NURS 20025: Exam 2
1/252
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
253 Terms
Stroke Volume (SV)
The volume of blood pumped forward with each ventricular contraction.
Preload
the amount of blood left in the left ventricle (at the end of diastole)
Afterload
resistance to left ventricular ejection
Contractility
ability of heart muscle to contract
Cardiac output
amt of blood pumped by the heart each minute
CO equation
HR x SV = CO
Cardiac conduction pathway
SA node, AV node, bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
coronary circulation
receive blood during diastole; the right and left arteries branch off the base of the aorta
Pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
pulse pressure represents what?
filling pressure of coronary arteries
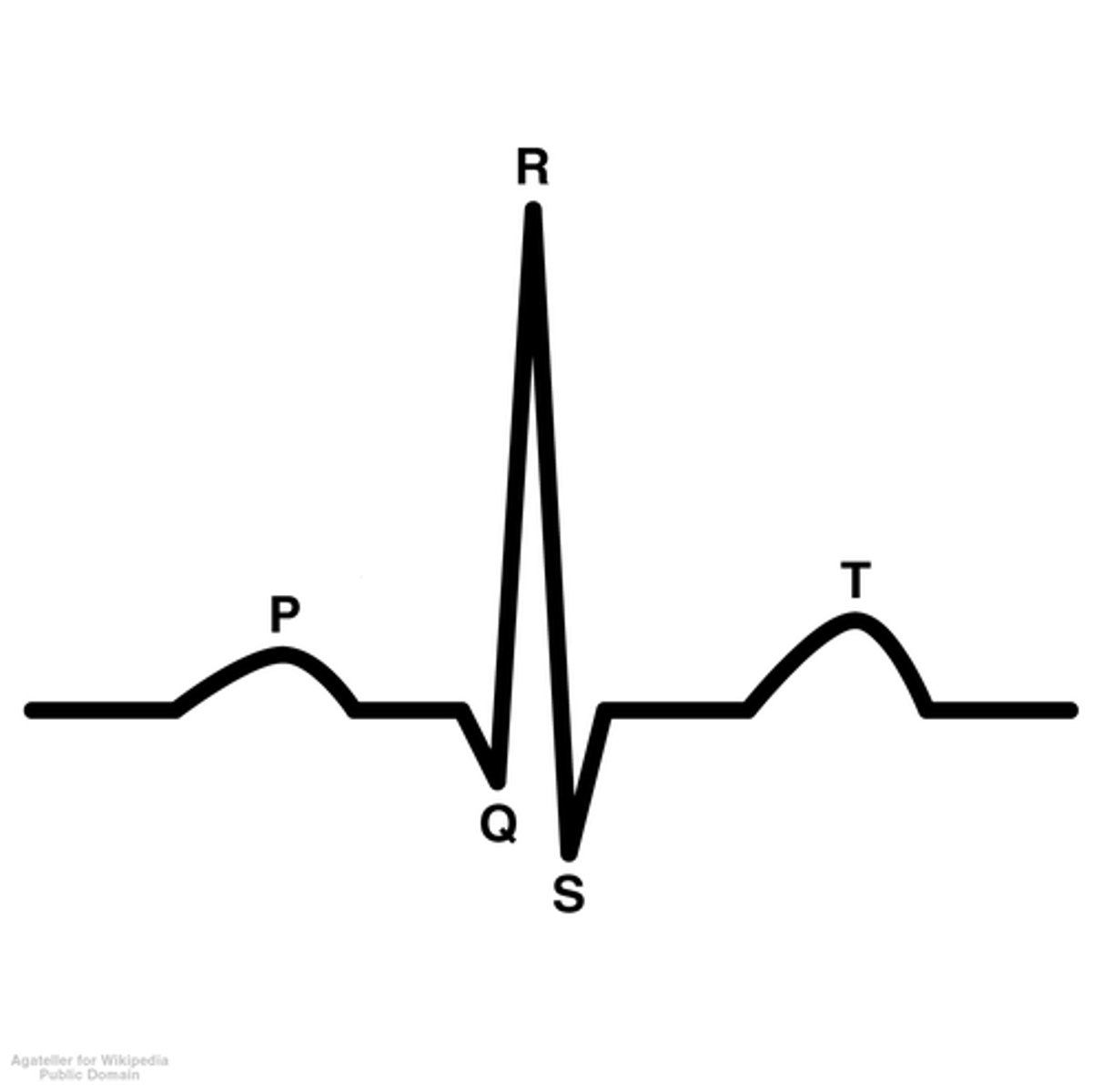
electrocardiography
process of recording the electrical activity of the heart
P wave
atrial depolarization
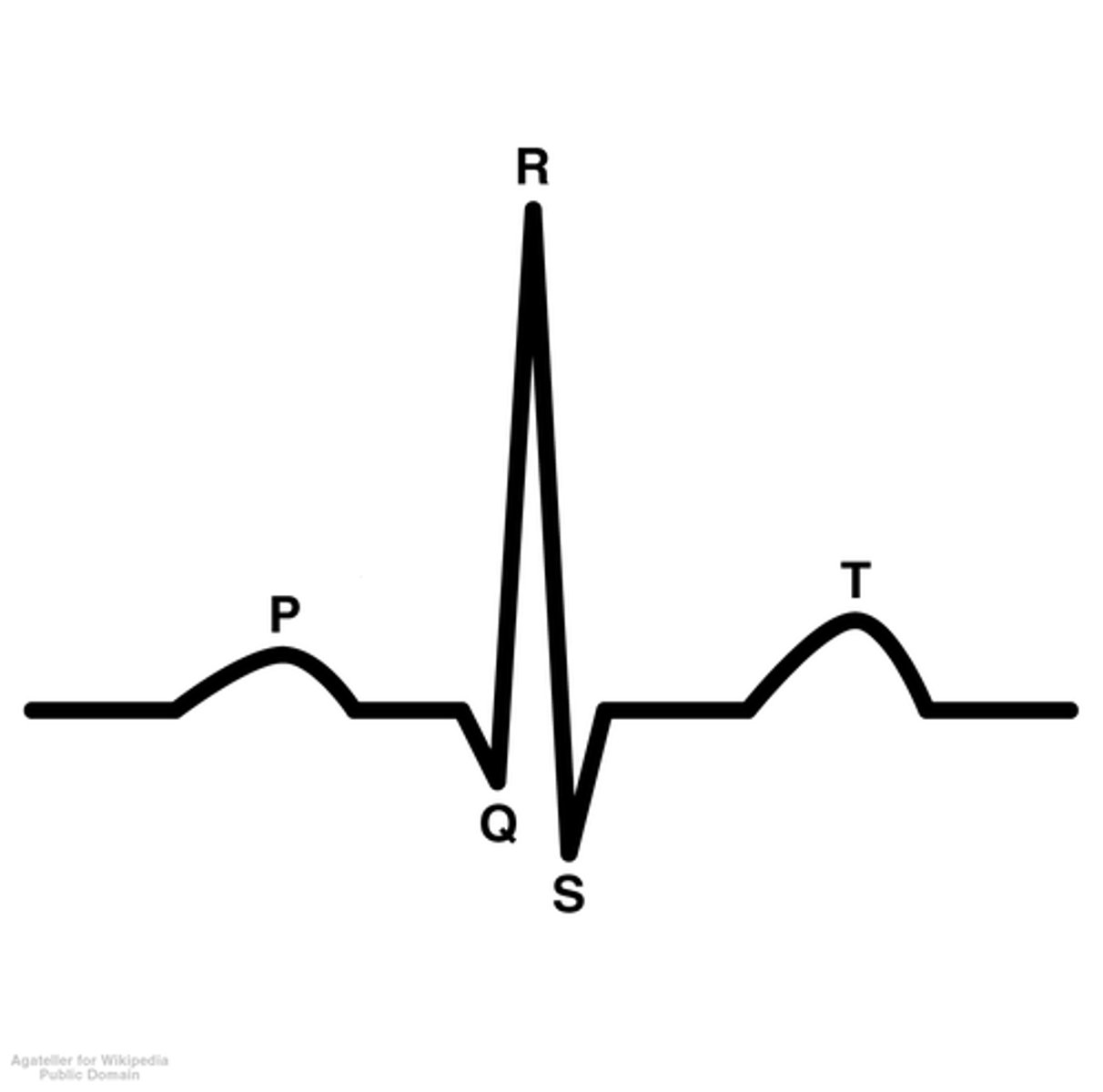
PR wave
tracks the atrial impulse through the AV node, bundle of HIS, and bundle branches
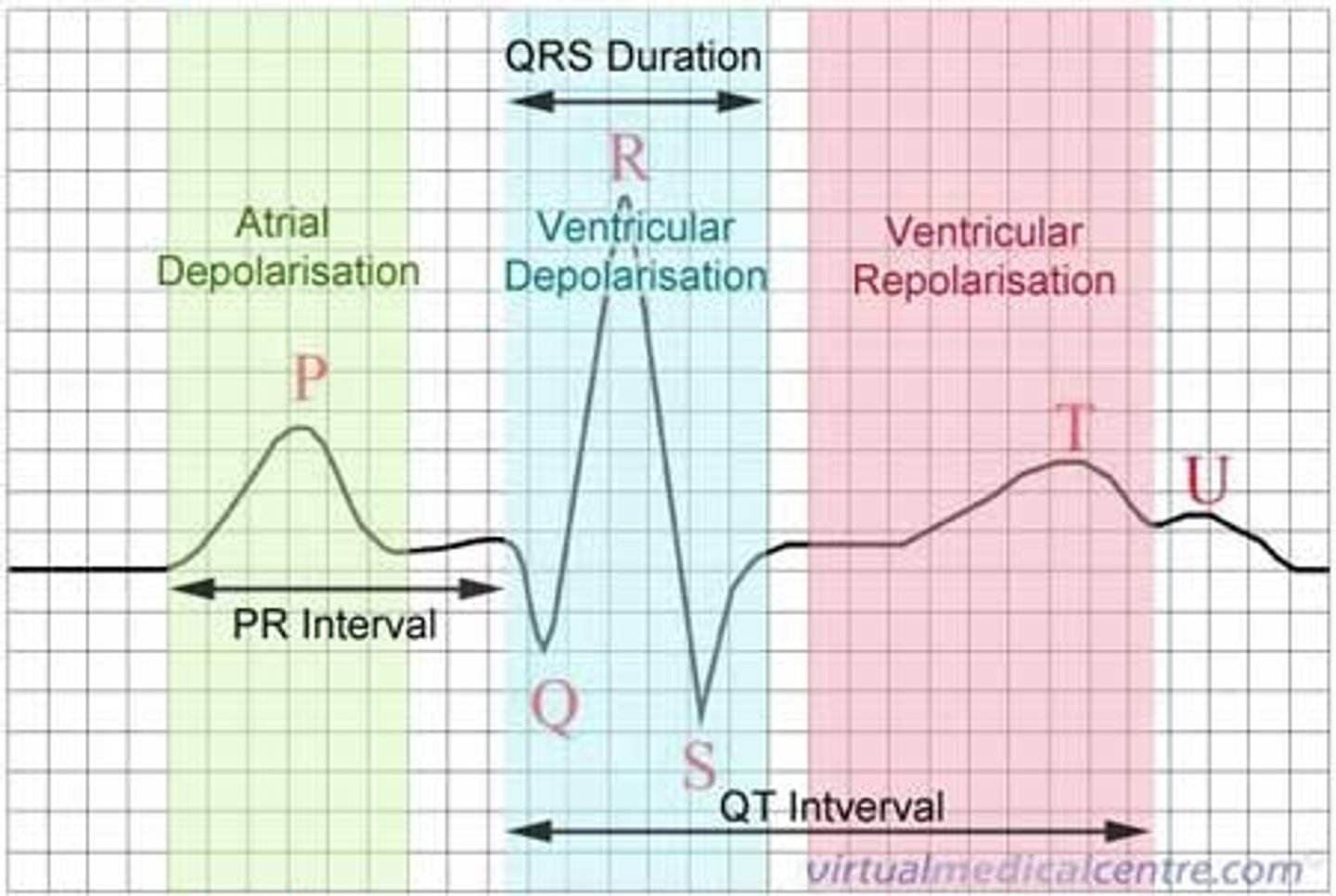
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
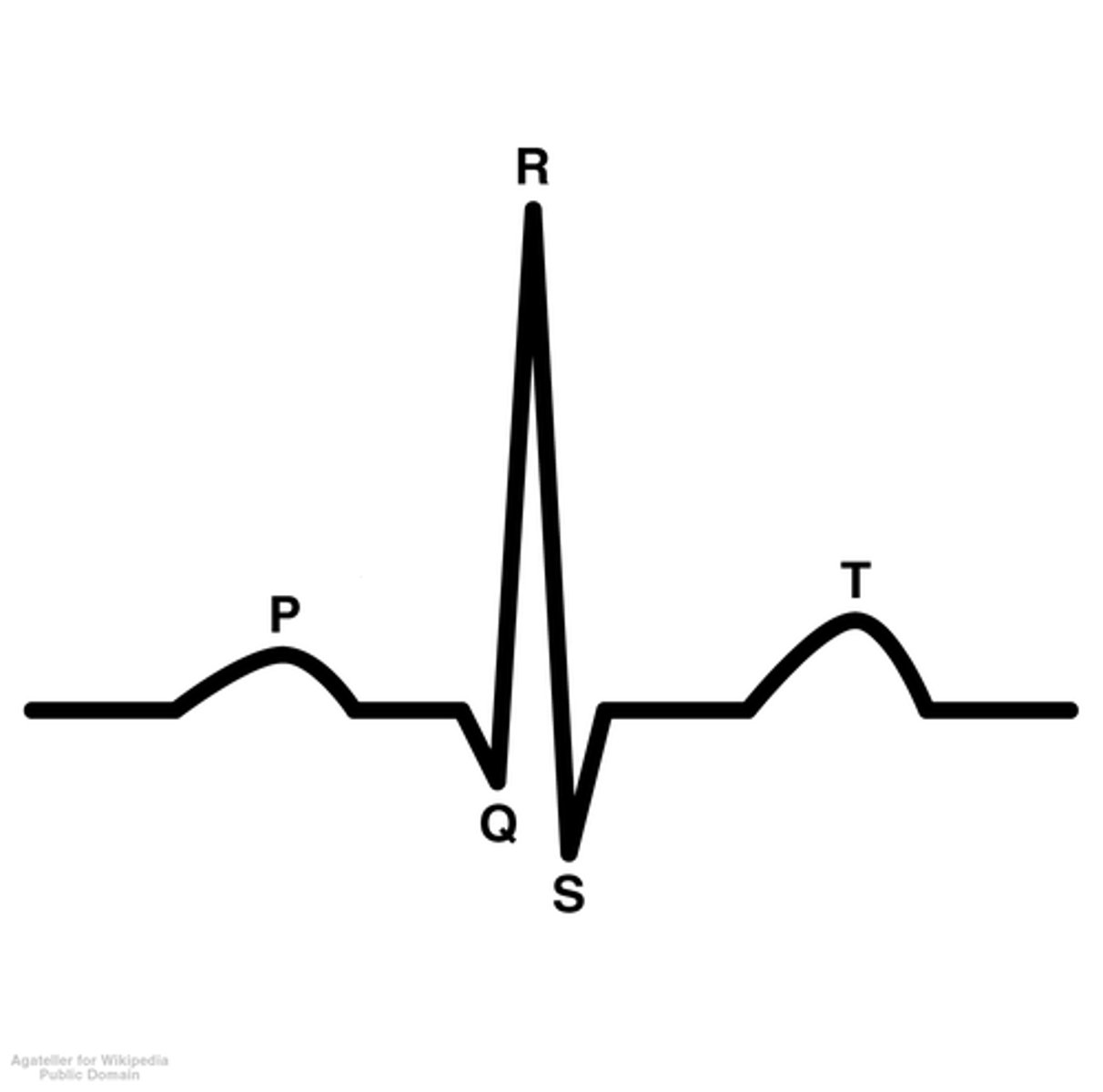
ST segement
end of ventricular conduction/depolarization; beginning of ventricular repolarization
