PSY202 Intelligence
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
What is Intelligence?
* A person’s capacity to learn and their ability to apply their knowledge
2
New cards
What does **Sir Galton** define intelligence as?
A person’s sensory capacity indicates their intelligence.
3
New cards
What does **Edwin Boring** define intelligence as?
“Intelligence is whatever intelligence tests measure“; IQ and Standardized test results indicate a person’s intelligence.
4
New cards
What does **Alfred Binet** define intelligence as?
Higher Mental Processes.
5
New cards
What is Psychometrics?
Use of psychological test to test and study the minds of humans and animals.
6
New cards
What did **Charles Spearman** contribute to the study of Intelligence?
* Factor Analysis
* General Intelligence (g Factor)
* Specific Intelligence (s Factor)
* General Intelligence (g Factor)
* Specific Intelligence (s Factor)
7
New cards
What is Factor Analysis?
* Used to evaluate relationships among a set of observed variables
* High correlations among scores on several questions measure the common ability of individuals
* High correlations among scores on several questions measure the common ability of individuals
8
New cards
What is General Intelligence?
* g factor
* The underlying performance of people on various tests
* The general/overall differences in IQ among people
* The underlying performance of people on various tests
* The general/overall differences in IQ among people
9
New cards
What is Specific Intelligence?
* s factor
* Each individual has a unique IQ score
* The specific skills an individual has
* Each individual has a unique IQ score
* The specific skills an individual has
10
New cards
What are the Components of General Intelligence?
* Visual-Spatial (how fast it takes to put together a puzzle)
* Quantitative Reasoning (how fast it takes to solve a math problem)
* Knowledge (learning from a textbook; long term memory)
* Fluid Reasoning (how fast it takes to solve a rubix cube)
* Working Memory (memories in mind for short period of time; short term memory)
* Quantitative Reasoning (how fast it takes to solve a math problem)
* Knowledge (learning from a textbook; long term memory)
* Fluid Reasoning (how fast it takes to solve a rubix cube)
* Working Memory (memories in mind for short period of time; short term memory)
11
New cards
What did **Cattell and Horn** contribute to the study of intelligence?
Crystalized and Fluid Intelligence.
12
New cards
What is Crystalized Intelligence?
* Knowledge that is used for long term memory
* It is also facts based (learned through textbooks)
* It is also facts based (learned through textbooks)
13
New cards
What is Fluid Intelligence?
* Knowledge that is used for reason/to solve problems on the spot
* It is the capacity to learn new things
* Abstract Thinking and Problem Solving
* It is the capacity to learn new things
* Abstract Thinking and Problem Solving
14
New cards
What did **Howard Gardner** contribute to the study of Intelligence?
* A case study approach that states every person possessed a set of independent intelligence that vary in types; Multiple intelligences
15
New cards
What are Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences?
Linguistic (well spoken), Musical (enjoy conducting, listening, or making music), Bodily-Kinaesthetic (sporty), Logico-Mathematical (good at mathematical problem solving), Spatial (think and reason in 3D), Interpersonal (social), Intrapersonal (self aware), Naturalistic (plants and animals), Savents (autistic savents have many intelligences)
16
New cards
What did **Sternberg** contribute to the study of Intelligence?
* The Triarchic Model (A.P.C.)
17
New cards
What is the Triarchic Model?
Analytical Intelligence, Practical Intelligence, and Creative Intelligence
18
New cards
What is Analytical Intelligence?
* Provides academic success
* A person with this intelligence will do well on school tests, but they are not very creative or street smart
* A person with this intelligence will do well on school tests, but they are not very creative or street smart
19
New cards
What is Practical Intelligence?
* Provides common sense
* A person with this intelligence will do well at problem solving in the real world, but they are not creative or good in school
* A person with this intelligence will do well at problem solving in the real world, but they are not creative or good in school
20
New cards
What is Creative Intelligence?
* Provides a creative way of thinking
* A person with this Intelligence will be able to solve problems creatively, but not do good at applying their thinking into school or the real world
* A person with this Intelligence will be able to solve problems creatively, but not do good at applying their thinking into school or the real world
21
New cards
What are the problems with Self Reports?
* Low correlation with objective measures
* People who are incompetent tend to overestimate their abilities
* Metacognitive skills; when people know what they know or don’t know
* People may not answer with full confidence when asked how smart they are
* People who are incompetent tend to overestimate their abilities
* Metacognitive skills; when people know what they know or don’t know
* People may not answer with full confidence when asked how smart they are
22
New cards
What is the Development of Norms?
Being compared to people the same age
23
New cards
What are Norms?
A collection of data in a designated population.
24
New cards
What did __Binet__ contribute to Intelligence Testing?
IQ= (mental age/chronological age) X 100
* the mental age is avg. performance of specific age grp; chronological age is physical age of an individual
* the mental age is avg. performance of specific age grp; chronological age is physical age of an individual
25
New cards
What did __David Wechsler__ contribute to calculating IQ?
* Deviation IQ
* WAIS
* WAIS
26
New cards
What is the Deviation IQ?
* A standardized score on an IQ test that is compared to individuals of their own age
* Average Score is 100 always on those tests
* Standard Deviation is always 15 on those tests
* Average Score is 100 always on those tests
* Standard Deviation is always 15 on those tests
27
New cards
What is Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)?
* Evaluations that are set up as 15 subsets that give 5 scores;
* Overall IQ, Verbal Communication, Perceptual Reasoning, Working Memory, Processing Speed
* Overall IQ, Verbal Communication, Perceptual Reasoning, Working Memory, Processing Speed
28
New cards
What are some of the problems for WAIS?
