Week 1 all
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
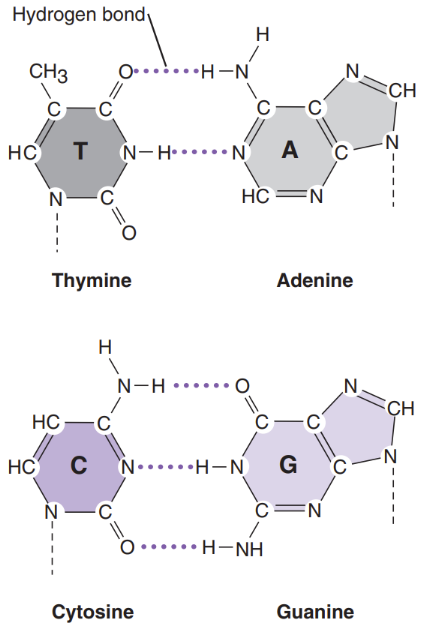
What is a nitrogen base
Nitrogen bases = attached to deoxyribose sugar. Are the 4 building blocks of life
Adenine
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
Purines = bases with a double-ring structure
Ex: G & A
Pyrimidines = bases with a single ring structure
Ex: C & T
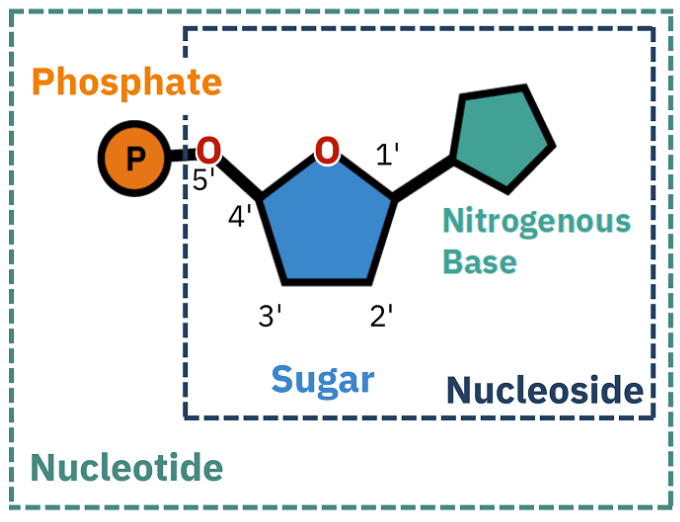
What is a nucleoside
Nucleosides = A nitrogen base bound to an unphosphorylated sugar
When the ribose sugar is phosphorylated...
Mono = nucleoside
Ex: Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
Triphosphate = nucleotide
Ex: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
di-phosphate = 2 phosphorylation
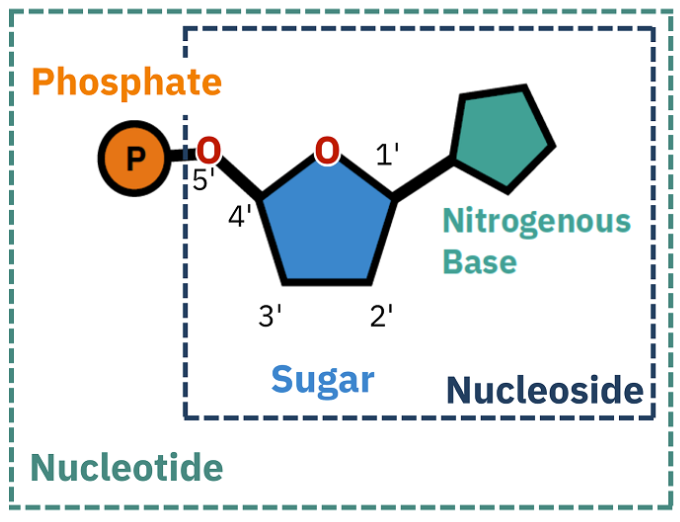
What is a nucleotide?
