The need for transport systems: Scaling up: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Need for transport systems
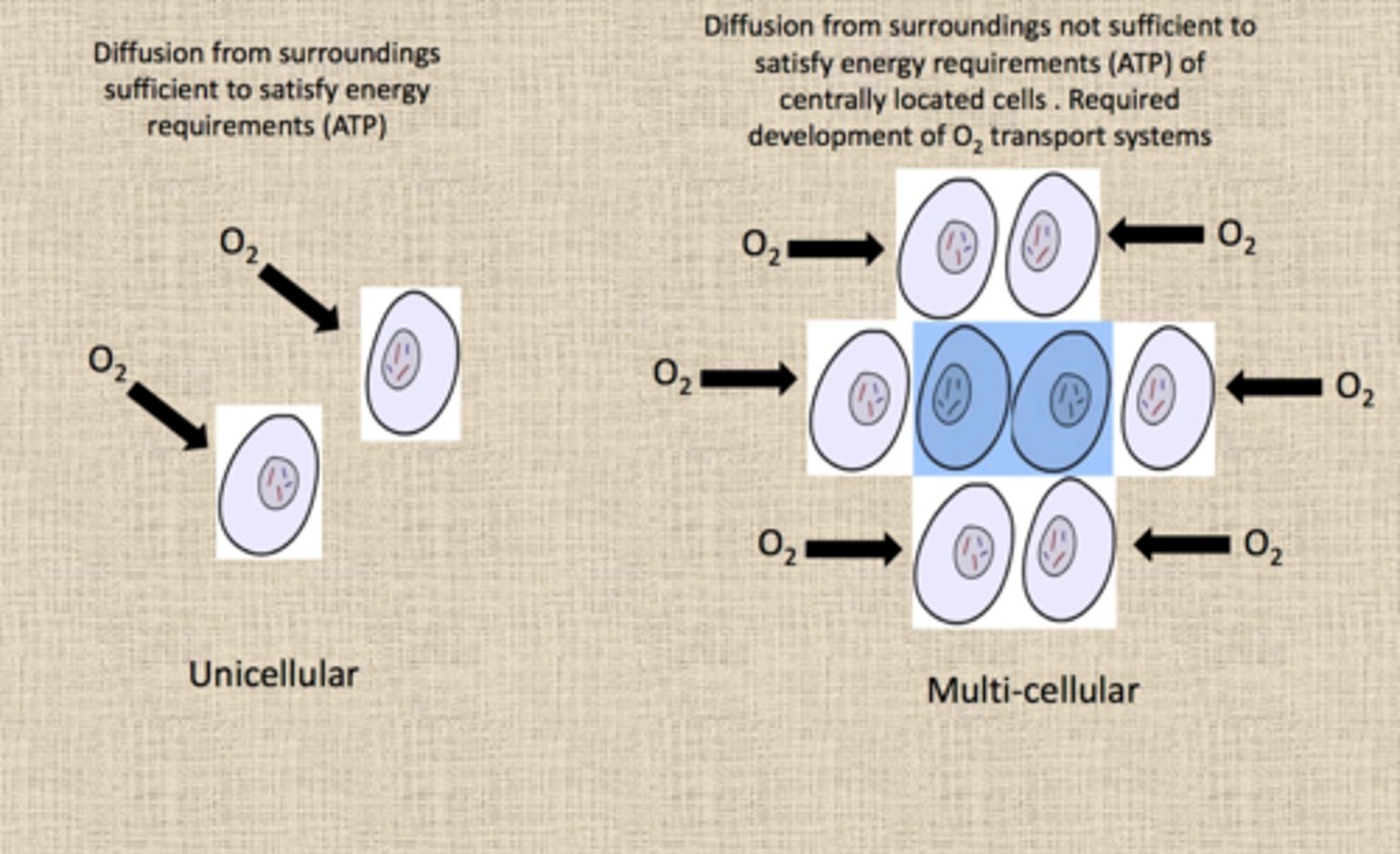
Larger organisms have smaller surface area to volume ratios and are unable to directly obtain useful substances from their environment like single-celled organisms can
Transport system
A system that is used for transporting substances around a multicellular living organism
Surface area
The total area of the surface of an object
