Cell Membrane Transport
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Last updated 5:42 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Active Transport
Process that moves materials across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient
Requires energy
Requires energy
2
New cards
Passive Transport
Follows the concentration gradient (materials move from an area of high concentration to low concentration)
Does NOT require energy
Does NOT require energy
3
New cards
Concentration Gradient
When there is a difference in concentration of
molecules on either side of a cell membrane
molecules on either side of a cell membrane

4
New cards
3 types of Passive Transport
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
5
New cards
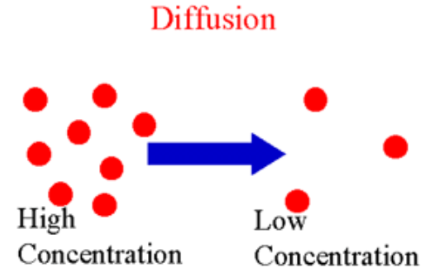
Diffusion
Process in which molecules move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
6
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of molecules across a membrane by carrier proteins
Does not require energy
Does not require energy
7
New cards
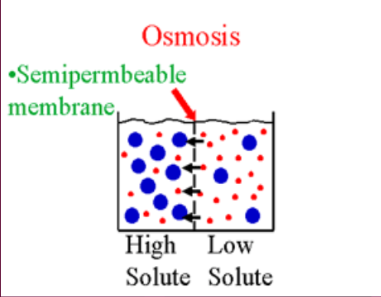
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. Water will move from areas of high concentration of water to areas of lower concentration.
8
New cards
Osmotic Pressure
the force exerted to move water through a membrane
9
New cards
Turgor
the rigidity or stiffness of plants due to the water present in their cells
10
New cards
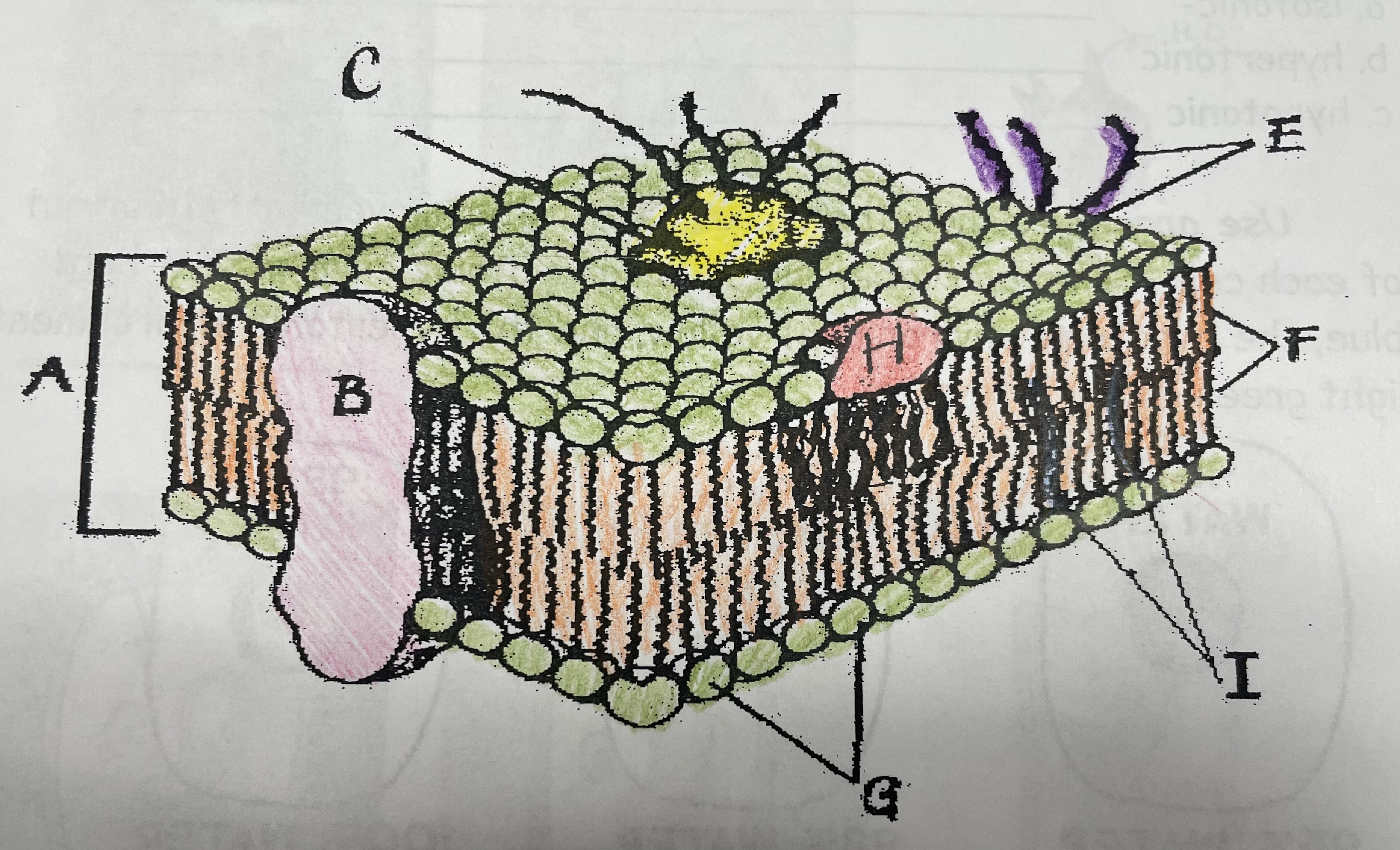