Nucleotides = essential building blocks of DNA and RNA, composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group
What is a nucleic acid? What is it’s structure
Nitrogen bases attached to a deoxyribose sugar form a polymer with the other deoxyribose sugars of other nucleotides via phosphodiester bonds
Nucleic acid = a macromolecule made of nucleotides bound together by the phosphate and hydroxyl groups on their sugars
Grows by the attachment of 5’ phosphate group of an incoming nucleotide to the 3’ hydroxyl group of the last nucleotide on a growing chain
Gives the chain polarity (5’ & 3’ end)
Hybridization = formation of hydrogen bonds between 2 complementary strands of DNA
What are the steps of DNA replication
Unwind the DNA via helicase
Primase adds the primer
DNA elongation via DNA polymerase
Makes leading and lagging strand
DNA ligase seals nicks and joins strands
What is polymerase
Polymerase = responsible for polymerizing the nucleotide chains
Uses a guide/template strand to know what nucleotides to add to a chain
What is exonuclease
Exonuclease = degrade DNA from free 3’ hydroxyl or 5’ phosphate ends
Don't work on closed/circular DNA
protects the sequence of nucleotides
What is endonuclease
Endonuclease = break the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA
What is ligase
Ligase = an enzyme that forms phosphodiester bonds between existing DNA strands
Catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between adjacent 3’ hydroxyl and 5’ phosphoryl nucleotide ends
What is nuclease
Nuclease = natural components of cellular lysates
Important to eliminate or inactivate when preparing nucleic acid specimens for clinical analysis
What is helicase
analysis
Helicase = unwinds and untangles DNA for replication
The release of DNA for transcription, replication, and recombination without tangling is brought about through cutting and re-closing of the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone
What is methyltransferase
Methyltransferase = catalyze the addition of methyl groups to nitrogen bases, usually adenines and cytosines in DNA strands
What is gel electrophoresis?
Electrophoresis = movement of molecules by an electric current through a matrix/gel
DNA is negatively charged (because of the phosphate backbone) so it moves towards the positive pole
DNA travels at speeds inversely related to its size
Big molecules go slower (don’t migrate far in gel)
Small molecules go faster (further in gel)
What are the principles of electrophoresis
Principles:
Determine method for separation
Type of gel/matrix
Concentration (%)
Running parameters (time/voltage)
Select molecular weight marker (ladder)
Loading
Prepare samples (loading dye)
Load wells/column & document loading order
Perform electrophoretic separation
Visualize and document results
Stain
Chemiluminescence/UV/fluorescence
What’s the difference between agarose and polyacrylamide gels
Agarose | Polyacrylamide |
Very safe material/easy to work with
Ran in a horizontal format Lower resolving power
Good for separating larger fragments (very porous) Made from seaweed & agar components Concentration used: 0.5-5%
| Components can be toxic Usually ran vertically Finer size resolution (small DNA) DNA sequencing, capillary electrophoresis (1 base pair difference) Use for separating small fragments (& single stranded DNA)
Protein electrophoresis (western blotting) Concentration used: 3.5-20% |
Gels are porous like a sponge (allowing DNA to squeeze through with the electric field/matrix sieve
The concentration of gel/buffer affects the resolution of fragments of different size ranges
What’s the difference in agarose and polyacrylamide gel prep.
