Instruments and Equipment - Operative
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Hand Instrument Materials
Carbon Steel - Hard but corrodes
Stainless Steel - Dull and loses edges but does not corrode
Carbide - Durable but brittle
Hand Instrument and Rotary Instrument Parts
Hand Instrument
Handle/Shaft
Shank
Blade (Cutting)/Nib (Non-cutting)
Rotary Instrument
Head
Neck
Shank
Instrument Formula
Width of blade in tenths of mm
Cutting edge angle in centigrade (sometimes skipped)
Length of blade in mm
Blade angle in centigrade
Mirror
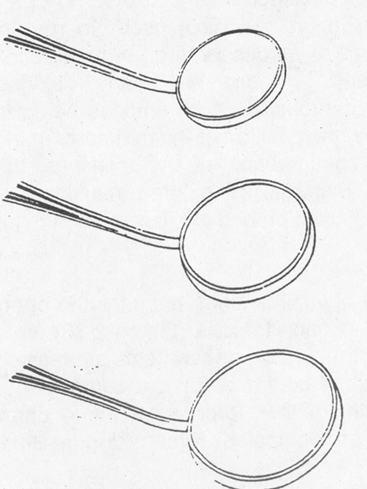
#2 (5/8” diameter)
#4 (7/8” diameter)
#5 (15/16” diameter)
Explorer
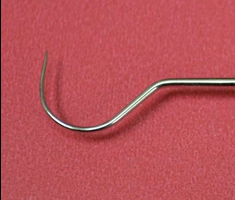

#23 explorer
#17 explorer
Used to examine around tooth surfaces to look for cavitites
Both images: Feel for smoothness of tooth, surfaces and assess, and quality of margin
Probe

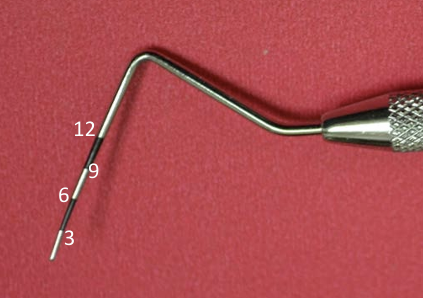
Periodontal probe (William’s Markings: 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10 mm)
Probe (3, 6, 9, 12 mm)
First picture: Perio: Measure periodontal pockets and assess gingival health. Operative: Measures pulpal floor depth and remaining marginal ridge (William’s Markings)
Second picture: Also perio characteristics
Amalgam Carrier

Has hollow tip and plunger
Carries mixed amalgam to cavity preparation
Condensers



0/1 Plugger
1/2 Plugger
Markley Plugger
First two images: Condense amalgam into prep
Last image: Condense amalgam into smaller preps (<1 mm)
Burnisher

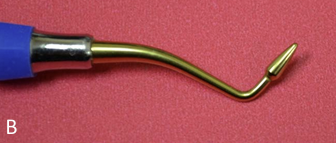

Examples are ball, acorn, and football burnishers
Polishes surface of amalgam restoration
Burnishes margins so they are flush with tooth surface
Forceps

Typically used for holding articulating paper
Also carries things to and from mouth
Tofflemire Retainers
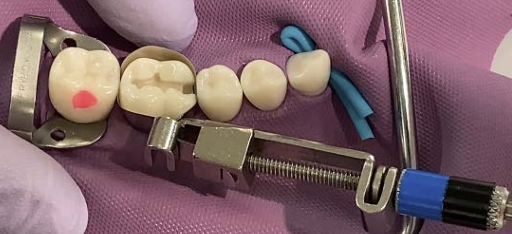
Holds matrix bands
Clamps end of matrix band and tightens it around tooth
Needed for interproximal restorations
Automatrix Tightening Tool

