BIOS-150: Human Body Systems & Nutrients Review for Exam 2 Questions with expert curated solutions with 100% Accuracy (PASSED)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is the smallest unit of an element?
Atom
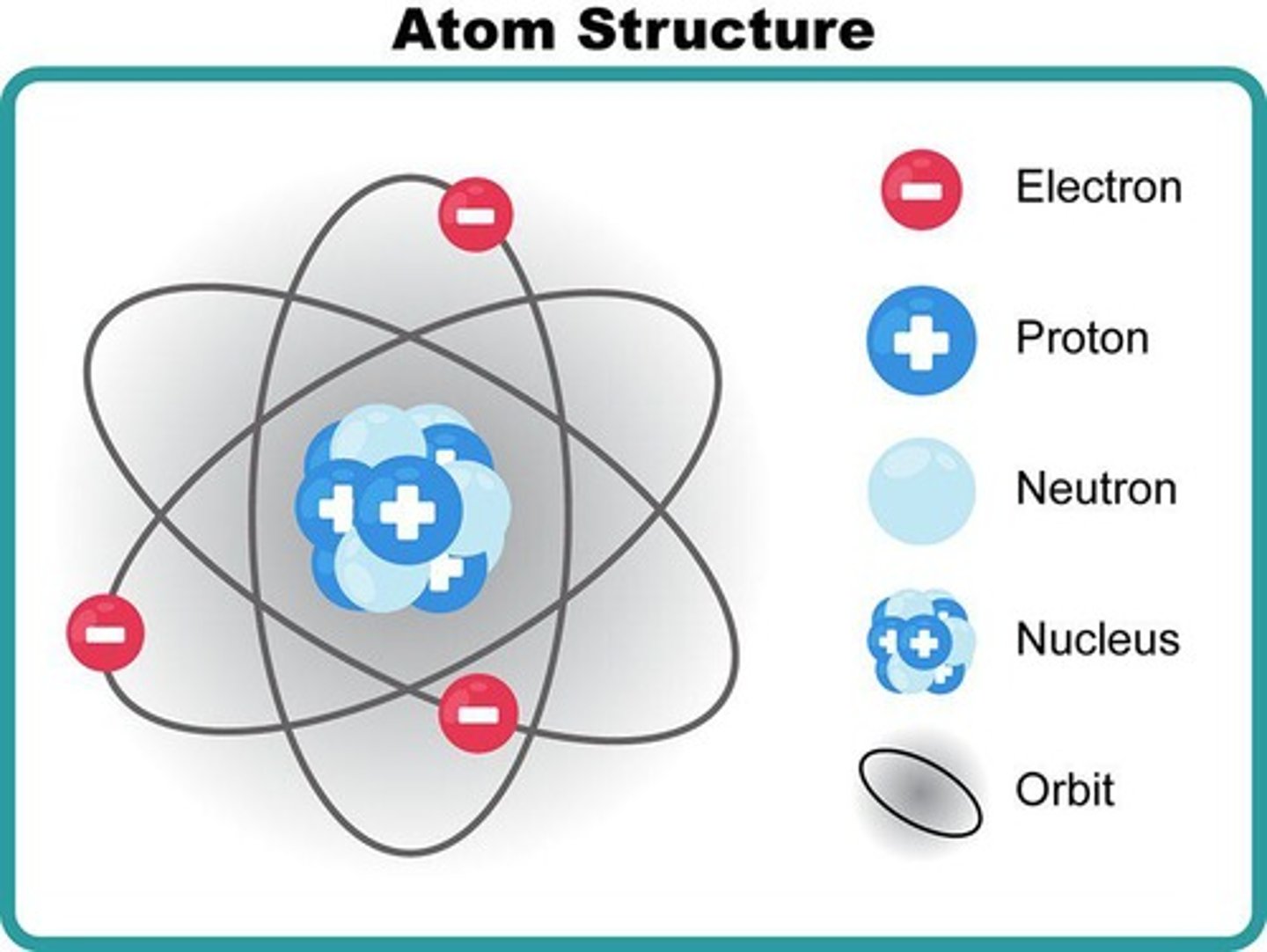
What are molecules?