Agarose prep | Polyacrylamide prep |
|
|
What are the buffers that can be used in electrophoresis
Buffers:
Carries the current and protects the samples during electrophoresis
Typically comes as 10X or 50X stock
Dilute to 1X for working solution
Tris acetate EDTA (TAE) = DNA moves faster, but buffering capacity is smaller
Tris borate EDTA (TBE) = better buffering capacity, DNA moves slower
What’s the difference between TAE and TBE
TAE | TBE |
|
|
* Both buffers can be used interchangeably for PCR/many molecular diagnostic applications
What is the purpose of a loading dye
Loading dye = Gives color to DNA for easier visualization
Makes DNA denser than water so it sinks to bottom of well (weighs down)
Has tracking dyes that separate during electrophoresis to indicate progress of electrophoresis
Allows for visualization while loading
What’s the purpose of nucleic acid stain and detection reagents
make DNA visible
What is the purpose of a molecular weight marker (ladder)
Molecular weight markers (ladders) = a concentrated control stock of DNA fragments of known size
Necessary for determining the actual size of the DNA bands in your finished gel
Included in every gel
What are the general type of equipment used for electrophoresis
UV light box (transilluminator)
Gel documentation systems
Well combs = used to make wells when casting gel
Microwave = used to heat agarose
Casting tray = used to make gel
Gel box = runs reaction
Gel power supply = powers reaction
What’s the difference between the 3 nucleic acid application detection systems (ie. gelred)
Ethidium bromide | SYBR Green | Gel red |
|
|
|
How do you Calculate a sample mixture for loading onto an agarose gel (DNA, loading dye, water)
From the total final desired volume, subtract the loading dye and water amount. From there, subtract the amount of DNA you will use
If you have the DNA conc. From the Nanodrop. And you want to use DNA that is Xng. You will divide the desired ng by the DNA conc. To get the volume of DNA to pipette in (ul).
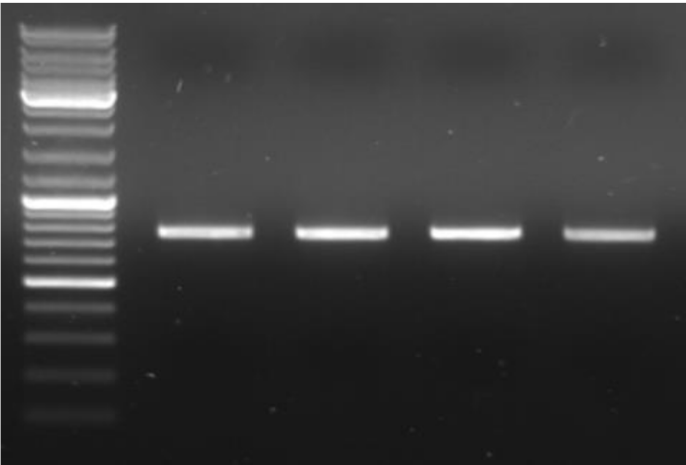
What is a problem with the shown image
No wells seen and no labeling
What is a restriction endonuclease
Restriction endonucleases = recognize specific short DNA sequences
Originate in nature (by bacterial cells as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA –phage)
Protect host by methylation of host DNA and cleavage of unmethylated DNA
Named after the bacteria it comes from
3 different types: Type I, II, III
Most are type II = cleave at specific recognition sites. Only unmethylated DNA
Recognize palindromes (in general)
Can cut 1 of 3 ways (sticky or blunt ends)
Type I: methylation/cleavage (3 subunits)
cuts >1,000 bp away from binding site
Ex: EcoAI
Type III: methylation/cleavage (2 subunits)
cuts 24-26 bp away from binding site
Ex: HinfIII
Can cut 1 of three ways: 5’, 3’overhang, or blunt end
Measured in units (U)
Check the compatibility of the enzyme with the buffer – not all buffers work with all enzymes (some enzymes can work with multiple buffers)
Use 10U of RE per microgram (ug) of DNA
They're named after the bacteria they come from
EcoRI = E. Coli (first one discovered)
Be aware of star acitvity
What is the molecular diagnostic use of restriction endonucleases?
