Anatomy test number 2
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is the primary purpose of the respiratory system?
Ventilation and oxygen exchange
What is the secondary purpose of the respiratory system?
energy source for speech
pulmonary apparatus
Lungs and airways
boundaries of the thoracic cavity
Ribs, Sternum, Vertebral column, Diaphragm
sections of the vertebral column
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum, Coccyx
atlas and axis
C1 atlas, C2 axis
features (facets, foramina, etc.) of vertebrae
Provide attachment points, facets, and foramina that allow the spinal cord and nerves to pass through.
how do the vertebrae attach to each other?
Intravertebral discs
types of ribs
True ribs, False ribs, Floating ribs
how do the ribs connect to the vertebrae and the sternum?
They are connected to the coastal cartilages.
type/amount of movement enabled at these joints
Allow for some gliding
factors that contribute to flexibility of the rib cage
Some ribs articulate with costal cartilage via synovial joints, costal cartilage= hyaline cartilage; some flexibility
parts of the sternum
Manubrium, corpus(body), xiphoid process
Pectoral girdle
(clavicle+scapula) provides a point of attachment for many of the accessory muscles of respiration
Pelvic girdle
provides an important attachment point for our abdominal muscles.
tissue composition including tissues involved in providing internal support (e.g., tracheal rings)
Blood, Vessels, Cartilage rings, Tissues involved in gas exchange like alveoli, trachea/bronchi, lining
L vs. R lung
The right lung is bigger than the left lung which makes room for the heart
purpose of high surface area (re: number of alveoli)
Necessary for gas exchange
path air travels to enter the lungs
Nasal cavities, pharynx, glottis, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchiole, alveolar duct, alveoli
basic characteristics of how alveoli communicate with the blood supply for gas exchange
Increase in size and number for O2 exchange
contents/location of the mediastinum
Middle space, contains the heart
mechanisms enabling pleural linkage and why pleural linkage is important
Changing the size and shape of the thoracic cavity changes the size and shape (volume) of the lungs. Important because Pleural linkage is how the lungs stay attached to the inside of the thoracic cavity.
different parts of the pleural lining (e.g., visceral vs. parietal pleura)
Visceral pleura lines lungs, parietal pleura lines ribs(outside tissue layer of lungs)
role of pleural fluid
Lubrication and increasing surface tension
Why should the interpleural space always have negative pressure? What could happen if the pressure in the interpleural space ever became positive?
To keep the lungs properly inflated, if pressure become positive your airway could possibly collapse.
mechanisms for improving (warming/humidifying) and filtering incoming air supply
Mucus (moistens) and abundant blood supply is sent to the lining of the respiratory passages.
general patterns of developmental changes that occur in the lungs (i.e., what happens to your lungs, rib cage, thoracic cavity, interpleural pressure, number of alveoli, color of your lungs, etc., as you grow and get older?)
Alveoli increase in size and number (increased surface area for O2 exchange)
Lung size and weight increases
Thoracic cavity enlarges and changes shape
Rib cage muscle bulk increases
Intrapleural pressure becomes more negative
Maturation of nervous system increases efficiency
Boyle's law
Volume and pressure inversely related
Air moves from high pressure areas to fill areas of low/negative pressure
The muscles of inspiration
increase the size of the thoracic cavity
the muscles of expiration
decrease the size of the thoracic cavity
subsequent changes in pressure and volume
Increased volume CAUSES decreased pressure in the lungs_.
Higher atmospheric pressure pushes air in to the area of low pressure.
Decreased volume CAUSES increased pressure in the lungs_.