Tightens matrix bands
Automatrix Snipper

Cuts outer matrix band for removal
Composite Instruments

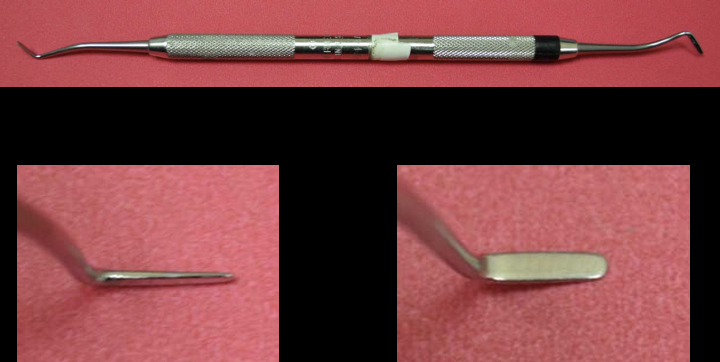
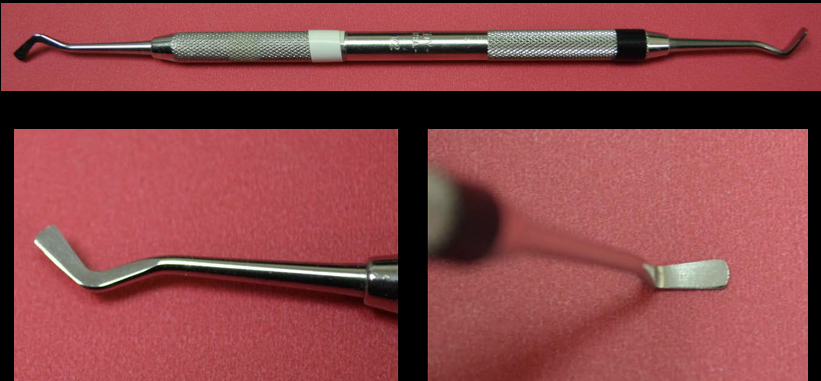
All gold instruments
8A Composite
Trico Composite
Place, sculpt, contour dental composites
Cement Spatulas

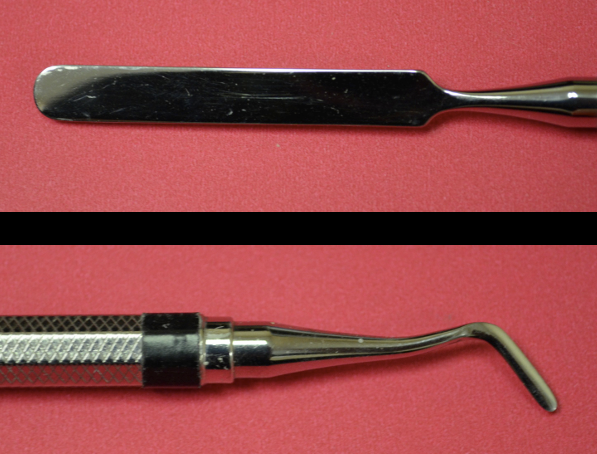
Spatula/Dycal
Spatula/Blade
Dycal end picks up med to transfer to tooth
Blade transfers mixed cement to indirect restoration
Spoons
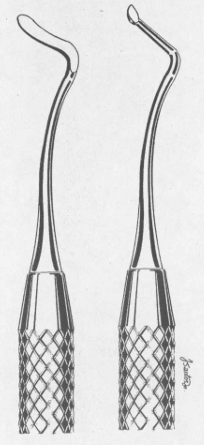
Type of Excavator
Removes carious dentin
Curved blade has outer convexity, inner concavity
Hoe

Type of excavator
Forms line angles and planing tooth prep walls
Straight Chisel

Cuts enamel
Wedelstaedt Chisel

Curved binangle chisel
Cuts enamel
Enamel Hatchet

Break open teeth and smooth cavity walls
Cuts enamel
Marginal Trimmer

MT 29 (mesial edge)
MT 28 (distal edge)
Cuts and planes enamel walls and margins
Interproximal Carver

Contour embrasures of restoration
Anatomical Carver

Place initial tooth anatomy and grooves in amalgam or composite
Cleoid-Discoid


3/6 Cleoid-Discoid
4/5 Cleoid-Discoid
Cleoid End: Placement of anatomy, removing excess amalgam
Discoid end: Rounding marginal ridges, removing excess amalgam
Hollenback Carver

Contour and carve surfaces of amalgam restoration and carve interproximal areas
Two types of grasps
Pen grasp
Palm-thumb grasp
Rubber Dam Clamps

Keep rubber dam tight around tooth
Rubber Dam Forceps

Tightens clamp
Rubber Dam Frame and Curved Iris Scissor
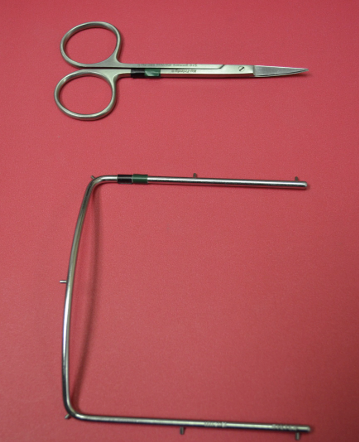
Cut rubber dam after use
Maintains borders of rubber dam in position and supports retraction of soft tissue
Rubber Dam Punch

