Aromatic Electrophilic Substitution
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
im crying so bad ohmygod. never take orgo 2 guys.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
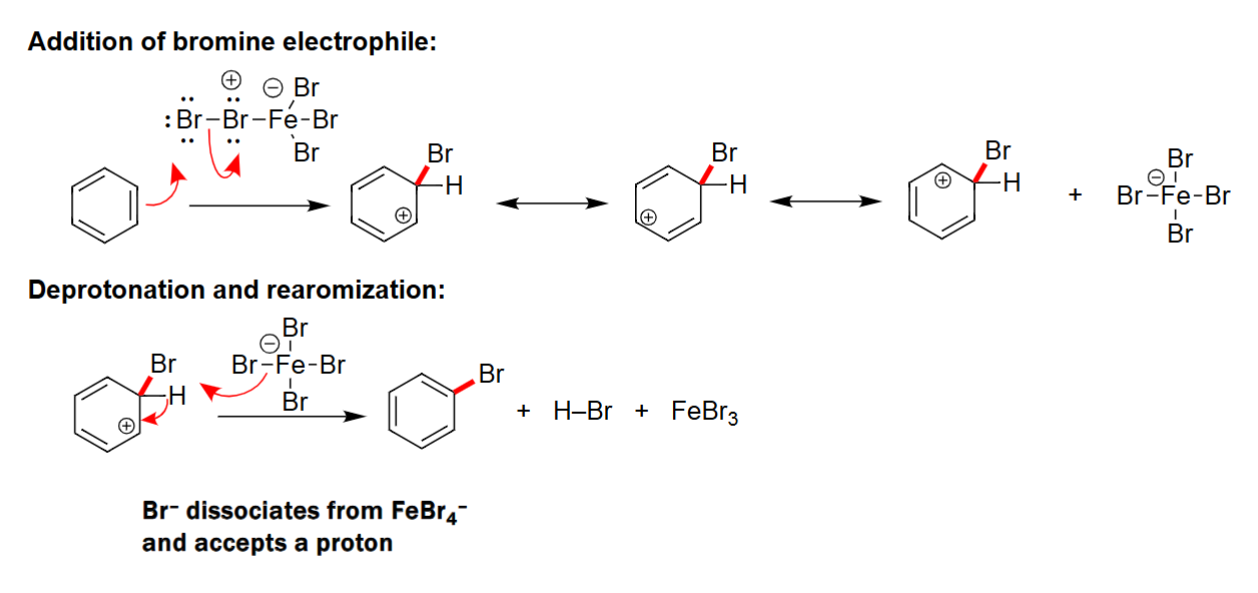
EAS Halogenation
To create a strong electrophile either AlCl3 or FeBr3 is needed.
Carbocation intermediate is formed.
Formulates a benzene ring with a halogen attached.
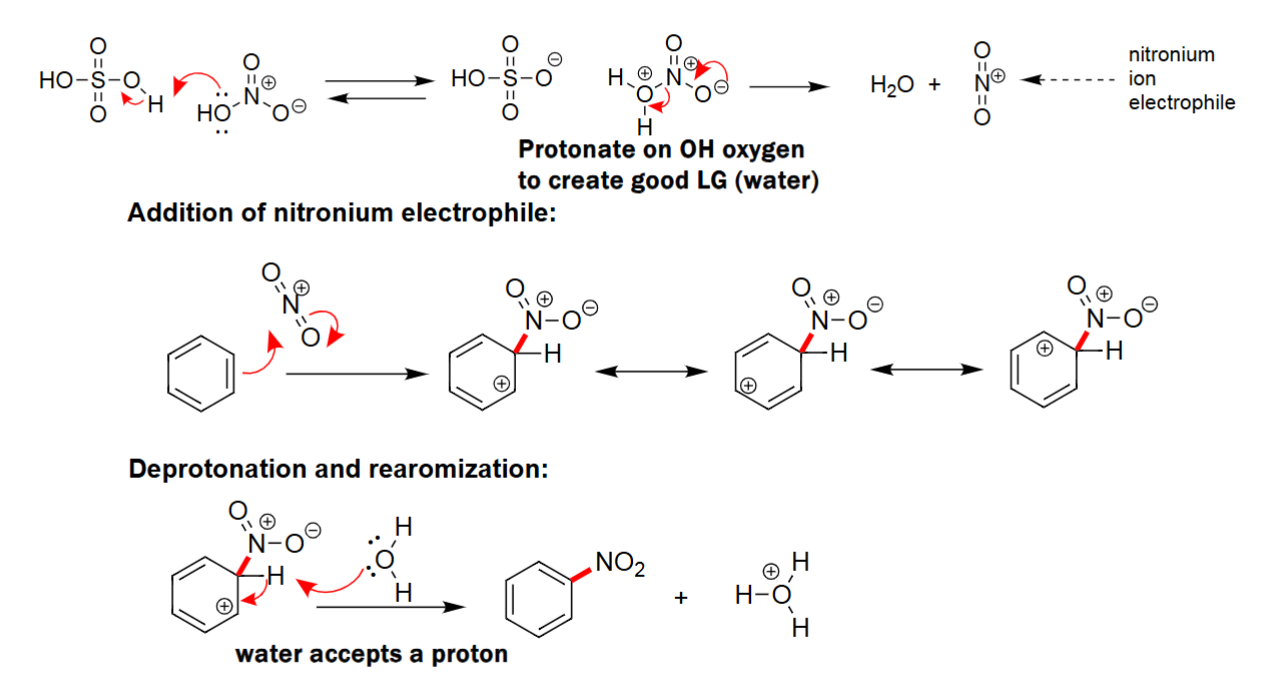