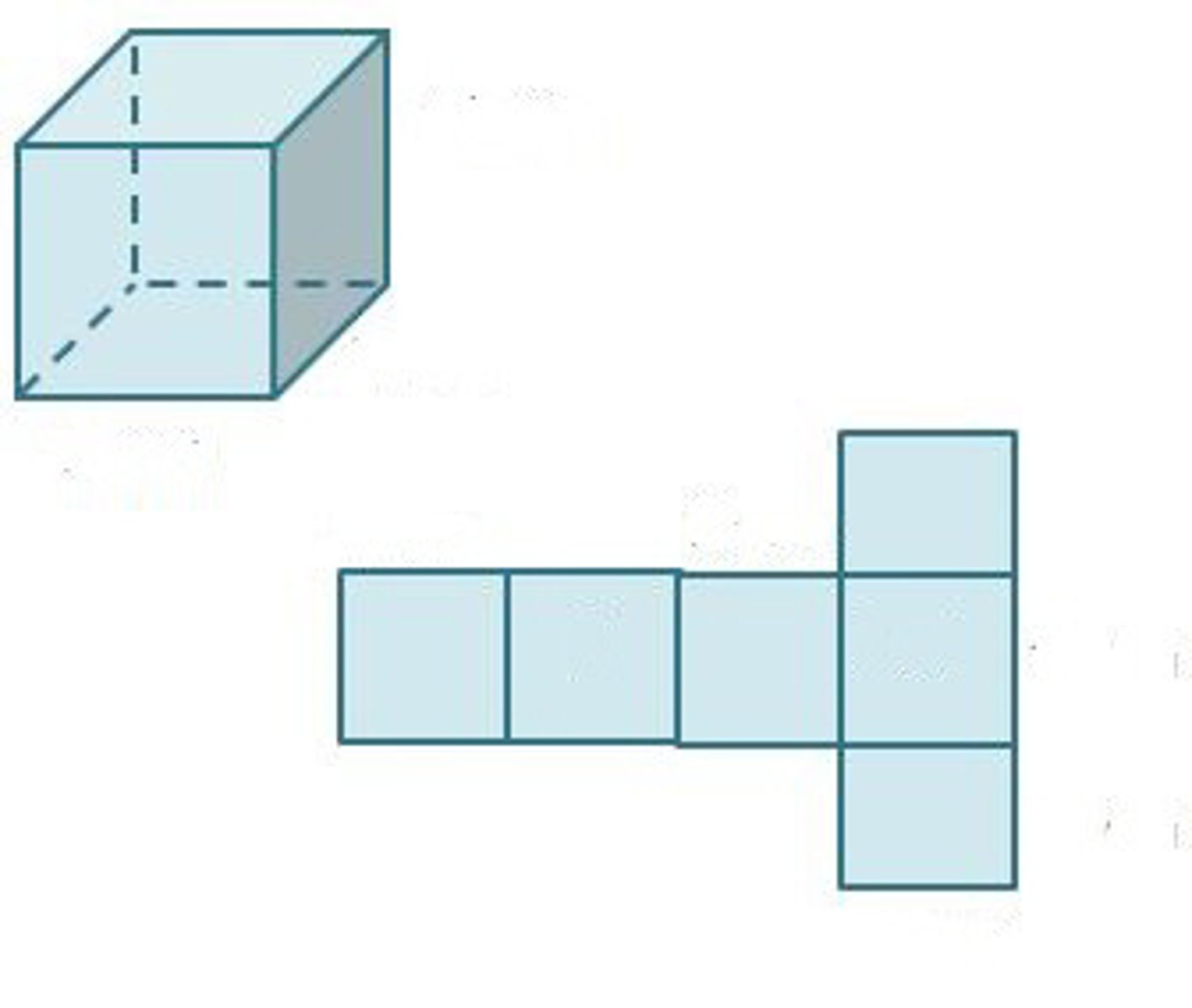
Surface area to volume ratio
The amount of surface area in relation to how large something is
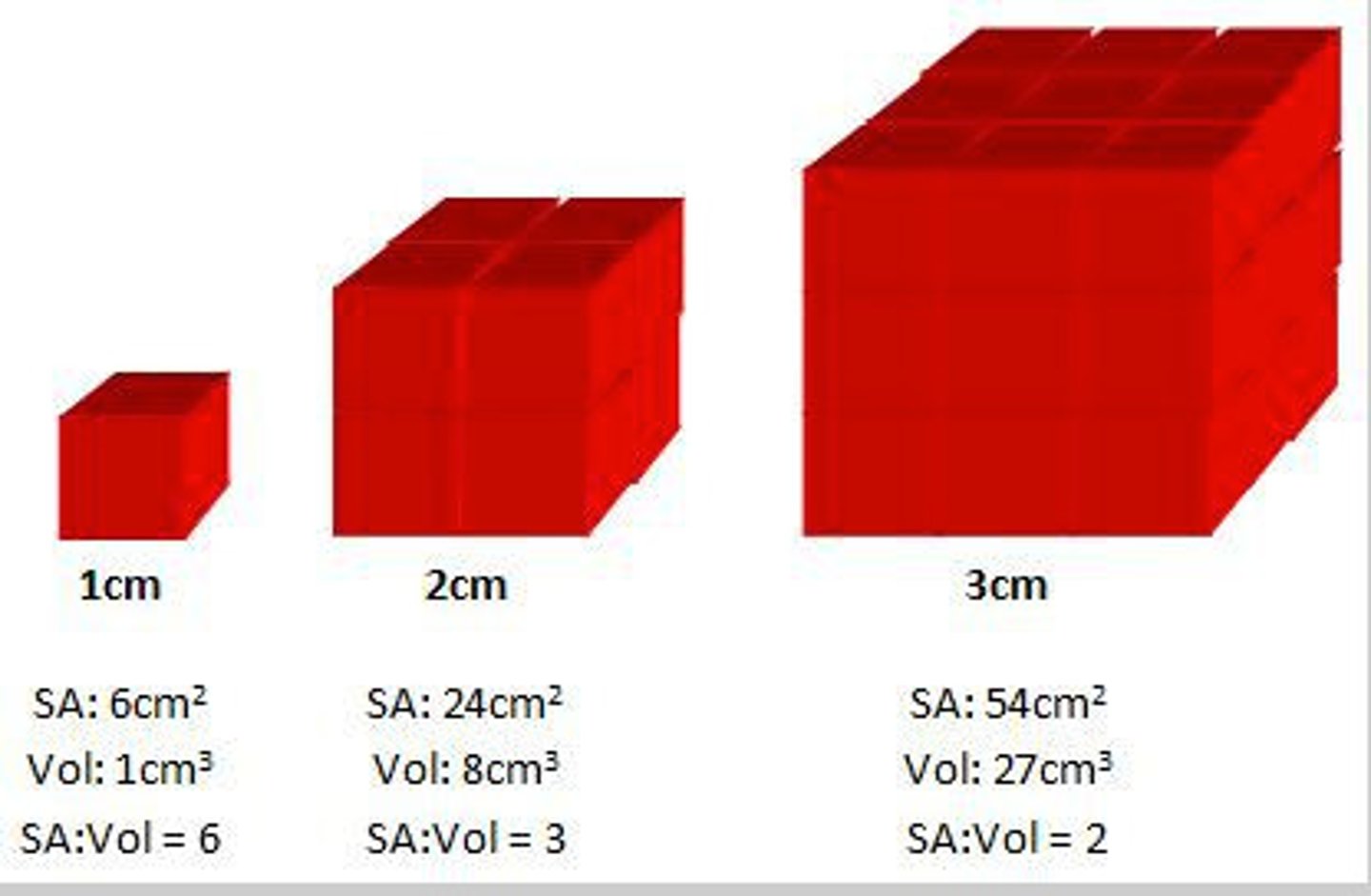
Large surface area to volume ratio
Leads to faster diffusion rates, as there is more room for particles to diffuse through a membrane

Diffusion
The movement of substances such as gas particles or substances in solution, from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
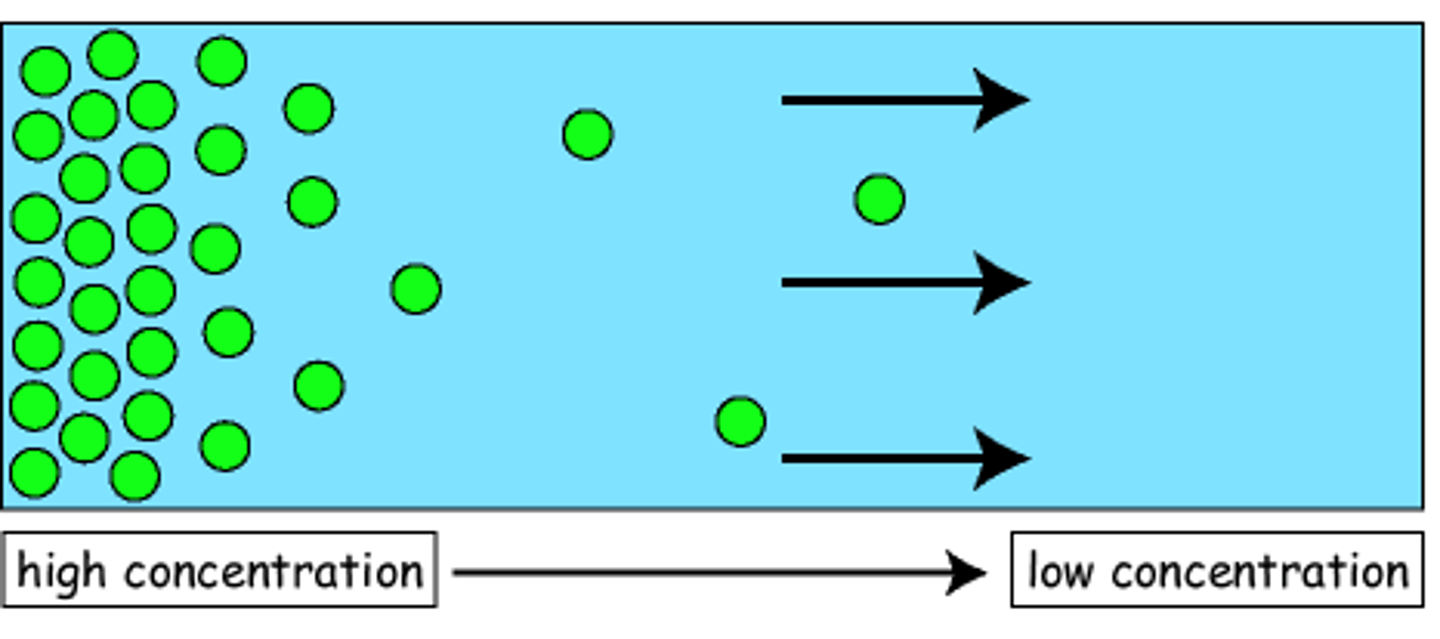
Gas exchange
