Slavery in the Americas DBQ
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Transatlantic Slave Trade
The kidnaping and enslavement of 12 million Africans from 1500s to the 1700s. Transporting West Africans across the Atlantic and to the Americas in order to be sold for profit. Terrible abusive conditions traumatized and killed millions.
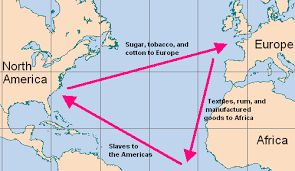
Triangular Trade
The movement and trade of resources/commodities connecting Europe, Africa, and America
Middle Passage
The middle part of the Transatlantic slave trade, where Africans were brought from West Africa to the Americas across the Atlantic Ocean, 10% of all enslaved Africans died during the journey on boats due to poor conditions, abuse, disease, and suicide
African Diaspora
The spread of people of African descent due to mainly the Transatlantic slave trade but also voluntary movement
Cash Crop/Pleasure Crops
Crops that are farmed for their commercial value rather than their need. Ex. sugar, rice, tobacco, cotton
Sugar Trade
The increased demand for sugar in Europe led enslavers to create large-scale sugar plantations in the Americas as well as the Caribbean. This free labor assisted Europe and made it rich.
Racial Slavery
A system where people were enslaved solely based on race. Built on a false belief that one race is superior to another.
Ogun
A powerful Yoruba deity (Orisha) of iron, war, and technology
Abolition
The ending of a policy or movement, or referring to the legal abolishment of slavery in 1865
Syncretism
The natural blend or conjoining of something, ex. Cultural Syncretism: the blending of cultures
Vodou
A blend of French Catholicism and Haitian religion, which developed during enslavement. Recognizing one central power that can be connected to through praying to lesser spirits, very similar to the Christian God and saints.
Commodification
The process of transforming something into a commodity
Commodity
Something that can be bought and sold
Olaudah Equiano
A male writer and abolitionist who purchased his freedom from slavery in 1776. Taken from West Africa as a child, he was enslaved in the Barbados for most of his life
Chattel Slavery
A form of slavery in which slaves are seen as property or livestock belonging to their owners
Capitalism
A social and economic system in which resources and businesses are mostly owned by individuals and operated for profit.
Monopoly
When one company controls an entire industry, ex. Amazon
Oshun
Yoruba goddess/orisha of love, fertility, femininity, sexuality
Orisha
Yoruba deities originating in West Africa who’s stories traveled to the Americas through the African Diaspora (mainly slave trade)
Elite
Powerful people controlling wealth, including European Aristocrats, Wealthy Merchants, and American Slaveholders. Often created by multinational corporations and liberalism, which opened the transatlantic trade to many more Europeans
Plantation system
An agricultural model based on the mass production of cash crops using the physical labor of enslaved people or forced laborers,
European Countries involved in the transatlantic slave trade
Portugal, Britain, Spain, France, the Netherlands, and Denmark (much smaller scale)
Joint-Stock Company
A business whose ownership is divided into shares of stock, which can then be bought by shareholders
Royal African Company (RAC)
Created in 1672, this was Britain’s way of controlling trade from Africa, later specifically the slave trade. Assisted England in leading the world trade, which was a monopoly until 1689. Demand was high, and political power was lost (King James II). Traded people, gold, silver, and other commodities
Zong
A British slave ship that sailed the middle passage in 1781, carrying 481 Africans (2x the limit). Due to a lack of resources and starving slaves, they massacred 132 African people in order to claim insurance. As they would receive more insurance from casualties than from natural, avoidable deaths
Insurance
During the slave trade, insurance covered enslaved people as if they were cargo, and protected slave holders from financial loss because of death or injury
Yoruba
An ethnic group from Western Africa whose culture impacted most of the African Diaspora
Slavery Before Age of Exploitation
Slavery can be traced back to Mesopotamia in Hamurabi’s code, usually involving debt bondage and prisoners of war. Never determined as racial or chattel slavery.
