Lecture 12: LABOR FORCE & UNEMPLOYMENT
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Working-age population
The total number of people aged 16 years and over who are not in jail, hospital, or some other form of institutional care or in the military.
employed
working-aged individuals who work, including self-employed individuals.
Part-time/full-time status does not matter
unemployment
the number of people who are actively looking for work but aren't currently employed
labor force
employed + unemployed
Does not include:
- not working and not looking for jobs
- Ex: retirees, full-time students who do not hold jobs
labor force participation rate formula
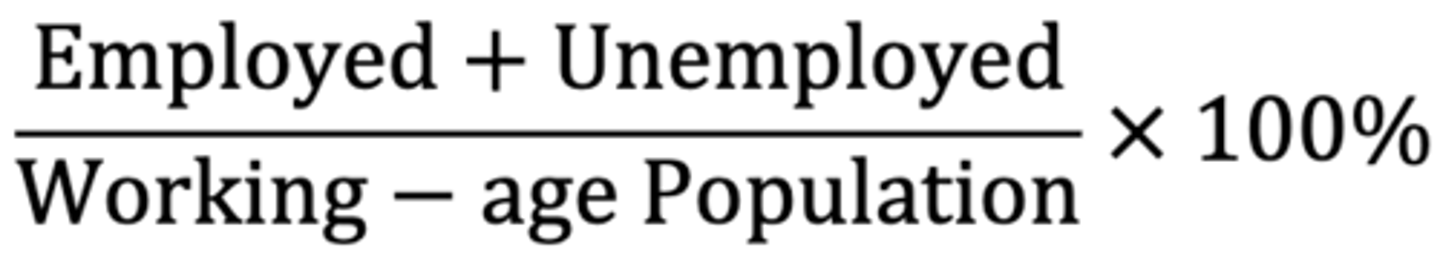
unemployment rate
- Fluctuates a lot, BUT NEVER 0
- Snapshot measure: even if it stays the same, it does not have to represent the same people
- There is a flow from employment into unemployment (and vice versa)
unemployment rate formula

Longterm unemployment
unemployment that lasts longer than six consecutive months
- has negative effects and reduced likelihood of exit from unemployment due to the loss of social and human capital
marginally attached workers
would like to be employed and have looked for a job in the recent past but are not currently looking for work
(not included in unemployed population)
discouraged workers
1/4 of marginally attached workers:
individuals who would like to work but have given up looking for a job (not included in unemployed population)
Underemployment
counts as employment; however, there is either a want for more hours or a job that better matches their skills
involuntary part-time workers
Individuals who would like a full-time job, but who are working only part time (counts as employment)
