Economics Unit 3 Exam
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Circular Flow
a model showing how money moves through society.
\
Ex. money flows from producers to workers as wages and flows back to producers as payments for producers.
\
Ex. money flows from producers to workers as wages and flows back to producers as payments for producers.
2
New cards
GDP Equation
C+I+G (X-IM)
3
New cards
Aggregate Demand
the sum of all goods for all goods and services in the economy at all prices for one year.
4
New cards
(A.D) Slopping Downwards; Wealth Effect
when prices rise people buy less stuff so they feel less wealthy.
5
New cards
(A.D) Slopping Downwards; Inflation Rate Effect
as price levels increase, interest rate will increase.
Ex. people spend more, thus there is less left over to loan out.
Ex. people spend more, thus there is less left over to loan out.
6
New cards
(A.D) Shift to the left
LEFT=BAD
* a reduction in demand at all price levels.
\
Reminder:
* any change in the GDP equation will cause a shift
* a reduction in demand at all price levels.
\
Reminder:
* any change in the GDP equation will cause a shift
7
New cards
(A.D) Shift to the right
RIGHT=GOOD
* an increase in demand at all price levels
Reminder:
* any change in the GDP equation will cause a shift
* an increase in demand at all price levels
Reminder:
* any change in the GDP equation will cause a shift
8
New cards
Aggregate Supply
is the total of all goods supplied in the economy
9
New cards
Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
when there is a change in quantity supplied less than 1 year
10
New cards
What shifts (AS)
Key resources
* oil/gas
* energy products (electricity)
* transportations
* Government intervention
* taxes
* laws
* subsides
* oil/gas
* energy products (electricity)
* transportations
* Government intervention
* taxes
* laws
* subsides
11
New cards
Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
represents how much an economy is capable of producing when using its resources fully. The level is also known as Quantity Full Employment (QFE)
12
New cards
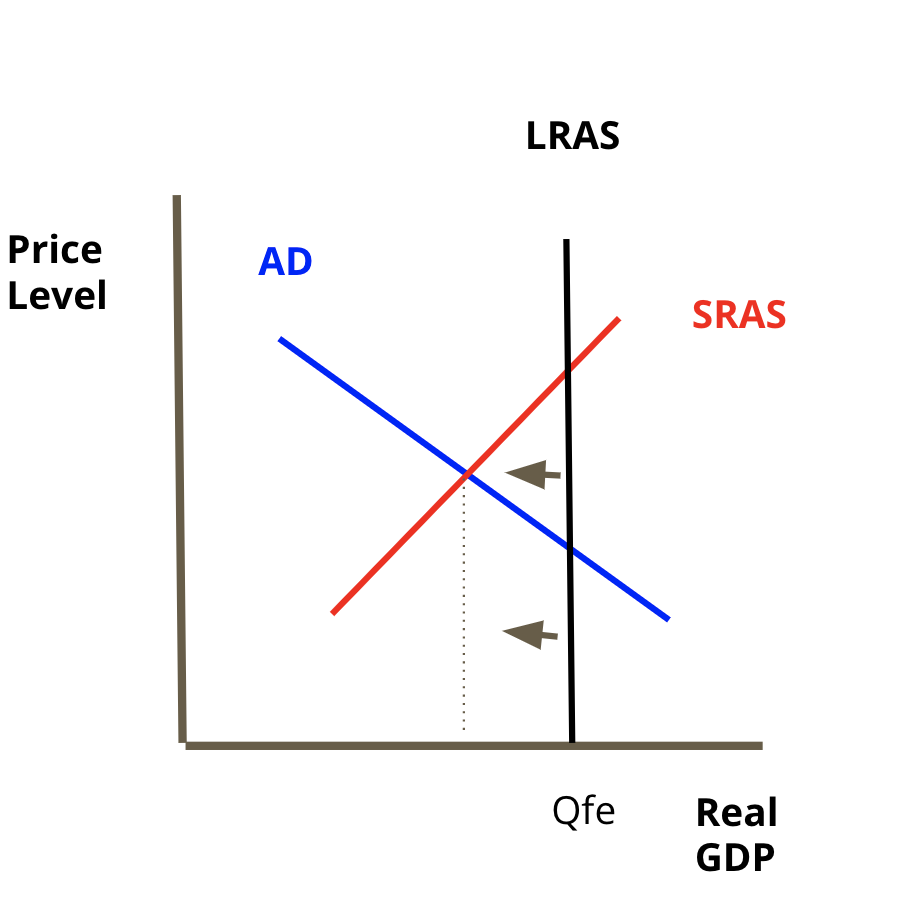
Recession Gap
when the equilibrium of AD and SRAS is to the ==left== of LRAS the economy is in a recessionary gap.