When two or more atoms bond together.
What are the building blocks of structures and substances in our body?
Molecules
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
What are electrolytes?
Ions dissolved in water or body fluids.
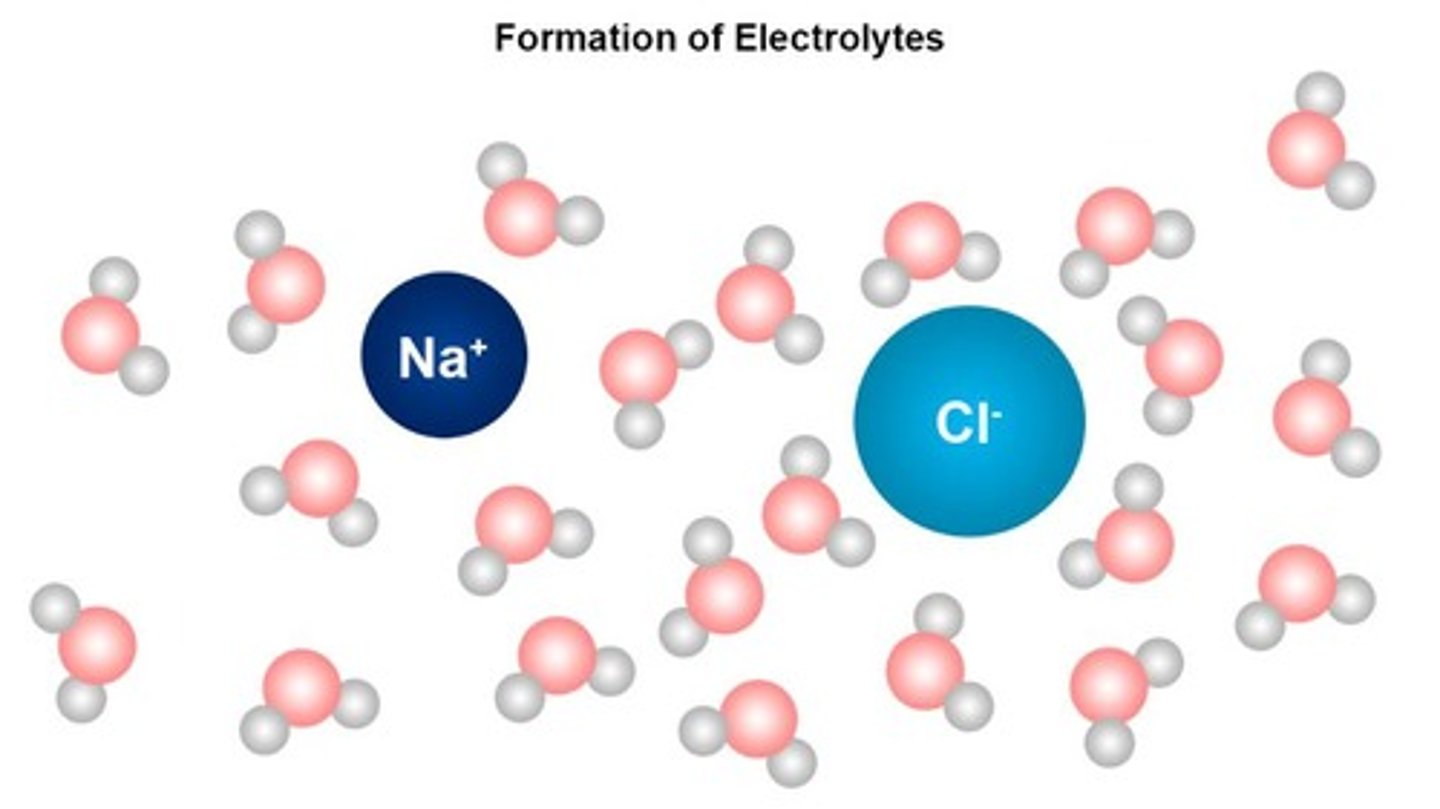
What happens to sodium chloride in water?