When oxygen and carbon dioxide move in and out of cells by diffusion
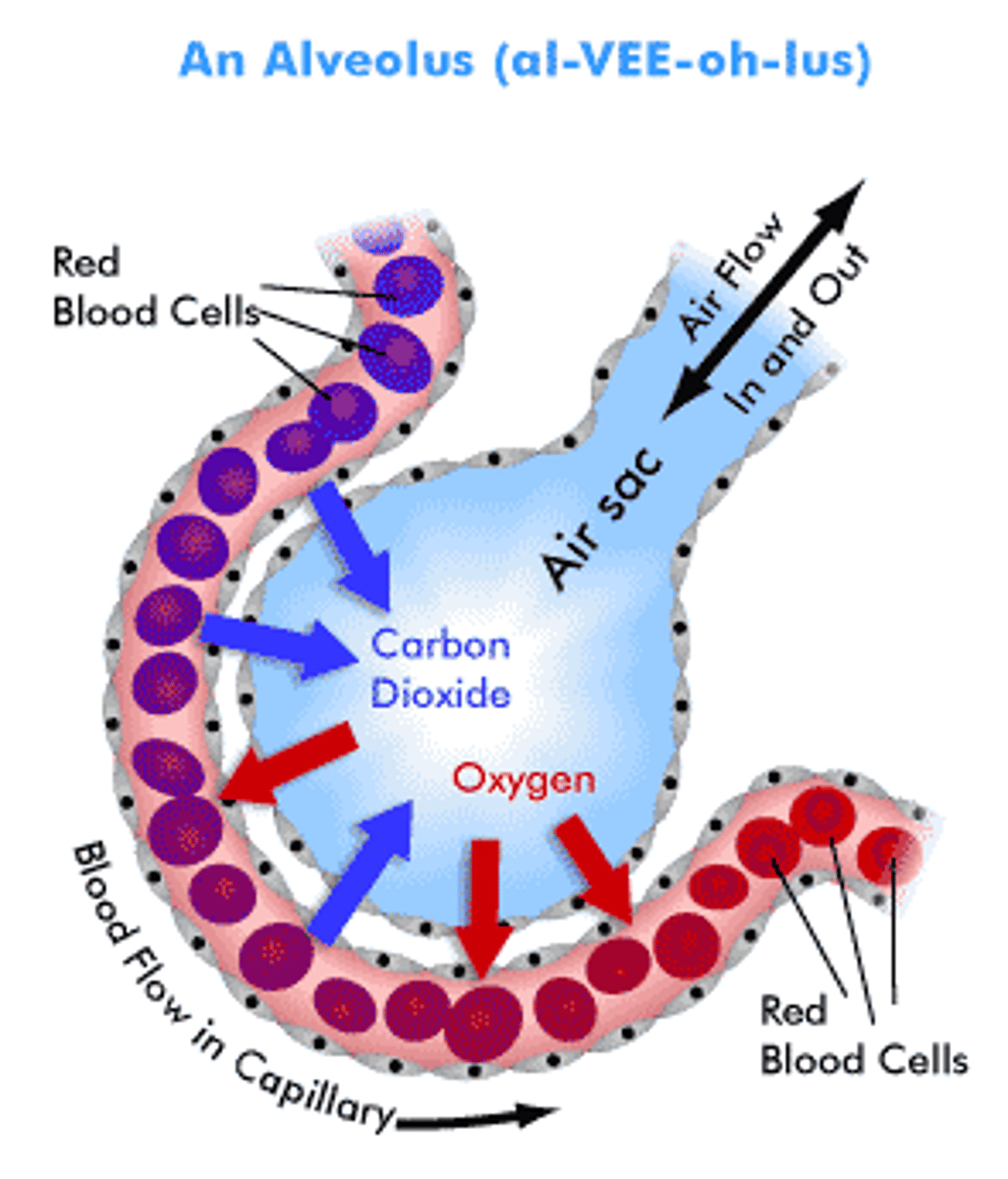
Purpose of gas exchange
Organisms need oxygen for aerobic respiration, they also need to remove carbon dioxide which is a waste product in some organisms

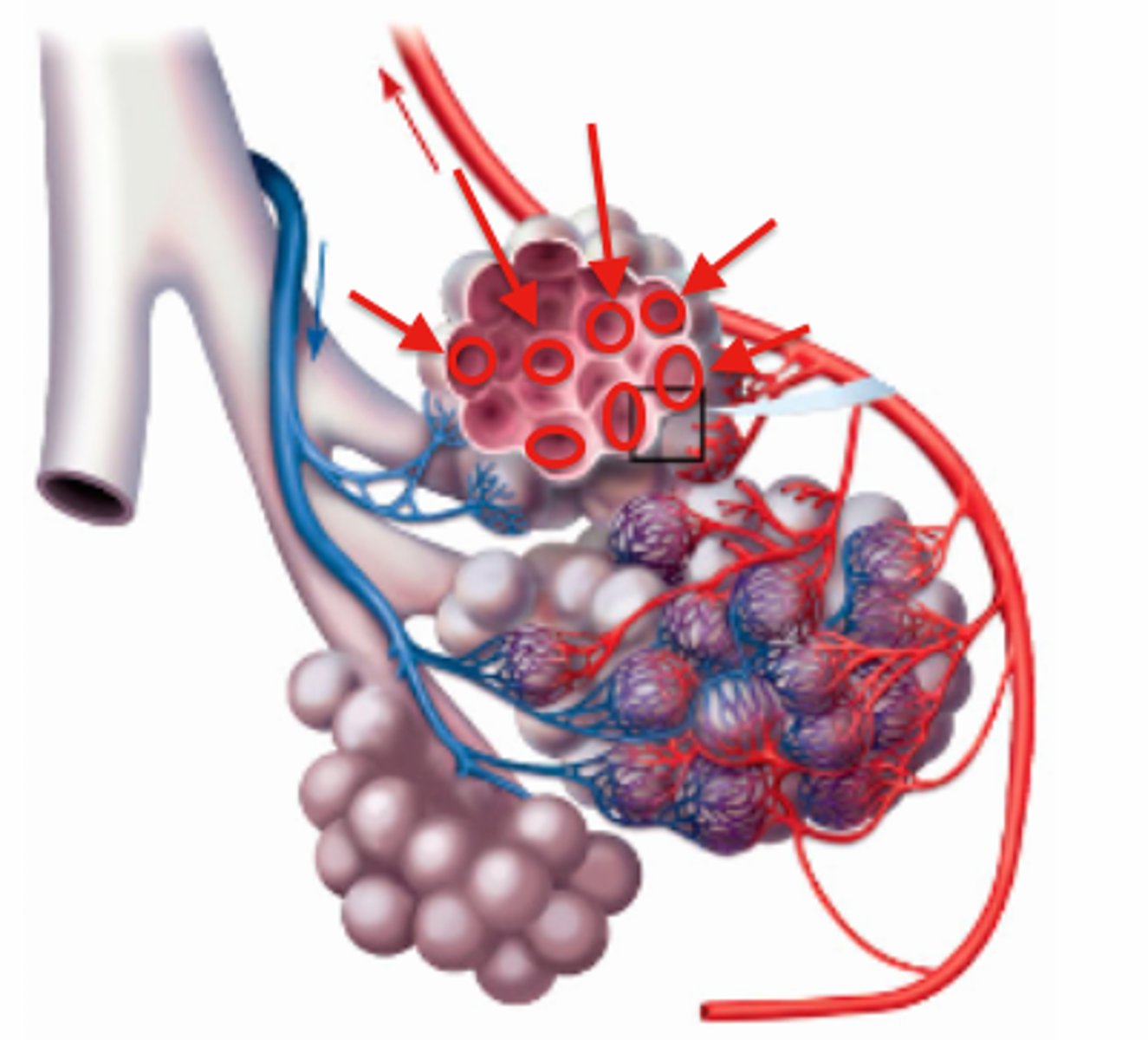
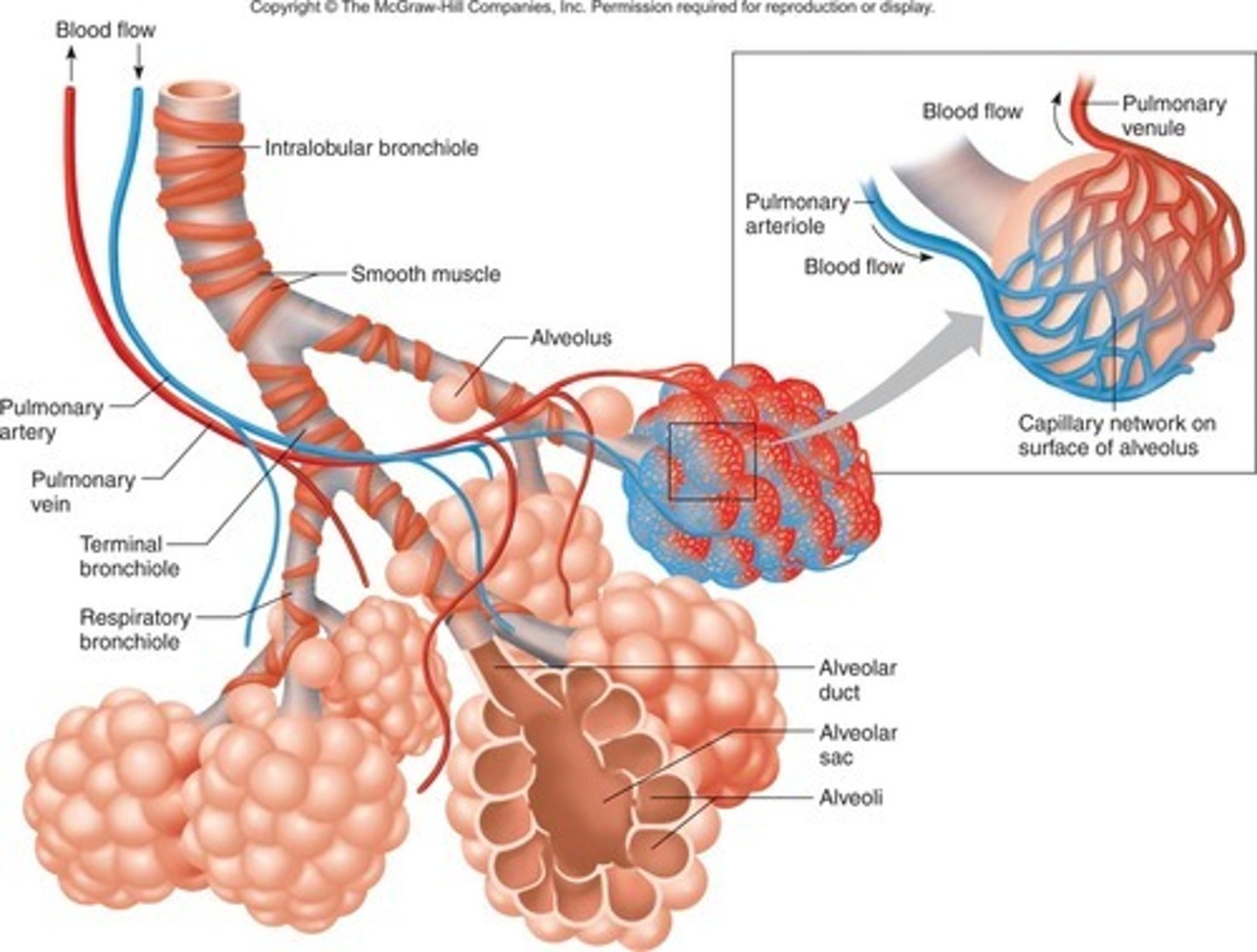
Sites of gas exchange
The alveoli of the lungs and respiring cells around the body
An effective exchange surface
Has a large surface area, a good blood supply, is well ventilated for gas exchange and has a thin membrane for diffusion