* A recessionary gap looks like a decline in spending, employment, and production.
* A recessionary gap looks like a decline in spending, employment, and production.
13
New cards
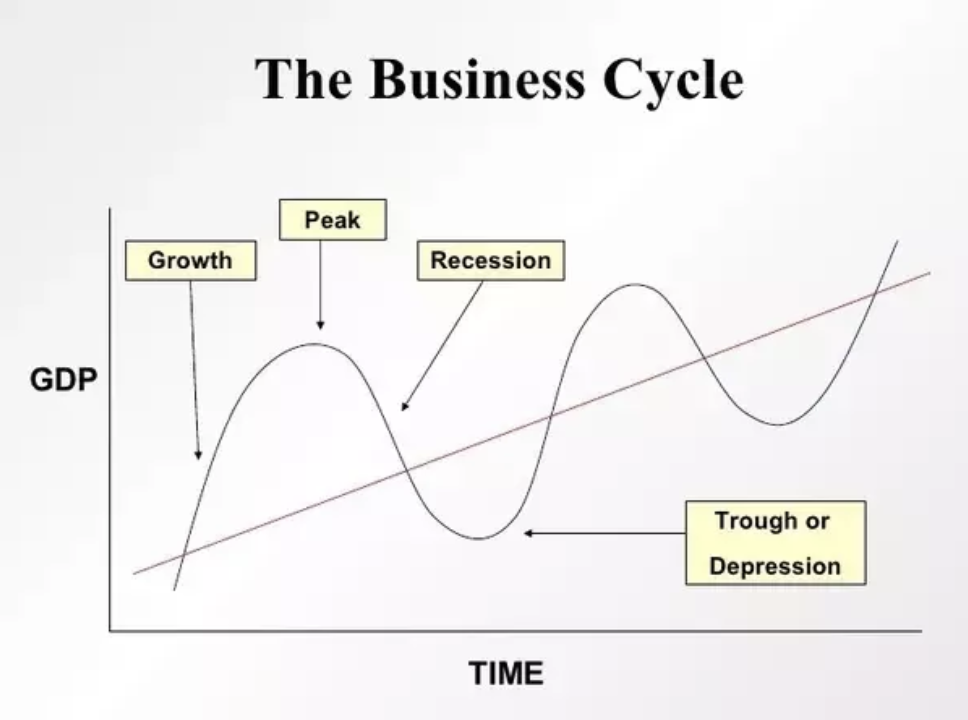
The Business Cycle
Growth: 7-10yrs
Peak: when economic activity reaches its highest point
Recession: (6months- 2 years)