It separates into sodium ions and chloride ions.
What are reactants in a chemical reaction?
The starting materials of a chemical reaction.
What are products in a chemical reaction?
The outcomes of a chemical reaction.
What are synthesis reactions?
Chemical reactions where smaller molecules combine to form larger ones.
What are decomposition reactions?
Chemical reactions where a larger molecule breaks down into two or more smaller parts.
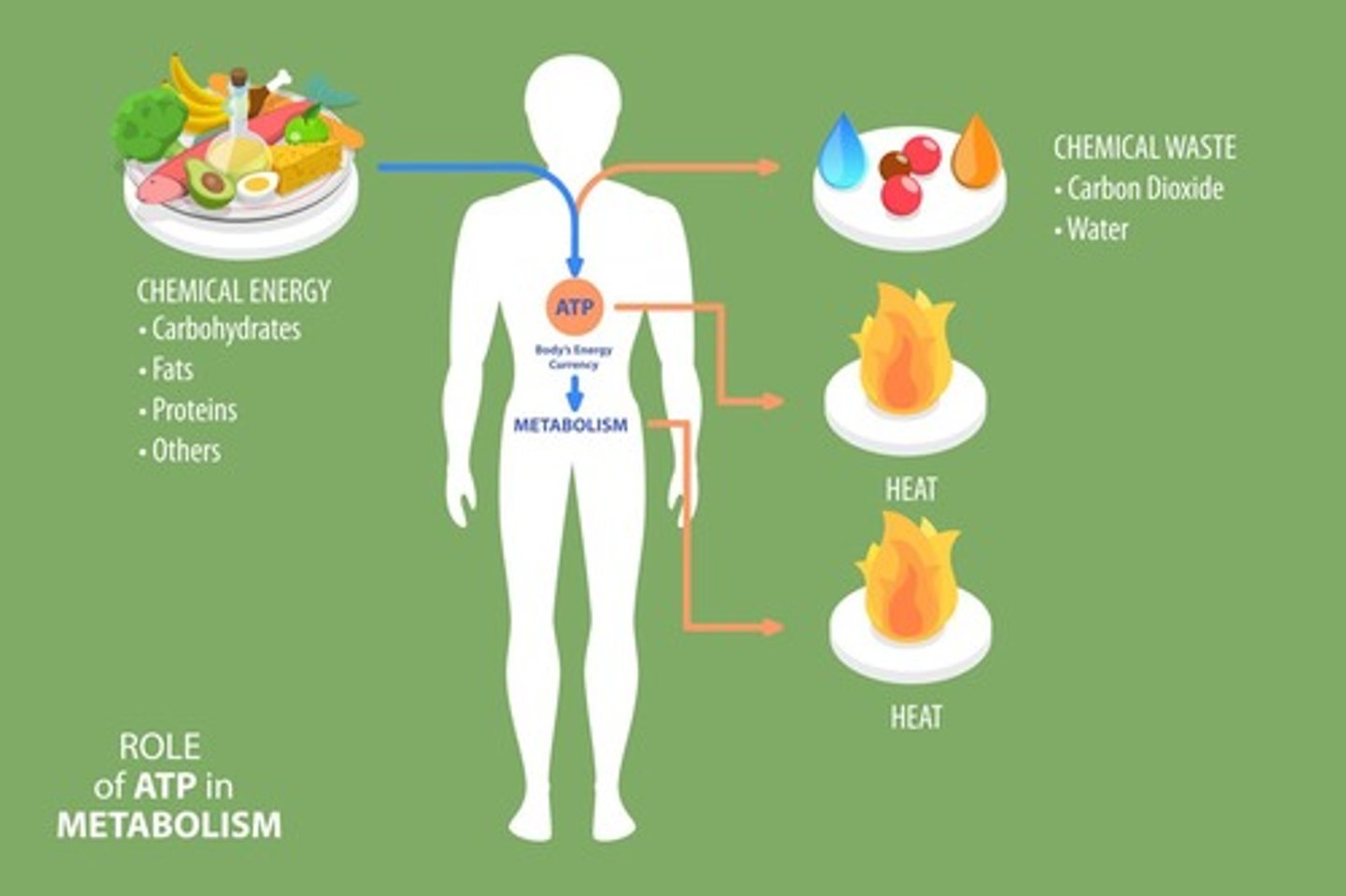
What is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
The energy currency of the cell.
