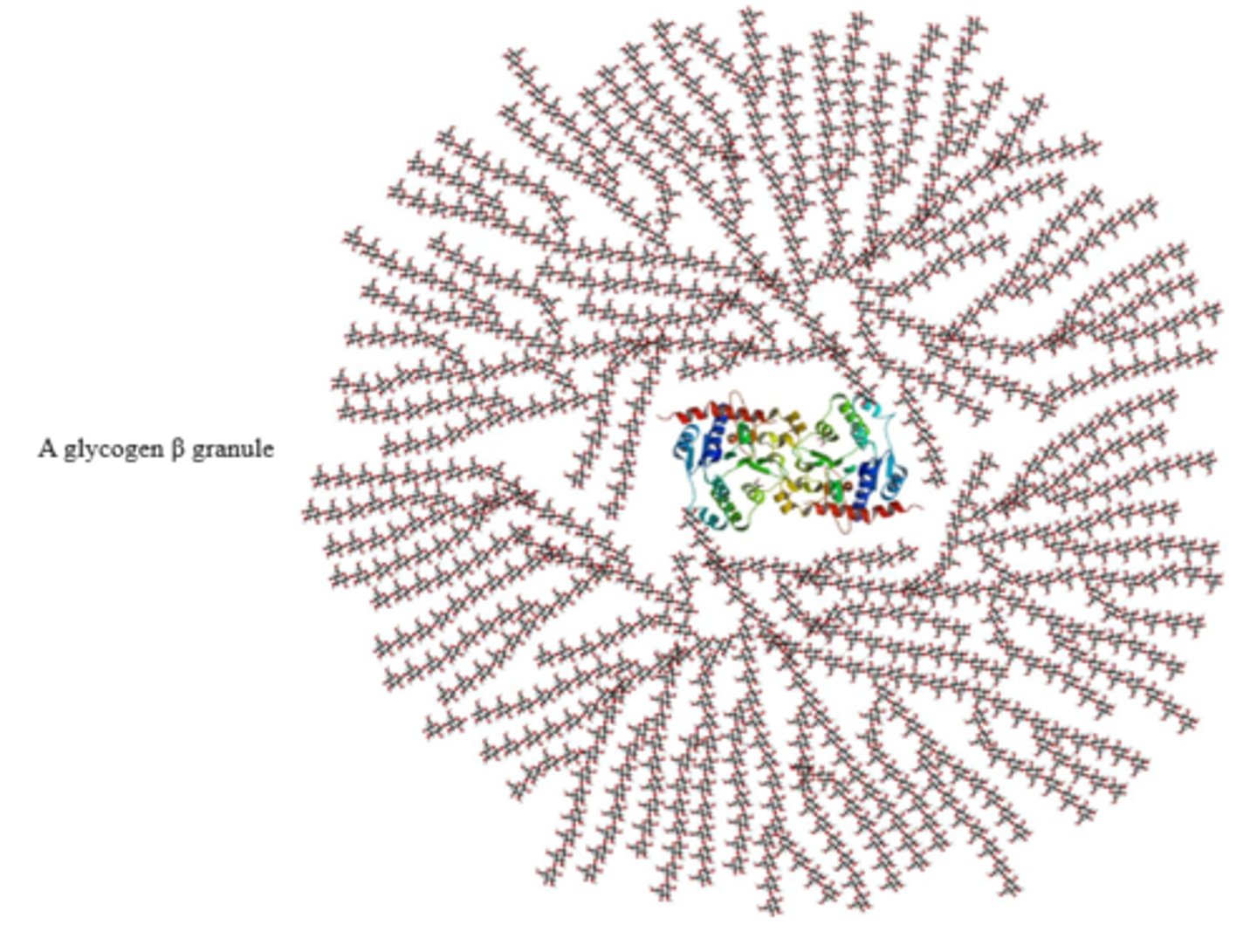
Glycogen
a polymeric storage form of glucose in animals
-storage units called "granules"
How is glycogen stored in the cellular cytosol of hepatocytes and myocytes?