Trough/Depression: 3 years +
Peak: when economic activity reaches its highest point
Recession: (6months- 2 years)
Trough/Depression: 3 years +
14
New cards
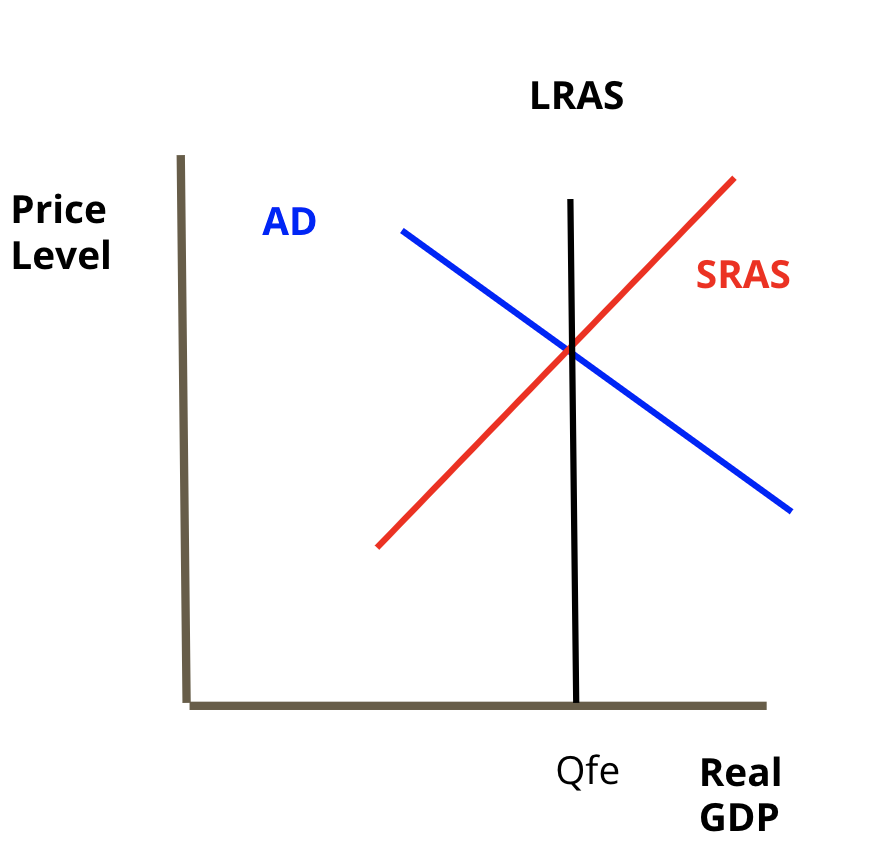
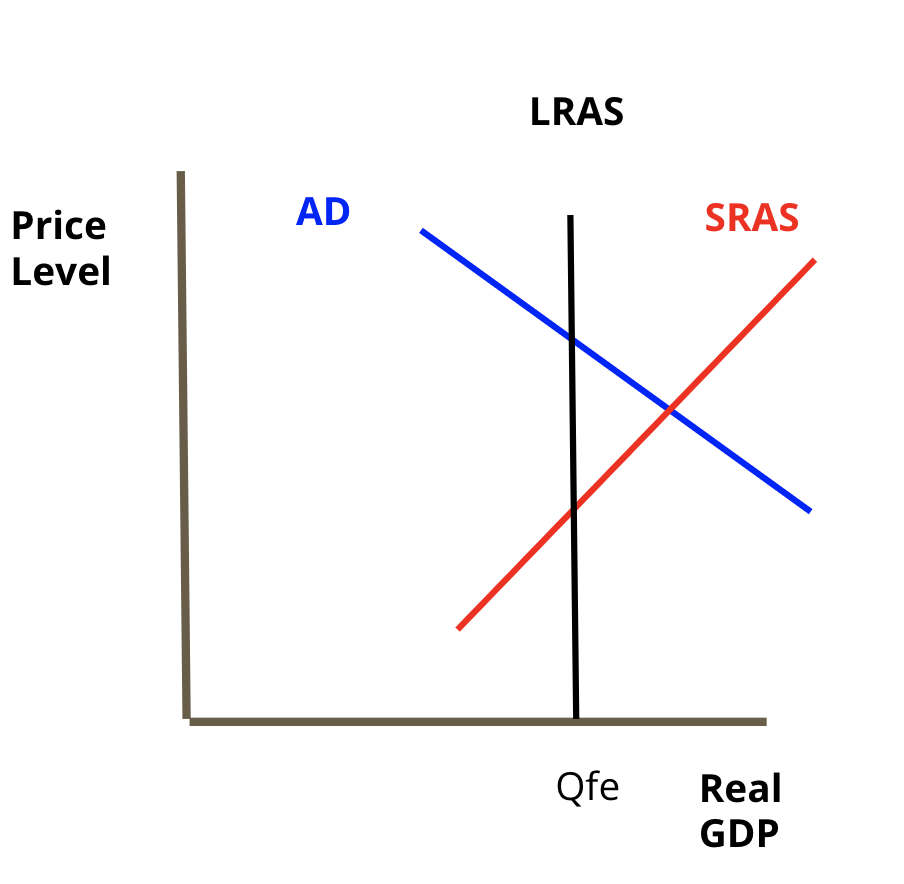
Equilibrium
When AD and SRAS ==cross== at the LRAS for macroeconomics crosses at its LRAS.