What are the four essential macromolecules in the human body?
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats (lipids), and nucleic acids.
What is the role of carbohydrates in the body?
They are the body's preferred source of energy.
What do simple carbohydrates lead to?
Quick energy spikes.
What do complex carbohydrates offer?
More sustained energy.
What are proteins essential for?
Building muscle, repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and creating enzymes and hormones.

What are proteins made of?
Amino acids.
What are the essential functions of fats?
Long-term energy source, fat-soluble vitamin absorption, organ protection, and hormone production.
What is the role of nucleic acids?
Storing and transmitting genetic information.

What does DNA do?
Stores genetic information used for growth, development, and reproduction.
What does RNA do?
Reads and interprets the DNA code to help produce proteins.
What is metabolism?
The chemical processes that occur within our bodies to convert food into energy.
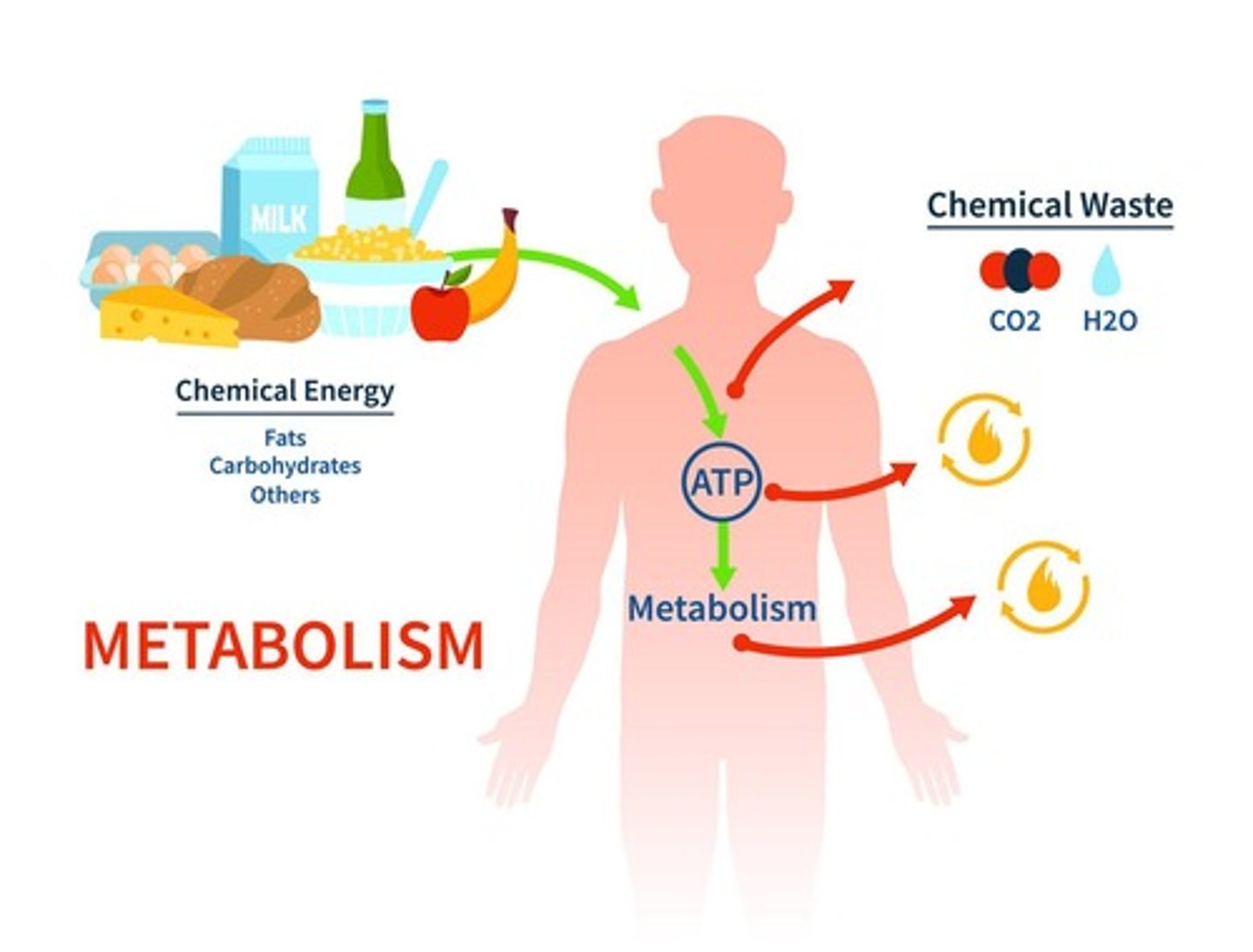
What is cellular respiration?
A specific process inside of the cell that turns food into energy (ATP).
What are the four major stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, Pyruvate Oxidation, Krebs Cycle, and Electron Transport Chain.
What is Type 1 diabetes?
A condition where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
What is Type 2 diabetes?
A condition where the body doesn't respond well to insulin and may not make enough insulin over time.
What is hypothyroidism?
A condition involving an underactive thyroid gland which slows one's metabolic rate.
What is metabolic syndrome?
A cluster of health problems including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
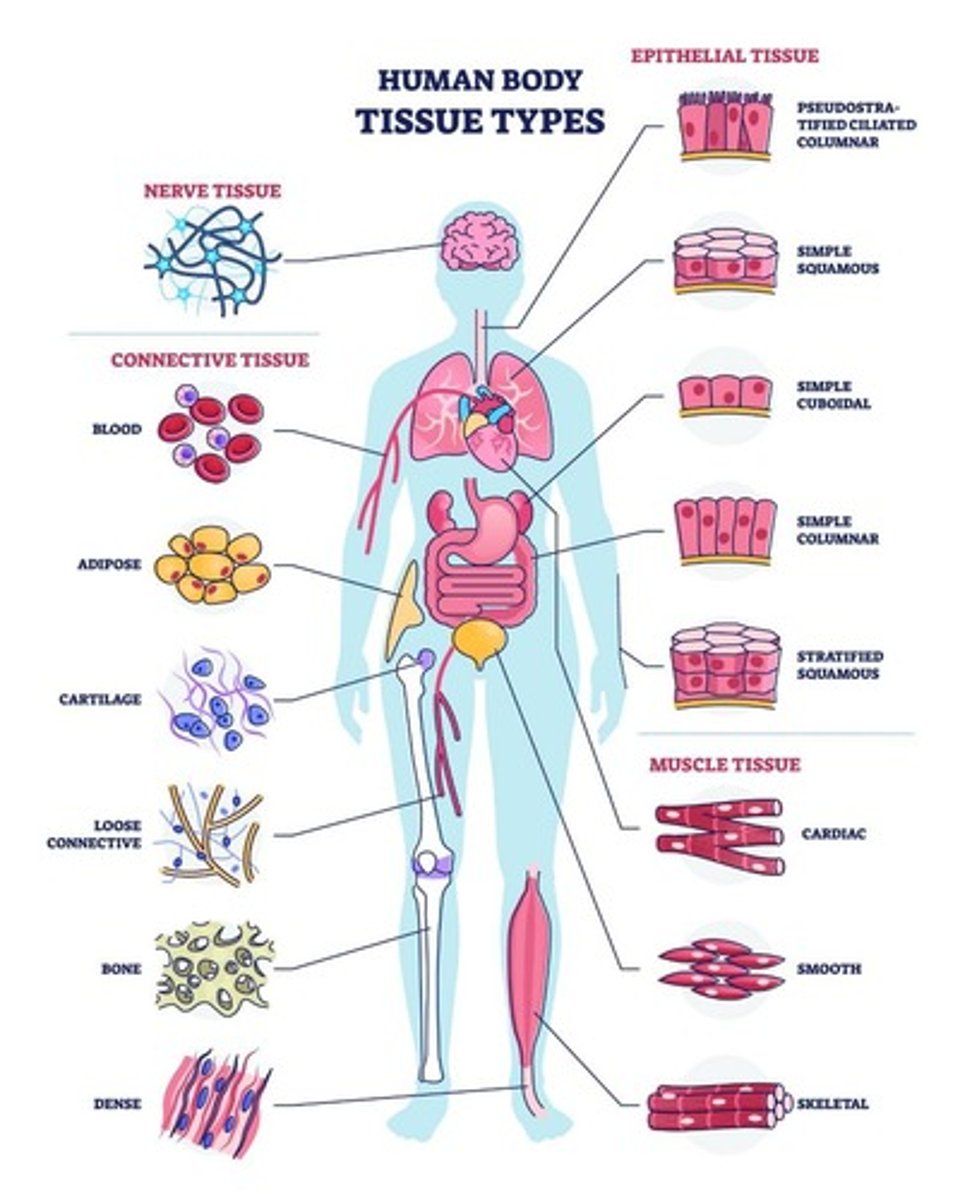
What are the four primary tissue types in the human body?
Epithelial Tissue, Connective Tissue, Muscle Tissue, Nervous Tissue.
What is histology?