EAS Nitration
Acid (i.e. H2SO4) reacts with HNO3 to form a unstable electrophile.
Benzene reacts with the electrophile.
Adds NO2 to the benzene.
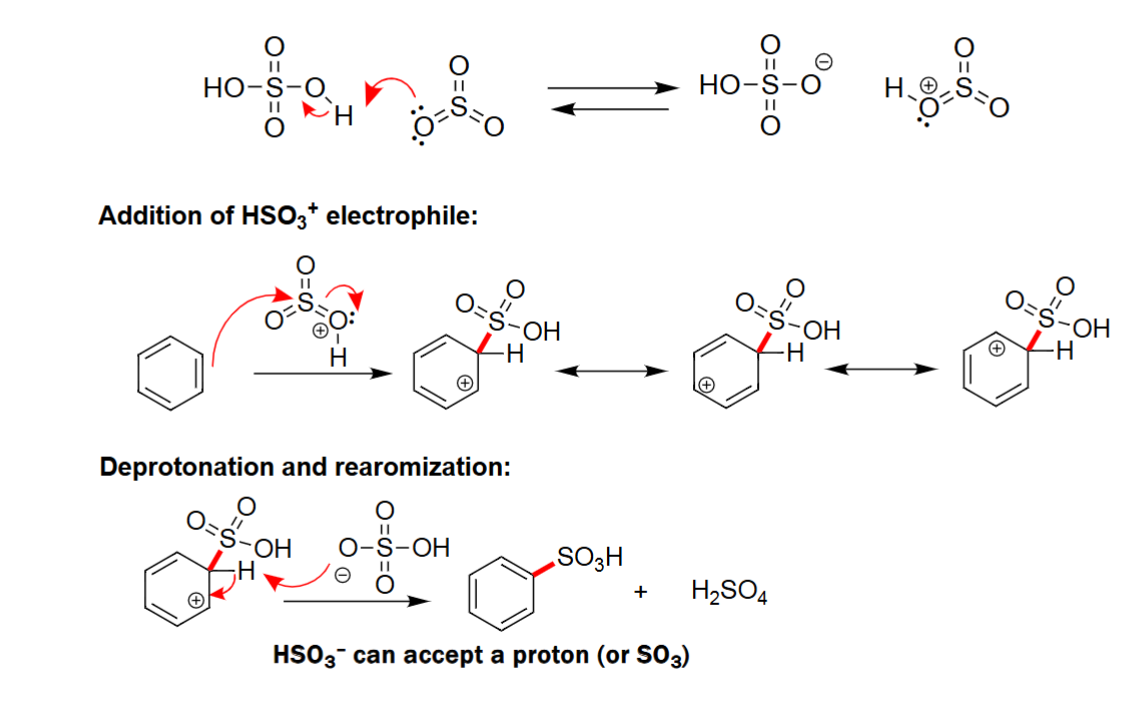
EAS Sulfonation
Forms its conjugate base and acid as byproducts.
Benzene reacts with unstable electrophile.
Forms a benzene with a HSO3 group attached.
Needs acid and heat to react.
EAS Alkylation
Reacts with AlCl3/FeCl3.