Molecular diagnostic use = can see if there is some sort of mutation because a change in bp won’t allow for the RE to bind anymore (maybe a different RE will bind)
If there is a mutation, the RE will not cut (sample will look like control)
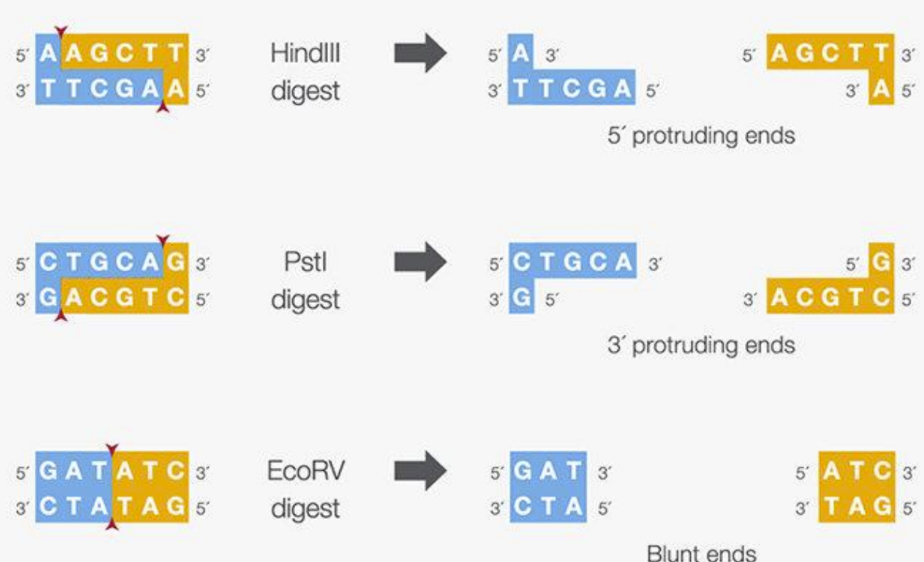
What' are the 3 types of ends an endonuclease can make
5’ overhang = sticky end because of anti-parallel nature
3’ overhang = sticky end because of anti-parallel nature
Blunt end endonuclease = leave no overhanging bases after separation because it is a palindromes
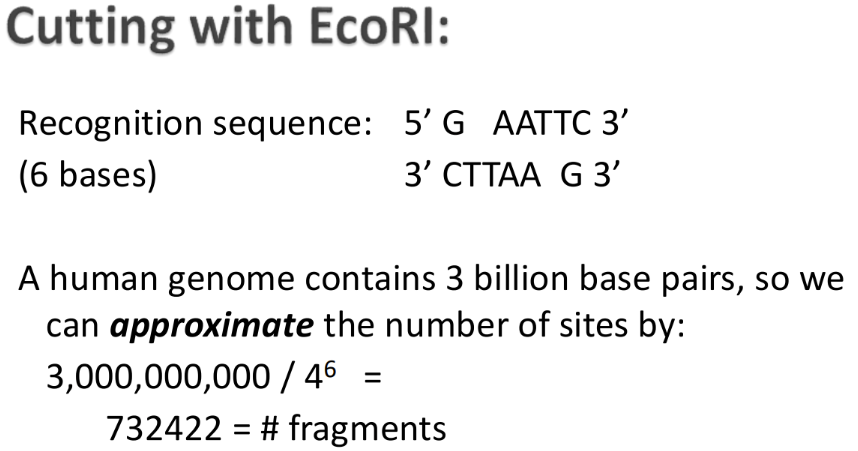
How do restriction enzymes cut DNA (#fragments)
Restriction enzymes
Recognize specific sequence (usually 4-6 nucleotides)
Cut the DNA by breaking the phosphodiester bond on both strands
Cutting results in 2 or more fragments
Smaller recognition sequences results in more fragments generated because it is easier to find a match for a short sequence
Resolve fragments by gel electrophoresis
* The number of times a specific sequence occurs in a given organism is approximated by...
Genome size in nucleotides/4^n
n = the length of the recognition sequence
* Master mix should be on cold block and gently mixed
What is restriction enzyme mapping?
Restriction Enzyme Mapping: After digesting the DNA with RE and resolving the fragments by gel electrophoresis...
Number of bands indicates the number of restriction sites
Size of the bands indicates the distance between restriction sites
What are the detailed steps of restriction enzyme cutting process?
Detailed steps:
Consult the enzyme data sheet for details
It's important to find out the correct conditions for the enzyme that you’re using (usually provided by manufacturer)
Set up master mix on cold block
Mix gently by flicking, then briefly spin
For human genomic DNA = RE reactions typically incubate at 37°C for 5-18hrs
Enzymes often must be heat inactivated after reaction is completed
Usually between 55-88°C for 20 mins.