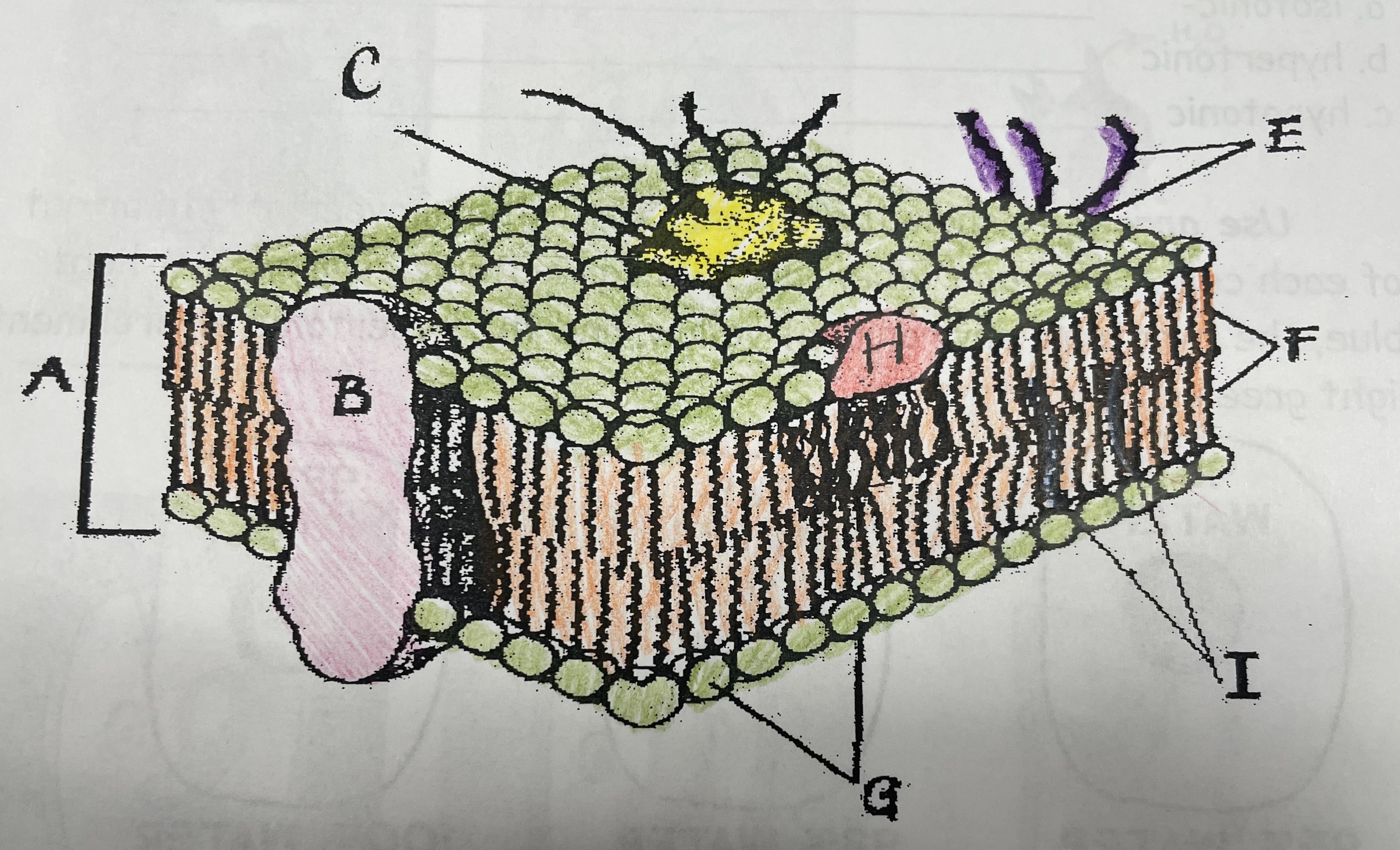
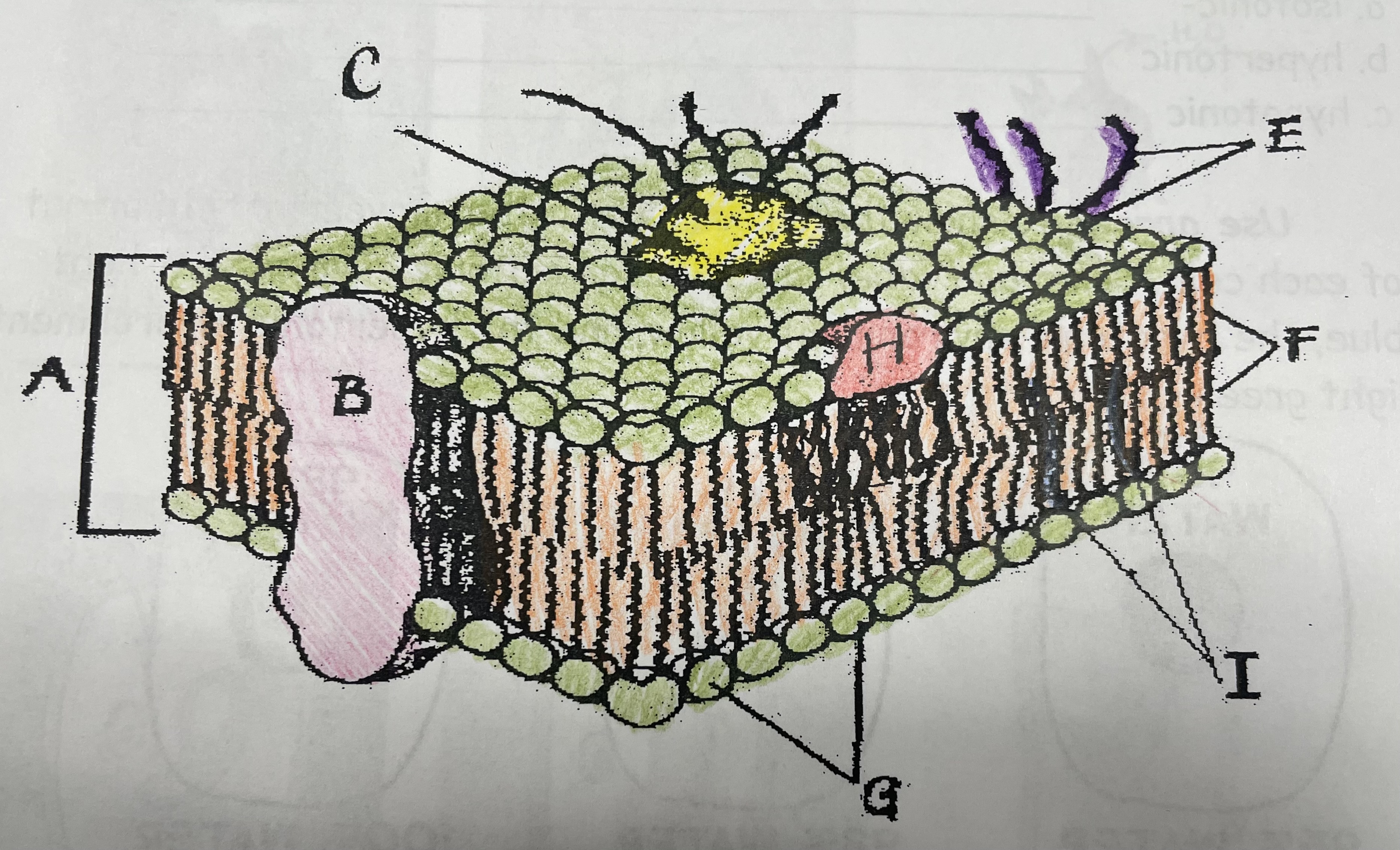
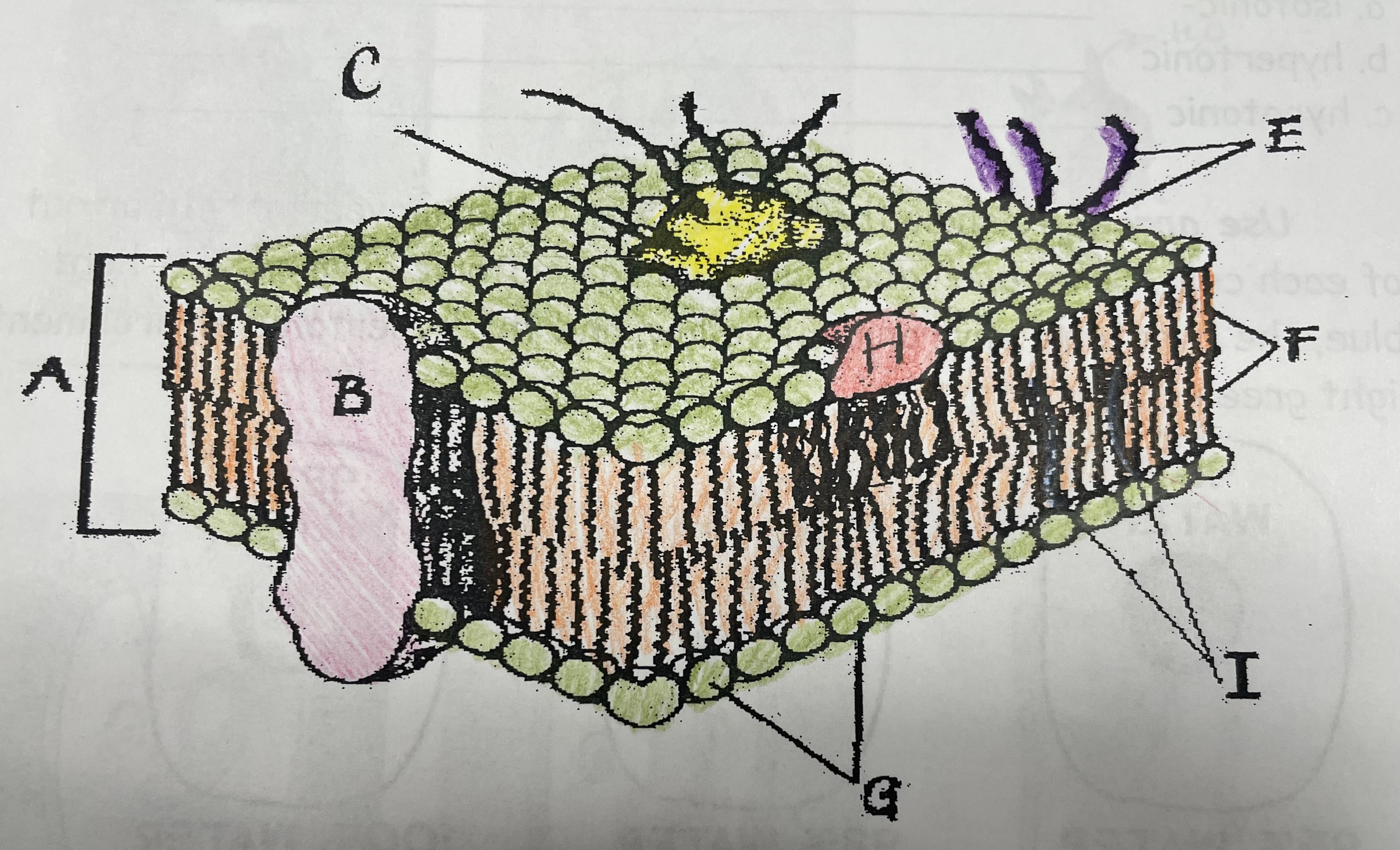
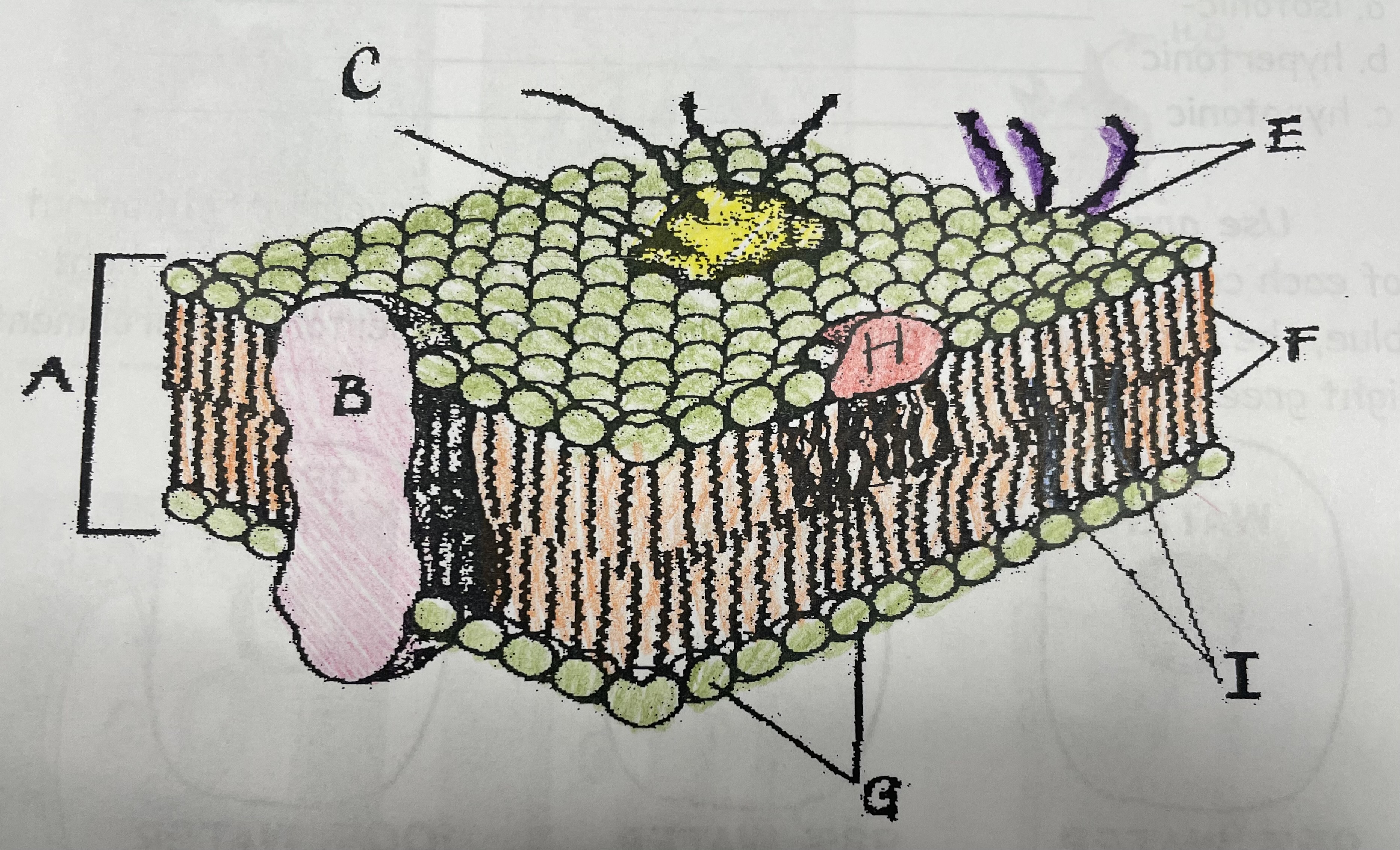
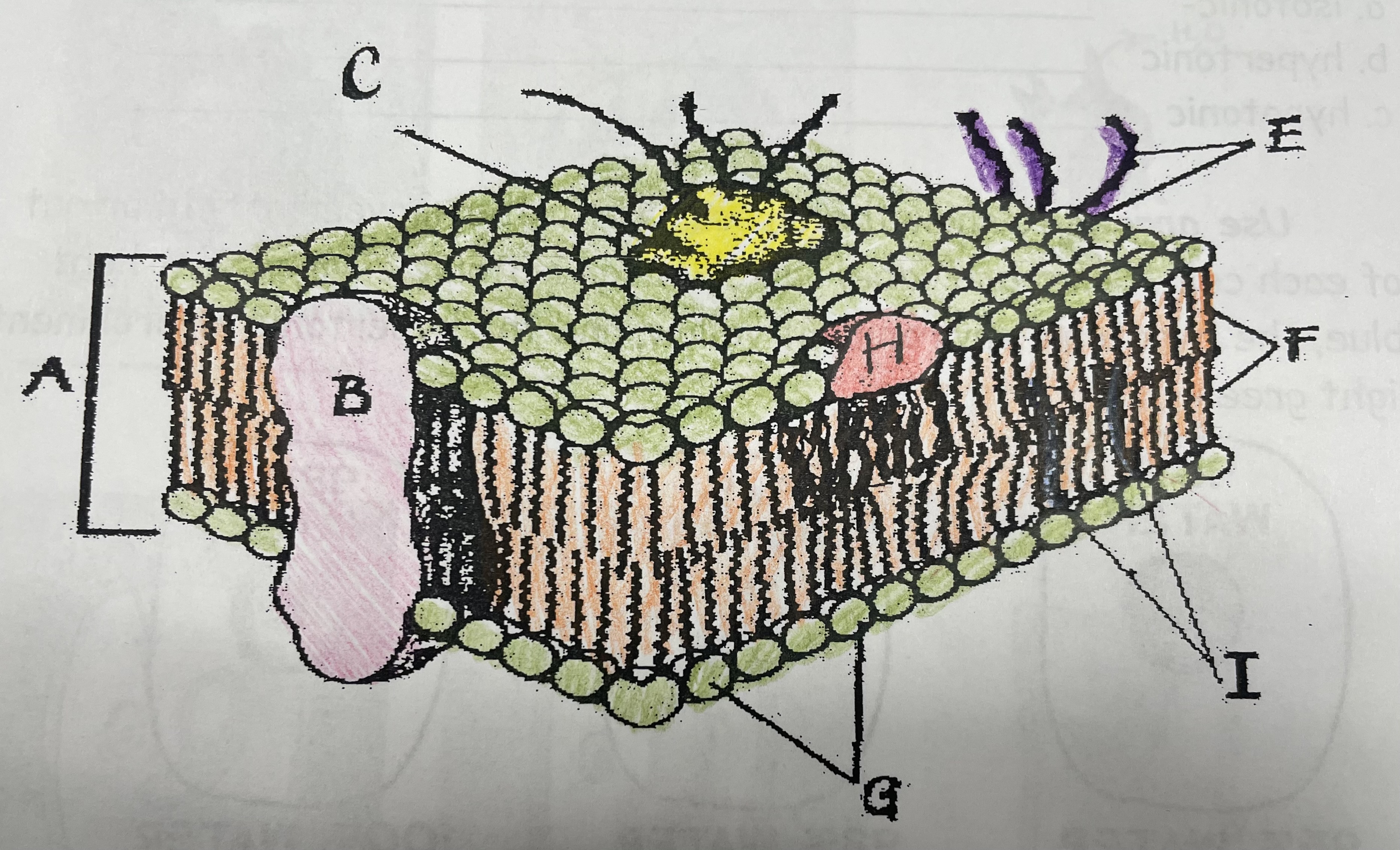
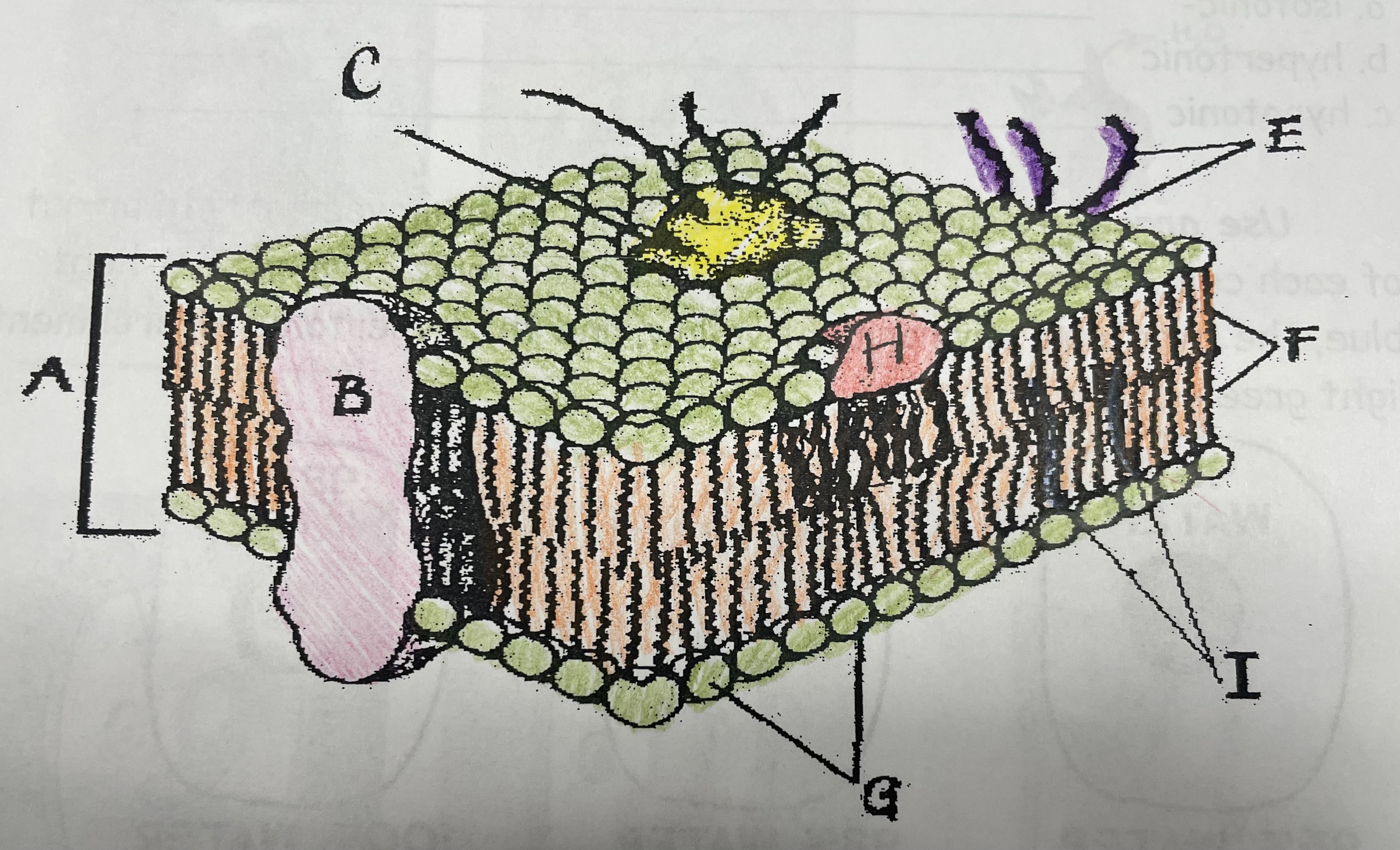
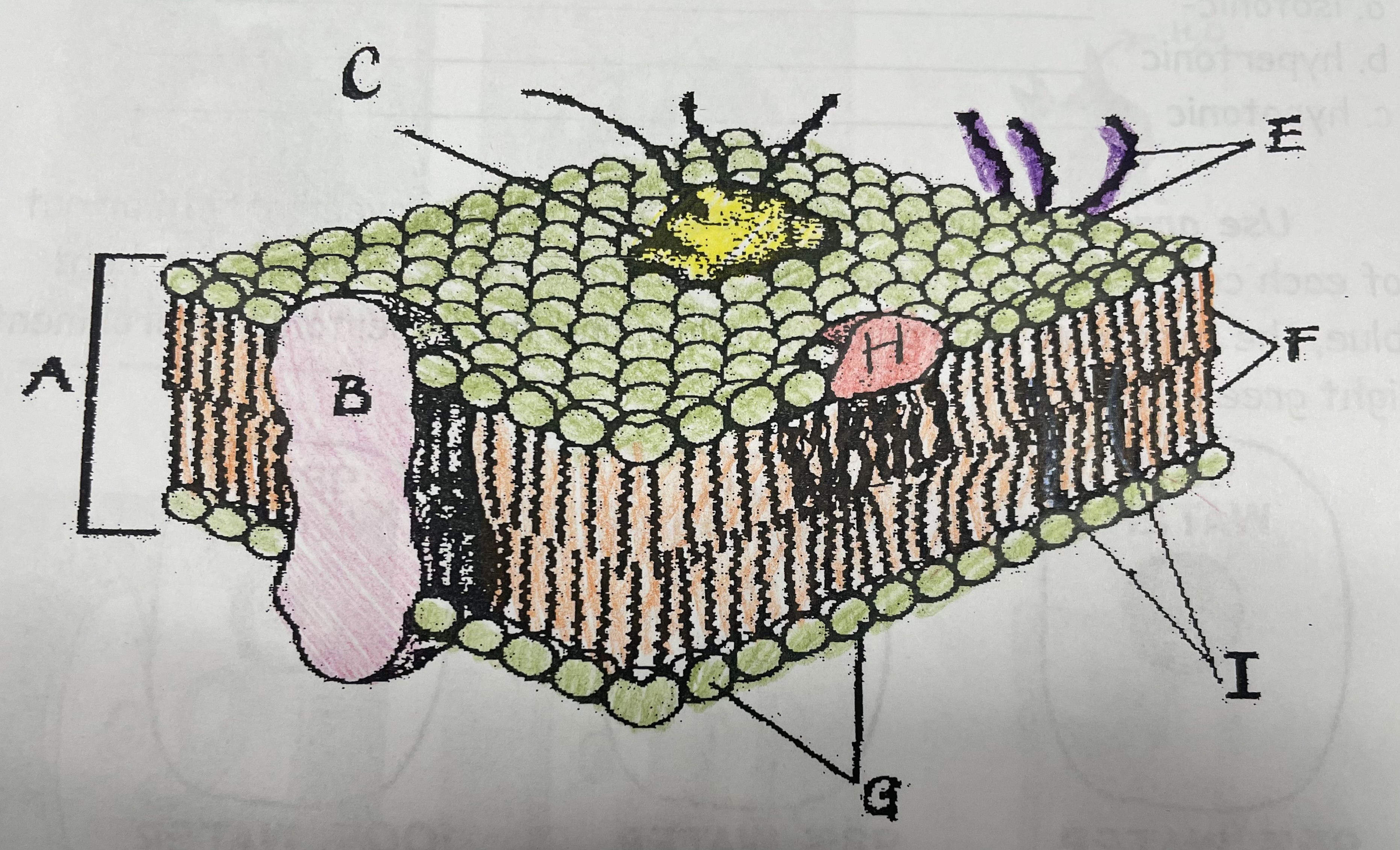
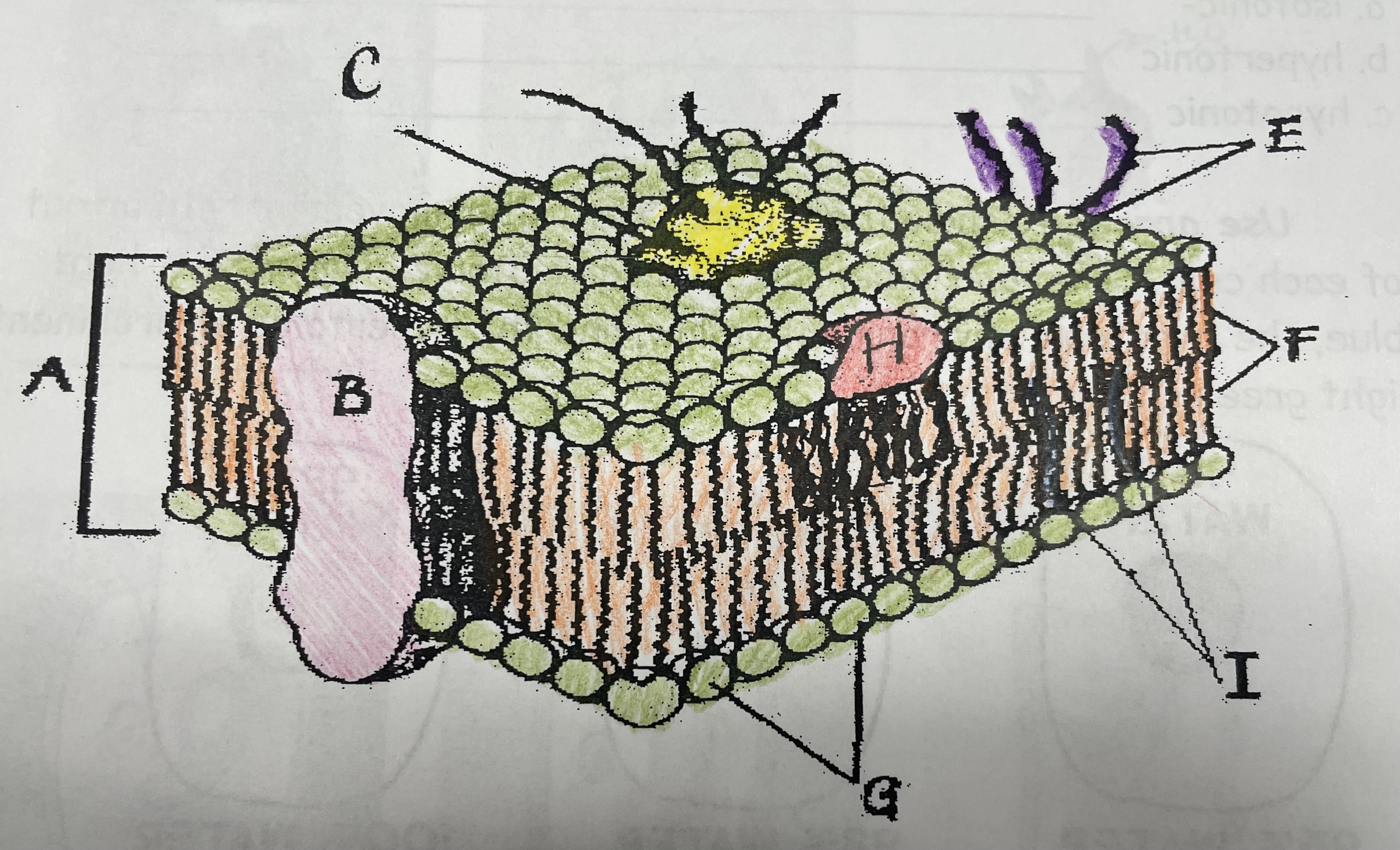
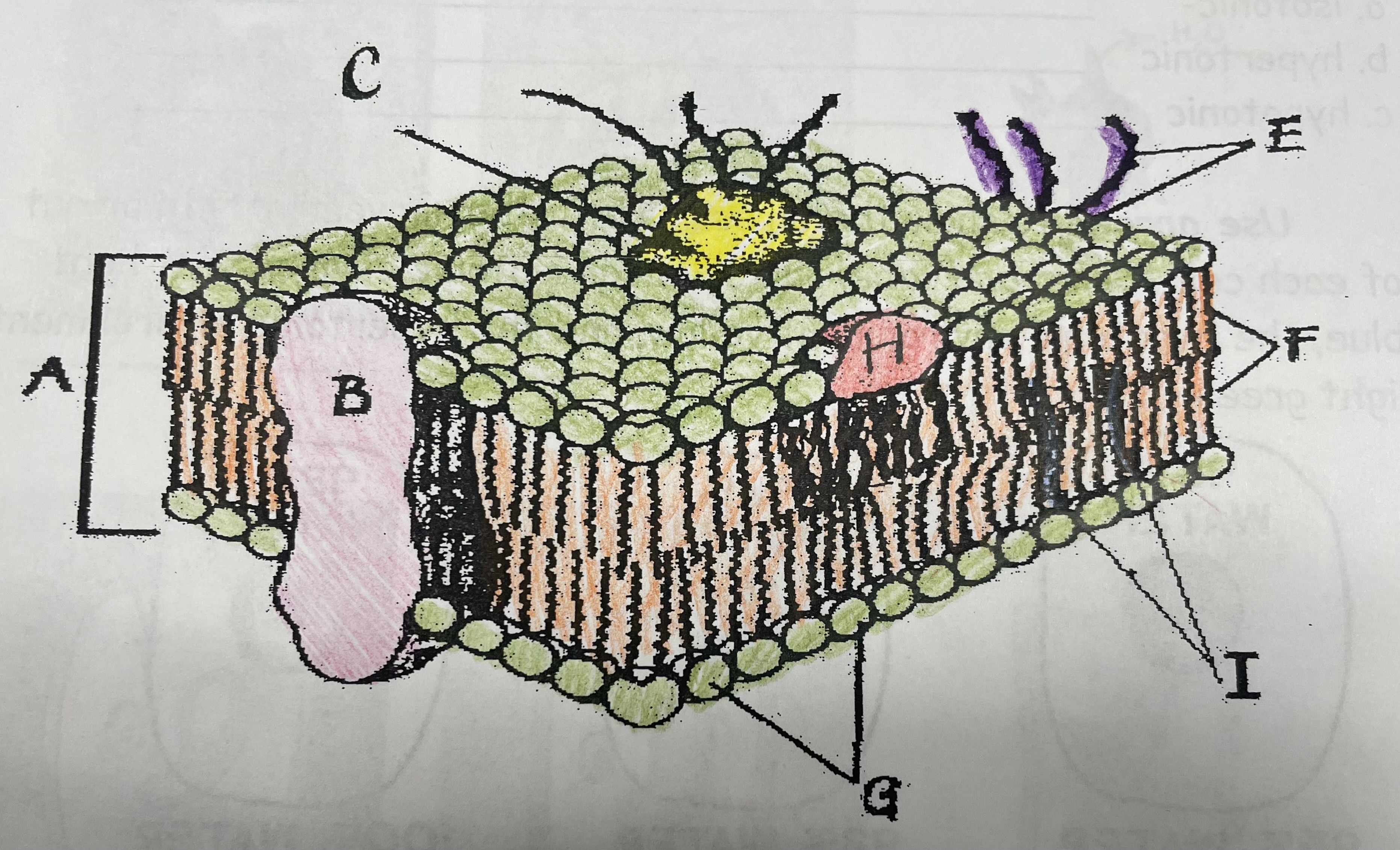
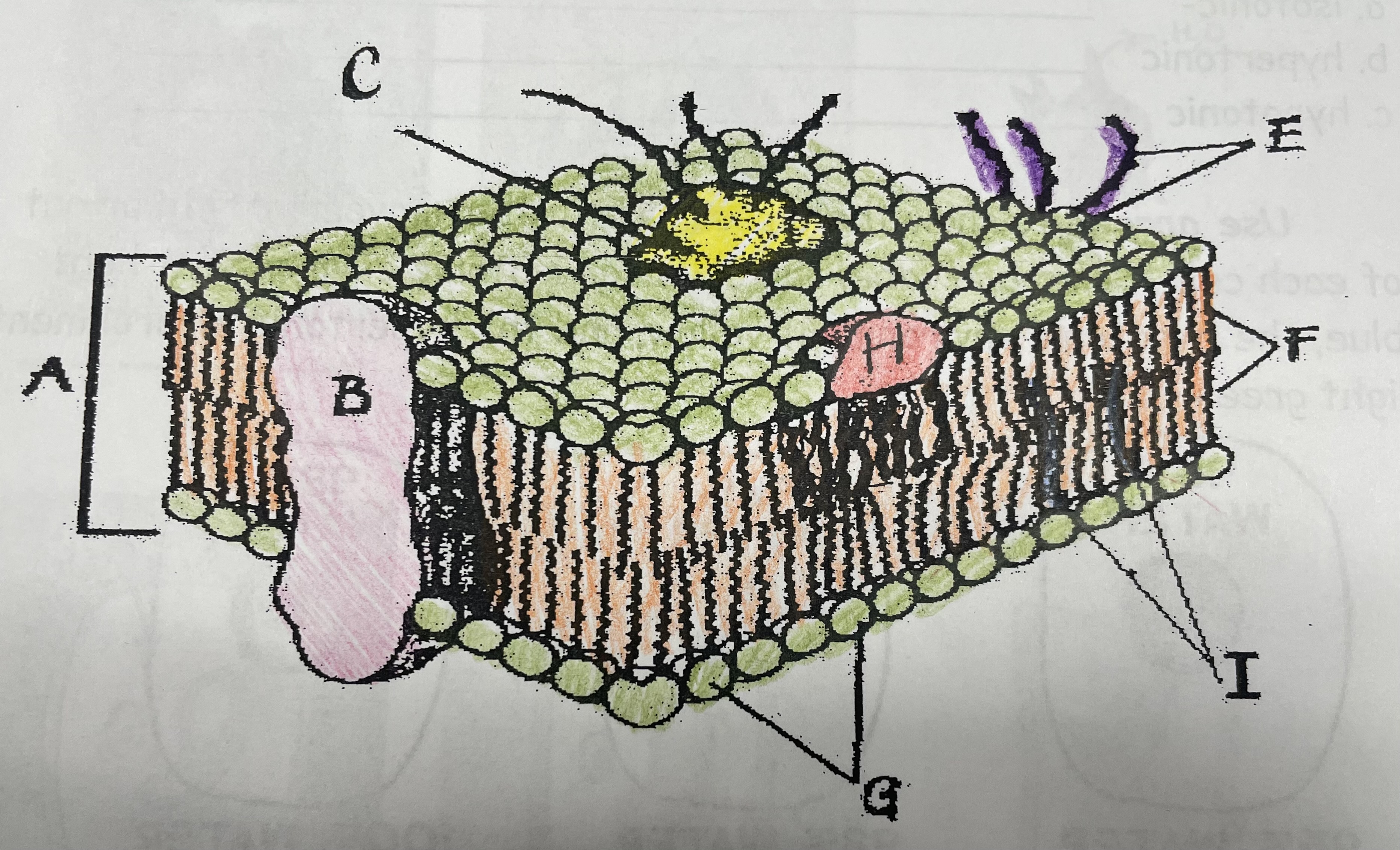
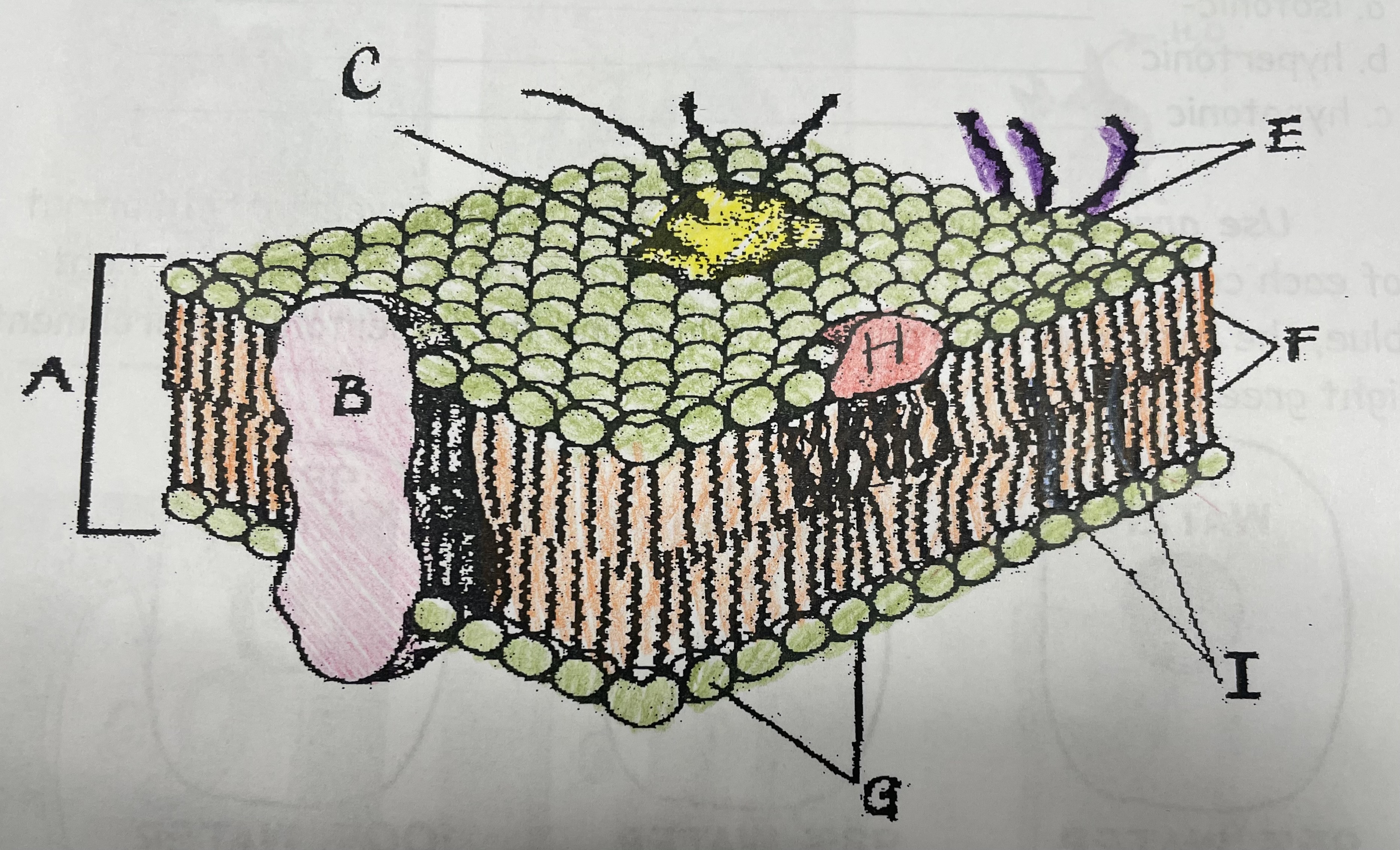
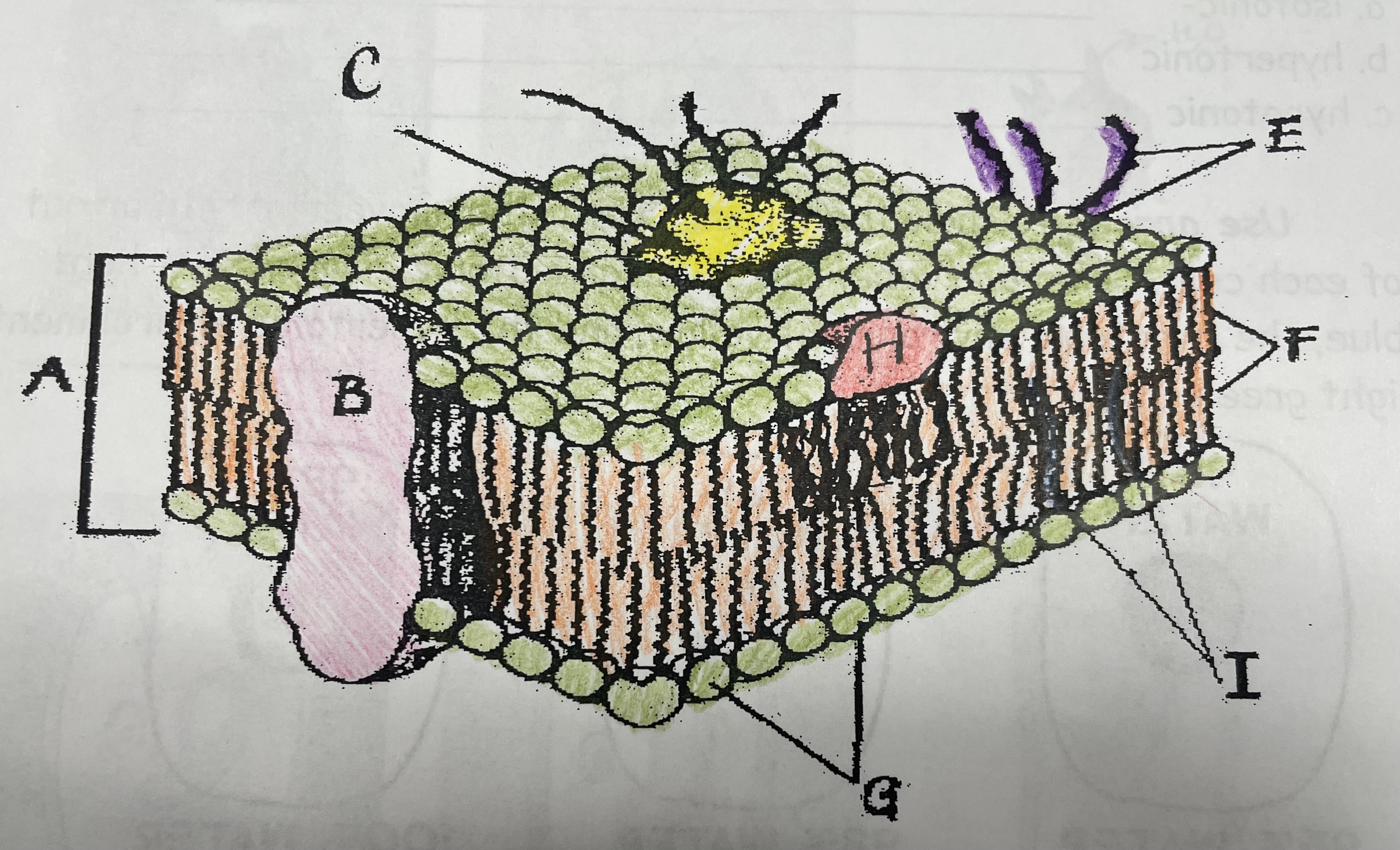
What is A?