as β-granules
-Vary in size, structure, and subcellular location
-Have many branched chains of D-glucose
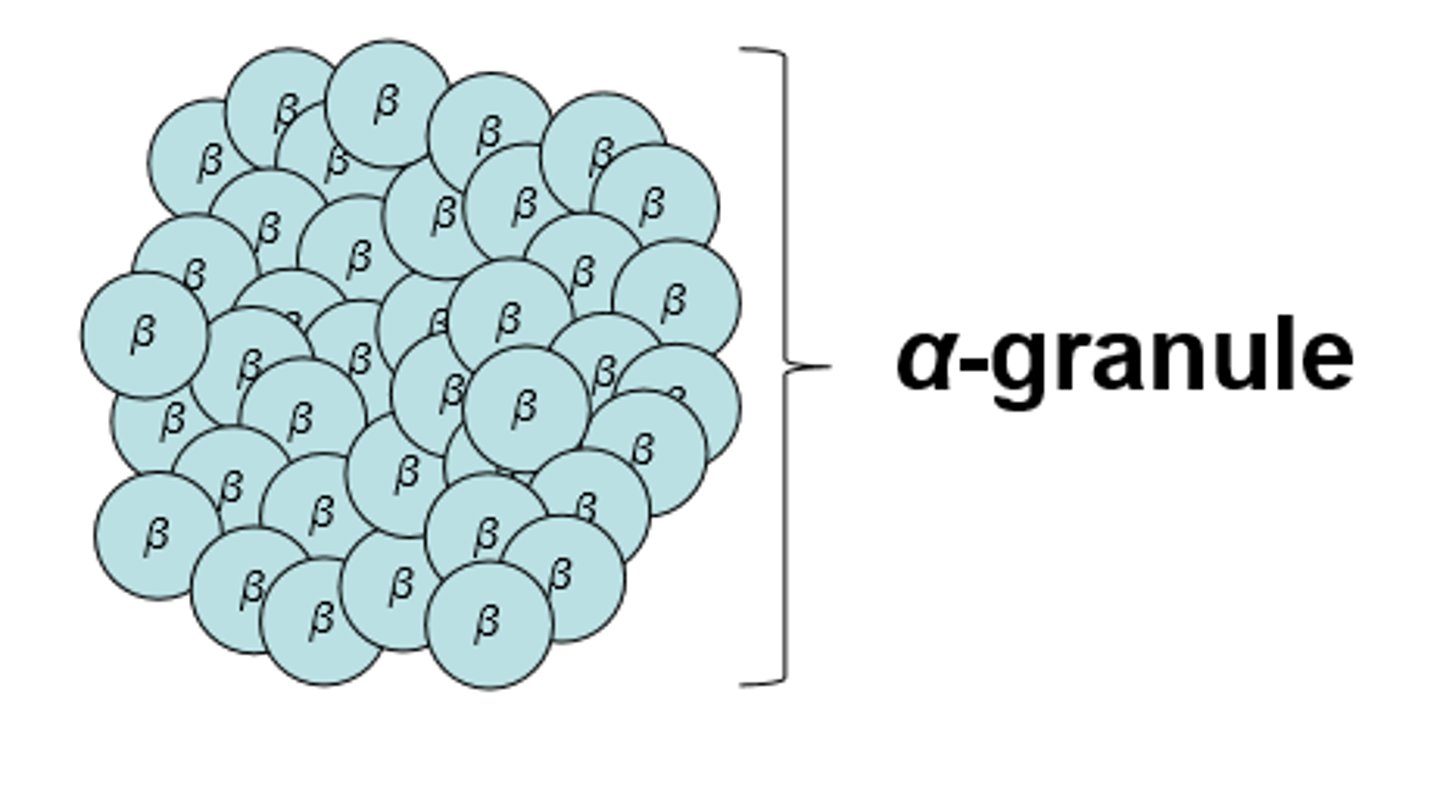
α-granules
β-granules cluster in the liver
-protein-rich granules composed of 2-40 clustered β-granules
-Release glucose slower than β-granules
-Visible in well-fed animals, but absent after a 24-hour fast
-Often are found on tubules of the smooth ER
Glycogenin dimers