Structures adapted for exchanging materials
Small intestine, kidneys, lungs, gills in fish, roots and leaves in plants all have adaptations such as thin membranes and increased surface area
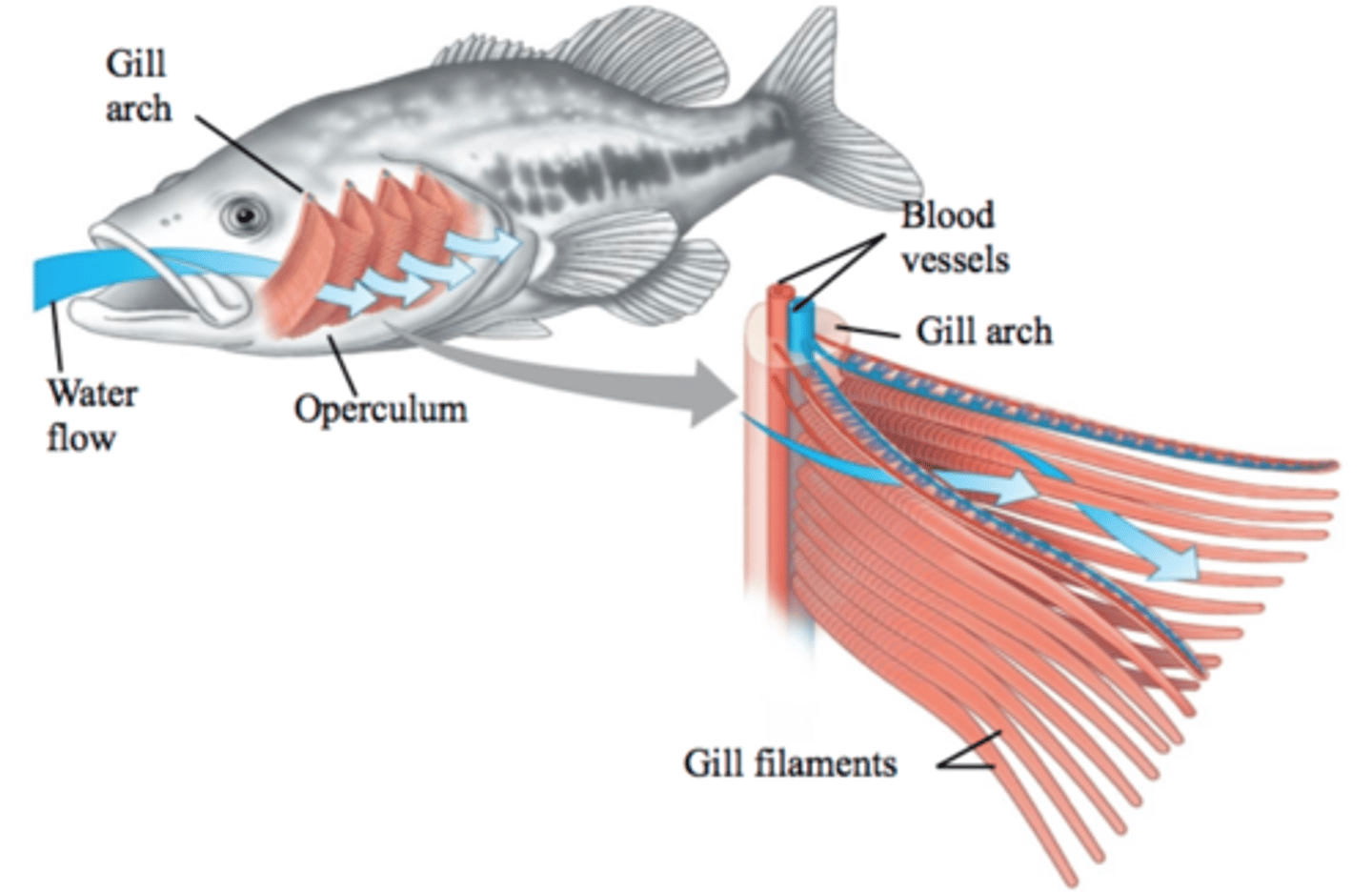
Specific cells, tissue and sacs adapted for exchange
Alveoli in mammal lungs, ciliated epithelial cells in the intestines, gill filaments in fish gills and some amphibian gills, root hair cells in plants, guard cells in plants