* Culturally/Racially Based and Language dependant
* Some items call for “comprehension“
* Impact of Socioeconomic status
* Some items call for “comprehension“
* Impact of Socioeconomic status
29
New cards
What did __John Carlyle Raven__ contribute to Intelligence Testing?
* A form of Culture-Fair testing called Progressive Matrices
30
New cards
What is Raven’s Progressive Matrices?
* Tests that progressively get harder and harder
* There are versions that support both children 5 ^ and adults
* Culturally fair and nonverbal groups
* There are versions that support both children 5 ^ and adults
* Culturally fair and nonverbal groups
31
New cards
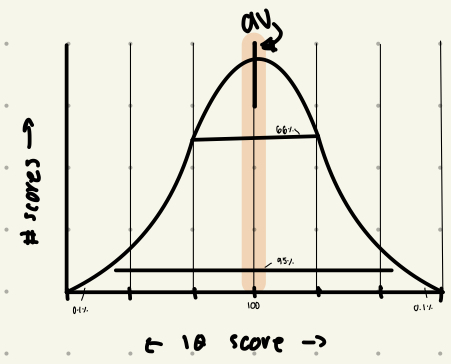
What is the Bell Curve IQ Distribution?
* Indicates that 100 is an IQ that is normal and average for most populations
* Middle is the normal IQ range
* AV=100; SD=15 (this tells us how distributed the data is compared to the mean)
* Scores less than 70 = Intellectual Disability
* Scores more than 130 = Gifted
* Middle is the normal IQ range
* AV=100; SD=15 (this tells us how distributed the data is compared to the mean)
* Scores less than 70 = Intellectual Disability
* Scores more than 130 = Gifted
32
New cards
What does it mean when a person is Intellectually Disabled?
* They have a childhood onset of an IQ below 70 (1% of North America, mostly males)
* The inability to engage in daily functions
* 4 Levels (Mild, Moderate, Severe, Profound)
* The inability to engage in daily functions
* 4 Levels (Mild, Moderate, Severe, Profound)
33
New cards
What are the causes of Intellectual Disability?
* Genetic Causes
* Fragile X Syndrome, Down Syndrome, Trisomy 21 (when 21st pair of chromosomes is a trio that causes mutations)
* Enviornmental Causes
* the environment a person grew up
* Fragile X Syndrome, Down Syndrome, Trisomy 21 (when 21st pair of chromosomes is a trio that causes mutations)
* Enviornmental Causes
* the environment a person grew up
34
New cards
What does it mean when a person is a Genius/Gifted?
* They have an IQ of 130 or more, which is the cut off
* Top 2%
* To be successful, you still needs to put in the effort
* Top 2%
* To be successful, you still needs to put in the effort
35
New cards
What are some Influences on IQ?
Nature, Nurture, Heritability, and Environment.
36
New cards
What does Nature refer to?
The Genetics that are passed on Biologically.
37
New cards
What does Nurture refer to?
Everything else that is not Genetics.
38
New cards
What is Nature VS. Nurture?
* Family Studies states that IQ is either genetically or environmentally passed on in biological families
* Twin Design
* Adoption Design
* Twins reared apart
* Genotype VS Phenotype (environment affects how genes are expressed)
* Twin Design
* Adoption Design
* Twins reared apart
* Genotype VS Phenotype (environment affects how genes are expressed)
39
New cards
What is Heritability?
* The degree to which traits vary depending on genetic differences
* All behavioural traits are heritable to some extent, but it depends on the trait
* All behavioural traits are heritable to some extent, but it depends on the trait
40
New cards
How to determine Heritability?
* Using the *Heritability Coefficient (H) →* ranges from 1-0
* Variable that determines the amount of variation in a trait due to genetic differences, the bigger the number the more heritable a trait is
* Variable that determines the amount of variation in a trait due to genetic differences, the bigger the number the more heritable a trait is
41
New cards
What are Environmental Influences on IQ?
* Family size affects IQ (Children are competing for resources, with a larger family, it is harder to fund their children)
* Amount of schooling; US has a Head Start program
* Expectancy by Teachers
* Poverty
* The **Flynn Effect** (developing countries have improved IQ scores)
* Amount of schooling; US has a Head Start program
* Expectancy by Teachers
* Poverty
* The **Flynn Effect** (developing countries have improved IQ scores)
42
New cards
What are the Sex Differences in IQ?
* There are no substantial differences in genders, but there are in distribution between genders
* Females → better verbal ability and emotional recognition
* Males → better spatial reasoning ability
* Females → better verbal ability and emotional recognition
* Males → better spatial reasoning ability
43
New cards
What are some factors that influence Sex Differences in IQ?
* Biological (Brain and Sex Hormones)
* Environmental (Roles in Society and Experience)
* Environmental (Roles in Society and Experience)
44
New cards
What are the Racial Differences in IQ?
* There are some differences in IQ between races which appear to be environmental in origin
* There are between-group differences due to environmental factors
* There are within-group differences due to genetic factors
* There are between-group differences due to environmental factors
* There are within-group differences due to genetic factors
45
New cards
How do the environmental differences account for the racial differences in average IQ scores?
Socioeconomic Factors and Social Designation Influences
46
New cards
What are the Socioeconomic Factors that influence IQ?
* Economic differences lead to there being no unequal distribution of resources across races
* Early Intervention leads to short-term increased IQ
* Equal Environment leads to comparable IQ
* Early Intervention leads to short-term increased IQ
* Equal Environment leads to comparable IQ
47
New cards
What are the Social Designation Influences on IQ?
Prejudice and discrimination leads to minorities being judged as inferior by dominant majority which also leads to the stereotype threat.