Public Health Midterm Review
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What (Case Definition)
Clinical criteria (the more specific the better)
Who? (Person)
Consider genetics and socioeconomic factors
Where? (Place)
Geographical differences; resident, birth, employment locations
When? (Time)
Secular trends over years and seasonal patterns
Why?
why lol
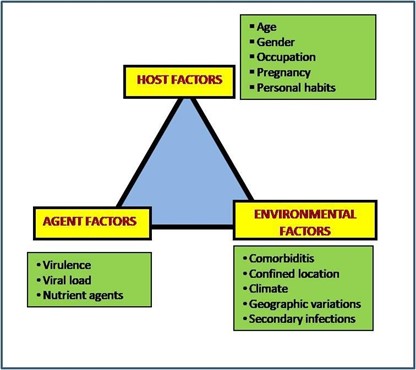
Epidemiological Triad
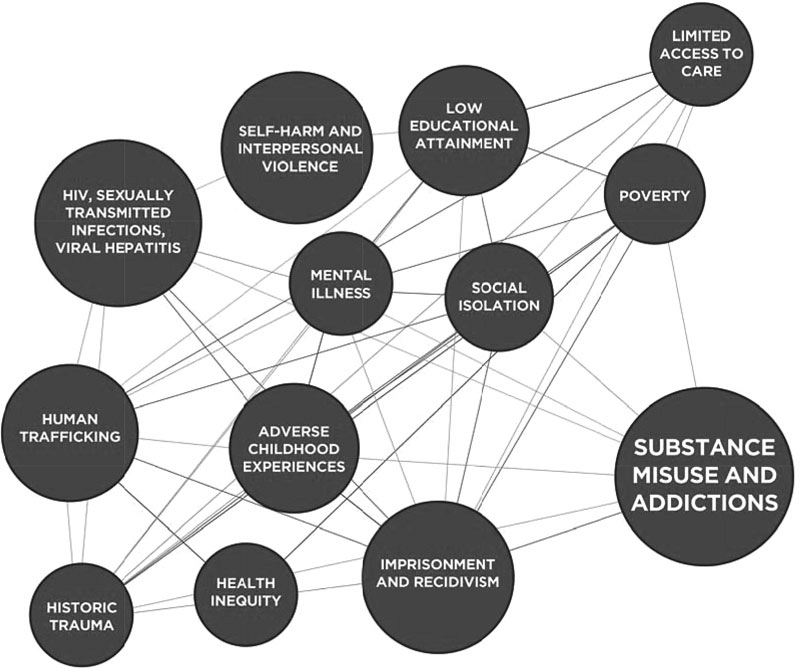
Web of Causation
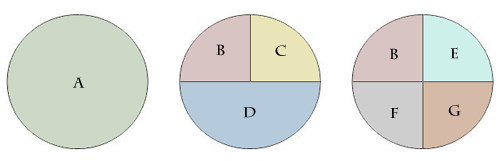
Sufficient Cause and Component Causes Model
Pulmonary
relating to the lungs
John Snow
cholera pump dude
made a ghost map
actually talked to people
Paracelsus
toxicology
dose-response relationship
organ targeting
John Graunt
quantative methods
“Columbus of statistics “
Ramazzini
Occupational medicine
“whats ur job”
Sir Percival Pott
environmental cause of cancer
chimney sweeps —> scrotal cancer
first environmental protection: baths
William Farr
system to code conditions
links mortality rates and population density
Robert Knock
Association between a microorganism and disease

Variolation
Infecting healthy with smallpox through cuts or nose
Edward Jenner
Created vaccinations through cowpox on a dairymaid
Global eradication campaign
US-AID funded campaign to remove smallpox everywhere
Konner and Eaton
Current diets and lifestyles are mismatched to evolutionary environments
Code of ethics includes…
Evidence-based public health, timely dissemination of information, tailoring for diverse audiences
Tuskegee Syphilis Study
1932 600 black men not told some had syphilis, not given cure after development
Vertical transmission
women transferring diseases to their children
Henrietta Lacks
1951 cells doubled every day, harvested and spread without her consent (HeLa cells)
Moore vs Regents of the University of California 1990
HeLa cells are not her property and can be commercialized lol
The Common Rule 1991
enforces informed consent
Etiology
the cause, set of causes, or manner of causation of a disease or condition
deontology
ethics are determined by right or wrongness or individual event consequences
Consequentialist
ethics are determined by individual event consequences
Sufficient cause (SCM)
Set of factors that inevitably cause disease
Component cause (SCM)
Individual factors forming sufficient cause
Necessary cause (SCM)
Component mustb e present for the disease
Stages of disease
Susceptibility, subclinical disease (latency), clinical disease (symptoms), outcome (recovery or death)
[Point] Prevalence
Frequency of existing cases
Number of cases / Total population
Incidence Rate/Density
Frequency of new cases
New cases / Total person-time at risk
Cumulative incidence (Risk)
New cases / Population at risk at start
Odds
Cases / non-cases
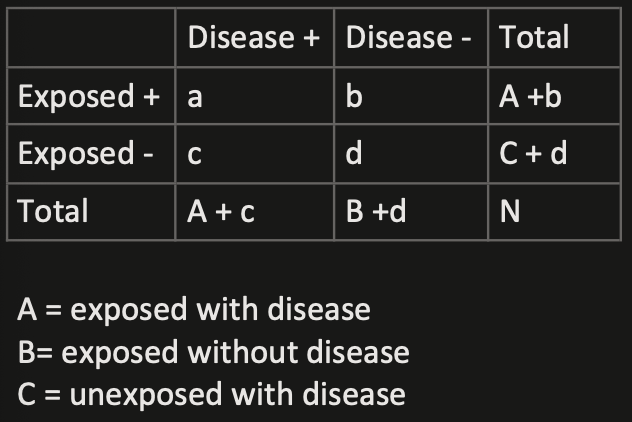
Risk Ratio (Relative Risk)
Risk in exposed / Risk in unexposed
[a(a+b)]/[c(c+d)]
Odds Ratio
Odds in exposed / odds in unexposed
(a x d)/(b x c)
[Incidence] Rate Ratio
Incidence rate in exposed / Incidence rate in unexposed
Total person time
Sum of time each subject observed disease-free
Use prevalence when…
Burden of disease at a point in time
Use risk (CI) when…
Probability over a fixed period in closed populations
Use incidence rate when…
dynamic populations, varying follow-up
Use relative risk when…
cohort studies, interpretable as risk reduction/increase
Use odds ratio when…
case-control or rare outcomes
Use incidence rate ratio when…
longitudinal studies with person-time
The ICD system
the international classification of diseases, injuries, and causes of death
published by WHO
Patterns to relationships process
Quantify associations (measures of effect), design studies to test hypotheses, evaluate evidence for causation
The 2×2 Table
Relative Risk = 1
No association between exposure and disease