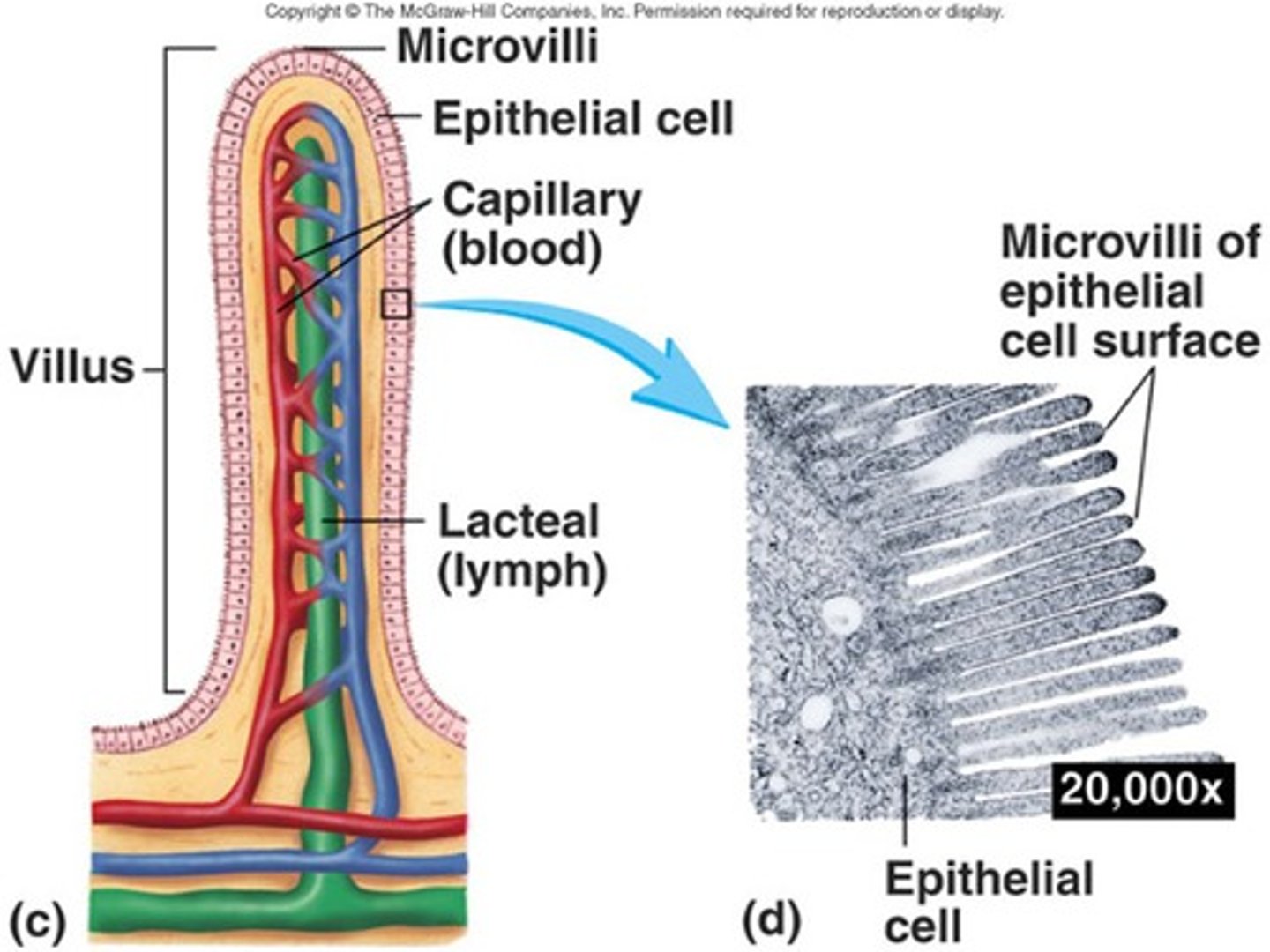
Dissolved food molecules
Products of digestion that are essential for respiration and other important cell functions, these molecules need to be transported by the blood in animals
Urea
A waste product that is filtered and removed from the blood plasma via diffusion in the kidneys
Oxygen
A gas that is needed for aerobic respiration to release energy, oxygen is transported into the body by the respiratory system and around the body by the circulatory system