Alkyl group is attached.
Carbocation rearrangement can occur.
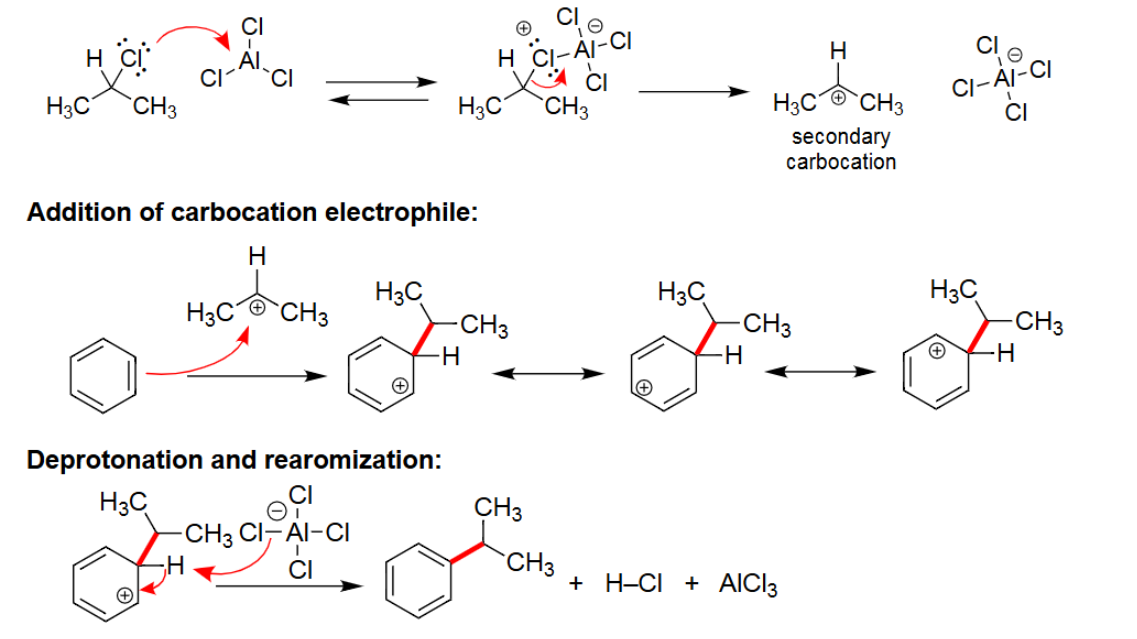
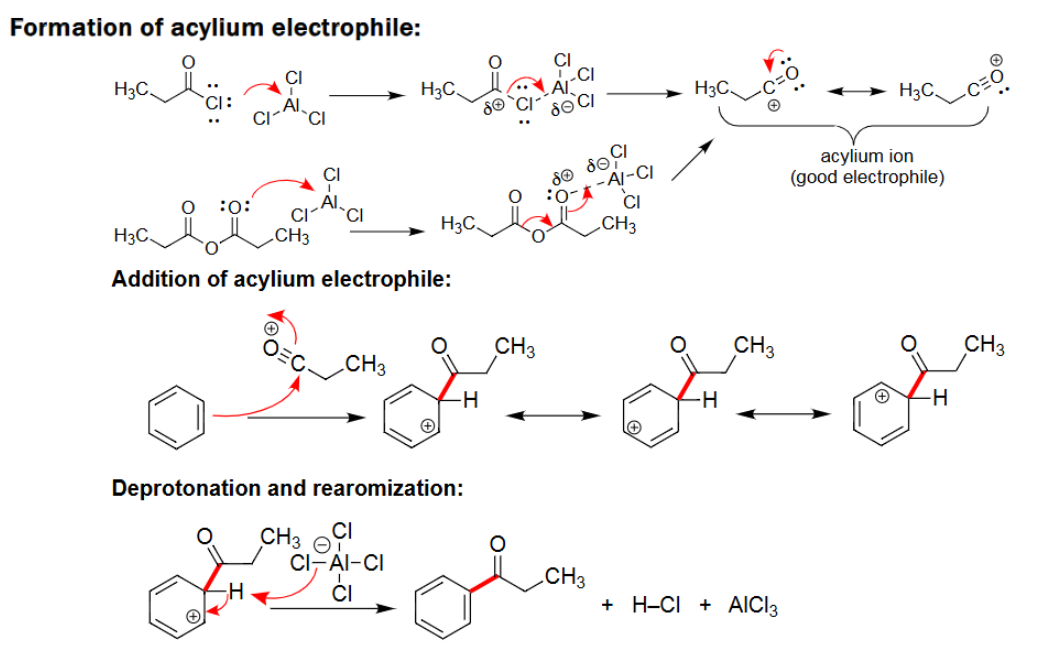
EAS Acylation
Reacts with AlCl3/FeCl3.