Relative Risk > 1
Exposure increases disease risk
Relative risk < 1
Exposure decreases disease risk
Odds ratio = 1
No association
Odds ratio > 1
Higher risk of exposure in cases (positive association)
Odds ratio < 1
Lower odds of exposure in cases (protective association)
Cause of cases
Why certain people get sick
Cause of incidence
Why populations differ in disease rates
Prevention paradox
A preventative measure which brings much benefit to the population offers little to the individual
ex. wearing seatbelts
High risk strategy
focus on high risk individuals
cost effective generally
costly screening wise
only small percentage of people
Population strategy
Bring down risk of everyone
very expensive
small benefit for each individual
prevention paradox
Public health
The organized effort of society to prevent disease, prolong life, and promote health through population-level interventions
Focus of public health
populations over individuals
prevention over care
Hominid era
Plant-based remedies
Burial practices
Mobility reduced disease spread
Ancient cities
Sanitation
nutrition
crowding
plague, cholera, smallpox
case report
a detailed description of a single patient’s experience
(descriptive)
cross-sectional study
an observational research method that collects data from a population at a single point in time
(descriptive)
Cohort studies
Following a group of people over time
(analytical)
Case-control study
inflicted cases versus controls to determine association with past exposure
(analytical)
Ecological study
Examines relationships between health outcomes and environmental factors that the population level rather than the individual level
(analytical)
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs)
a scientific experiment that uses random assignment to divide participants into different groups to compare the effects of an intervention or treatment
randomization is “gold standard” in experiments
(experimental)
primordial level of prevention
prevent risk factors
ex. urban planning and poverty reduction
primary level of prevention
prevent disease onset
ex. vaccines, sanitation
secondary level of prevention
early detection and treatment
ex. screening programs
tertiary level of prevention
reduce complications, disability, recurrence
ex. rehab
quaternary level of prevention
prevent over diagnosis and medical harm
Wilson & Jugner screening criteria 1968 - definition
10 principles for deciding whether a disease should be included in a population screening program
Wilson & Jugner screening criteria 1968 - requirements
Disease is important, has latent stage, effective treatment exists
Tests must be acceptable, cost-effective, and part of ongoing care
Lead-time bias
Earlier detection does not mean improved outcome
could be same life span anyway
length-time bias
screening detects slow-growing disease, not good for fast
overdiagnosis
Identifying disease that wouldn’t cause harm
APHA code of ethics
prevent disease, respect rights, include community input, address social determinants, evidence-based action
Virtue ethics
compassion, integrity
Kantain ethics
Individuals are ends, not means
Utilitarianism
Greatest good for greatest number
Belmont report
Created in response to public outrage over tuskegee study
established respect for persons, beneficence, and justice
Havasupai case
2004 lawsuit by havasupai tribe against ASU over misuse of blood samples
thought it was only for diabetes but they kept using it
informed consent violations
Infant mortality
Deaths under 1 year / 1,000 live births
Maternal mortality
deaths during pregnancy or postpartum
Leading causes of maternal mortality
mental health, cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, infection
Reading peer-reviewed articles
identify purpose, understand methods, interpret results, evaluate discussion, check of limitations