glycoprotein glycogen primer for chain formation
-required for glycogen synthesis
-the first few glucose molecules attach to glycogenin
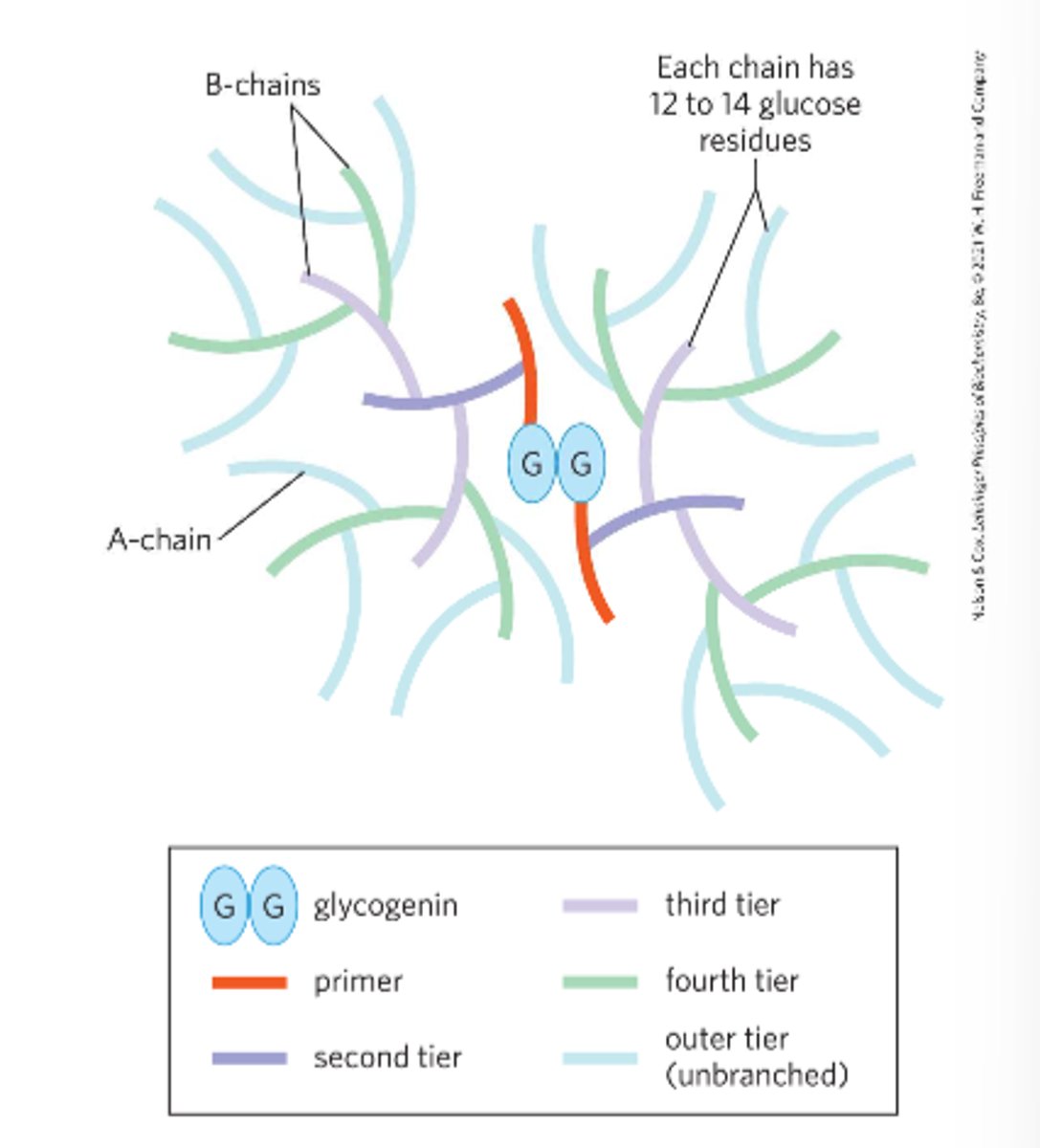
what is the structure of tiers of glucose residues?
tiers of glucose residues are in (α1->4) linkage, with (α1->6)-linked branches
-many free ends = efficient glucose release/addition
What adds more glucose monomers to form glycogen?
