Kingdome Amalia - INVERTEBRATES PT. 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Radial Symmetry
An animal with body parts arranged around a central axis
Bilateral Symmetry
An animal where sides of the body are mirror images of each other
Cephalization
Concentration of sensory structures in the head of the animal
Incomplete gut
a digestive tract with only one opening
Complete gut
a digestive tract with two openings
Pseudocelom
A fluid filled space within the body surrounding an unsupported gut
Coelom
a fluid filled cavity surrounded by muscle tissue
Cnidoblast
stinging cell in cnidarians
Nematocyst
tiny extendable barb for stining
Sessile
non motile; attached to a solid substrate
Polyp
non motile; form of a cnidarian
Medusa
motile form of a cnidarian
Monoecious
an organism with both male and female reproductive organs
Dioecious
an organism with either male or female reproductive organs (not both)
Name the two openings of a complete gut
mouth and anus
An animal with no body cavity is classified as an
acoelomate.
All animals are heterotrophic
true
Kingdom Animalia is composed of multicellular ____ ____ without cells that digest internally.
eukaryotic heterotrophs
_____ reproduction is the dominant mode or reproduction in animals, ____ reproduction also occurs.
Sexual, asexual
Asymmetry
lack of symmetry
Bilateral symmetry is associated with ______
cephalization
Acoelomate
no body cavity
Invertebrate
no spinal column
Vertebrate
possesses a spinal column
Phylum Porifera
Simple aquatic animals also known as sponges, characterized by porous bodies and a lack of true tissues and organs. They filter feed by drawing water through their pores.
Sponges are the ____ animals, retaining many features ancestral to the animal kingdom.
simplest
T/F sponges have true tissue
false
Sponges are ____ ____, removing microscopic organisms and particulate matter from the water through their bodies.
filter feeders
In sponges, water enters through ____ (pores) on the outside of the body, pass into the _____ (central cavity), and then passes out through the ____.
ostia, spongocoel, osculum
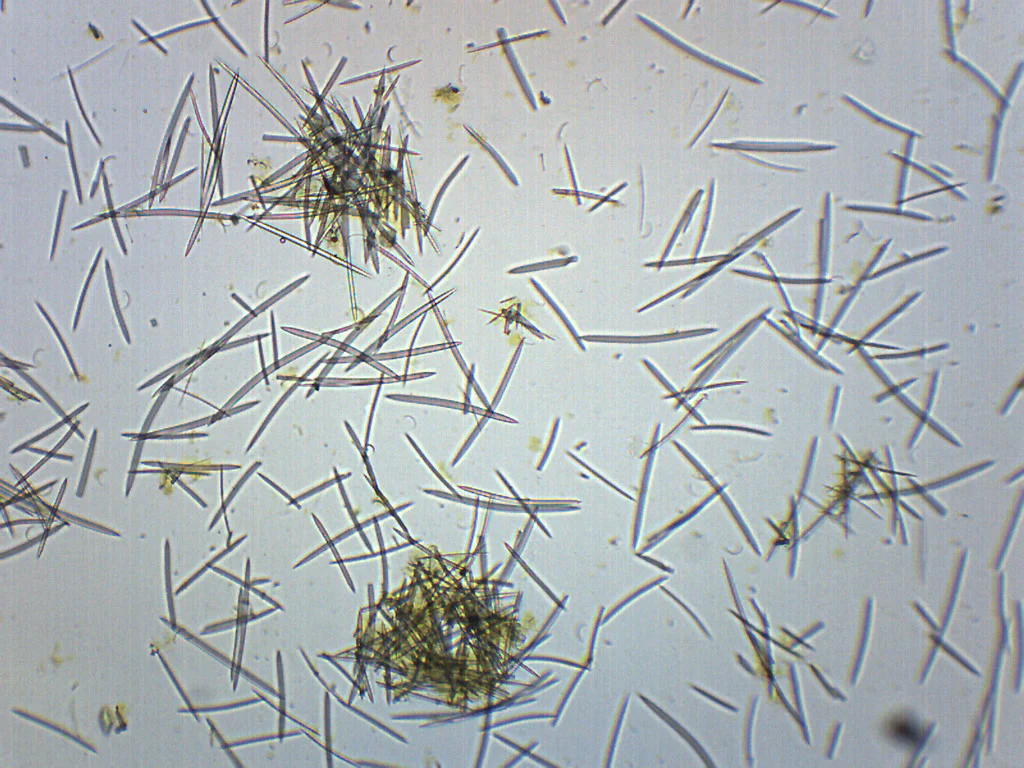

sponge spicules
How do sponges reproduce?
can reproduce asexually via budding and fragmentation, sexual reproduction does occur
Adult sponges are sessile or non sessile?
sessile
Do sponges have a complete or incomplete gut?