Analyze by gel electrophoresis
What is star activity
Star activity = When RE cuts the DNA too many times, results in extra bands (RE GONE NUTS)
Heat inactivation required to stop RE from over cutting
On a gel, there will not be a DNA smear visible at the top of the gel because DNA is degraded
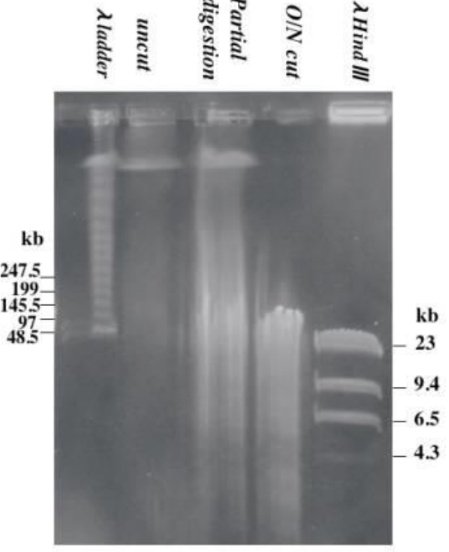
What could have happened to this gel (top)
* If there is a DNA smear at the top of the gel, then the enzyme only possessed partial activity. You must check the reaction conditions because there may be inhibitors present.
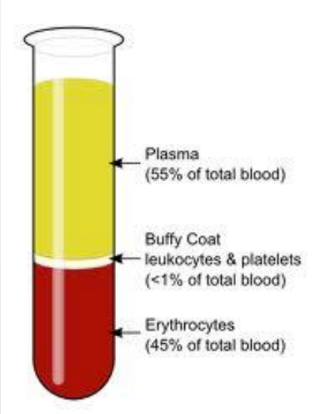
What are the parts of a blood specimen?
Plasma = may contain some genetic material (used for HIV)
Buffy coat = DNA (WBCs &platelets)
Eryhtrocytes = RBCs
What are the steps of an organic DNA isolation? (w/purpose of each reagent)
Lyse the cell (using detergents/proteases) (break the cell contents open)
Acidification if needed (via acetic acid) (if pH needs to be lowered)
Mix lysate with PCI reagent
Forming upper aqueous (DNA) & lower organic phase
Separate aqueous phase
Add ammonium acetate or sodium acetate to encourage precipitation (due to salts)
Add 100% ethanol (promotes DNA precipitation because it’s insoluble in alcohol)
Incubate at –20 to –70 (freezer) (further encourages DNA precipitation)
Centrifuge & pour out supernatant
Wash DNA pellet with 70% ethanol (dissolves salt and not DNA)
Resuspend DNA in TE buffer or water (DNA dissolved and ready for use)
What is the purpose and workflow of ethanol precipitation of DNA
A technique for purifying and concentrating DNA from an aqueous solution
The 100% ethanol promotes DNA precipitation because it is insoluble in alcohol
The 70% ethanol dissolves the salts ONLY without dissolving the DNA
* You first want to encourage the most DNA precipitation as possible, once this is achieved, the salt is removed so the DNA alone can be extracted
Add Salt (sodium acetate) to neutralize DNA’s negative charge
Add cold 100% ethanol (precipitates DNA out of solution & cold enhances it)
Incubate at -20C (allow precipitation to complete)
centrifuge to form pellet of DNA
Wash with 70% Ethanol (dissolves salt and not DNA)
centrifuge again to repellet DNA
Air dry pellet to remove ethanol
resuspend DNA in TE buffer or nuclease-free water
What are the steps of solid phase DNA isolation? Purpose of each reagent
Qiagen
1. Lysis using AL (L = lysis) buffer and proteinase K
Disrupting cells open & stops proteins that can degrade the DNA
2. Incubation at 56 degrees
Accelerates protein breakdown (Proteinase K digests better)
3. Addition of 100% ethanol
Encourages DNA precipitation
4. Addition of AW1/AW2 (W = wash) buffers
First wash removes proteins/contaminants
2nd wash removes the salt/contaminants
5. Elution with AE (E = elution) buffer
DNA released from silica membrane (DNA released for use)
Compare/contrast the spin-column method to the magnetic bead (Chelex) DNA isolation method
Chelex reagent/resin = Used in DNA purification where Chelex beads bind to the cellular debris after cell lysis. Allowing the DNA to be in the supernatant (used in forensics)
Spin-column =
Magnetic (Chelex) | Both | Spin |
|
|
|
What is Salting out
Salting out = inorganic DNA extraction = purification of nucleic acid by precipitating proteins and other contaminants with high salt at low pH
An alternative to using Phenol (toxic reagents)
Low-pH & high salt conc. Causes proteins to be precipitated and DNA left in solution.