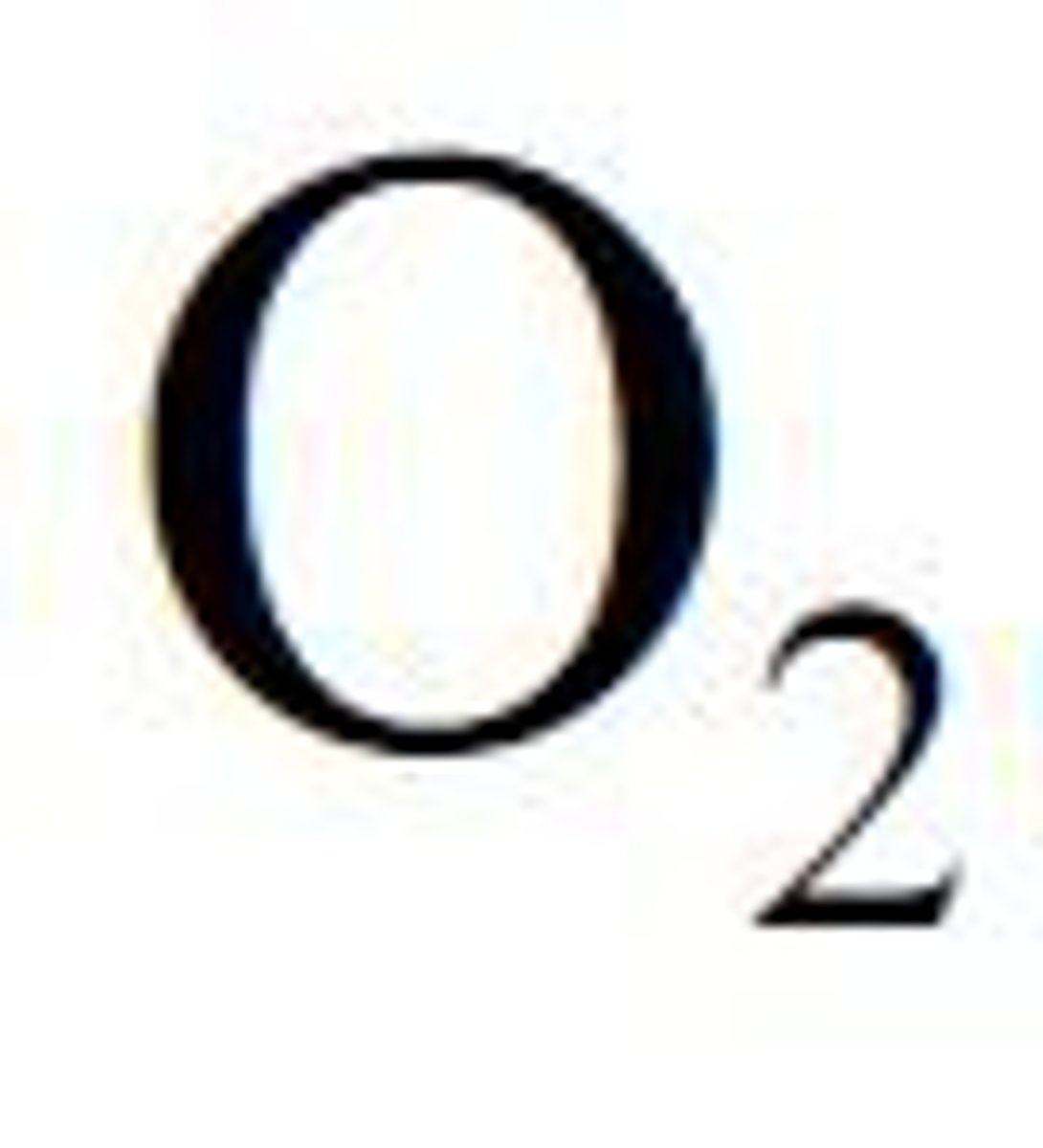
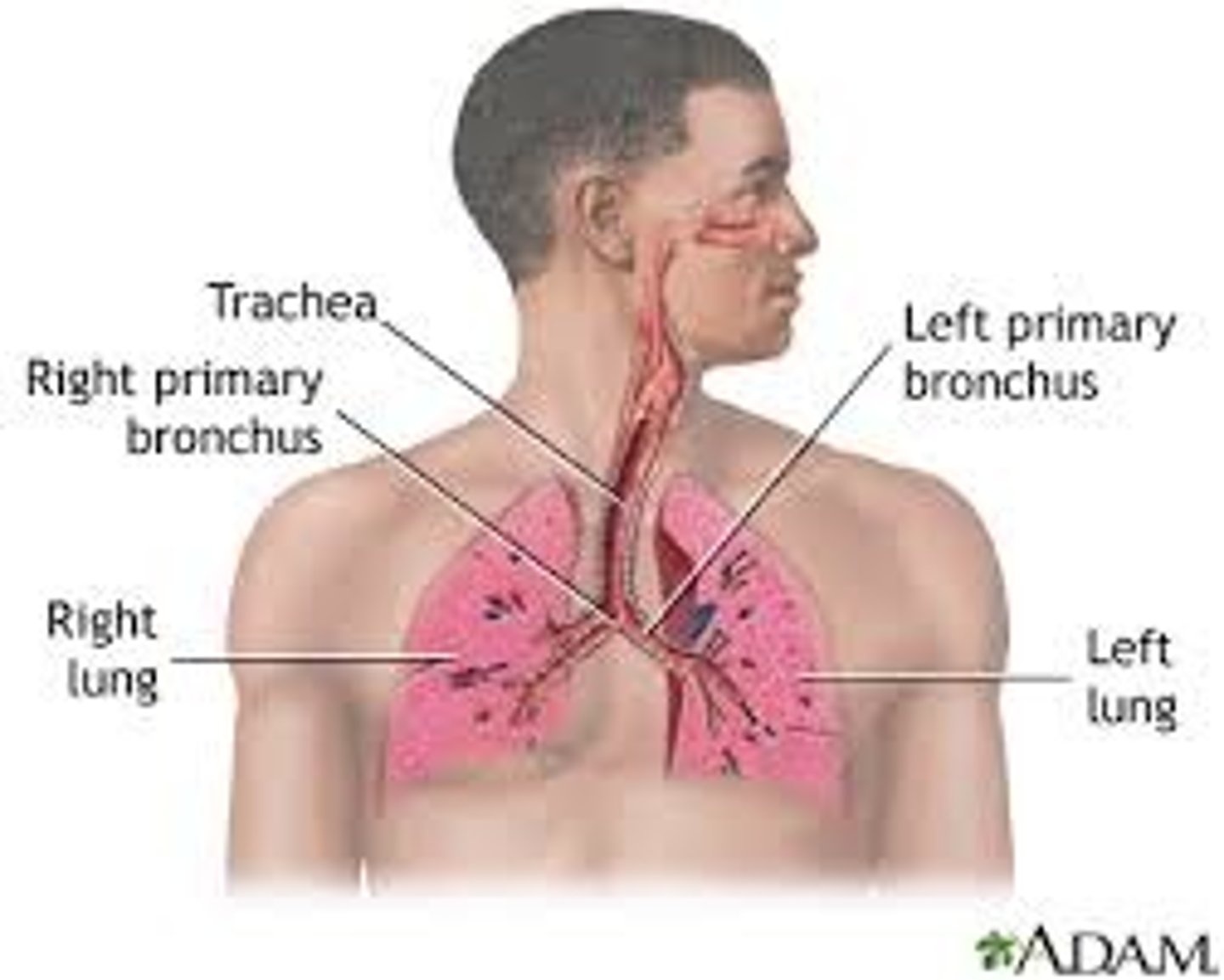
Respiratory system
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting of the trachea, bronchi and lungs
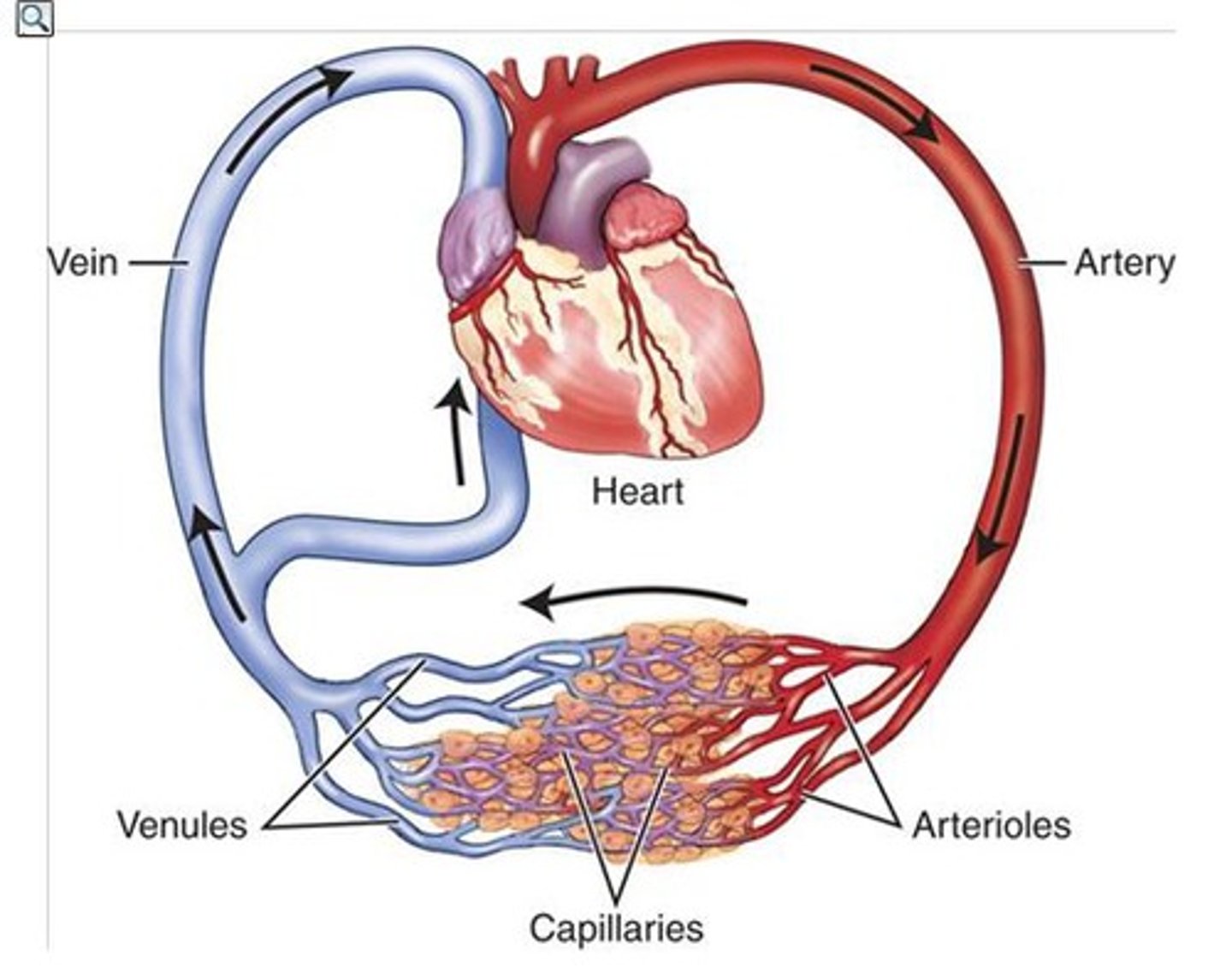
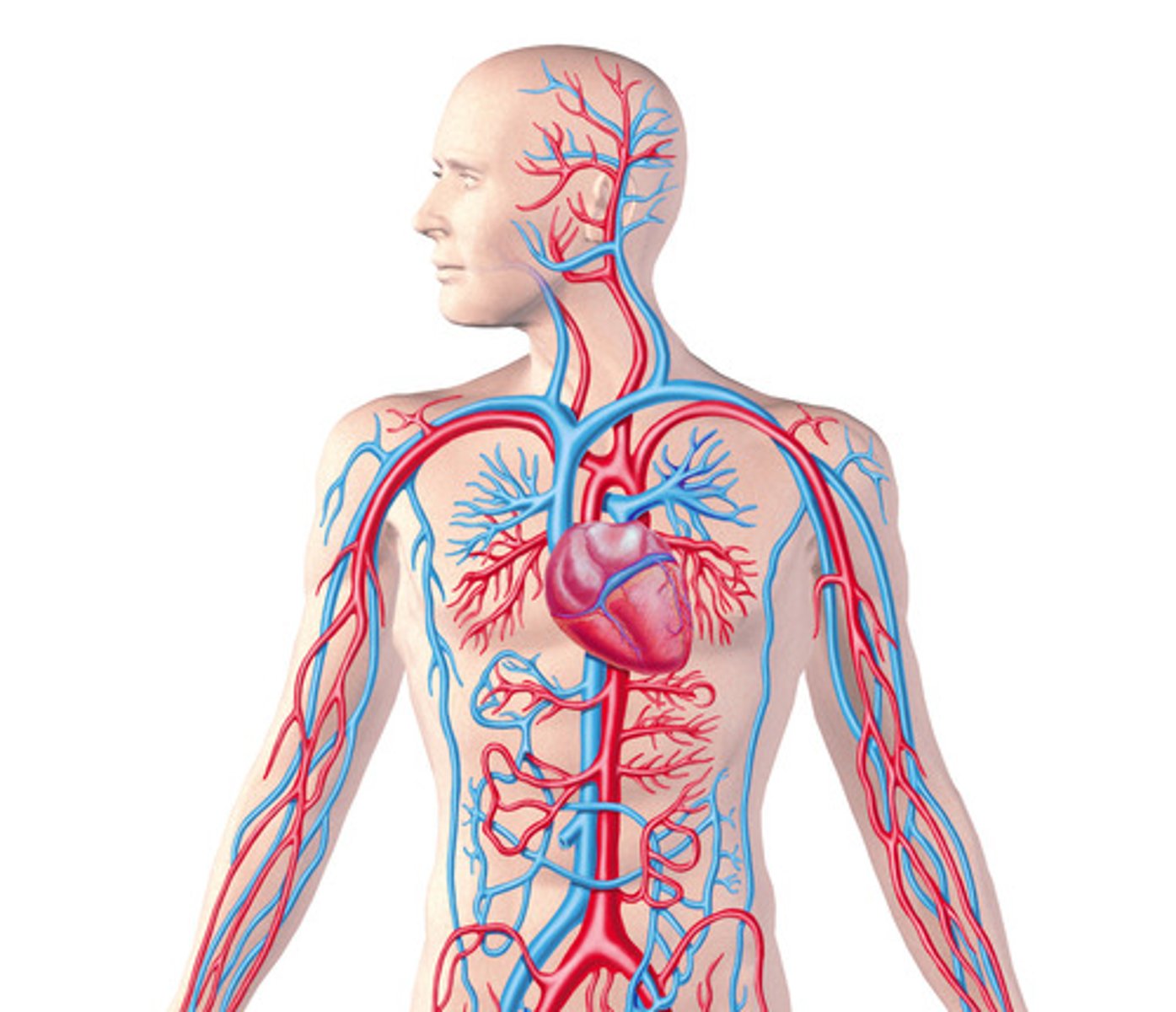
Circulatory system
An organ system that transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, waste such as urea, nutrients, hormones and heat around the body
Carbon dioxide