Phospholipid bilayer
11
New cards
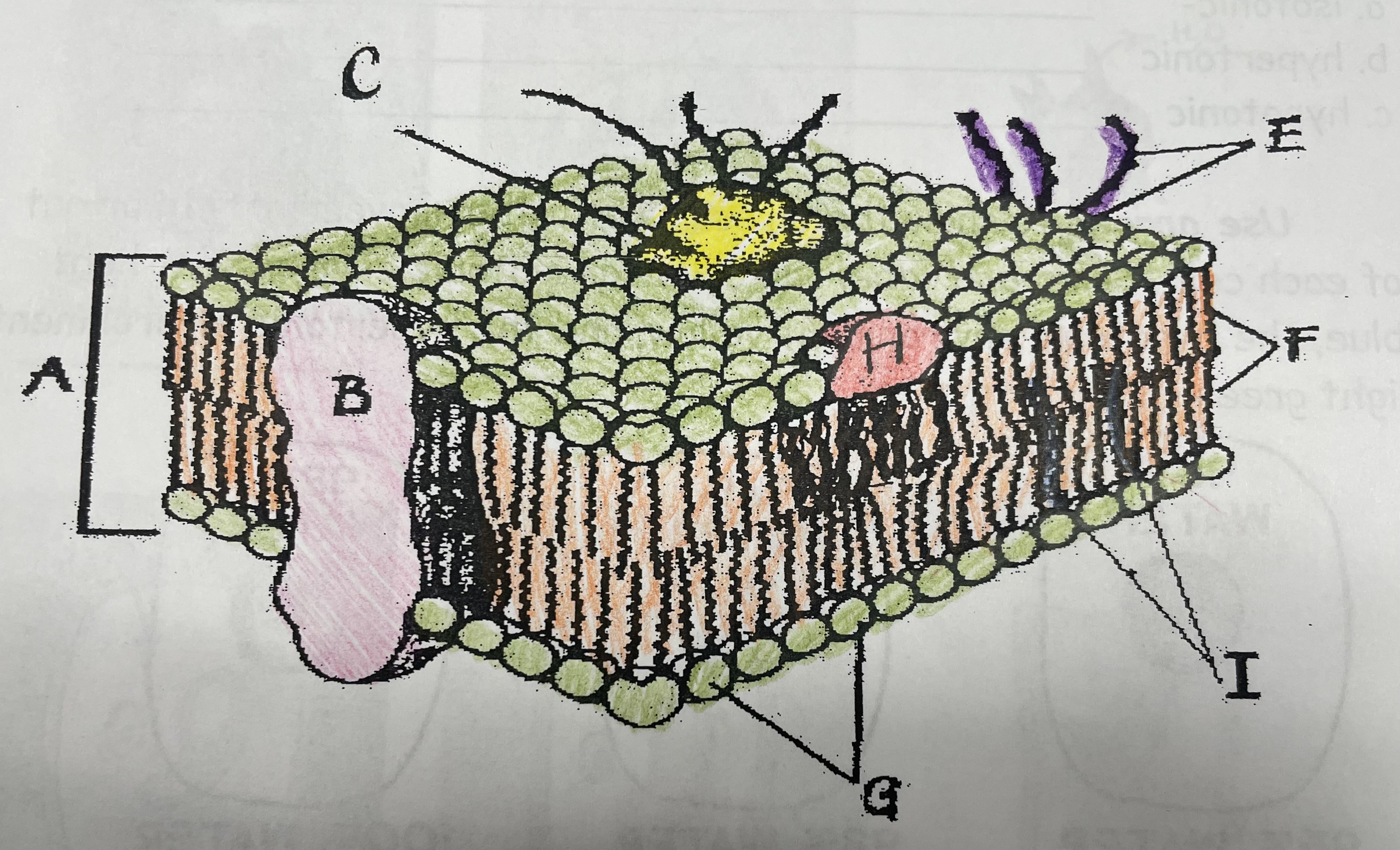
What is B?
Integral protein
12
New cards
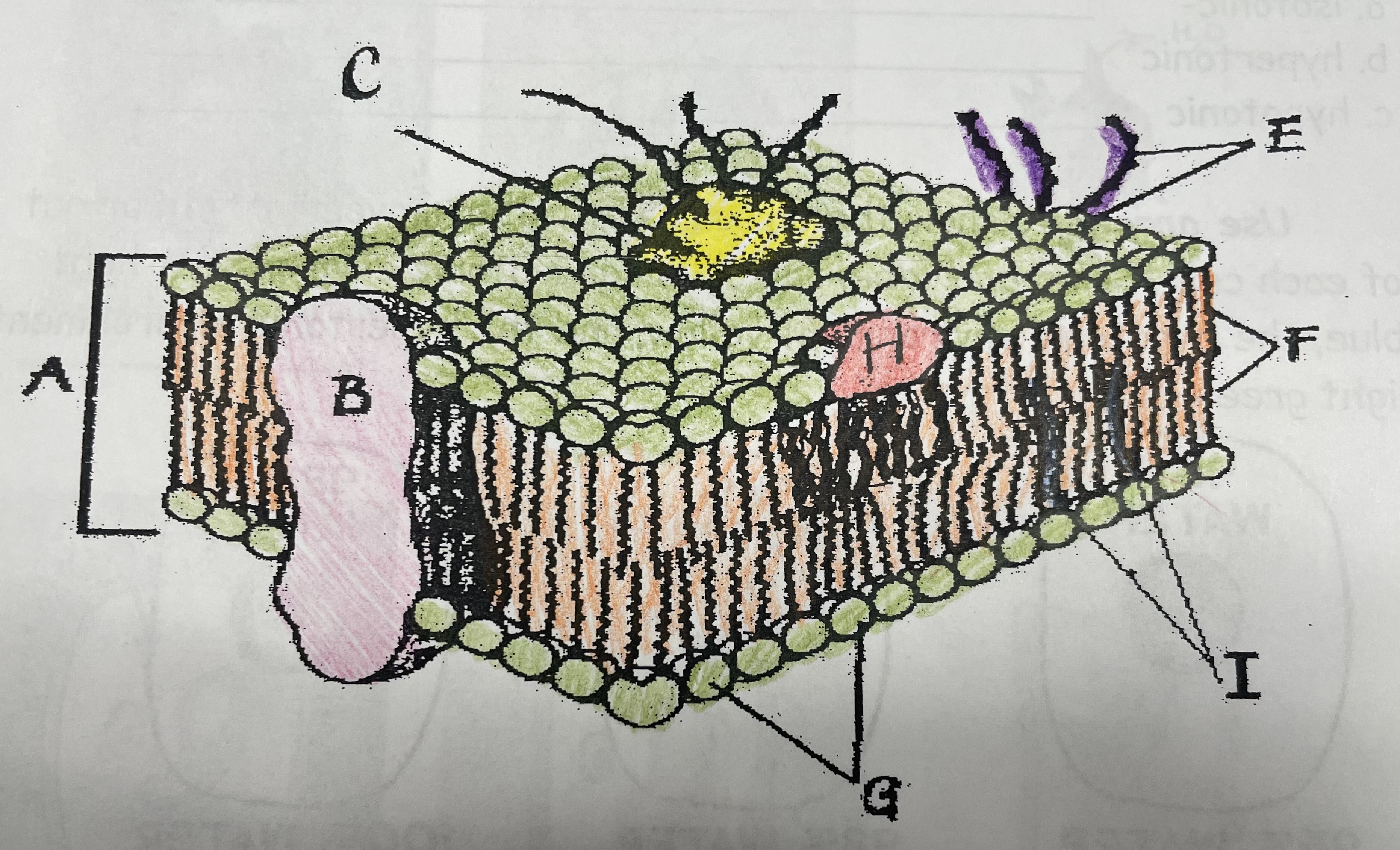
What is F?
Fatty acid tails
13
New cards
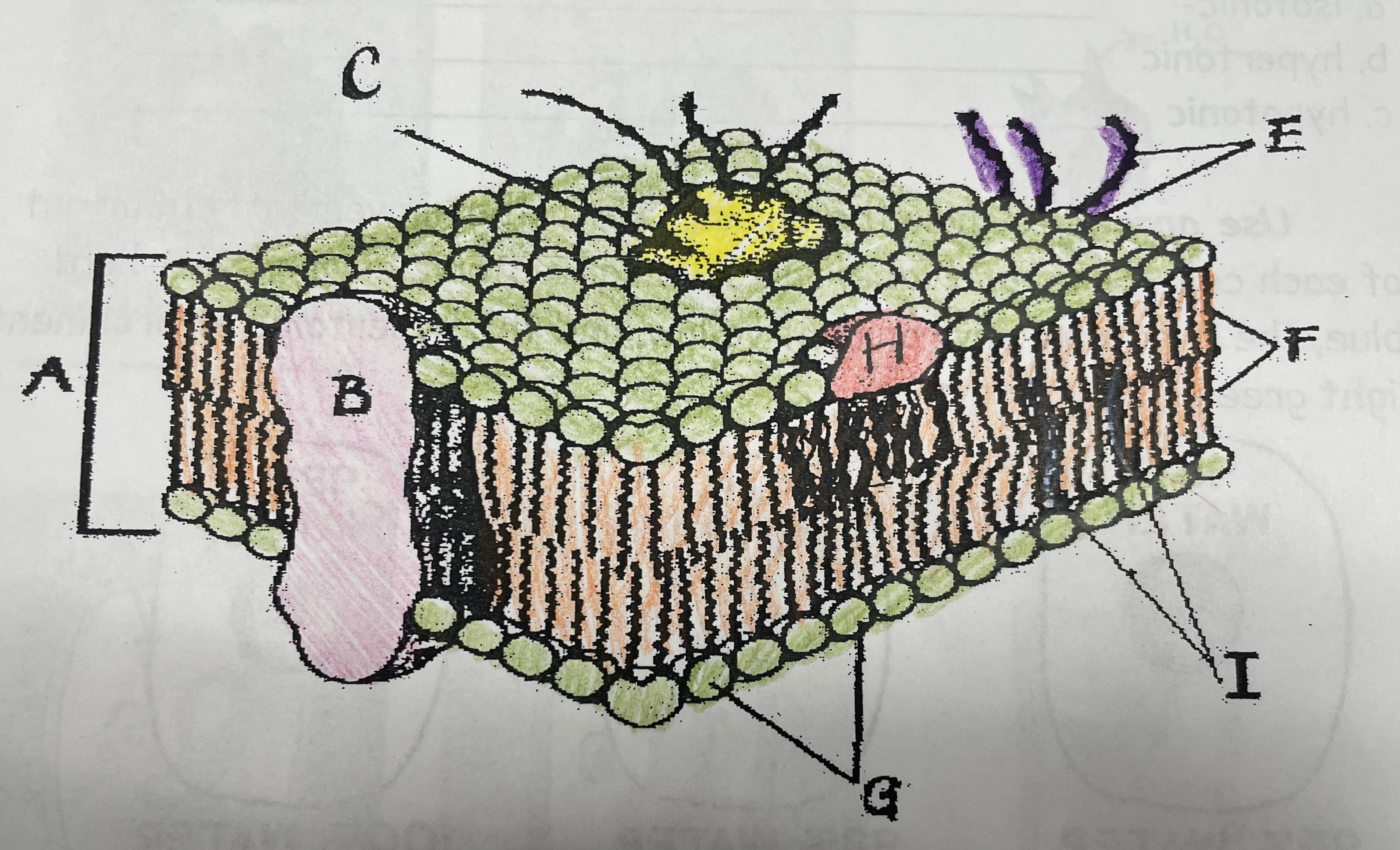
What is G?
Phosphate head
14
New cards
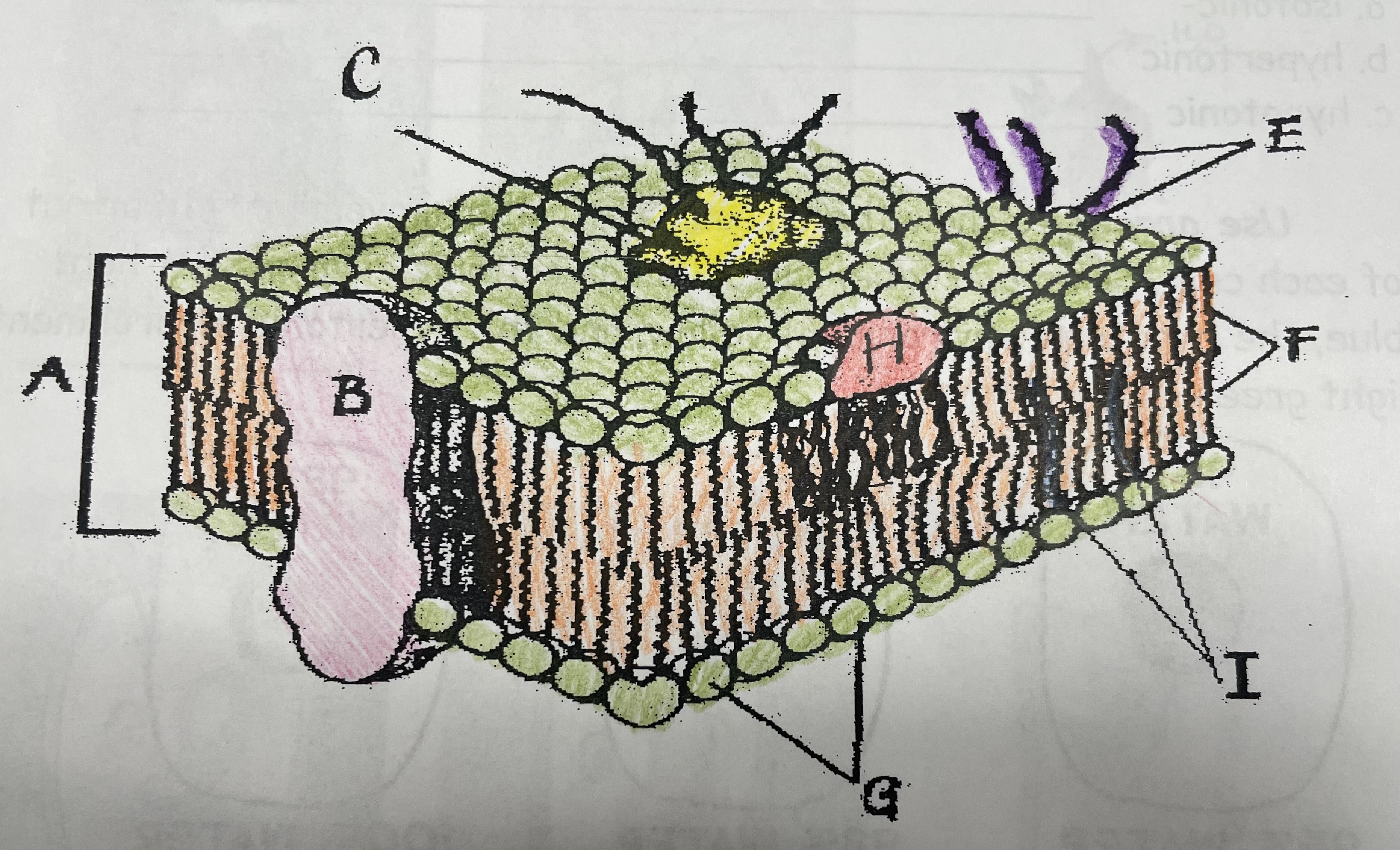
What is H?