DNA is separated and then precipitated in isopropanol (ultimately resuspended in TE buffer/water)
What are the steps to a DNA isolation using a Qiagen spin column
Lyse cells (detergent protease)
Add to column, spin (DNA binds to matrix & waste flows through)
Wash, spin (removes contaminants from column)
Add elution buffer and spin (low salt will release the DNA from the column into a new clean tube)
How are gel-based methods used to determine quality/quantity of DNA preparations?
Quantity = intensity of gel bands
Via densitometry
Quality = no smearing on gel & high molecular weight bands
Excessive smearing means there is degraded DNA
How are spectrophotometric methods used to determine quality/quantity of DNA preparations?
Spectrophotometric = instrument used to measure the absorbance of light at a particular wavelength (QUALITY + QUANTITY)
Nucleic acids absorb light at 260nm
Proteins absorb light at 280nm
Expect a purified sample to have a high A260 and low A280
260/280 ratio indicates QUALITY
Low = protein contamination
High = other contamination
Nanodrops give you the DNA concentration which gives you QUANTITY
Can't distinguish between DNA & RNA
How are fluorometric methods used to determine quality/quantity of DNA preparations?
Fluorometric = Binding fluorescent dyes to DNA and detecting it via a fluorometer
More sensitive than spectrophotometric method (QUANTITY)
Can distinguish between DNA/RNA/contaminants
Good for very SMALL amounts of DNA (smaller than nanodrop)
Not affected by phenol, EDTA, protein, and high salt contamination
How do you calculate concentration and yield of DNA from a preparation
Concentration = amount/volume
Yield = (starting DNA/RNA concentration) / (ending DNA/RNA concentration)
How do you read a spectrophotometric curve (what does it mean)?
A high 280 wavelength means that there is a high amount of purity in the sample
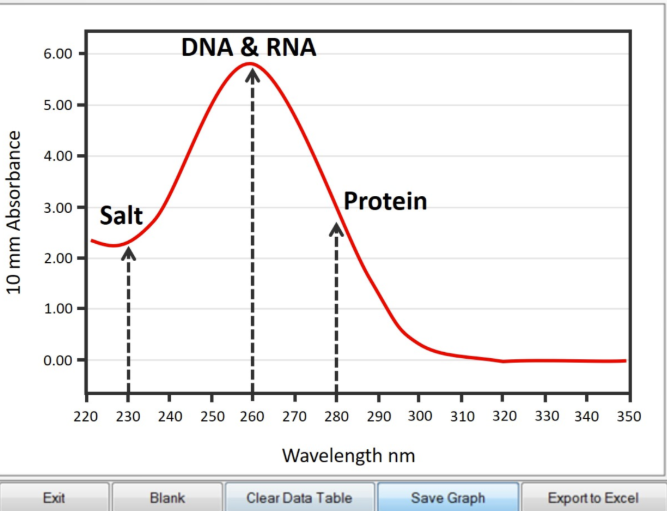
How does a nanodrop give you DNA’s concentration/purity?
Concentration = ng/ul
Purity = A260/280