A waste product of respiration that needs to be removed from the body via the circulatory system, also an essential reactant in plants that is transported in to plant leaves via the stomata
Water in animals
Essential for osmosis and cell functions, water is transported around the body by the blood in animals
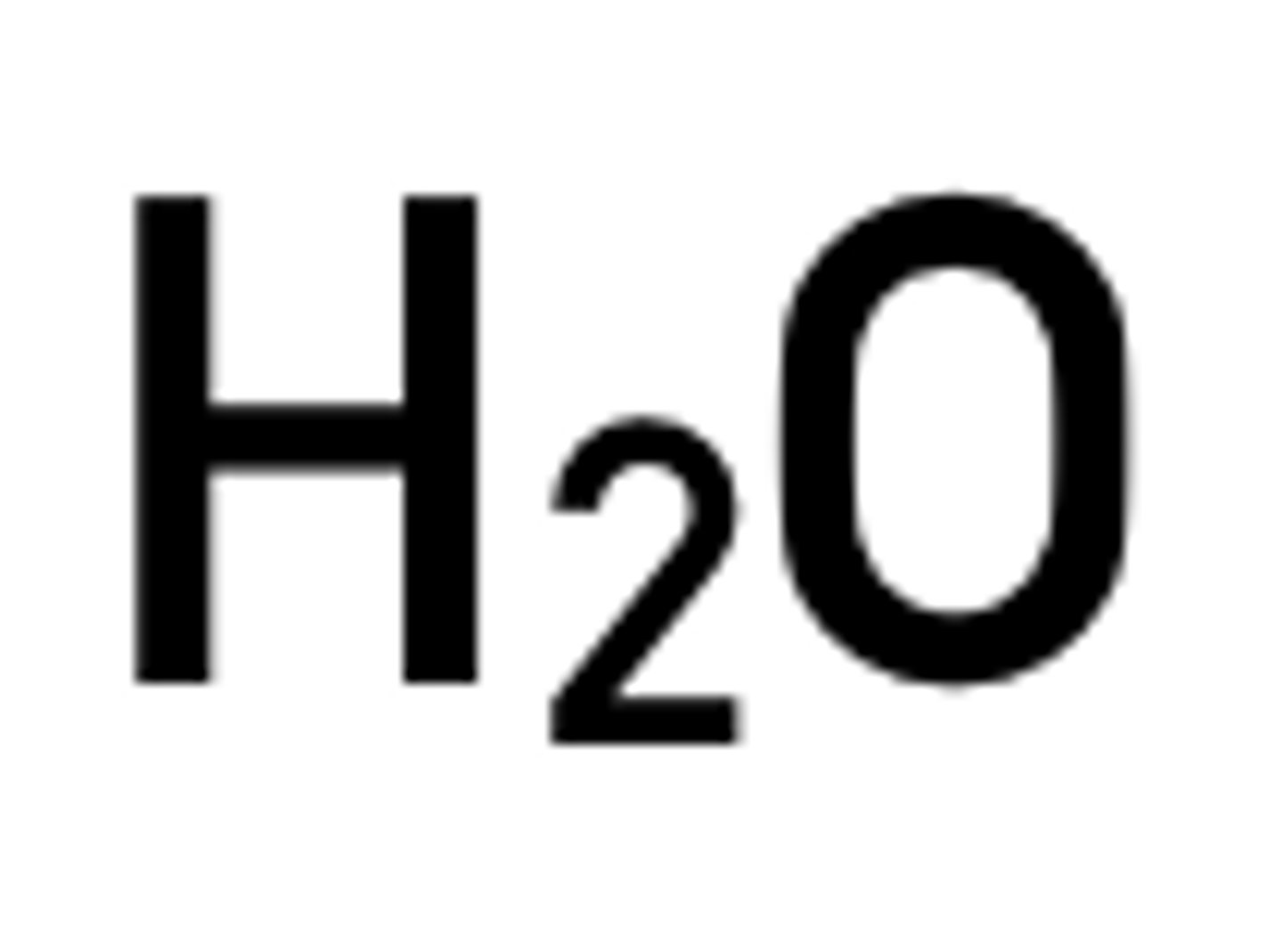
Water and mineral ions in plants
Water and minerals are needed for cell functioning and proper plant development, they are obtained in the roots and are transported to the leaves via the xylem
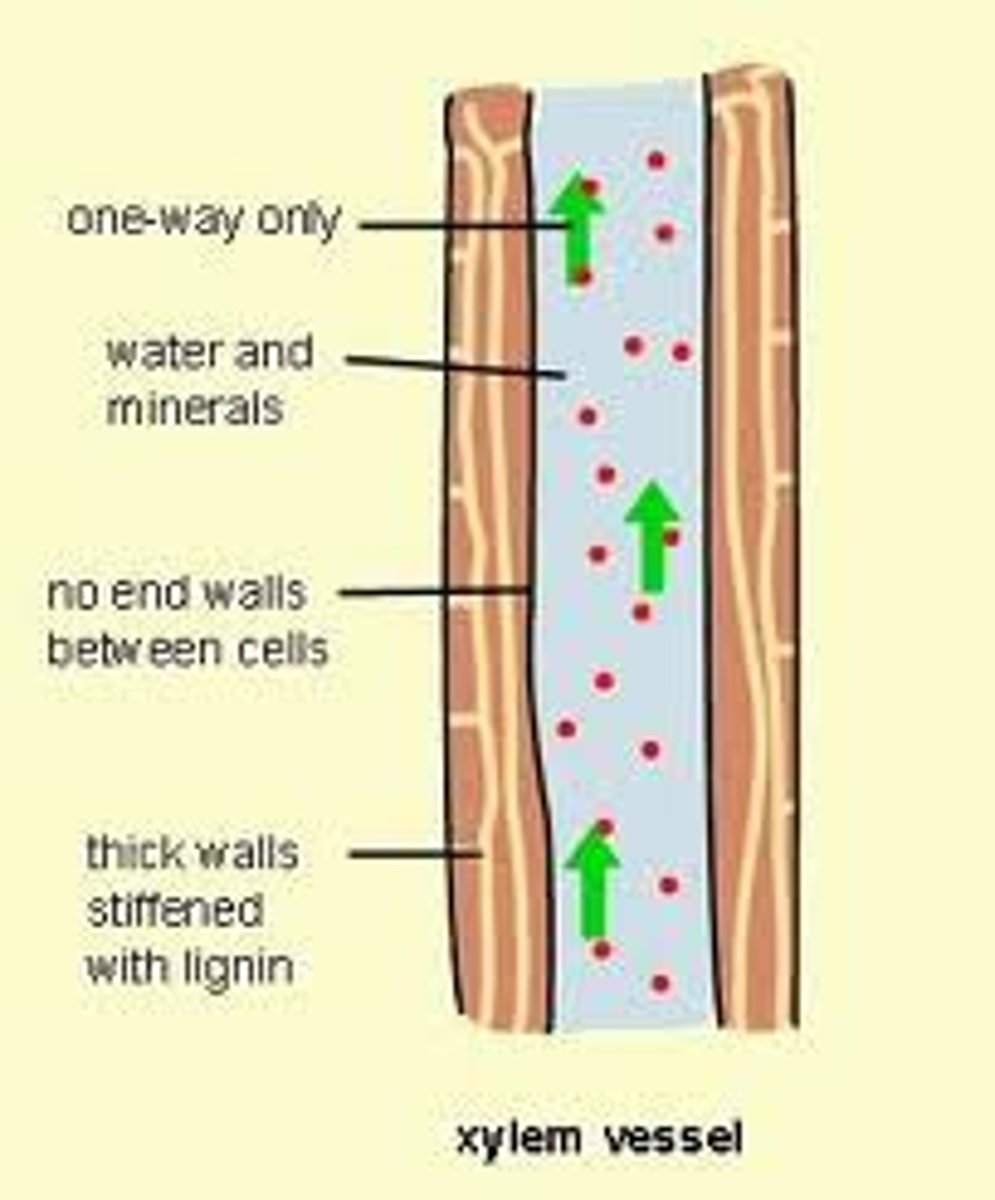