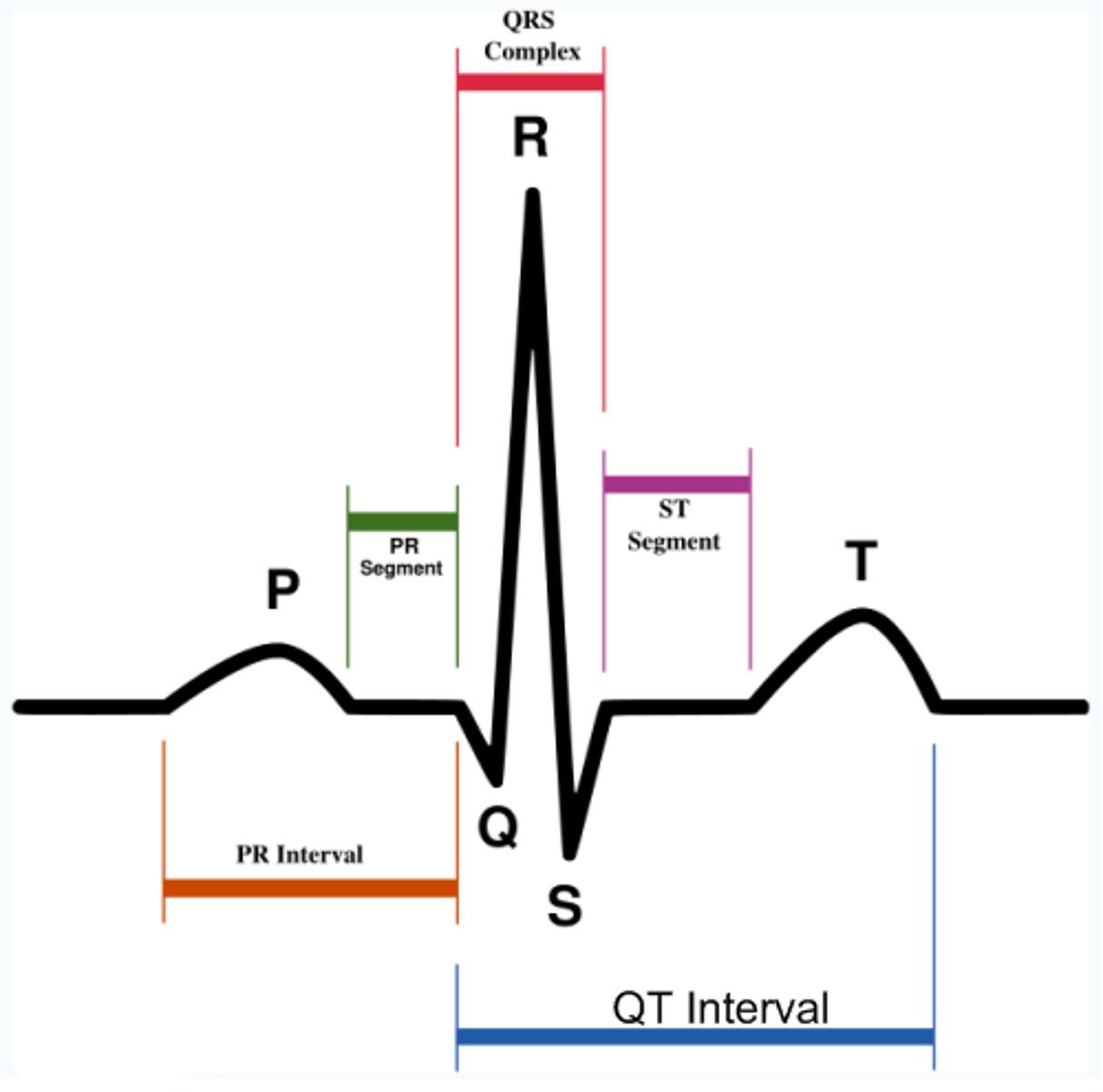
T wave
ventricular repolarization
What are three physiological features that effect blood pressure?
vasomotor center; hormones; emotions
vasomotor center
regulates blood pressure and flow by dilating and constricting blood vessels
Baroreceptors
Cells that are sensitive to blood pressure changes.
Chemoreceptors
respond to pH; oxygen; carbon dioxide
Name some emotions that affect BP
Anger; depression; stress; lethargy
Name hormones that affect BP
ADH; RAAS
ADH
antidiuretic hormone
RAAS
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Fluid loss that leads to a decrease in blood volume
dehydration
Hormones involved in fluid retention
ADH; Aldosterone
Peripheral resistance responds to which nervous system?
Sympathetic
Increase in blood viscosity effects _______.
peripheral resistance which affects blood pressure
Renin and Angiotensin II effects
peripheral resistance which affects blood pressure
Blood pressure is affected by cardiac output: T or F?
True. Along with peripheral resistance and blood viscosity.
autoregulation of blood flow
ability of organ to regulate own blood flow
Histamine
When released, blood vessels dilate and blood pressure decreases.
Bradykinin
potent vasodilator; peptide
prostaglandins include both vasodilators and vasoconstrictors: T or F
True
response to hypertension
Renal secretion increases (increase in urine output) which leads to fluid loss and lowers BP
response to hypotension
Adrenal Medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. Angiotensin II and Aldosterone are formed. Kidneys retain fluid, and BP increases.
Prehypertension
120-139/80-89
Hypertension
140/90 or higher
primary hypertension
denotes high blood pressure from an unidentified cause; also called essential hypertension; 90-95% of cases.
secondary hypertension
high blood pressure caused by the effects of another disease
Can patients be asymptomatic for years, if they have hypertension?
