Cartilage and Bone
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LSU SVM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are the components of cartilage?
chondroblasts/cytes + ECM
Does cartilage have any blood supply or innervations?
no
What is the function of chondroblasts?
to actively make the matrix of cartilage
Where do chondroblasts grow?
within cartilage
What are chondrocytes?
less active chondroblasts
Where do chondrocytes grow?
in lacunae within cartilage
What is perichondrium?
fibrous connective tissue of cartilage
What are the two layers of the perichondrium?
outer fibrous layer and inner cellular layer
What is the function of hyaline cartilage?
foundation for fetal skeletons and provide stiff but somewhat flexible support and reduces friction between bony surfaces
What type of collagen is hyaline cartilage made of?
very fined-sized type 2 collagen fibers
What is the most abundant cartilage? Identified by it’s semitranslucent matrix.
hyaline cartilage
Where can you find hyaline cartilage?
covering bone surfaces at synovial joints
What cartilage only has perichondrium on non-articular surfaces?
hyaline cartilage
Which cartilage has the most amount of matrix?
hyaline cartilage
What cartilage has a scant amount of matrix?
fibrocartilage
What cartilage always has perichondrium present?
elastic cartilage
What are the components of elastic cartilage?
type 2 collagen and elastic fibers interwoven in small amount of ground substance
What is the function of elastic cartilage?
provide support while being able to tolerate distortion without damage and return to original shape
What kind of cartilage is found where resilient and springiness are needed?
elastic cartilage
Which cartilage has no perichondrium cover at all?
fibrocartilage
What is the collagen component of fibrocartilage?
type 1 in annulus and type 2 in pulposus
Where is fibrocartilage located?
intervertebral disks
What is the function of fibrocartilage?
resist compression/deformation to prevent bone to bone contact
Which cartilage is capable of withstanding compression forces?
fibrocartilage
What is the only cartilage that does not undergo calcification?
elastic cartilage
Which cartilage grow via interstitial and appositional growth?
hyaline and elastic cartilage
Which cartilage grows only via interstitial growth?
fibrocartilage
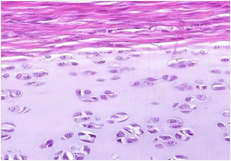
Which cartilage is shown in the following image?
hyaline cartilage
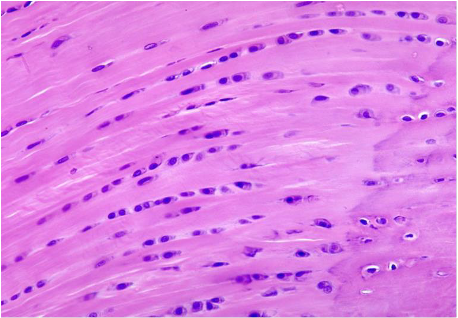
Which cartilage is shown in the following image?
elastic cartilage
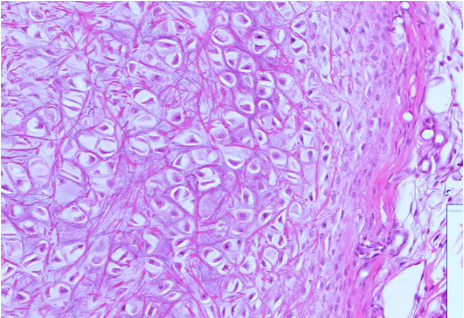
Which cartilage is shown in the following image?
fibrocartilage
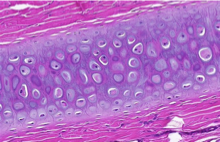
Which cartilage is shown in the following image?
elastic cartilage
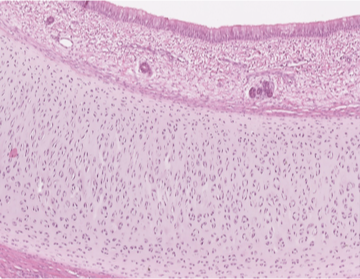
Which cartilage is shown in the following image?