Peripheral Protein
15
New cards
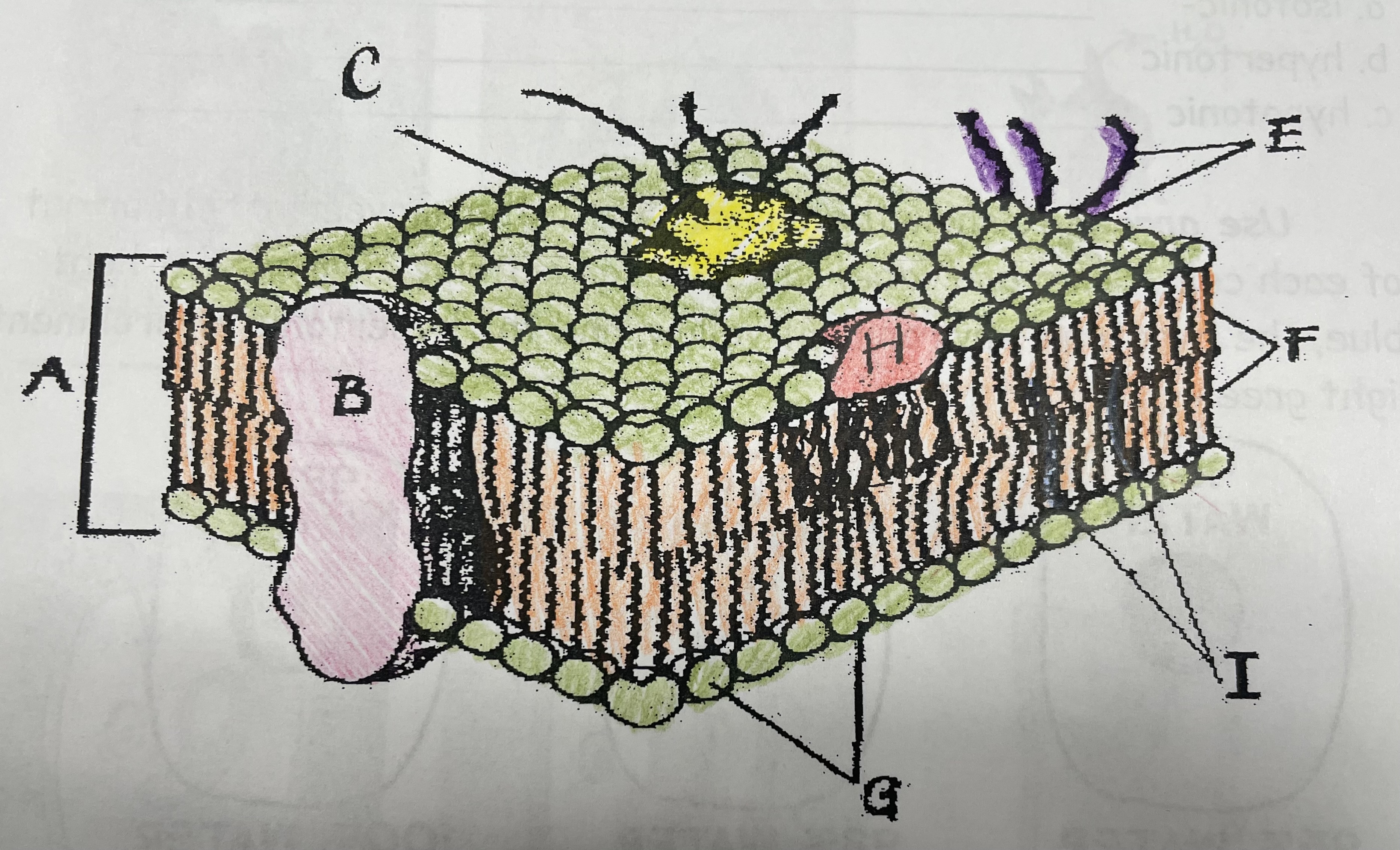
What is I?
Cholesterol
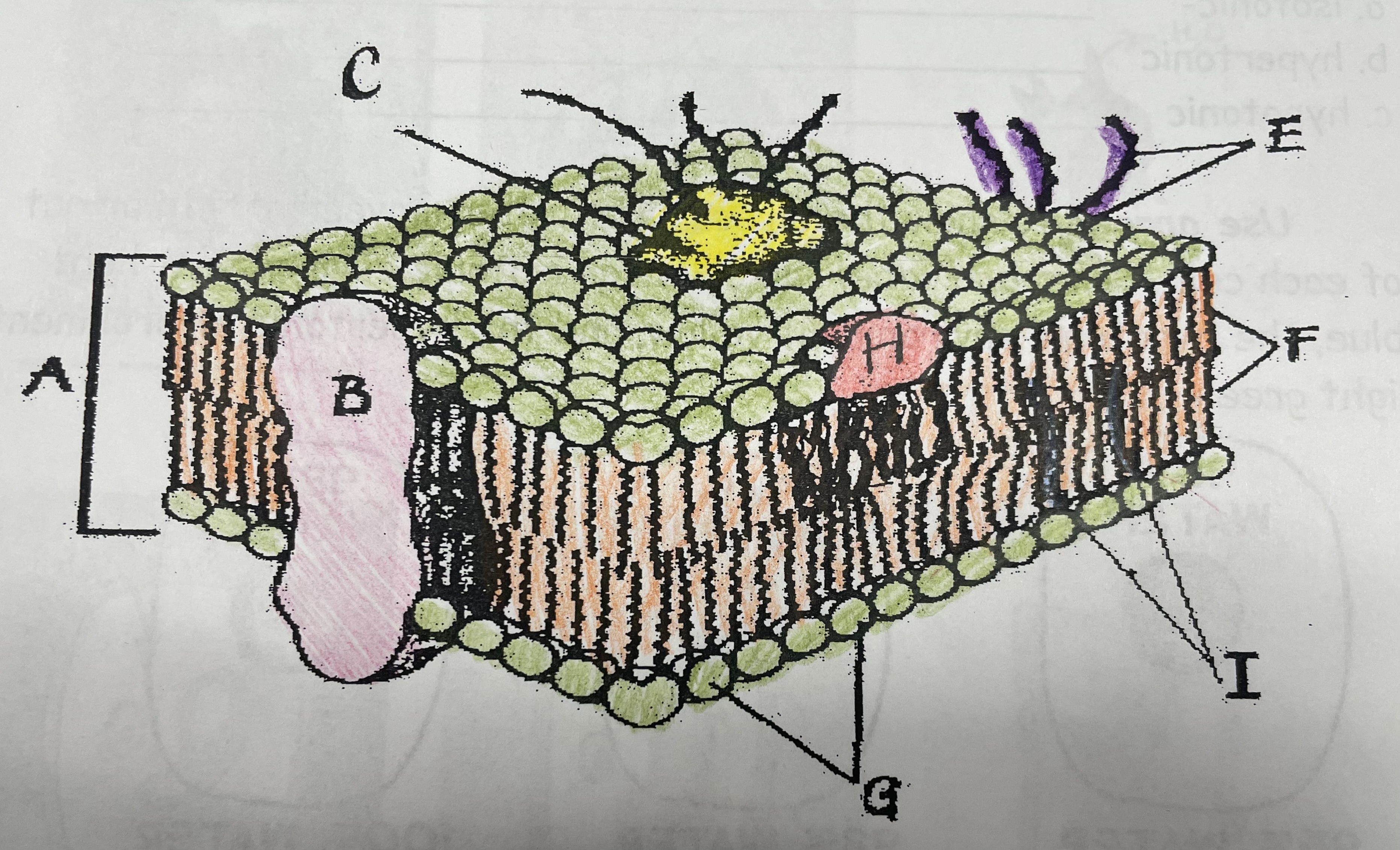
16
New cards
What is C?
Glycoprotein
17
New cards
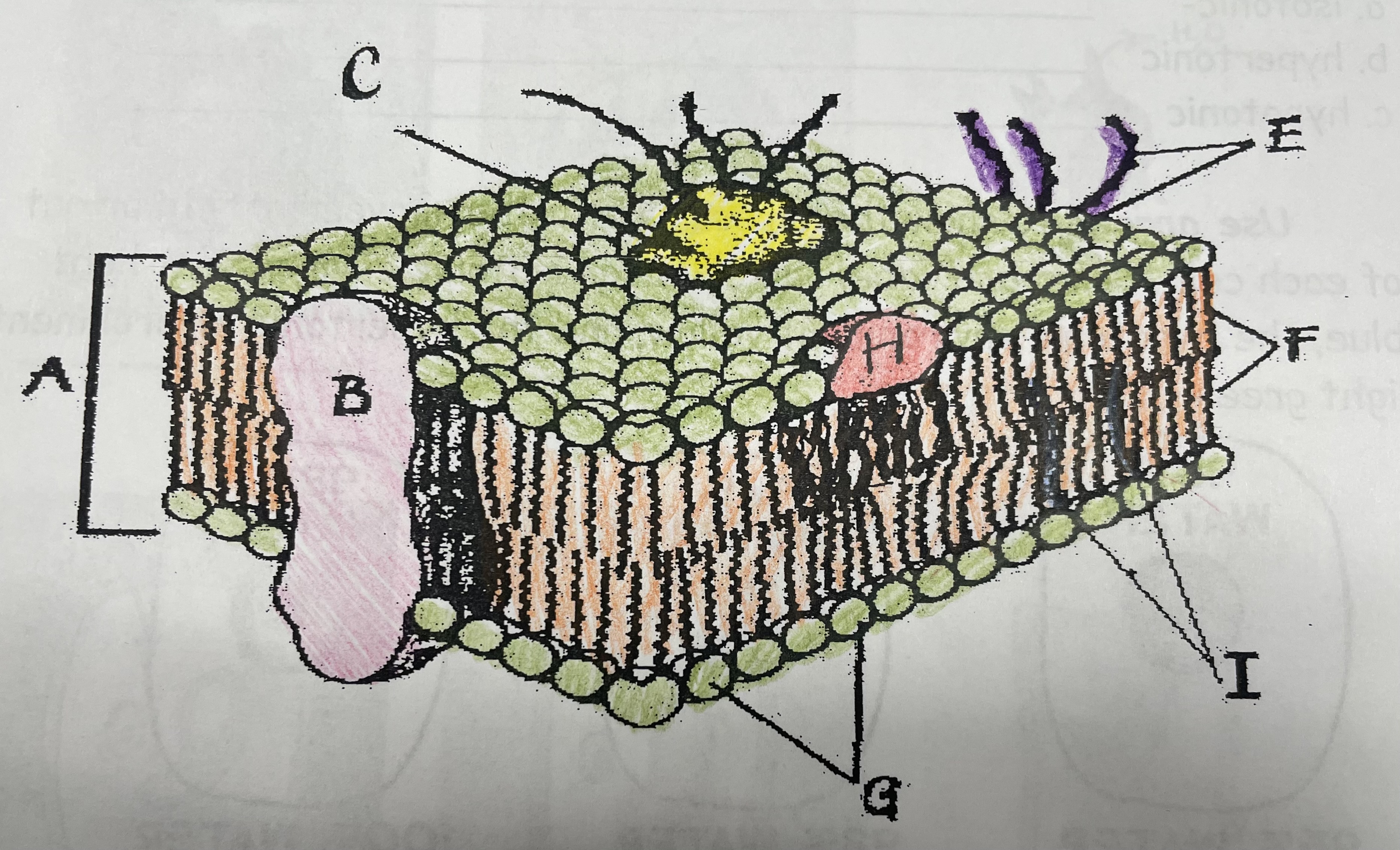
What is E?
