PSYC 301 Final - Dysfunction Associated with Psychiatric Disorders 1
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychiatric Dysfunction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Why classify psychiatric dysfunction (mental illness) into types?
To seek similarities + differences amongst patient groups
Guide treatment choices
Allow clinicians to communicate
To serve parties who require a diagnosis (ex. Insurance, legal system)
To permit research (via categorization)
into causes
Into treatment responsiveness
into prognosis
What version of the DSM do we use?
Version 5-TR
What are 3 properties of the DSM?
Atheoretical (does not take any position)
Operationalist
Categorical
Name the three components a condition must have to be included in the DSM
Clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotional regulation, or behaviour
Dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or development process underlying mental functioning
Associated with significant distress/disability in social, occupational, academic, or other important activities
What are the explicit exclusions of the DSM-5?
An expectable/culturally approved response to a common stressor/loss (ex. death of a loved one) is not a mental disorder
Socially deviant behaviour (ex. political, sexual) and conflicts that are bw individual + society (unless the deviance/conflict results from a dysfunction in the individual)
What are some criticisms of the DSM criteria?
Major criticism is the heterogeneity of the criteria
Level of Detail
Ex. nearly 24,000 possible symptom combinations for panic disorder, with one possible combination for social phobia
Overlap
For many diagnoses, 2 people could be diagnosed with no overlapping symptoms
High overlap between some diagnoses (ex. PTSD and MDD)
Authority (Who judges the distress/impairment?)
Clinician vs. self vs. unclear… inconsistent
Comparator
Sometimes compare a person to themself (ex. More talkative than usual)
Sometimes comparing a person to a normal/typical person (Ex. excessive/inappropriate levels of guilt)
Some cases there is no comparator (ex. Feelings of worthlessness)
Normative Assumptions
Normative: Evaluation of right or wrong (ex. Ought, should)
Descriptive (What is/what would be)
In Classification Criteria:
Manic or hypomanic episodes
“excessive involvement of activities in …”
ADHD
“often fails to … when it is expected”
Homosexuality
Classified as a disorder in DSM-I and DSM-II
Removed for DSM-III following protests by gay activists at the American Psychiatric Association’s annual meetings
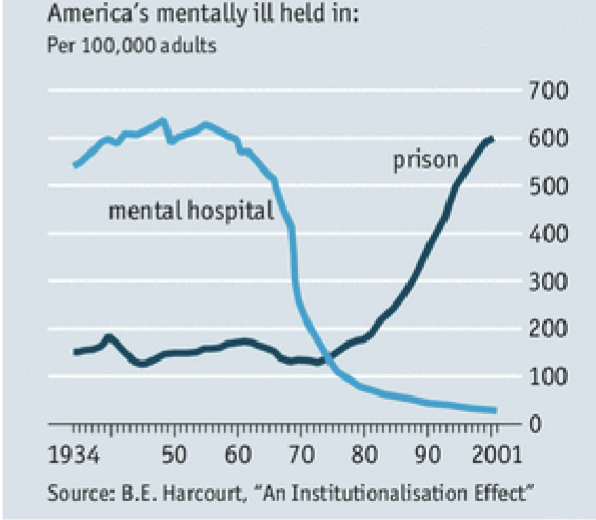
Deinstitutionalization
Movement starting in 1950s-60s to replace long stay psychiatric facilities with community mental health services
Possible with antipsychotic drugs (ex. chlorpromazine)
Balloon theory - without support, ppl w/ mental illness are more likely to be held in prisons/unhoused
What is the relationship between mental illness and violence?
Mental illness is not associated with violence!!!
In the absence of substance abuse disorder, people with mental illnesses are not more violent than others from their same neighbourhoods
More likely to be victims