Sponges have an incomplete gut, meaning they do not have a defined digestive tract.
Phylum Cnidaria
Aquatic animals distinguished by stinging cells called cnidocytes, which are used for capturing prey. This phylum includes organisms such as jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones.
Do cnidarians have true or false tissue?
true
T/F cnidarians have coelomate?
false, acoelomate
What are the stinging cells or cnidarians
cnidoblasts
What are the tiny barbs called in cnidoblasts?
nematocysts
Many cnidarians have ______ which surround a central mouth, the only opening into their _____ ____.
tentacles, gastrovascular cavity
Cnidarian - Physalia Man o’ war
sail - composed of gas filled polyps

Cnidarian - Corals
contain calcium carbonate skeleton (RADIAL SYMMETRY)

Cnidarian - Jellyfish

Cnidarian - Pennaria
a colonial hydrozoan with a shared living structure and individual polyps for feeding and reproduction.
Cnidarian - Hydra
polyp
tentacles with cnidoblasts
mouth
bud
gonads
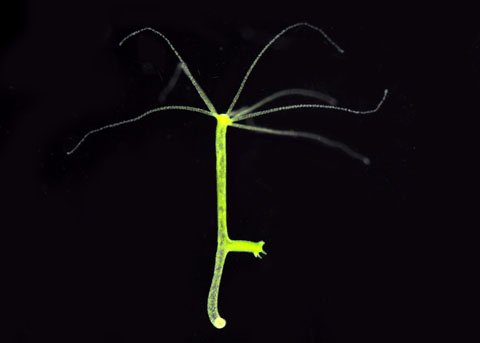
How do Hydra anchor to an aquatic surface?
By means of a basal disc that secretes adhesive substances to attach to substrates.
What do Hydra use for locomotion?
tentacles to gather food and to move
How do Hydra reproduce?
asexually via budding and sexually through production of sperm and ova.
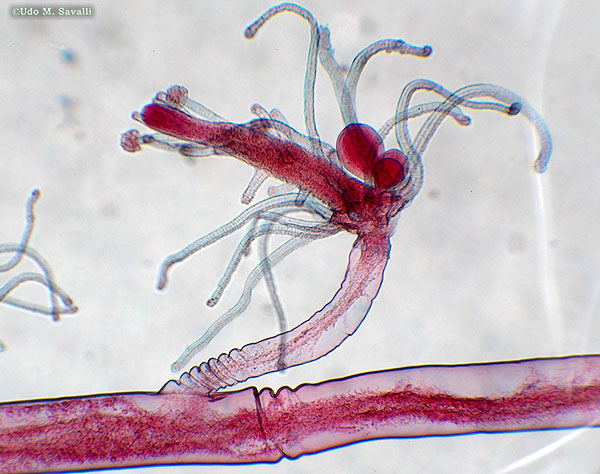
Cnidarian - Obelia
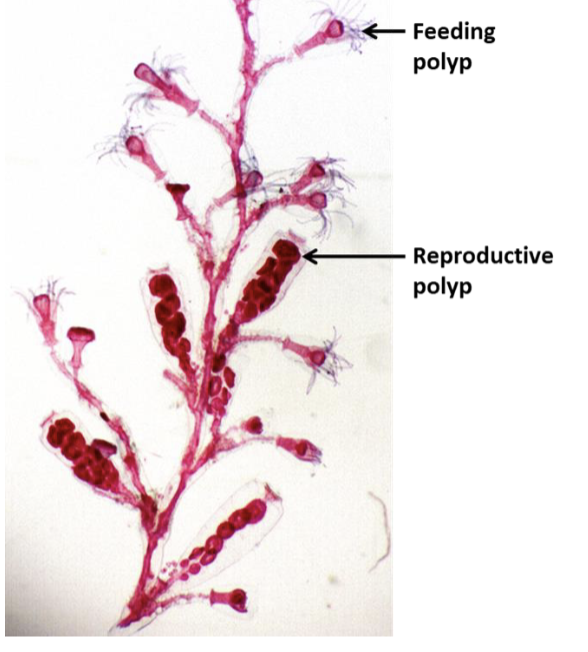

What are the two kinds of obelia?
feeding and reproductive polyps.