* This means we are at our natural rate of output and at full employment, both good economic indicators.
* This means we are at our natural rate of output and at full employment, both good economic indicators.
15
New cards
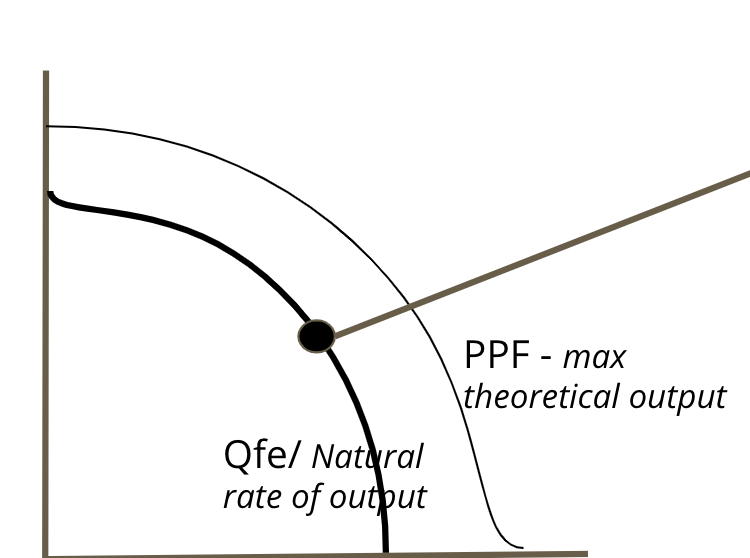
Equilibrium on PPC Curve
When we are at a natural rate of output
16
New cards
Recessionary Gap on the PPC Curve
We are BELOW are natural rate of output
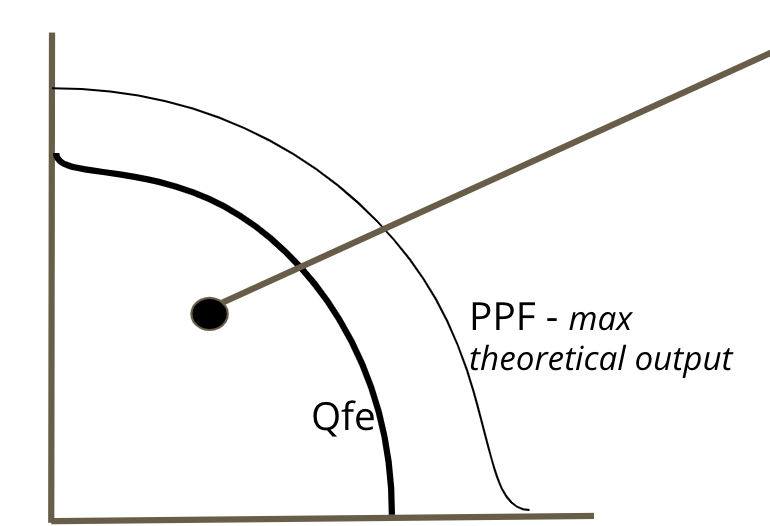
17
New cards
Inflationary Gap
when AD and SRAS are on the ==right== side of LRAS.
* we are experiencing higher inflation (beyond 3%) leading to price increases.
* very high consumer spending, and very less unemployment causing wages to rise.
* we are experiencing higher inflation (beyond 3%) leading to price increases.
* very high consumer spending, and very less unemployment causing wages to rise.