hyaline cartilage
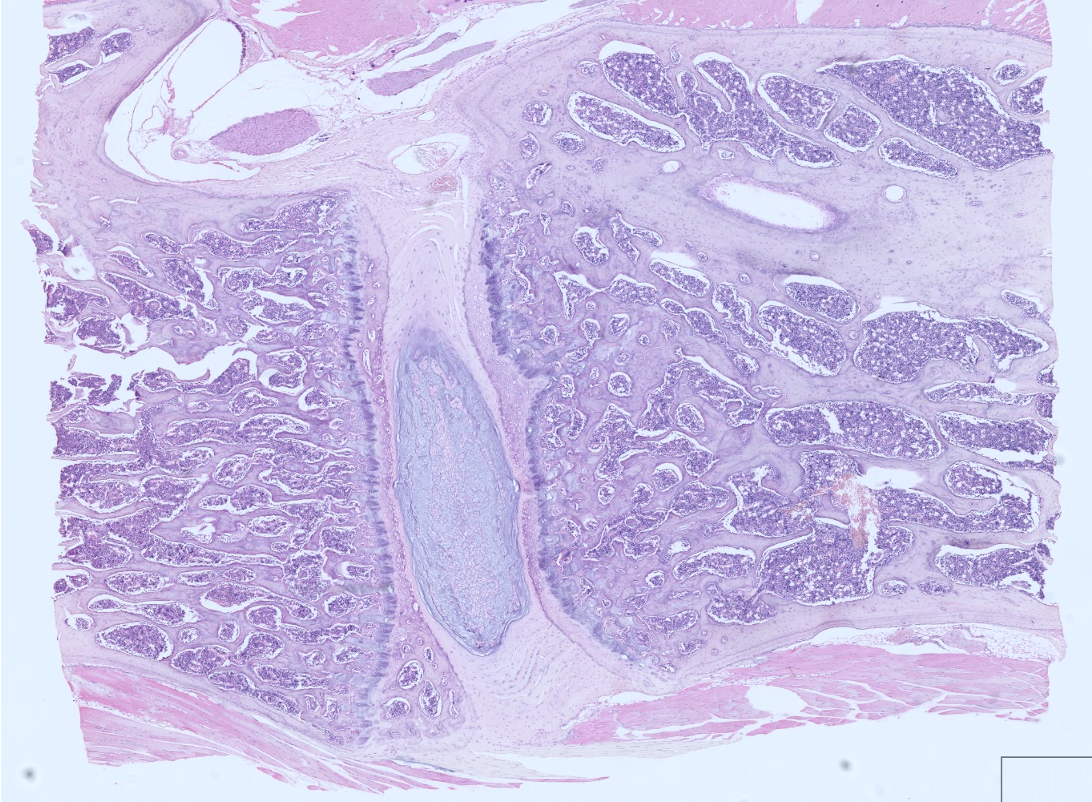
Which cartilage is shown in the following image?
fibrocartilage between two vertebra
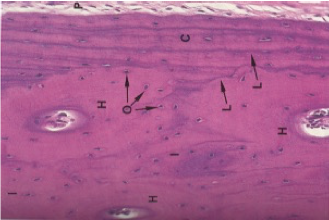
What kind of bone is shown in the following image?
compact bone
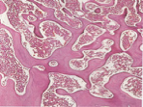
What kind of bone is shown in the following image?
trabecular (spongy)
What is the function of osteoblasts?
actively make matrix
What is the function of osteocytes?
maintains matrix
What is the function of osteoclast?
resorbs and regulates matrix
What is the lifespan of an osteoblast?
couple of weeks
What is the lifespan of an osteocyte?
10-20 days
What is the lifespan of an osteoblast?
few days
What bone cells only have one nucleus?
osteoblast and osteocytes
What bone cell is multi-nucleated?
osteoclasts
If you remove the organic bone matrix, what occurs to the bone?
becomes brittle
If you remove the inorganic bone matrix, what occurs to the bone?
becomes soft, flexible, and pliable