Higher pressure in the lungs pushes air out
Quiet inspiration
passive expiration usually involuntary
Speech breathing
active expiration, voluntary
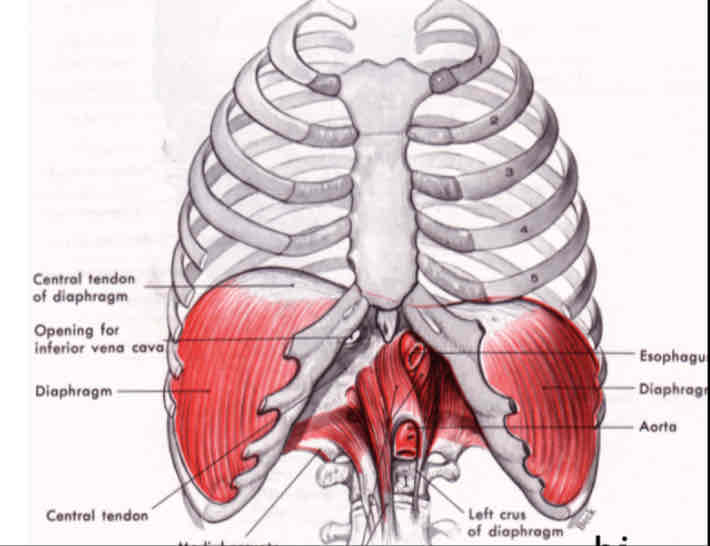
DIAPHRAGM
is one of the body's largest muscles, and it is the major muscle of inspiration (largely involuntary control, but can be voluntary).
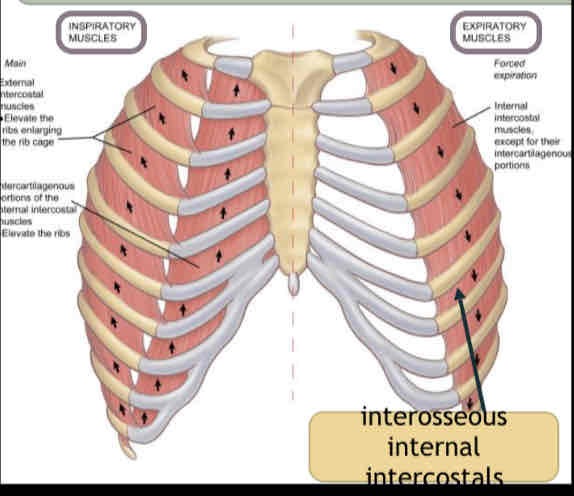
EXTERNAL intercostals
elevate the rib cage and are very important in supporting speech breathing.
INTERCHONDRAL
(cartillage) portion of the internal intercostals helps to elevate the rib cage.
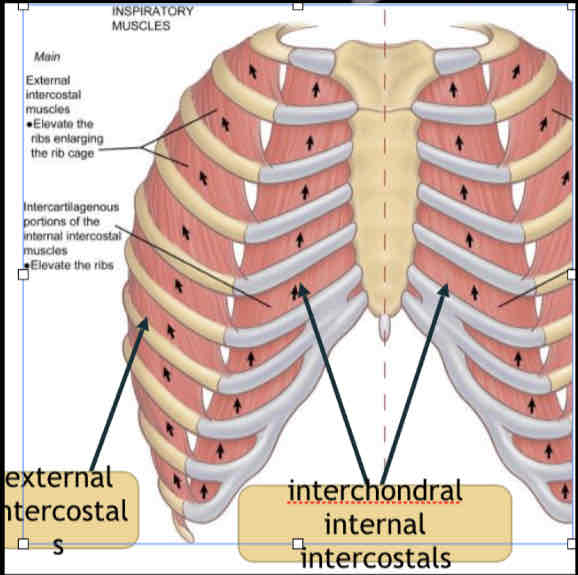
INTEROSSEOUS
portion of the internal intercostals lies DEEP to the external intercostals.