The branch of biology and medicine that focuses on the microscopic study of the four main tissue types.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Protective barrier, lines organs, plays key roles in absorption, secretion, and filtration.
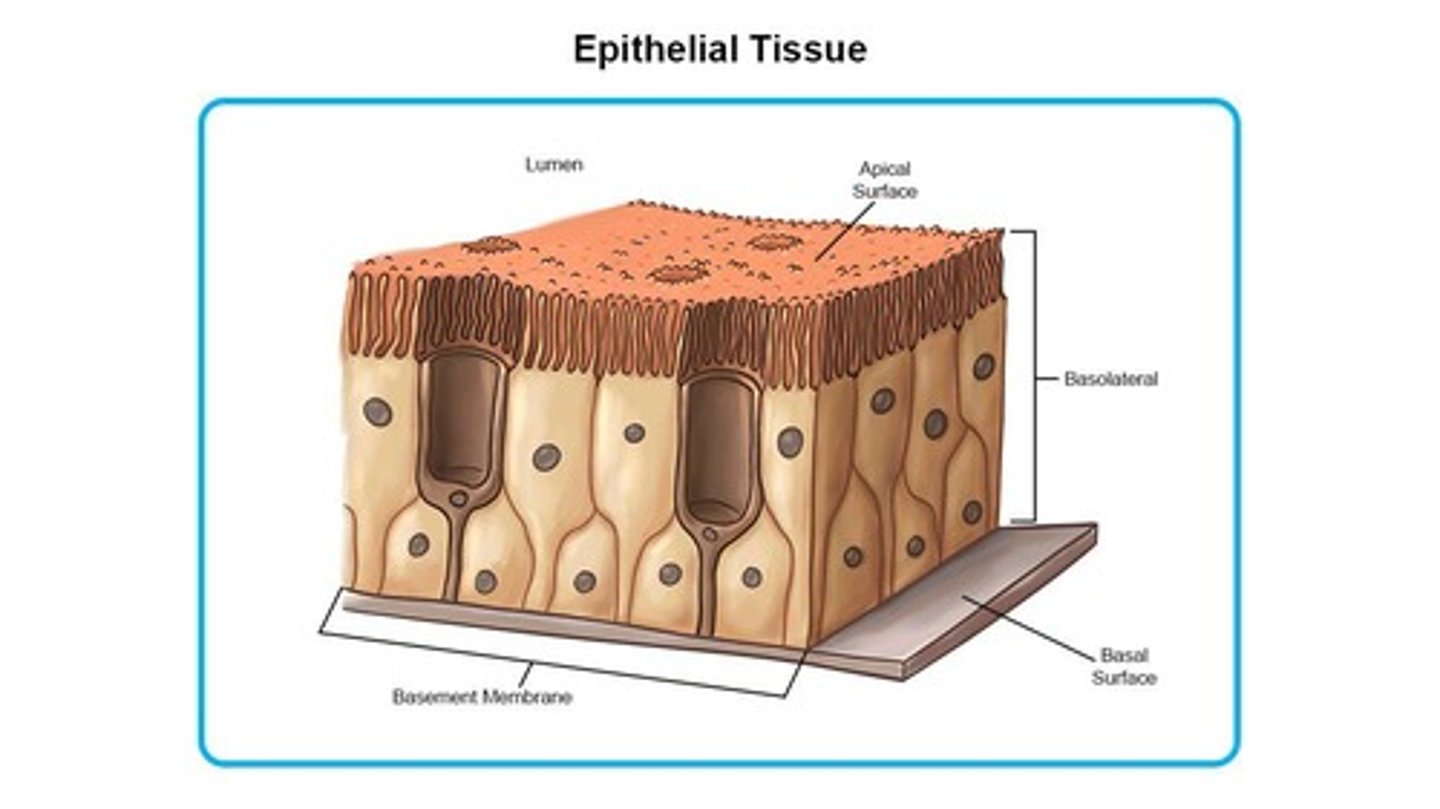
What are the classifications of epithelial tissue based on the number of layers?
Simple Epithelium, Stratified Epithelium, Pseudostratified Epithelium.
What are the cell shapes found in epithelial tissue?
Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar.

What is connective tissue?
Tissue that supports, connects, and protects various structures in the body.
What are the types of connective tissue?
Connective Tissue Proper, Specialized Connective Tissue.
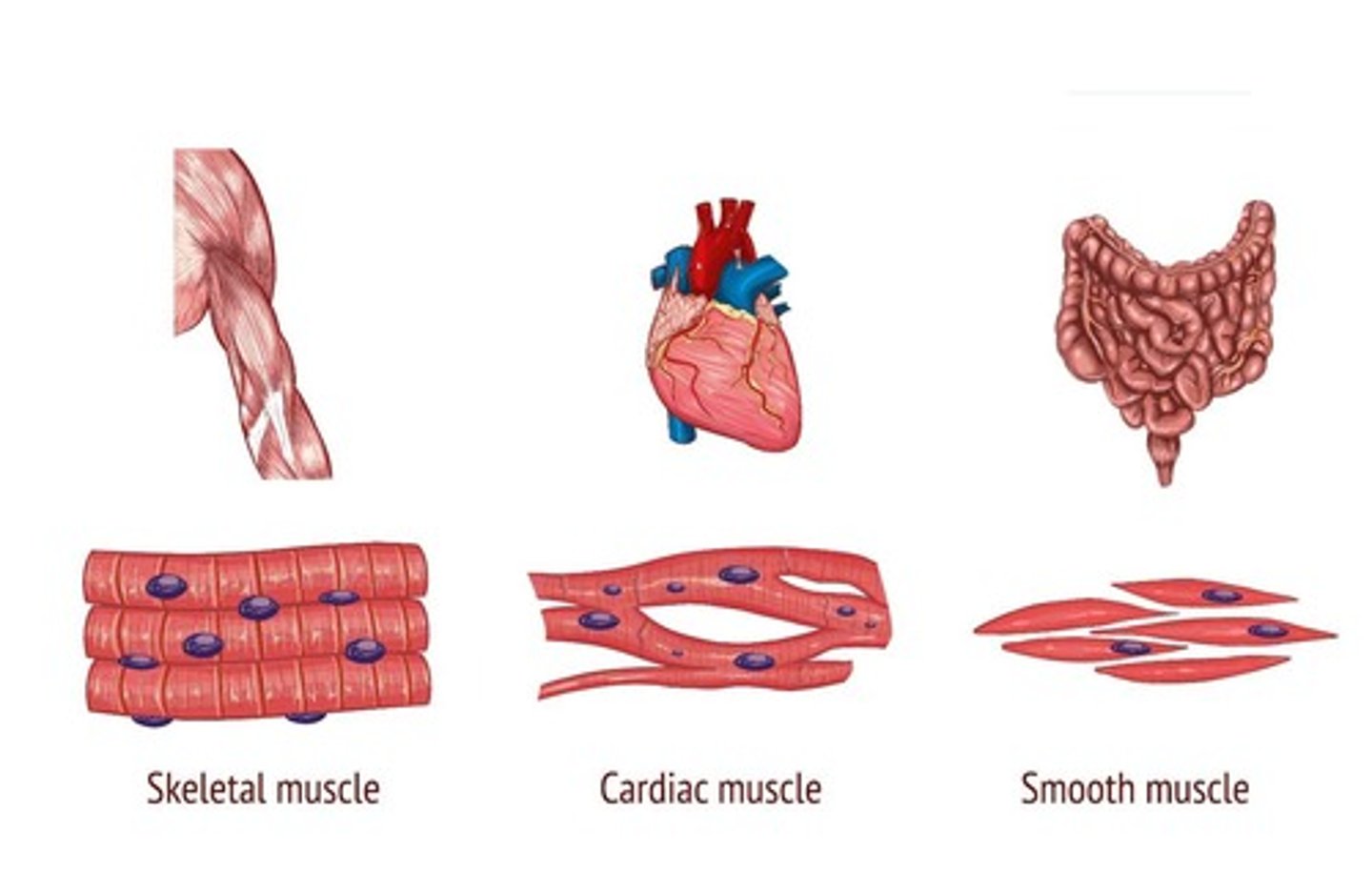
What are the types of muscular tissue?
Skeletal Muscle, Cardiac Muscle, Smooth Muscle.
What is the function of nervous tissue?
Involved in communication, control, and coordination by transmitting electrical impulses.