Punches holes in rubber dam to go around teeth
Makes clean-cut holes in rubber dam
Rotary handpiece speeds
Low speed - <12000 rpm
Medium speed - 12000-200000 rpm
High-speed - >200000 rpm
Dental Bur Types
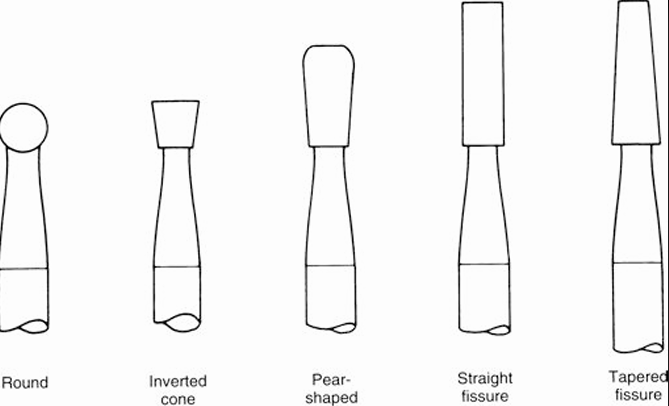
Round - Initial entry and caries removal
Inverted cone - Provides undercuts
Pear shape - Class 1 (gold foils and amalgam)
Straight Fissure - Amalgam tooth prep
Tapered Fissure - Indirect restoration, no undercuts
High-speed vs Low-speed handpieces
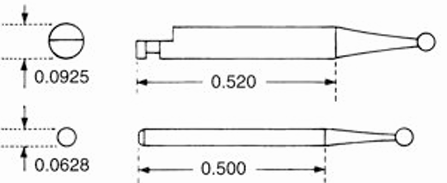
Slow-speed - Latch-type
Removal of caries, refining a cavity prep wall, performing prophylaxis
High-speed - Friction grip
Cavity prep and removal of tooth structure
Clearance Angle
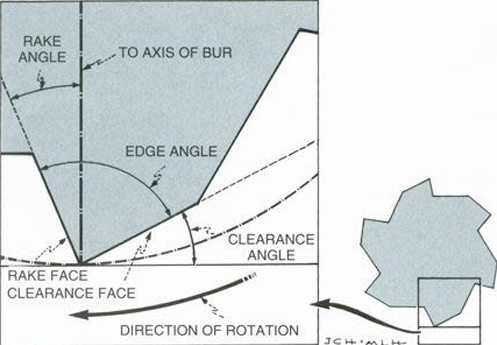
Angle of leading edge of cutting tool from surface being cut
Rake Angle
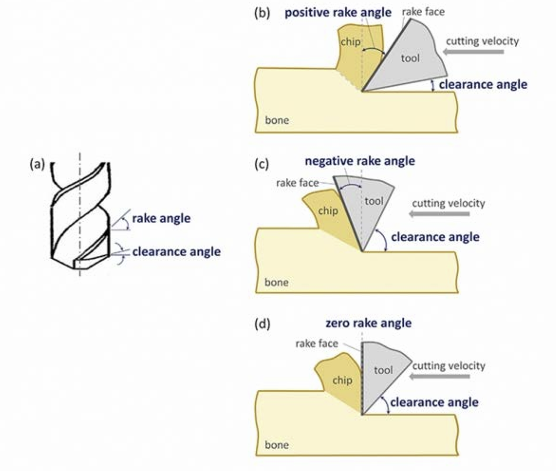
Angle of tool contact perpendicular to surface
Carbide vs Diamond Burs
Carbide Burs
Better end-cutting
Produce low heat
More blade edges per diameter
Diamond Burs
Abrasive over blade-cutting
Coarse to Fine in Microns
Ultra Coarse (180) - Black
Super Coarse (150) - Blue
Coarse (130) - Green
Standard (110) - No Color
Fine (40) - Red
Extra-Fine (15) - Yellow
Ultra-Fine (10) - White
Hazards with Cutting Instruments
Pulpal Precautions
Soft-Tissue Precautions
Eye Precautions
Ear Precautions
Inhalation Precautions
Enamel Composition
Inorganic matter (90%)
Organic matter (2%)
Water (8%)
Is enamel semipermeable?
Yes, it takes in acid, caries, remineralization, fluoride and bleach
What properties of enamel decrease with age?
Acid solubility
Pore volume
Water content
Permeability
What property should restorative material have?
Compatible wear, smoothness, and strength
Crystal Rod Head and Tail differ in what property?
Solubility due to orientation