18
New cards
Inflationary Gap on the PPC Curve
When we are ==beyond== our natural rate of output (QFE).
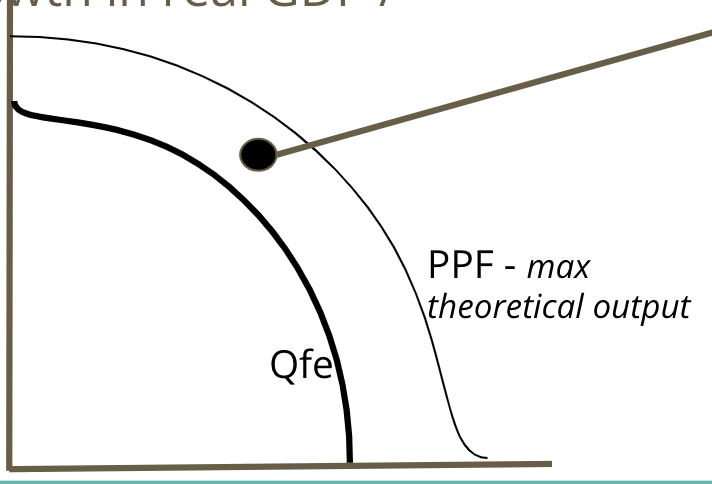
19
New cards
Fiscal Policy
the use of government taxation and spending to alter macroeconomics outcomes.
20
New cards
Spending (direct) affects
Government Spending (G)
21
New cards
Taxation (indirect) affects
Consumer Spending and Investments (C+I)
22
New cards
Expansionary Policy
when the economy is in a recessionary gap and we want to speed up GDP.
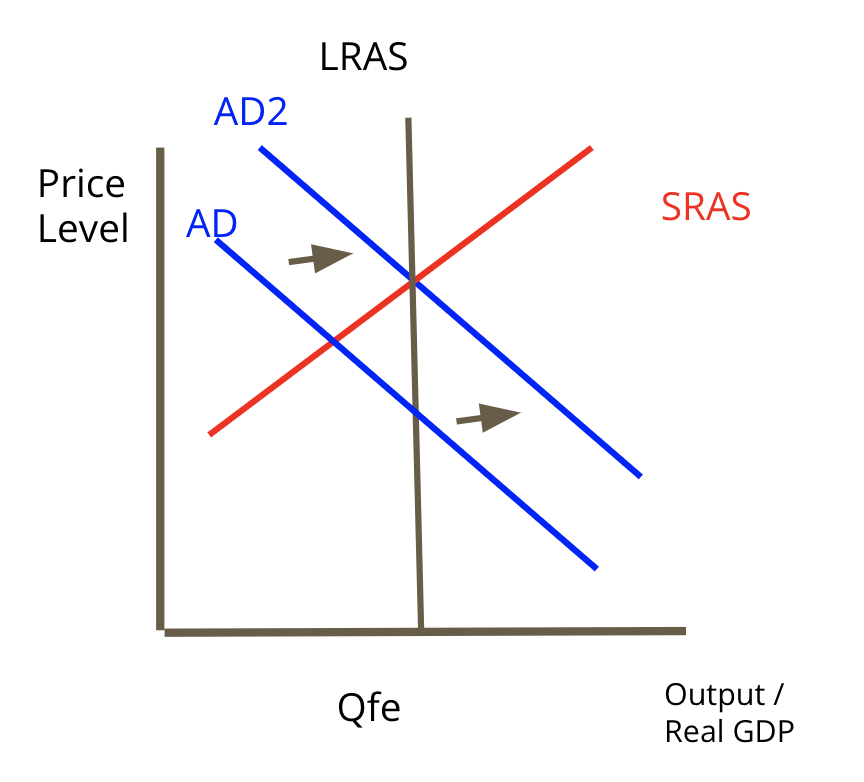
23
New cards
What happens when we use Expansionary fiscal policy?
Government Spending goes up and lower taxes.