glycogen synthase
Glycogen phosphorylase
cleaves nonreducing ends of glycogen chains
-reducing ends = hemiacetal
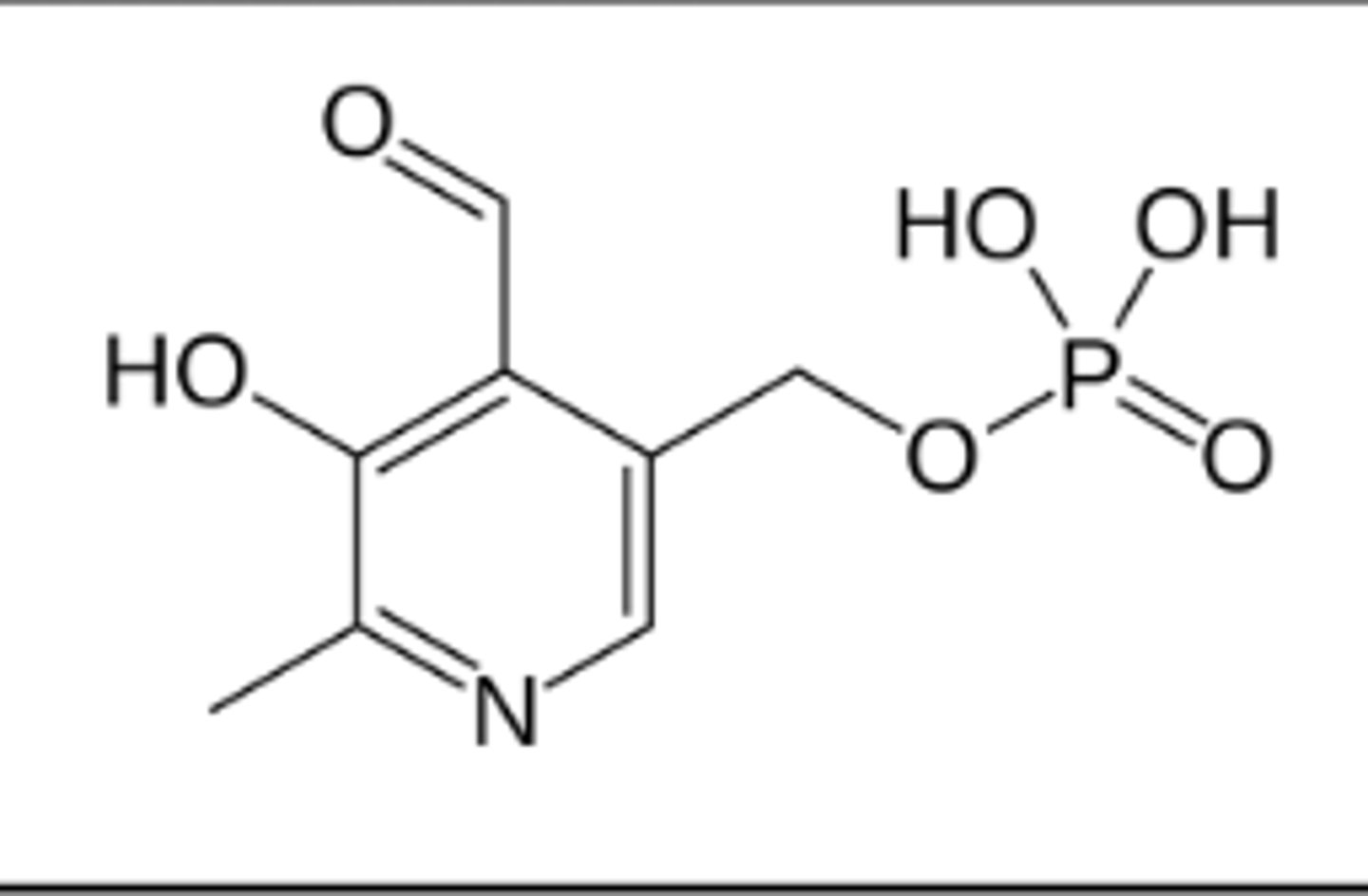
-Requires pyridoxal phosphate (a coenzyme)
-acts repetitively until reaches four residues about from (α1->6) branch point
What coenzyme is required for glycogen phosphorylase?
pyridoxal phosphate
Debranching enzyme
transfers branches onto main chains
-Also releases the residue at the (α1->6) branch as free glucose
What form are glucose residues after lysis from glycogen?