What do acid etchants due to enamel?
Removes a bit of enamel and allow resin monomer to bind
Dentin Structure and Composition
Apatite crystals and collagen fibrils
50% inorganic
30% organic
20% water
Outer Dentin vs Inner Dentin
Outer dentin has more intertubular dentin
Has lesser and thinner tubules as well
Dentin close to DEJ is 8x more permeable
Outline Form for Class I Prep
Prep is centered on central groove
Pits and grooves removed
Smooth (no sharp angles)
Convenience Form for Class I Prep
Wide enough isthmus (to accept #0 condenser)
Resistance Form for Class I Prep
Deep enough depth
Marginal ridge is not compromised
Making mesial and distal walls diverge (preserves strength of marginal ridges)
Retention Form for Class I Prep
Concave walls
Dovetail
Issues with acute and obtuse cavosurface margins
Acute - Unsupported enamel rods
Obtuse - Very thin amalgam that can fracture
Importance of placing bur along axis of tooth
Prevents floor of prep from reaching the pulp
People retire from dentistry because of what disorder?
Musculoskeletal Disorder
70% dental students by 3rd year
What is PSP?
Prolonged Static Posture
Ergonomics
Study of science involving efficient and safe use of tools by humans
What seating positions should right and left-handed operators generally sit?
Right - 8 to 12 o’clock position
Left - 12 to 4 o’clock position
Natural Operator Seating Position
Feet flat on ground
Hips higher than knees
Chair tilted 15 degrees
Neutral shoulder position with elbows at sides
Reasonable shoulder range of motion
Operator head should not tilt more than 20 degrees
Use hips rather than wrist or waist
What should you do for maxillary teeth?
Place patient in supine position
What muscles does the Un-Twister target?
Quadratus Lumborum
Latissimus Dorsi
Teres Major
Triceps
3 P’s of Ergonomics
Posture
Positioning
Periodic Stretching
Esthetic Materials for Class 5 Restorations
Resin Composite
Glass Ionomer
Resin modified glass ionomer
Compomer
Why are Class 5 Preps and Restorations common?
They are deep gingivally
Located in non-self-cleansing area gingival to height of contour
What is trituration?
Process of mixing amalgam
Things to know about amalgam
Each condensed amalgam increment should fill 1/3 to ½ of prep depth
Make sure to condense apically and laterally with 5-10 lb of pressure
Use round end of cleoid along cavosurface margins perpendicular to tooth structure
Reasons for Rubber Dam Isolation
Moisture Control
Retraction
Harm Prevention
Increase operator efficiency
Potentially improve properties of dental materials
Types of Rubber Dam Isolation
Posterior Isolation - One tooth distal to treated tooth extending to contralateral canine
Anterior Isolation - From premolar to premolar
Single tooth Isolation - Only the tooth being treated
Order of Hole Punches
Anchor Tooth
Molar
Premolar/Canine
Upper Incisors
Lower Incisors
What type of lubricant is used on rubber dams?
Water-soluble lubricant
Modeling Compound for Rubber Dam
Low-fusing modeling compound used to secure retainer to tooth and prevent movement
Winged and Wingless Technique for Rubber Dams
Winged Technique - Clamp and frame are simultaneously carried to patient’s mouth for placement
Wingless Technique - Clamp placed on tooth first and dam is stretched over bow
Interproximal placement of dental dam
Operator passes dam by stretching dam faciogingivally or linguogingivally with fingers
Waxed floss passes through remaining contacts to tuck edges into gingival sulcus
Reasons for Tooth Preparations
Destruction from carious lesion (old and current reason)
Replacement/repair of existing restoration
Tooth fracture
Esthetic Reasons
Prosthesis on adjacent teeth
Preventative purposes
What is the purpose of lasers in diagnostics for dentistry?
Fluoresces bacteria
Can cause false positives
What is the purpose of light in diagnostics for dentistry?
Use to find carious lesions and fractures
High specificity but low sensitivity
What is the purpose of dye in diagnostics for dentistry?
Stains less well-mineralized dentin
Can lead to over-preparation and pulp exposure due to natural differences in collagen content
Challenge of radiographs
Some cavities are overlooked
Some radiolucencies are misdiagnosed
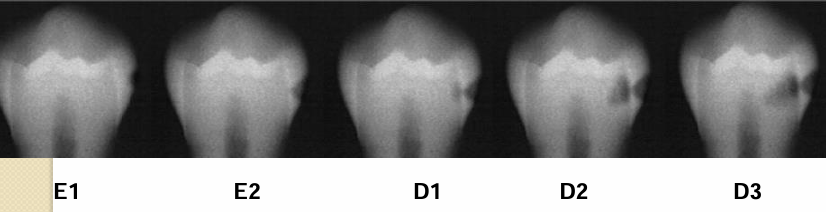
E1, E2, D1, D2, D3
In what scenario only would you still leave infected dentin in tooth
Only if patient is asymptomatic and it is located within 0.5 mm of pulp
Good instrument for removing infected dentin
Large round burs on slow speed handpiece OR
Ceramic round burs
What factors can affect pH in mouth?
Diet
Hygiene
Saliva
Detection of Pits and Fissures (with study findings)
Done visually
Explorer (and stick) does not help
Explorer has potential to transfer bacteria
Sharp explorers can create enamel defects
Explorers can make non-cavitated lesions cavitated
Clean and dry teeth for color changes or shadowing
Explorer should gently be used for tactile evaluation of surface texture
Best way to detect hidden caries
Clean and dry teeth