Decrease Taxes:
* sales
* income
Increase Government Spending:
* health
* education
* Infrastructure
Decrease Taxes:
* sales
* income
Increase Government Spending:
* health
* education
* Infrastructure
24
New cards
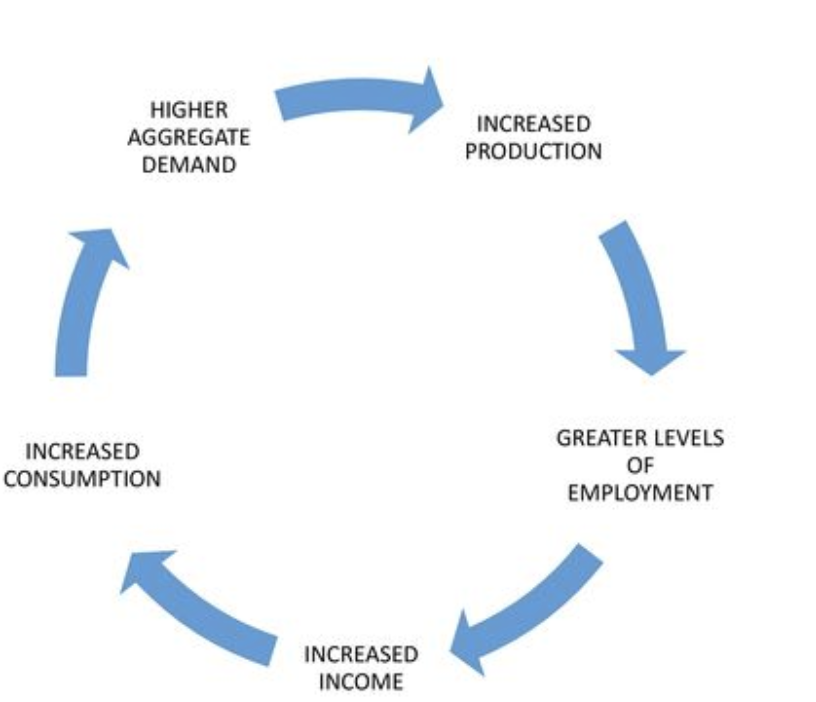
The prosperity Cycle
1. higher aggregate demand
2. increased production
3. greater levels of employment
4. increased income
5. increased consumption
25
New cards
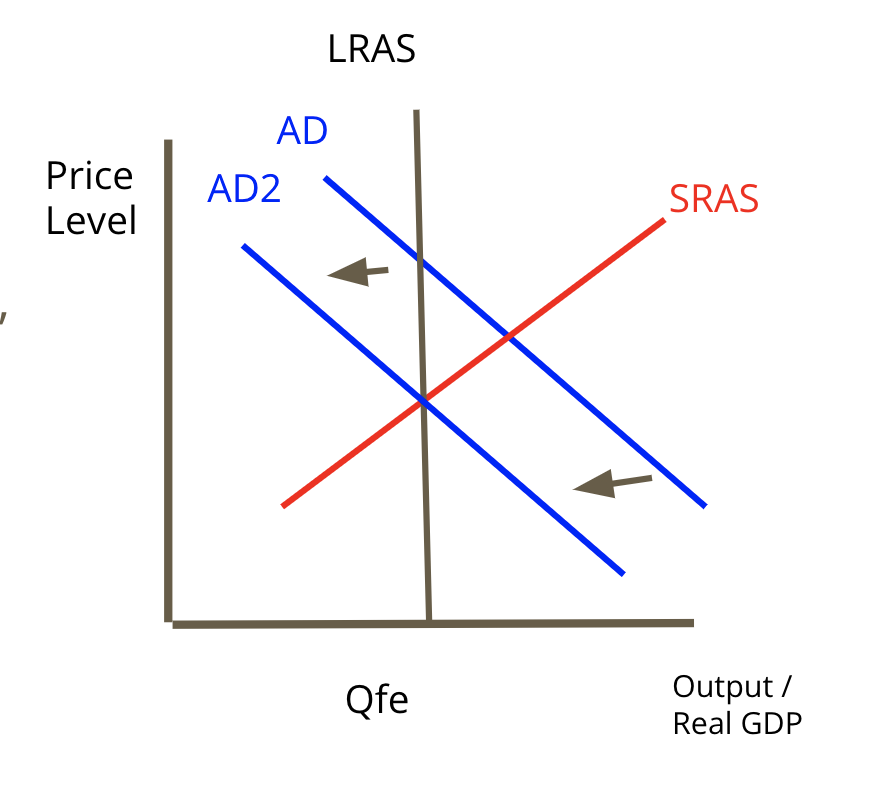
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
when the economy is in a inflationary gap, we want to slow down GDP.