frictional unemployment
unemployment that occurs when people take time to find a job
Four factors affecting frictional unemployment
- Normal functions of the economy: Fresh graduates looking for jobs are here
- Information problem: Better job search methods and job seeker-to-employer matching reduces this
- Skill matching problem: Takes time to find employment that matches an individual’s skills
- Policy effects: More generous policies can reduce hardship but prolong unemployment duration
structional unemployment
is long-term unemployment that is driven by the reorganization of the industries/economy and the nature of its institution
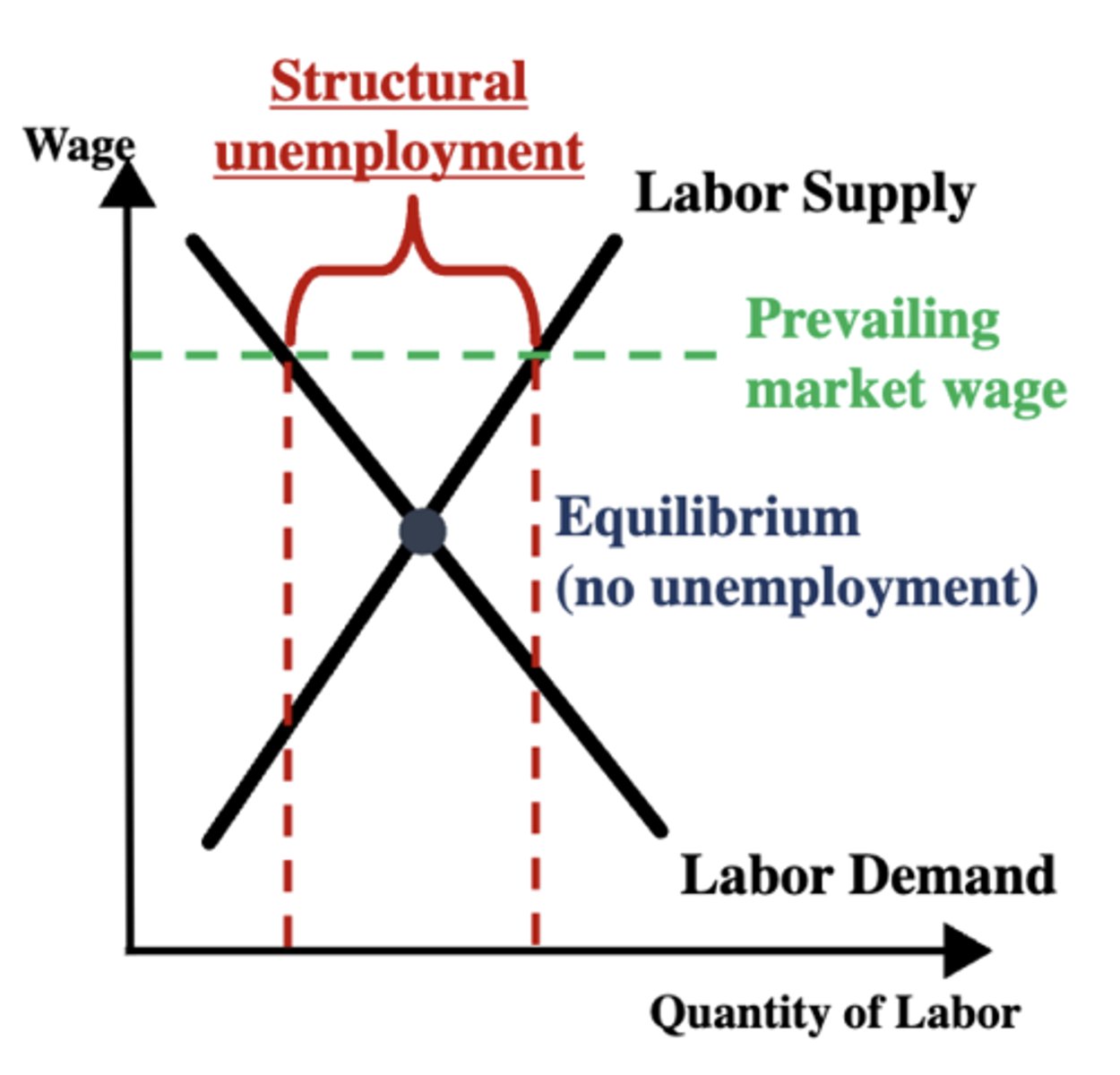
Factors affecting structural unemployment
- Normal functioning of the economy: Technological progress and globalization can make some industries shrink or disappear
- Retraining problem: May need to radically shift skills to find employment, but education is costly and takes time
- Prevailing market wage problem: Supply and demand mismatch due to above-equilibrium market wages
cyclical unemployment
unemployment that rises during economic downturns and falls when the economy improves
natural rate of unemployment
the normal rate of unemployment, consisting of frictional unemployment and structural unemployment
Costs of Unemployment
Long-term loss of wages and reduced career prospects, and reduction in taxes received by the government
Hysteresis (unemployment)
A period of high unemployment affects the economy such that the equilibrium rate of unemployment increases
Social costs of unemployment
- Impact on life satisfaction
- Long-term health and mortality consequences
- Generational effects