Yes
ADH functions
decrease urine volume output and cause vasoconstriction
RAAS function
vasoconstriction
HTN, Stage 1 Range
SBP 130-139 or DBP 80-89
HTN, Stage 2
SBP ≥ 140 or DBP ≥ 90
Elated BP
SBP 120-129 and DBP < 80
HTN: Goal for pts who are >60 years
<150/90
HTN: Goal for pts who are <60 years
<140/90
When treating HTN, before increasing dose you should
try a different medication group (pharmacological class)
ACE-I stands for
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitors
ACE-I meds typically end in
-pril
ACE-I side effects
Cough, hyperkalemia, angioedema
Black box for ACE-I
known to cause injury or death in fetus
ARB stands for
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
ARB meds typically end in
-sartan
ARB side effects
Angioedema, hyperkalemia, acute renal failure
Black box for ARB
known to cause injury or death to fetus
Calcium Channel Blockers meds can end in
-dipine
Calcium Channel Blockers
agents that inhibit the entry of calcium ions into heart muscle cells, causing a slowing of the heart rate, a lessening of the demand for oxygen and nutrients, and a relaxing of the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels to cause dilation; used to prevent or treat angina pectoris, some arrhythmias, and hypertension
Do not take ______ with Calcium Channel Blockers.
macrolide antibiotics (can lead to shock)
Macrolide Antibiotics
erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin
Antiadrenergic
blocks the neurotransmission of the sympathetic nervous system (decreases HR, force of contraction, and CO)
Alpha1 adrenergic receptor blockers
Dilate blood vessels & decrease peripheral vascular resistance
alpha 1 adrenergic receptors blocker examples
doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin (-osin)
Alpha 2 receptor agonists
inhibits norepinephrine which decreases BP
Beta Blockers end in
-olol
Black Box for Beta Blockers
titrate down to prevent rebound angina, MI, or ventricular arrhythmias
Thiazide diuretics
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
Thiazide diuretics function
Block Na reabsorption; Increase K and H2O secretion
Potassium sparing diuretics
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Potassium sparing diuretics function
Excrete Na and retains K
Loop Diuretics
Furosemide (Lasix)
Loop Diuretics function
inhibit reabsorption of Na+,
K+ and Cl- in the ascending loop of Henle (can cause hypokalemia)
direct acting vasodilators
nitroprusside (IV only); hydralazine
When to use direct acting vasodilators?
HTN Emergencies
Nurses should monitor for _______ when patients are on hypertensive medications.
bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension, and I&O (electrolytes)
Automaticity
ability of the heart to generate an electrical impulse
Conductivity
ability of cardiac tissue to transmit electrical impulses
SA node has the fastest rate of?
automaticity
Ectopic beat (ectopic focus)
Impulse origination other than in SA node (serious)
Possible causes of ectopic beats
Hypoxia, ischemia, hypokalemia
T or F: Antidysrhythmic drugs can worsen existing dysrhythmias, or may cause new dysrhythmias.
True
Name two non-pharmacological treatments of arrhythmias
Pacemaker; cardioversion; defibrillation; radiofrequency catheter ablation
Sodium Channel blockers
blocks the opening of sodium channels; now rarely used for arrhythmias
Sodium Channel blockers can treat...
atrial dysrhythmia and supraventricular tachycardia.
The sodium channel blocker MOA depends on...
its class (IA, IB, or IC).
Sodium Channel Blockers side effects
arrhythmias, bradycardia, and hypotension
Examples of sodium channel blockers
quinidine; lidocaine
Nursing concerns of sodium channel blockers
interfere with anticoagulants and caution when giving to pts with airway or breathing issues.
Most arrhythmia pts need to be on some kind of...
anticoagulant.
Beta Blockers
decrease cardiac excitability, cardiac workload and oxygen consumption (also decreasing automaticity and HR)
Beta blockers help manage...
dysrhythmia from excessive SNS stimulation (post MI)
Beta blockers side effects are...
bradycardia, hypotension, dizziness, and syncope
What happens if you abruptly stop beta blockers?
rebound hypertension/tachycardia/dysrhythmias
Which beta blocker is used for dysrhythmias?
propranolol
Nursing concerns for beta blocker
Verapamil can increase chance for HB
Erectile dysfunction can result from which heart medicine class?
beta blockers
Potassium Channel Blockers
Prolong the refractory period of the heart
Potassium channel blocker side effects
Pulmonary toxicity (IV), Hepatotoxicity
Potassium channel blockers example
amiodarone