26
New cards
What happens when we use Contractionary Fiscal Policy?
Government Spending goes down and increases taxes.
Increase Taxes:
* sales
* income
Decrease Government Spending:
* health
* education
* Infrastructure
Increase Taxes:
* sales
* income
Decrease Government Spending:
* health
* education
* Infrastructure
27
New cards
MPC
Marginal Propensity to Consume (express as %)
* the higher the MPC, the better for the economic growth
* the higher the MPC, the better for the economic growth
28
New cards
MPS
Marginal Propensity to Save (express as %)
29
New cards
Recognition Lag
hard to see the changes as GDP data is only reported monthly and quarterly.
30
New cards
Decision Lag
slow to create or change a fiscal policy.
31
New cards
Implementation Lag
slow to actually roll out the new policy, hand out the new money, ect.
32
New cards
Impact Lag
takes time to see if the policy you created actually worked.
33
New cards
The multiplier effect
an effect where a change in government spending cause a larger change in GDP.
34
New cards
The Bank of Canada (BOC)
Is the nation’s central bank. Its principal role is to promote the economic and financial welfare of Canada.
* The BOC provides banking services to the federal government
* The BOC provides banking services to the federal government
35
New cards
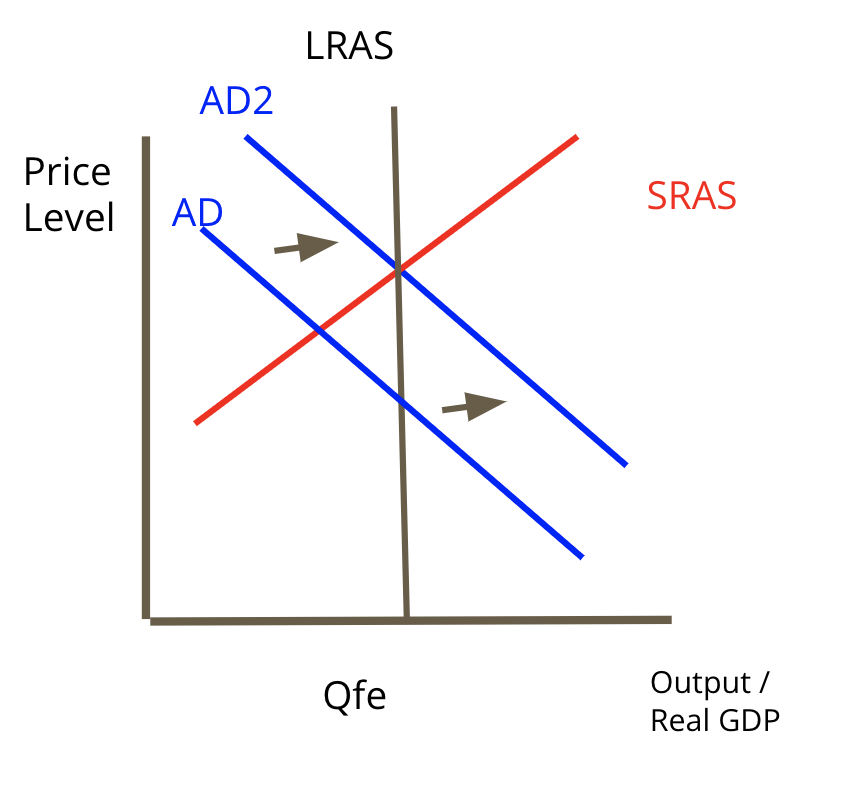
Easy/Loose money policy
the goal is to speed up economic growth.
