Intro to Human Communication Exam #2
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UCO Intro to Human Communication Exam #2 Ch. 5-7 and 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What is the definition of Doublespeak?
Evasive, ambiguous language used to deceive, mislead, and corrupt thought
What was the idea of Doublespeak based on?
Nazi propoganda
What terms is Doublespeak derived from?
Doublethink and Newspeak
What is Doublethink?
The ability to hold two opposing ideas in a person’s mind and believe them both.
What is Newspeak?
The official language used to express the ideas of doublethink
What book does doublespeak come from?
1984 by George Orwell
What are the specifics of Doublespeak?
Designed to mislead and distort reality
Pretends to communicate
Makes the negative appear positive
Avoids or shifts responsibility
Limits, conceals, corrupts, and prevents thought
Makes the unpleasant appear attractive or tolerable
What are the forms of Doublespeak?
Euphemism
Jargon
Gobbledygook
Inflated language
What is the definition of Euphemism?
Words that attempt to soften, hide, or distort reality by putting the thing described into a better light making the object it describes sound less frightening, threatening, or offensive
What is the definition of Jargon?
Specialized language used by a particular professional trade, or hobby group often used in discourse with lay audiences or to impress others
What is the definition of Gobbledygook?
Many long, sophisticated words, or gobs of words, used in long convoluted sentences to confuse the audience and hide the real issue of the discourse
What is the definition of Inflated Language?
Puffed up, important-sounding words used to give commonplace things and events an elevated, glowing appearance
What are the ways to stop doublespeak?
Look out for it
Expose it for what it is
Tell others about the incongruity between the author’s intentions and words
What are the ways to avoid doublespeak?
Don’t use it knowingly
Use technical terms and jargon correctly
Present complicated ideas in ways that are appropriate for the audience
What are the three A’s of Symbols and their meanings?
Arbitrary
Ambiguous
Abstract
What is this?
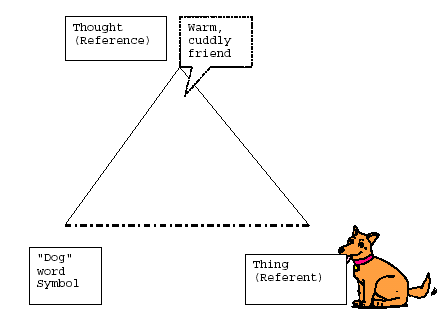
The Semantic Triangle
Why are symbols arbitrary?
They are not intrinsically connected to what they represent
What are examples of symbols being arbitrary?
Language and meaning changing over time (gay)
New words or phrases being coined in response to change (staycation)
Why are symbols ambiguous?
Their meanings are not fixed in an absolute way and vary based on one’s values and experiences
Why are symbols abstract?
They are not concrete or tangible
What is an example of using abstract symbols?
Overgeneralizations
How is communication guided?
It is rule guided
What are the types of rules in the principles of verbal communication?
Regulative
Constitutive
What is the definition of Regulative Rules?
Rules that specify when, how, where, and with whom to talk about certain things
What is the definition of Constitutive Rules?
Rules that tell us how to count certain kinds of communication
What is the definition of Symbols?
A representation of a person, event of other phenomenon
What is the definition of totalizing?
Using a single label to represent the totality of a person
What is the definition of Loaded Language?
Words that strongly slant perceptions and thus meaning
How do symbols organize perceptions?
They help to classify and evaluate experiences using cognitive schemata
What is the definition of hypothetical thought?
Symbols allow people to think about experiences and ideas that are not part of their concrete, present situation
What are examples of hypothetical thought?
Contemplate things with no real existence
Remember ourselves in the past
Project ourselves into the future
What does the I (Id) do in response to symbols?
Acts impulsively in response to inner needs and desires, regardless of social norms
What is the Me (Ego/Superego)?
The socially conscious part of the self that monitors and moderates the I’s impulses
What are the guidelines to enhance effectiveness in verbal communication?
Dual perspective
Own your feelings and thoughts
Respect what other’s say about their feelings and ideas
Strive for accuracy and clarity
What is the definition of Dual Perspective?
Recognizing another person’s point of view and taking that into account as you communicate
What are the ways to strive for accuracy and clarity?
Levels of abstraction
Qualify language by indexing
What percent of messages are misunderstood over text messages?
Approximately 50%
What are the ways symbolic capacities affect our lives?
Symbols define
Symbols evaluate
Symbols organize perceptions
Symbols allow hypothetical thought
Symbols allow self-reflection
What is the definition of Marginalization?
A condition and process preventing individuals and groups from equal participation in wider society, including social, economic, and political life.
What is the most important guideline for verbal communication?
Dual perspective
What is the definition of Static Evaluation?
Assessments that suggest something is unchanging or static.
What is the definition of Indexing?
A technique of noting that statements reflect specific times and circumstances and may not apply to other times or circumstances.
How did Rome influence non-verbal communication?
Gestures
Affirmative nod
Negative headshake
Romance
Kisses
Greetings
Handshake
What is the definition of Nonverbal Communication?
All aspects of communication other than words themselves
What does nonverbal communication do with verbal communication?
Supplements or replaces it.
How are verbal and nonverbal communication similar?