glucose 1-phosphate molecules
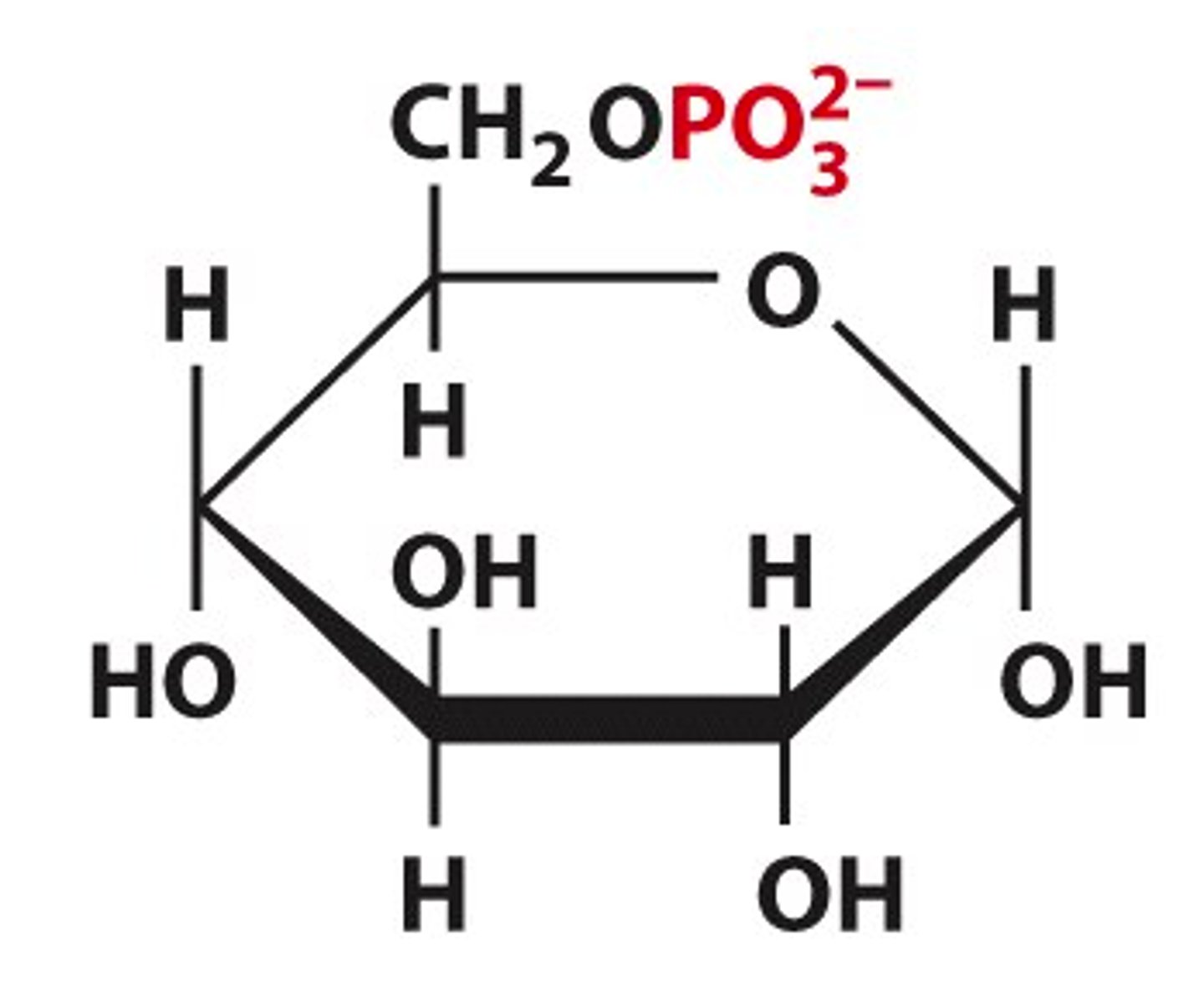
What are the options for G1P?
either enter glycolysis or replenish blood glucose
Phosphoglucomutase
converts glucose 1-phosphate <-> glucose 6-phosphate (G6P)
-G6P can enter glycolysis directly
-G6P ->glucose via glucose 6-phosphatase (gluconeogenesis) -> blood
What enzyme converts G6P to glucose?
glucose 6-phosphatase
Glucose 6-Phosphate
-In skeletal muscle = enters glycolysis
-In the liver = glucose 6-phosphatase converts glucose 6-phosphate to glucose in the ER for export to replenish blood glucose
Glycogen storage diseases
genetic defects in either glucose 6-phosphatase or glycogen enzymes cause glycogen storage diseases
-primary organs/cells affected = liver, skeletal and cardia muscle, leukocytes, and erythrocytes