Emancipation
The emancipation of something, in the context of the slave trade: the legal freeing of slaves after the abolition of slavery. (1863)
Beginning of Portuegese Trade
1336/1526/1444
The Arrival of the first Africans in English North America
1619
The End of the British Slave Trade
Slave Trade Act of 1807
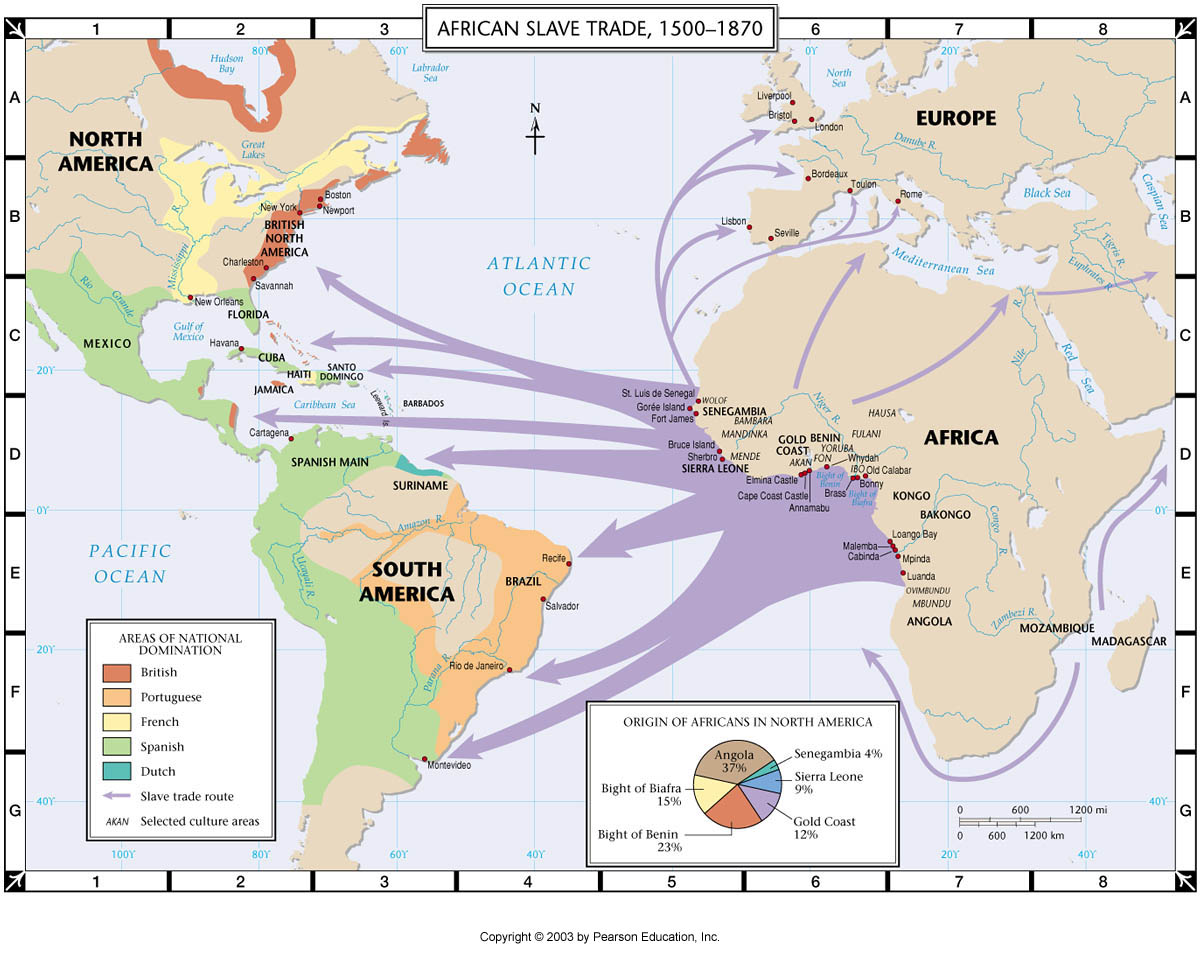
places slaves were taken from and where they were taken to
Oyotunji
A Yoruba Village located in South Carolina, was created in 1970, created to preserve African culture and history