Symbolic
Guided by constitutive and regulative rules
Culture bound
May be intentional or unintentional
What are the differences between verbal and nonverbal communication?
Nonverbal is perceived as more honest
Nonverbal is multi-channeled while verbal is single
Nonverbal is continuous while verbal discrete
In what ways does nonverbal communication supplement or replace verbal communication?
Repeat verbal messages
Highlight verbal communication
Compliment or add to words
Contradict verbal messages
Substitute for verbal communication
What are the principles of Nonverbal Communication?
Similarities and differences with verbal communication
Supplements or replaces verbal communication
Regulates interaction
Establishes relationship-level meanings
Reflects cultural values
What are the dimensions of relationship-levels meaning?
Responsiveness
Liking
Power
What are the categories of Nonverbal Communication?
Kinesics
Haptics
Physical appearance
Artifacts
Proxemics
Environmental factors
Chronemics
Paralanguage
Silence
How can you improve Nonverbal Communication?
Monitor your nonverbal communication
Interpret others nonverbal communication with personal and contextual qualifications
What percent of nonverbal communication accounts for the total meaning of communication?
65-93%
What is the definition of Kinesics?
Body position and body motions, including movements of the face
What is the definition of Haptics?
Nonverbal communication that involves physical touch
What is the definition of Artifacts?
Personal objects which we announce our personal identities and personalize our environments
What is the definition of Proxemics?
A type of nonverbal communication that involves space and how we use it
What is the definition of Chronemics?
A type of nonverbal communication that is concerned with time and how we use and perceive it to define identities and interactions
What is the definition of Paralanguage?
Vocal communication that does not use words
What was the crisis of the 3rd Century?
Civil war, invasion, plague, and economical and political collapse.
What was Rome’s influence in Western culture?
Language/alphabet
Government/legal systems
Architecture/engineering
Religion
What did Emperor Constantine do for the Roman Empire?
Legalized Christianity
Established Constantinople as the capital of the Eastern half
Called on Council of Nicaea to organize churches
What was the Council of Nicaea?
A group of 250-300 bishops that established Jesus as divine and created the Nicaea creed to summarize Christianity
What is the definition of Culture?
A system of ideas, values, beliefs, structures, and practices that is communicated by one generation to the next and that sustains a particular way of life
What are the material components of culture?
Tangible objects
Physical substances altered by human invention
What are the nonmaterial components of culture?
Intangible
Reflect a culture’s values
Influence behavior
What is the definition of Belief?
A conception of what is true, factual, or valid
What is the definition of Values?
Shared views of what is good, right, worthwhile, and important
What is the definition of Norms?
Informal rules guiding how members of a culture act, think, and feel
What are examples of nonmaterial components of culture?
Beliefs
Values
Norms
How are cultures a system?
They are a coherent system of understandings, traditions, values, communication practices, and ways of living
What dimensions do cultures vary on?
Individualism/collectivism
High uncertainty avoidance/low uncertainty avoidance
High power distance/low power distance
Masculinity/femininity
Long-term orientation/short term orientation
Why are cultures dynamic?
They change and evolve over time
What are the sources of change within a culture?
Invention
Diffusion
Calamity
Communication
What are the types of communication within a culture social community?
High-context communication
Low-context communication
What are examples of social communities?
Gender
Race
Economic class
Ethnicity
How does communication affect culture?
It sustains and expresses culture
How are cultures shaped?
By historical and geographical forces
What is the most common way of telling a story?
Through the Hero’s Journey format
What are ways to improve intercultural communication?
Resist ethnocentric bias
Recognizing that responding to diversity is a process
What is the definition of ethnocentrism?
Using one’s own culture and its practices as the standard for interpreting the values, beliefs, norms, and communication of others
What is the definition of cultural relativism?
Cultures vary on how they think, act, and behave, as well as in what they believe and value
What are the responses to diversity?
Resistance
Tolerance
Understanding
Respect
Participation (like being multilingual)
What are the key premises to culture?
Systematic
Dimensional
Dynamic
Include multiple social communities
What is the definition of cultural inteligence?
Motivational, cognitive, and behavioral abilities to understand and adapt to a range of contexts, people, and patterns of interaction.
What are the components of cultural inteligence?
Drive
Knowledge
Strategy
Action
How is public speaking an enlarged conversation?
Minor mistakes don’t ruin credibility
Consideration of others’ perspectives
Present ideas clearly
Organize what you say
Explain and support ideas
Present in an engaging manner
What are the steps to selecting your topic?
Choose a topic that matters to you
Choose an occasion appropriate topic
Choose an audience appropriate topic
Narrow your topic via mind mapping
What are the general puposes for public speaking?
To inform
To persuade
To entertain
What is the definition of specific purpose?
A behavioral objective or observable response that indicates you have achieved your communication goal
What is a thesis statement?
A short statement that provides the main idea of the speech
What are the steps to planning public speaking?
Identify a broad topic
Narrow the topic
Determine general purpose
Determine specific purpose
Develop thesis statement
What does the demographic of the audience tell you?
Identifies general features of a group of listeners
What is audience demographic data used for?
Adaptation
Inferences
Determining what and who listeners find credible
Connections
Guarding against stereotypes
What is situational audience analysis?
Discovering what the audience already knew or believe about a topic, speaker, and occasion