Glycolipids
18
New cards
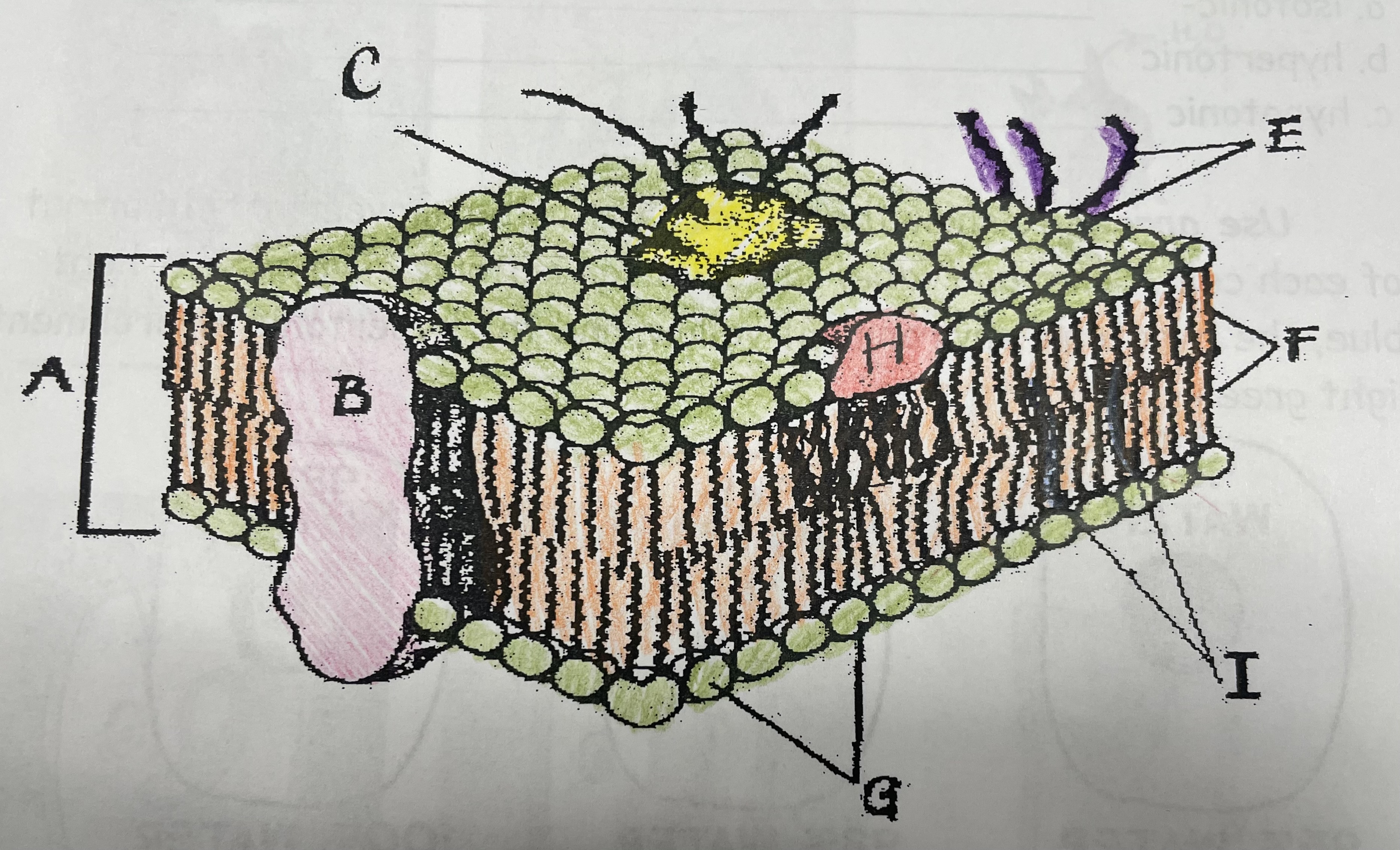
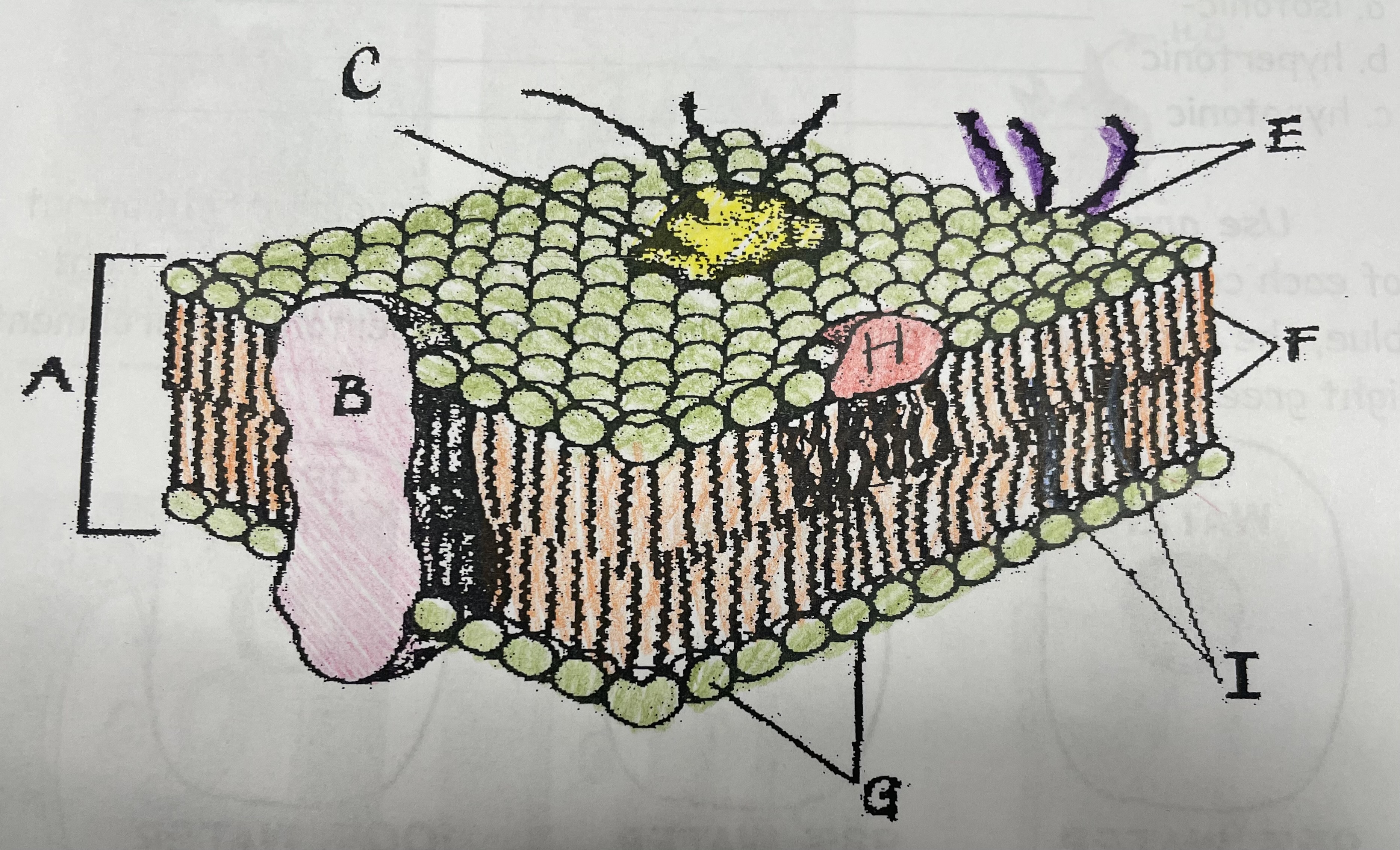
What does G do?
Attracts water
19
New cards
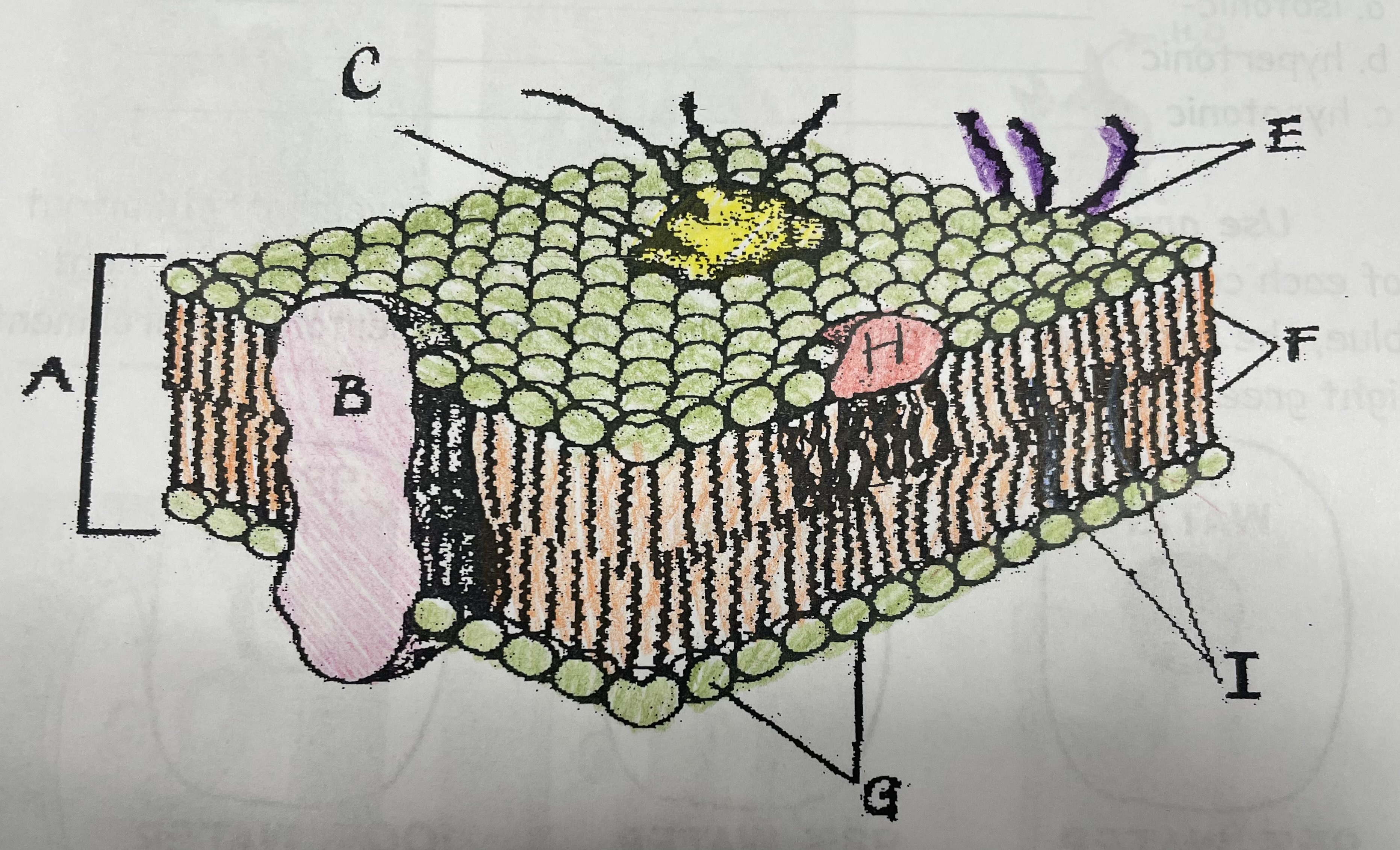
What does I do?