Adds carbonyl group to benzene; forms a ketone.
No carbocation rearrangement.
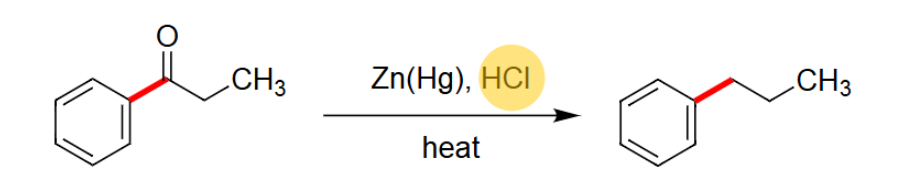
Clemmensen Reduction
Reacts using Zn(Hg) and HCl.
Needs heat.
Uses acidic conditions.
Takes off the =O.
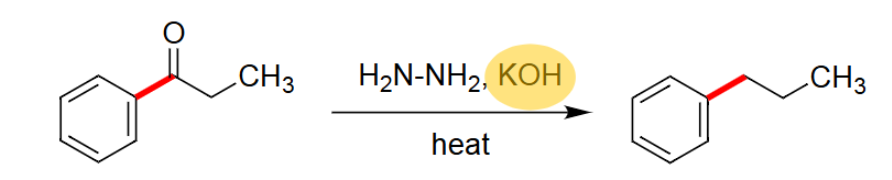
Wolff-Kishner Reduction
Reacts using H2N-NH2, KOH, and heat.
Uses basic conditions.
Takes off the =O.
EAS with Group on Ring
Electron-donating groups lower ΔG‡ (faster reaction) and electron-withdrawing groups raise ΔG‡ (slower reaction).
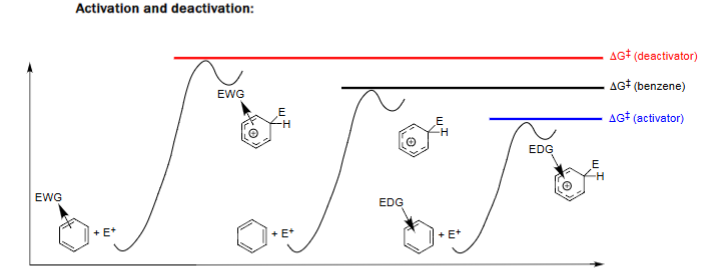
Weakly Activating Groups
CH3.
Alkyl.
Aryl (C6H5).
Moderately Activating Groups
-OCH3, -OAlkyl.
OC(=O)R.
NHC(=O)R.
Strongly Activating Groups
-OH, -O-.
NH2, -NHR, -NR2.
Weak Deactivating Groups
Cl, Br, F.
However, acts like a weak activator.
Moderately Deactivating Groups
C≡N.
C(=O)R, -C(=O)H.
C(=O)OH, -C(=O)OR.
SO3H.
Strongly Deactivating Groups
NO2.
NR3+, CX3 (X = F, Cl).
EDG with a Group on the Ring
When there is already a group on the ring, the specific substituent will determine the location of the second group.
Activating substituent = ortho/para (para is favoured).
One exception are the halogens.
EWG with a Group on the Ring
When there is already a group on the ring, the specific substituent will determine the location of the second group.
Deactivating substituent = meta.
Ortho/Para Direction
Weak activators favour o/p substitution though inductive stabilization.
Para is usually major (even though there are two ortho positions) unless it is blocked.
Ortho/Para Activation
Strong activators favour o/p substitution though extra resonance stabilization.
Resonance stabilization by strong activators wins out over inductive stabilization.
Can sometimes overactivate.
Decreasing Activation
In times of overactivation, the activating group can be made less activating.
Allows the other reactant to reach the proper position.
Meta Direction
Strong deactivators disfavour o/p subsitution though charge repulsion.