Obelia are ___ of polyps
a colonial form
Phylum Platyhelminthes
a group of flatworms that are typically bilateral, unsegmented, and lack a body cavity. They include free-living and parasitic species.
Platyhelminthes (flatworms and flukes) are what kind of symmetry?
Bilateral
T/F flatworms and flukes are acoelomate
true
What kind of gut do Platyhelminthes have?
incomplete
How do flatworms and flukes absorb their oxygen?
through diffusion across their skin.
Are flatworms and flukes monoecious or dioecious?
monoecious
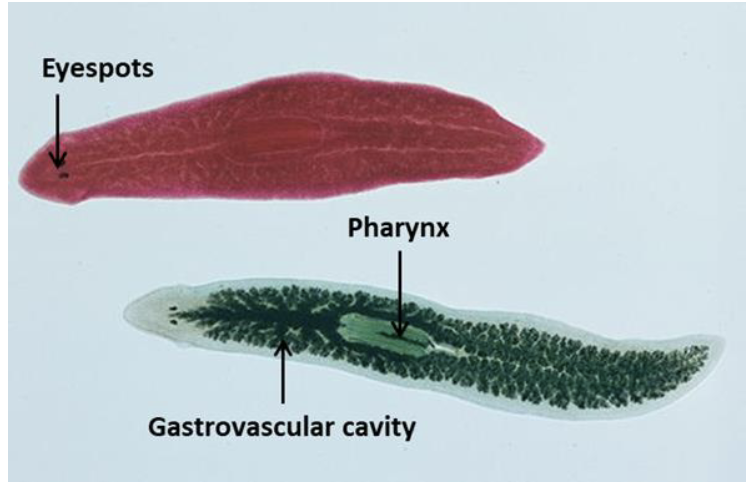
Platyhelminthes - Planaria (flatworm)
Use eyespots in their head to detect light and motion.
Branching gastrovascular cavity - digestion
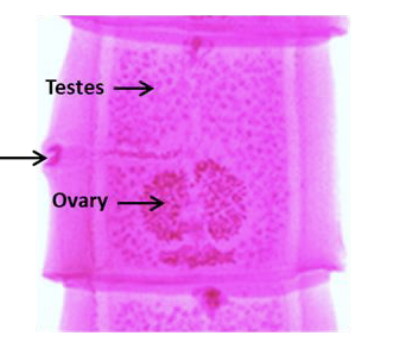
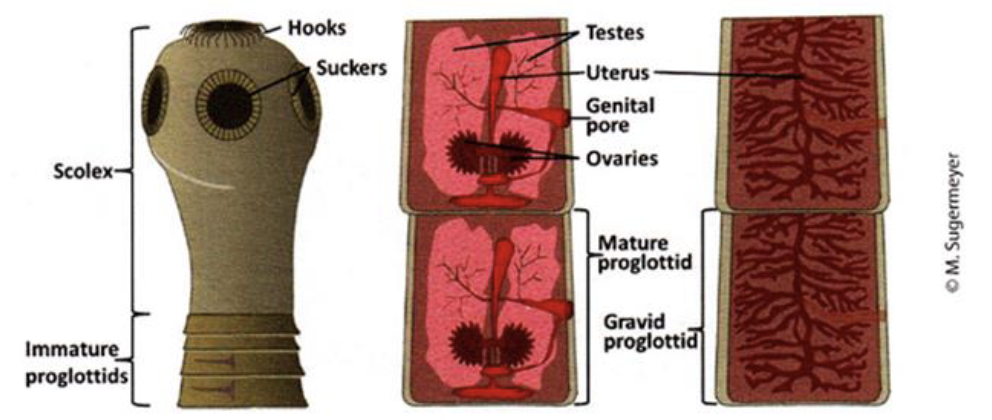
Platyhelminthes - Taneia (tapeworm)
No digestive tract
scolex - head-end of the worm, hooks and suckers
proglottids - segments that contain reproductive organs.
gravid - the condition of tapeworm segments that are filled with fertilized eggs.