Helps maintain flexability
20
New cards
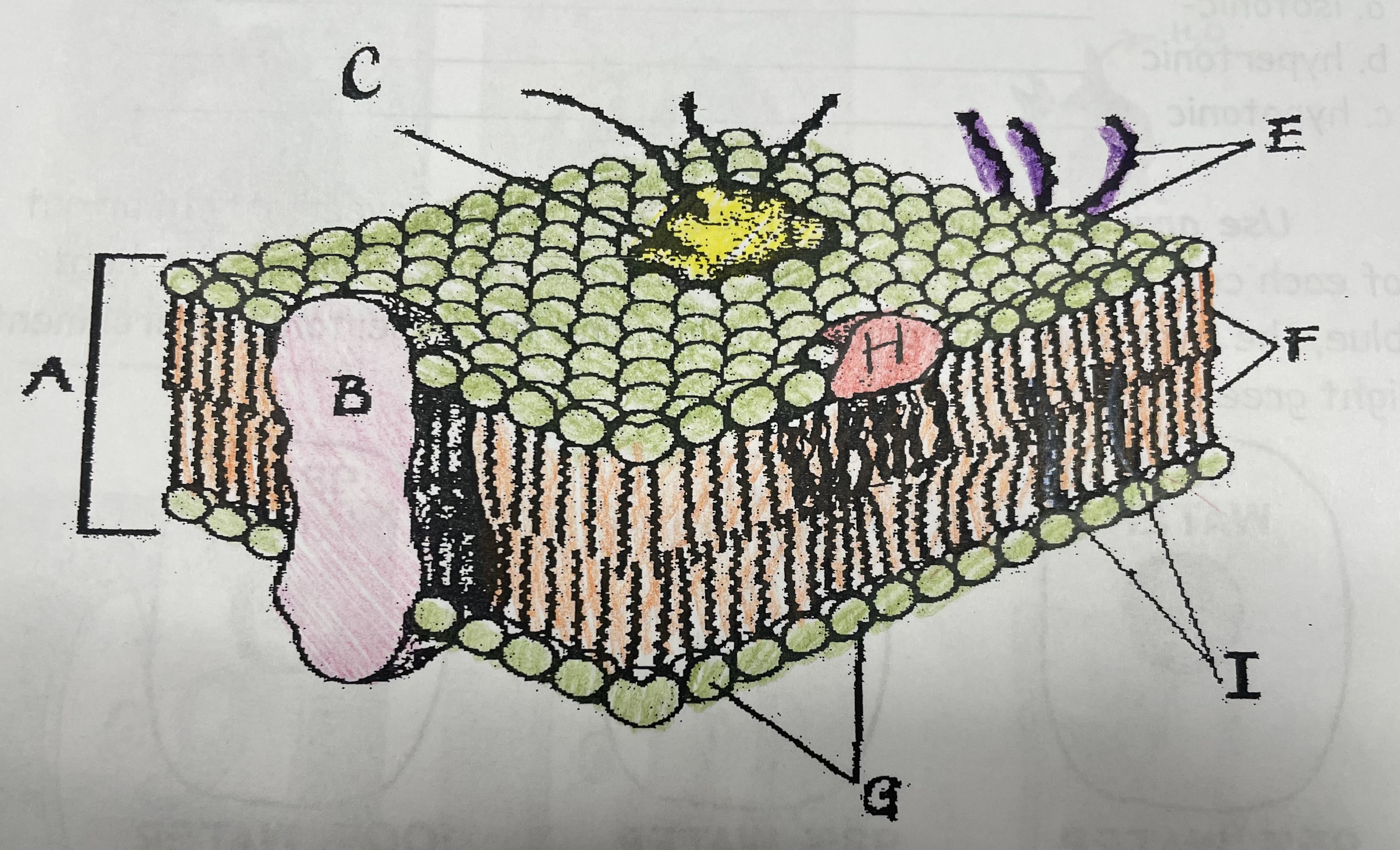
What does C do?
Involved in cell-to-cell recognition
21
New cards
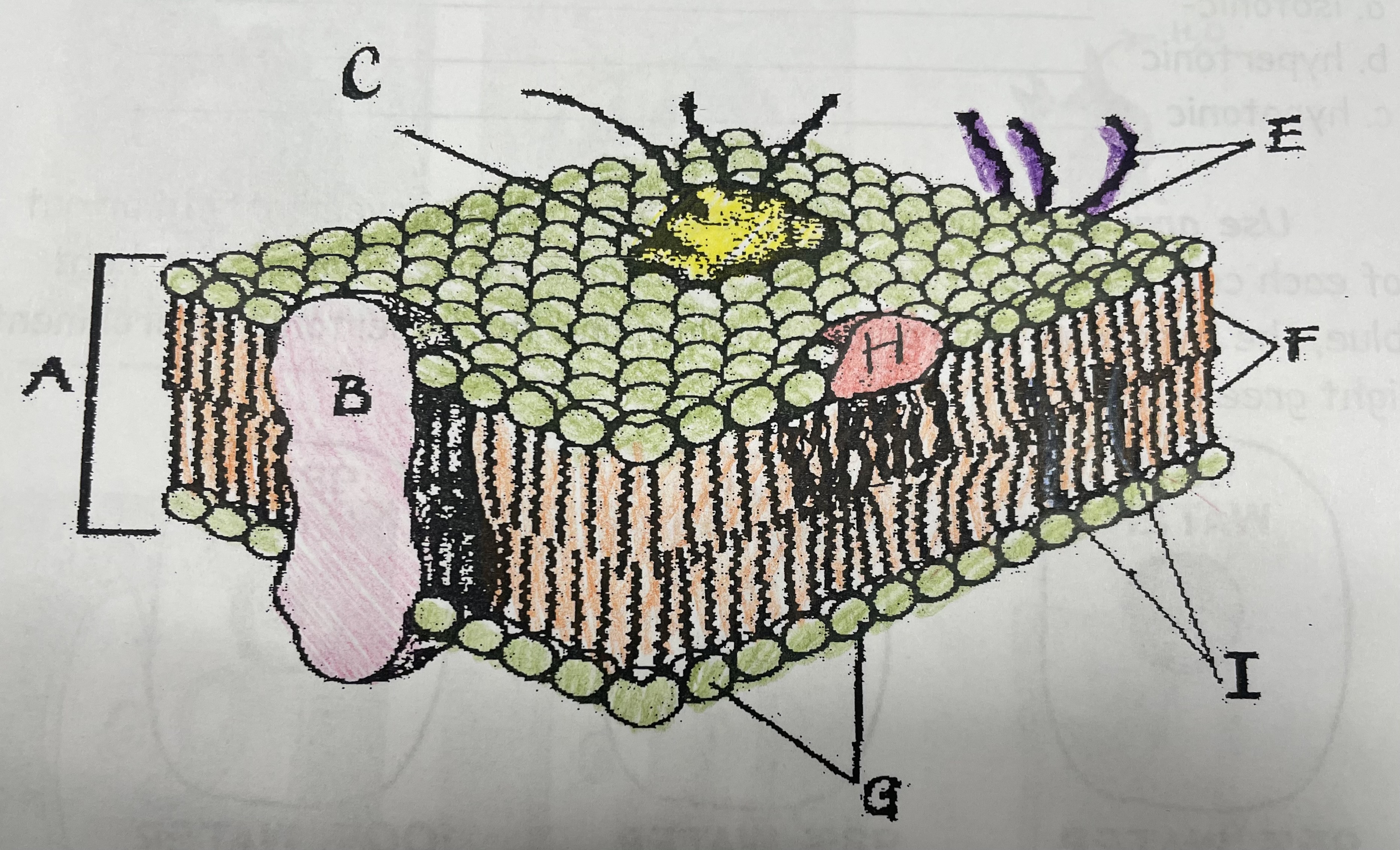
What does F do?
Repels water
22
New cards
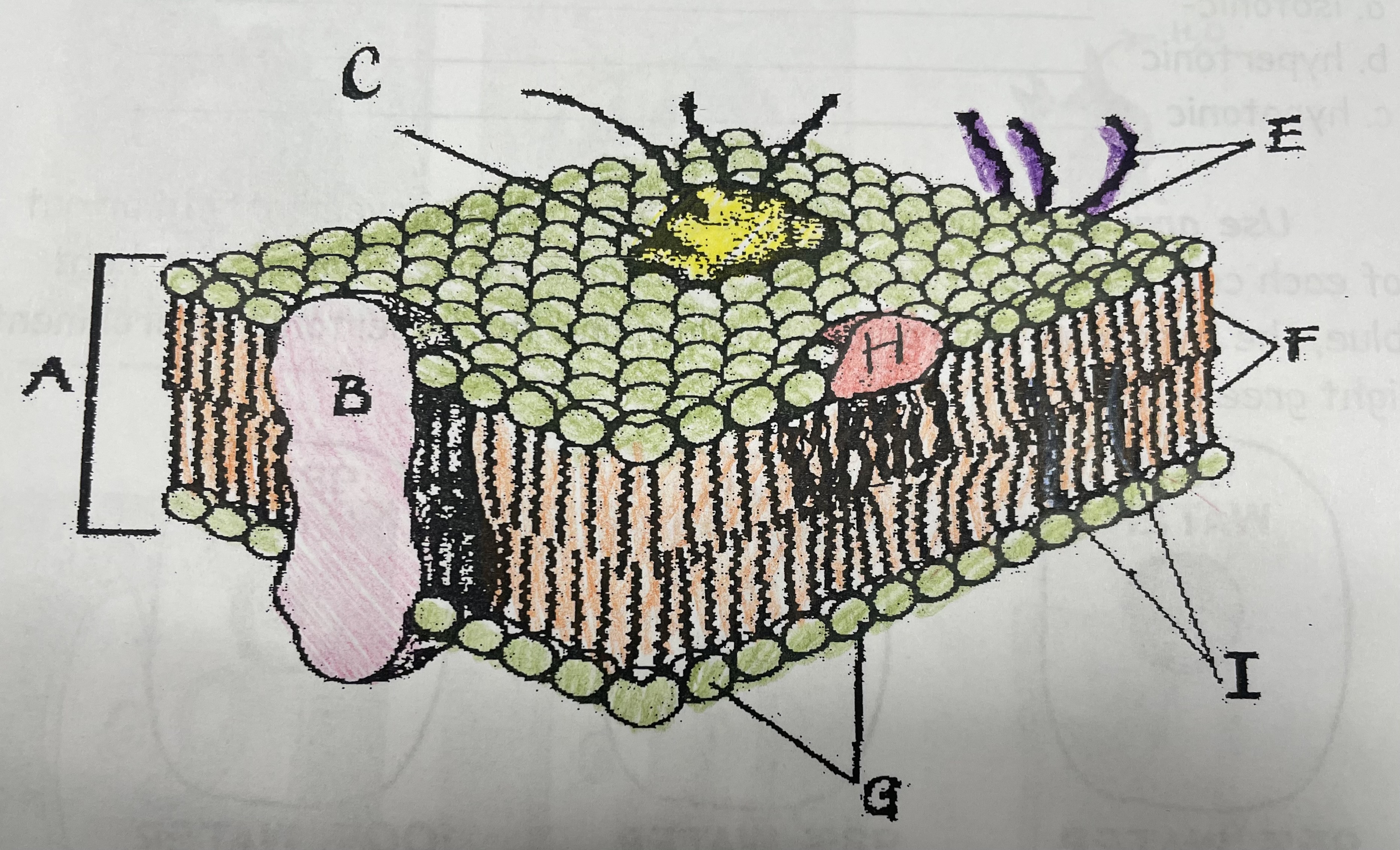
What does B do?
Helps transport certain materials across the cell membrane
23
New cards
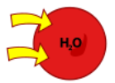
Hypotonic
Bursts
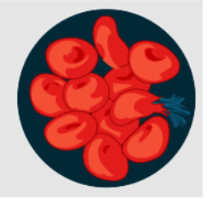
24
New cards
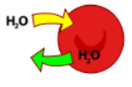
isotonic
stays the same

25
New cards

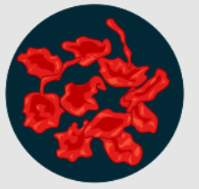
Hypertonic
Shrink
26
New cards
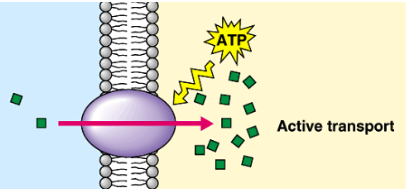
Membrane Pumps
Protein pumps that transport calcium, sodium,
and potassium ions across a membrane
and potassium ions across a membrane
27
New cards
Endocytosis
Taking materials into the cell by pockets and
infoldings of the cell membrane
infoldings of the cell membrane
28
New cards
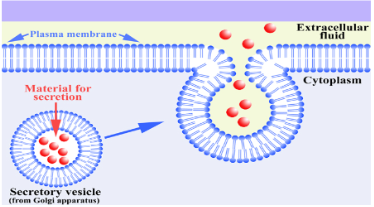
Exocytosis
Contents of the cell are forced out by the pocket
membrane fusing with the cell membrane
membrane fusing with the cell membrane
29
New cards
Examples of endocytosis
Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis
30
New cards
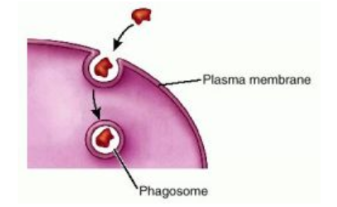
Phagocytosis
Large particles are taken in
31
New cards
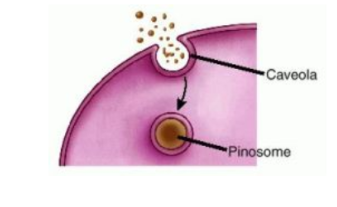
Pinocytosis
Cells take up liquid from the surrounding
environment
environment