What are the components of a feedback loop in homeostasis?
Receptor, Control Center, Effector.
What is homeostasis?
The process by which the body maintains a stable internal environment despite external changes.
What is negative feedback?
A mechanism that counteracts deviations from a stable state to restore balance.
What is positive feedback?
A mechanism that amplifies a process rather than reversing it.
What is an example of a negative feedback loop?
Temperature regulation.
What forms when two or more atoms bond together?
Molecule.
What are molecules created from?
Atoms bonding together.
What forms when electrons are gained or lost?
Ions.
What are tissues?
Groups of similar cells.
What are organs composed of?
Multiple tissues working together.
What does sodium chloride separate into when dissolved in water?
Sodium and chloride ions.
What are the starting materials in a chemical reaction called?
Reactants.
What occurs during a decomposition reaction?
A large molecule breaks into smaller parts.
What is the body's main quick energy source?
Carbohydrates.
Which macromolecule stores genetic information?
Nucleic acids.
How do enzymes function?
They speed up chemical reactions.
What is ATP described as?
The energy currency of the cell.
Which tissue type covers organs and lines body cavities?
Epithelial tissue.
Which epithelial cell shape is ideal for diffusion?
Squamous.
What does the control center do in a feedback loop?
Processes information and decides the response.
Which system breaks down food into usable nutrients?
Digestive system.
Which system produces hormones that regulate growth and metabolism?
Endocrine system.
Which system drains excess fluid and supports immunity?
Lymphatic system.
What do negative feedback loops do?
Reverse changes to restore balance.
Which scenarios demonstrate negative feedback?
Sweating when body temperature rises, decreasing heart rate after blood pressure rises, increasing insulin release when blood glucose is high.