* you are trying to create jobs by increasing the money supply (lower interest rates)
* shift AD right
* you are trying to create jobs by increasing the money supply (lower interest rates)
* shift AD right
36
New cards
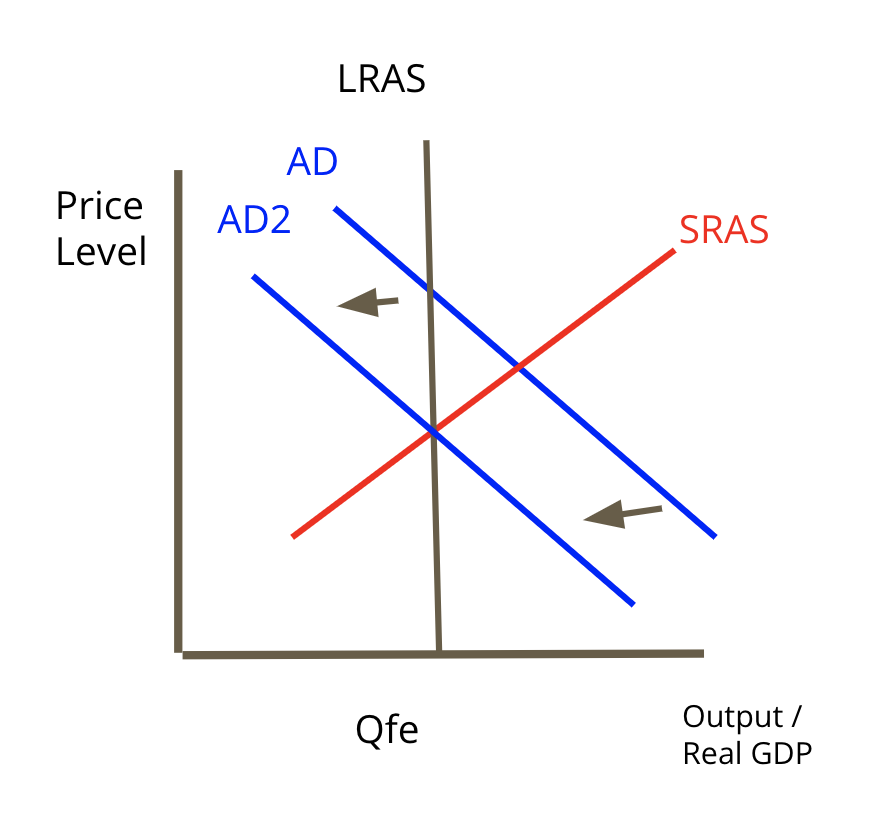
Tight Money Policy
the goal is to slow down the economy in order to fight inflation or prevent the economy from collapsing. The BOC will reduce money supply
shift AD left
shift AD left
37
New cards
Bank Rate
rate of interest that the BOC charges charted banks and other financial institutions.
38
New cards
Overnight Rate
the rate at which major financial institutions borrow and lend one-day (overnight) funds to and from each other
39
New cards
Prime Rate
the interest rate commercial banks charge their most credit-worthy business customers
40
New cards
Moral Persuassion
basically asking people nice (trying to encourage and persuade them)
41
New cards
CPI (consumer price index)
a way to measure inflation
42
New cards
Role of Bank of Canada
controls the money supply:
* how much money is in the economy (useful for controlling inflation)
setting the interest rate (bank rate):
* at which it will loan funds to chartered banks and other banking institutions
currency
* issuing new bills, printing new money and destroying old money.
* how much money is in the economy (useful for controlling inflation)
setting the interest rate (bank rate):
* at which it will loan funds to chartered banks and other banking institutions
currency
* issuing new bills, printing new money and destroying old money.
43
New cards
Money Supply
controlling how much money is in the economy
44
New cards
Which tool is uses to control the price of money directly?
Interest Rates