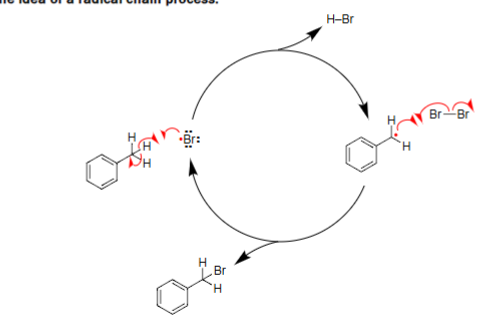
Benzylic Halogenation Radicalization
Generic free radical halogenation reaction.
Reacts with a halogen (X2) along heat or light.
Proceeds via hydrogen abstraction to form a free radical.
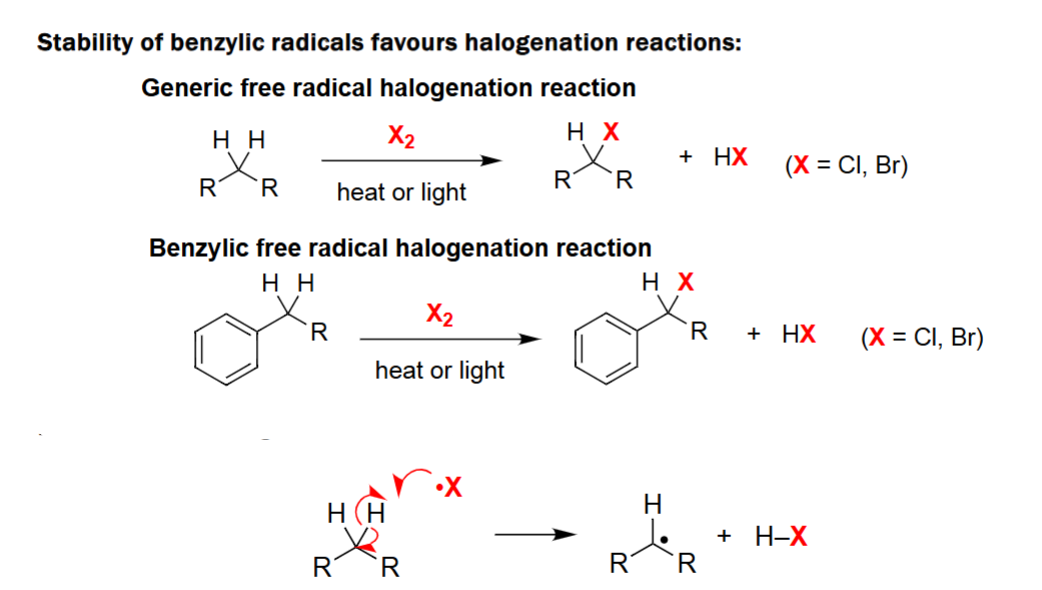
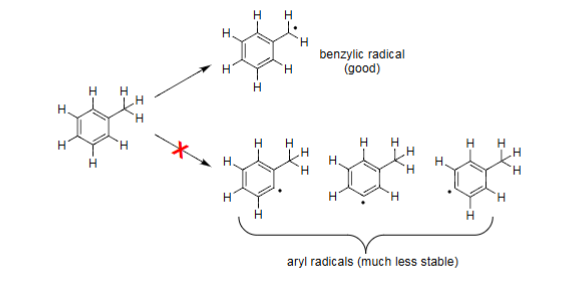
Benzylic Halogenation Radicalization Favour
Abstraction of benzylic H favoured over ring hydrogens.
Also favoured over other non-benzylic side-chain hydrogens.
Radical Chain Process
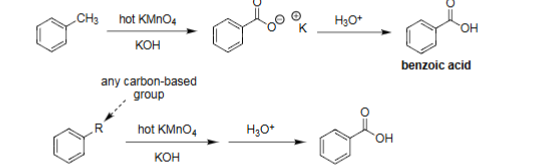
Oxidative Degradation
Hot KMnO4 with KOH for first reaction, then H3O+ for second reaction.
Leads to benzoic acid formation.
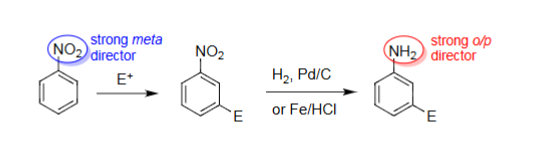
Catalytic Hydrogenation | Fe/HCl Reduction
Conversion of NO2 to NH2 (nitro to aniline).
However, other substituents on the benzene can react.
Fe, HCl can ensure no other reactions occur other than NO2 → NH2.