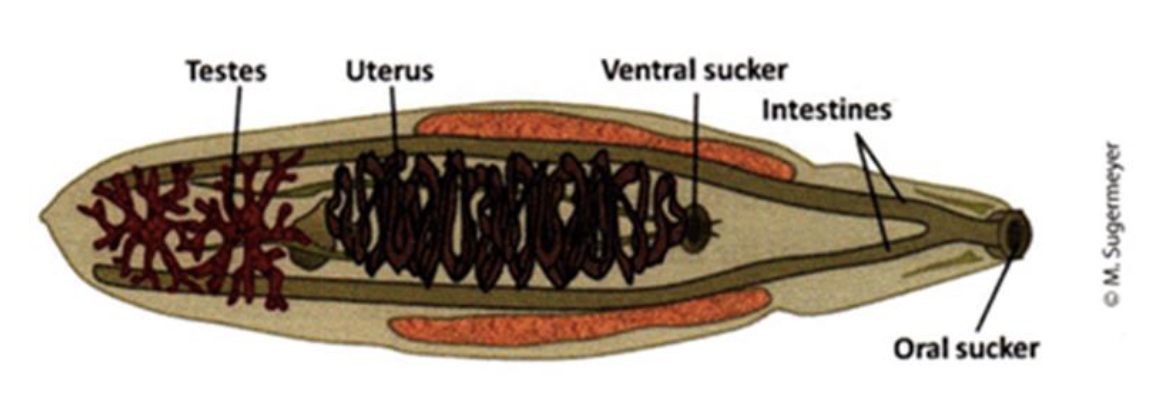
Platyhelminthes - Clonorchis (liver fluke)
parasitic
oral and ventral sucker
forked intestine
Phylum Nematoda
Roundworms, characterized by their elongated, cylindrical bodies and a complete digestive system. This phylum includes both free-living and parasitic species.
Unsegmented roundworms are the most _____ animal on the Earth.
abundant
Nematodes have what kind of gut?
complete
Nematodes have a Pseudocoelom?
true
What is the waterproofing coat on nematodes?
cuticle
Are nematodes dioecious or monoecious?
dioecious
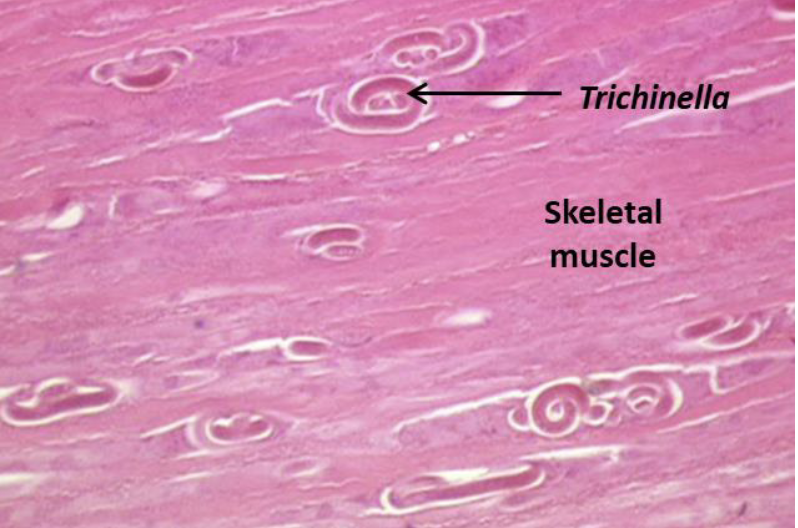
Nematode - Trichinella
A genus of parasitic roundworms that can cause trichinosis in humans when consumed undercooked meat containing larvae.
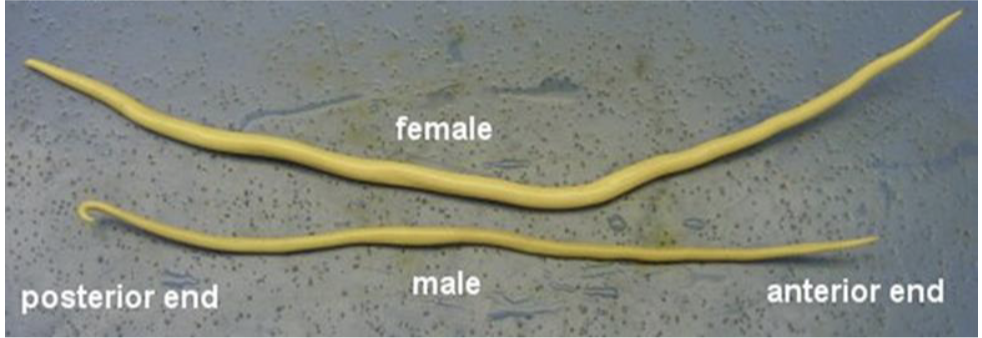
Nematode - Ascaris
A genus of parasitic roundworms that infects the intestines of humans and animals, leading to ascariasis.
tapeworm