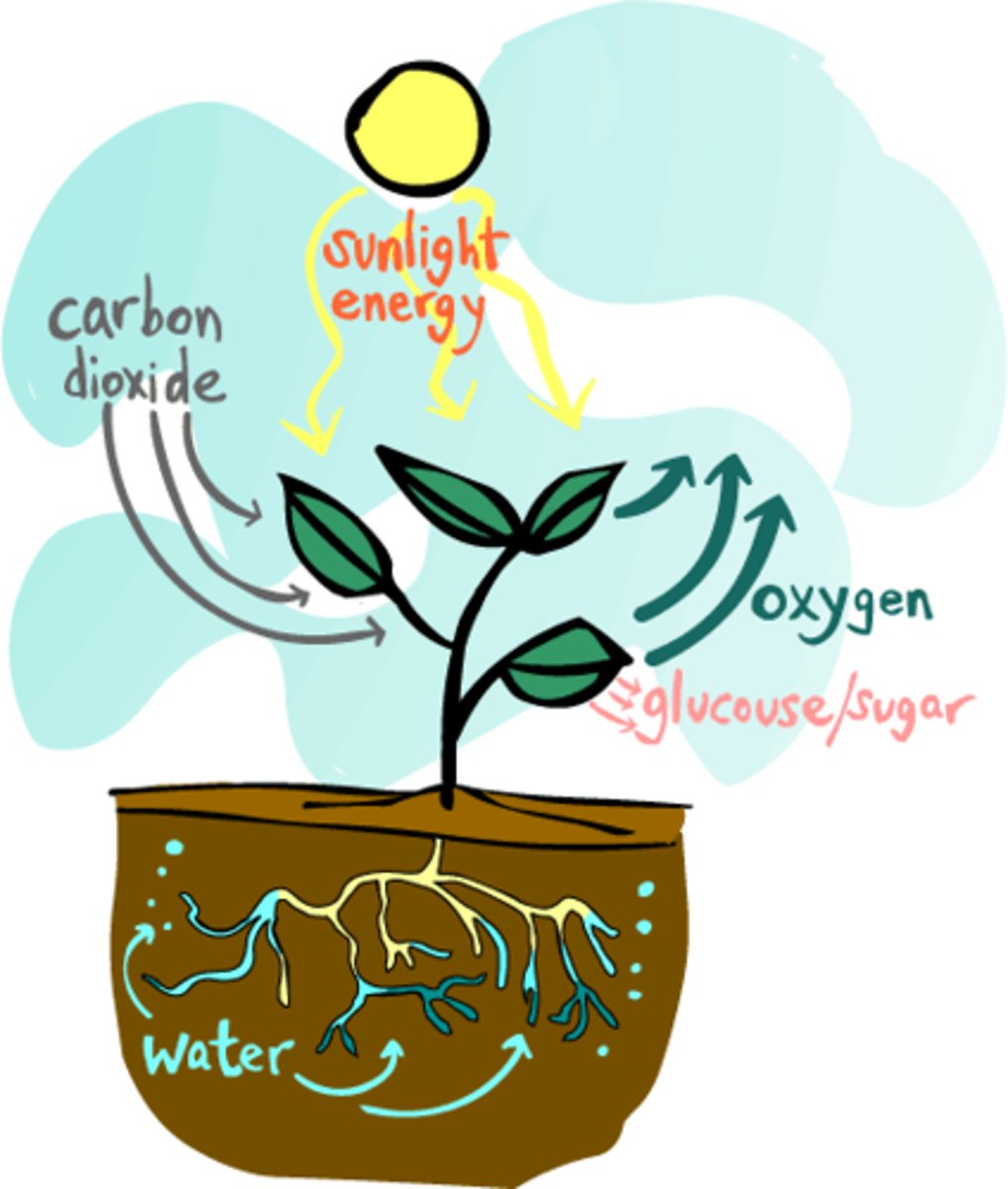
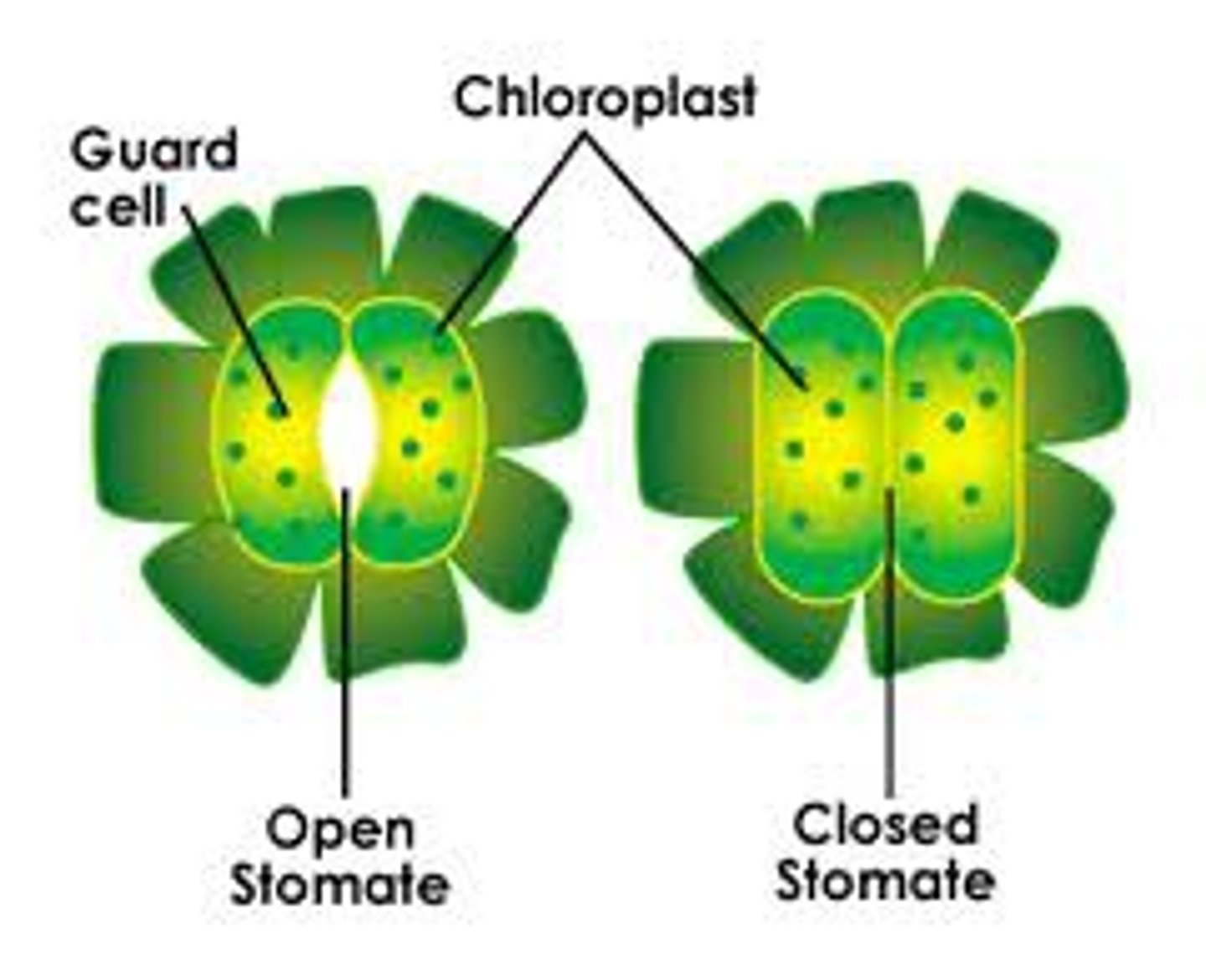
Gas exchange in plants
Carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant in exchange for oxygen that diffuses out of the plant, this process is regulated by guard cells in the leaves that can open and close the stomata efficiently
Lungs
Are specialised in gas exchange due to the presence of many tiny sacs called alveoli that are adapted for diffusion due to being moist, one cell thick and surrounded by capillaries