ABDOMINALS
reduce the vertical dimensions of the thoracic cavity_ by compressing the abdominal contents, which push up on the diaphragm
Sternocleidomastoid
Elevates sternum, clavicle and ribs by extension
external intercostals
most superficial layer of this muscle group- inspiration
interchondral portion of the internal intercostals
just the part that connects the cartilaginous portions of the ribs- inspiration
interosseous portion of the internal intercostals
just the part that connects the bony portions of the ribs- expiration
respiratory differences with body positioning
When lying down, gravity pushes abdominal viscera toward the back; takes more work for diaphragm to push down
Reduced lung capacity; more effort
Impact for those with respiratory compromise?
clavicular breathing
elevation of rib cage using accessory muscles of inspiration, especially sternocleidomastoid and scaleni
thoracic fixation
Upper body muscles are most powerful when they can pull against something rigid
Serratus Posterior Superior- inspiration
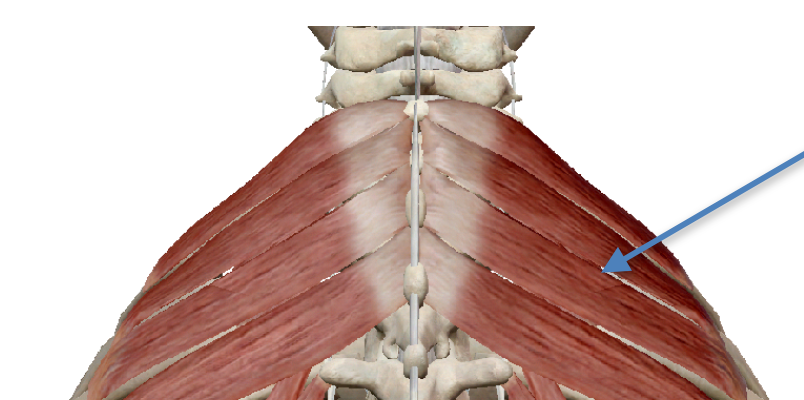
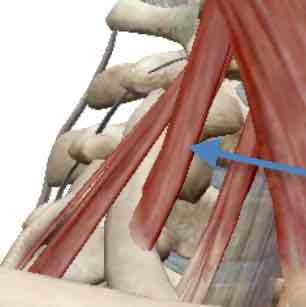
Levatores Costarum Brevis-inspiration

Levatores Costarum Longus-inspiration

Scalenes (Anterior, Middle, & Posterior)-inspiration
Pectoralis Major-inspiration
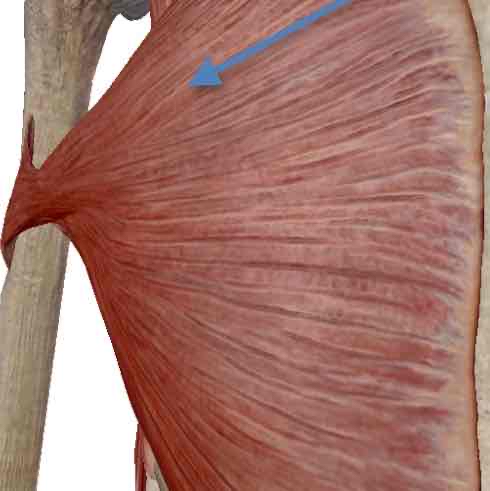
Pectoralis Minor-inspiration
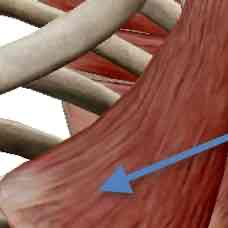
Serratus Anterior-inspiration
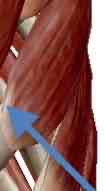
Levator Scapulae-inspiration
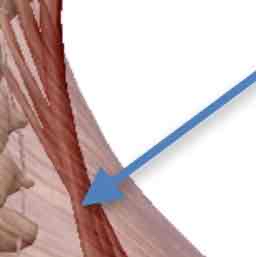
Rhomboids (major & minor)-inspiration
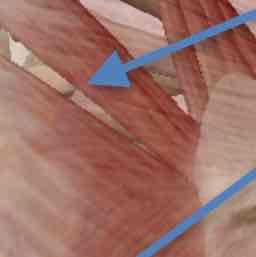
Trapezius-inspiration
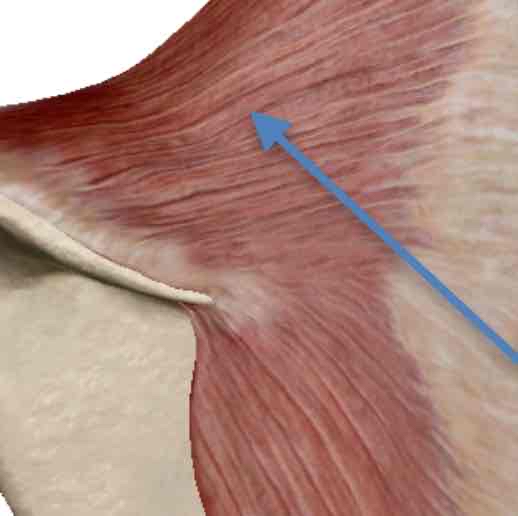
Quadratus Lumborum-inspiration
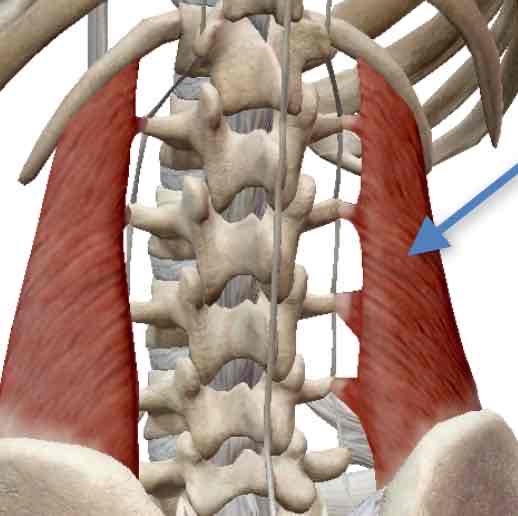
Transversus Thoracis-expiration
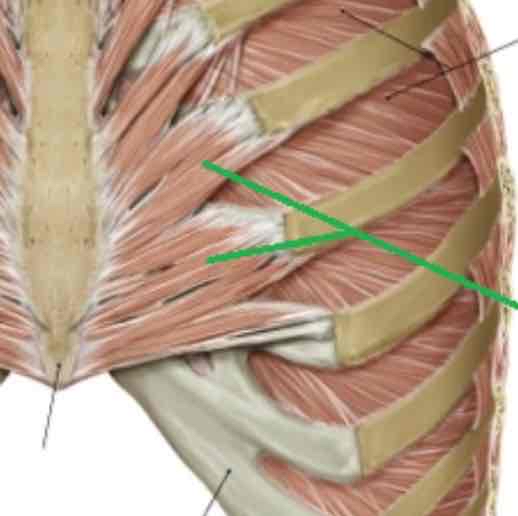
Serratus Posterior Inferior-expiration
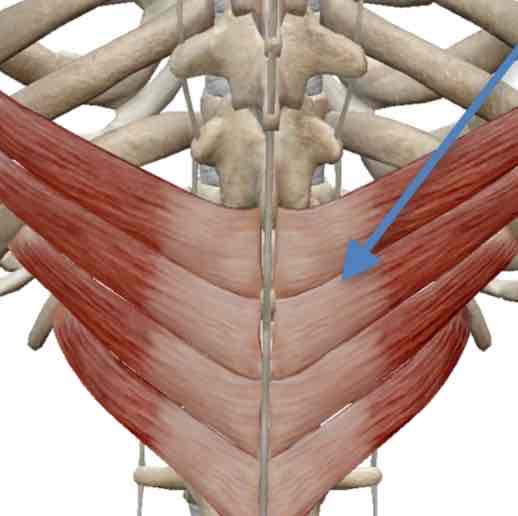
Latissimus Dorsi- both inspiration and expiration