Functions of human microbiomes
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What happens to a corn kernel in the digestive system?
hen you eat corn, the microbes in your gut digest the inside of the kernel, but the outer shell often remains undigested and can be found in the poop. The outer shell of the corn kernel is made of cellulose.
What makes everyone's gut microbiome unique?
Each person's gut microbiome has a unique composition of microbial species, but the metabolic potential of these species (their ability to process nutrients and produce metabolites) is what is most important for health.
Are twins' gut microbiomes identical?
Although twins share more similarities in their microbiomes than unrelated individuals, their gut microbiomes are still unique.
key roles of gut microbes
Regulating the immune system
Extracting energy from food
Controlling potential pathogens
Making essential metabolites (e.g., vitamins and cofactors)
Improving intestinal function
Removing toxins and carcinogens (convert toxic substances in food to non toxic)
When does a fetus acquire its first microbes?
The fetus is exposed to its first microbes when passing through the birth canal. Prior to this, amniotic fluid is sterile, so no microbes are present.
we acquire microbes mostly in those three stages
How does breastfeeding contribute to a baby's microbial acquisition?
Breast milk provides complex sugars that feed the baby's microbes, helping to establish a healthy gut microbiome.
What role does the environment play in microbial acquisition for infants?
Infants acquire microbes by interacting with their environment, such as through touching objects and putting them in their mouths, an evolutionary mechanism for gaining microbes.
Why is the first 3 years of life important for microbial acquisition
The first 3 years of life represent a narrow window during which the gut microbiome is established. Disruptions during this period can impact long-term health.
Ways that humans interfere with the normal acquisition of gut microbes
antibiotic use
C section
lack of breast feeding
indoor living
excessive sanitation
Why is high gut microbial diversity important?
High gut microbial diversity leads to a healthy ecosystem, with balance, functional redundancy, a high gene count, and resistance to damage.
Missing Microbiota Hypothesis
The Missing Microbiota Hypothesis suggests that loss of microbiota compounds over generations and that recent changes in lifestyle, such as exposure to antibiotics and cleaner living conditions, have exacerbated this loss.
Can lost microbiota be restored?
Sometimes lost microbiota can be restored through horizontal acquisition (e.g., from the environment or other individuals), but some microbes may not be recovered.
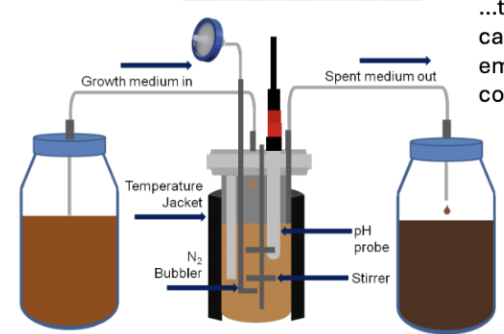
host free system allowing scientists to culture microbes in lab conditions that acctually allow for growth.
roboguts and robeeguts
a bioreactor that emulates the human colon environment that us used to study microbial ecosystems in humans and honeybees.
What happens when the microbiota breaches physical barriers or immune system defenses in a compromised host?
Normally, the microbiota is kept in check by physical barriers like gut lining, when it breaches this lining it can cause disease because now the microbiota has access to other areas like bloodstream.
in this case, the host is compromised.
opportunistic pathogens or pathobionts
microbes that are normally harmless in their usual location but can cause infections when they breach physical barriers or when the host's immune system is compromised. Can lead to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) if they gain access to areas like the bloodstream or other tissues.
How is the microbiota protective?
Competitive exclusion
Enviornment modification
Host stimulation
Direct pacification
Competitive exclusion example
Microbes like Staphylococcus epidermidis protect us by colonizing niches (e.g., skin, nasal passages), which prevents pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus from taking hold in the same space.
Enviornment modification (example)
Lactobacillus in the vagina lowers the pH, creating an acidic environment that is hostile to many pathogens, helping to prevent infections.
Host stimulation
Certain microbes like Bacteroides fragilis can stimulate host cytokine production, which helps regulate the immune system and prevent pathogen colonization.
Direct pacification
Some gut microbes secrete factors that prevent virulence gene expression in harmful bacteria like Salmonella enterica, helping to neutralize potential threats.
The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis
The two-way communication between the gut microbiota and the brain. Gut microbes may influence mood, behavior, and mental health through the metabolites they produce.
What do we see when microbial balance is disrupted
Containment breaches → cancerous lesion in colon allows bacteria to penetrate deeper tissue causing infection
Niche disturbance → ecosystem structure changed temporarily due to lifestyle changes and xenobiotics (drugs, pollutants)
Extinction events
What is the relationship between microbiome diversity and obesity?
Obesity is associated with a less diverse gut microbiome.
Microbes aid in nutrient absorption, and energy metabolism impacting obesity
no single microbe is responsible
Why is the word "dysbiosis" controversial?
Because it oversimplifies microbial imbalances and lacks a clear, consistent definition.
What is commonly seen in the gut of obese individuals as well as less diverse microbiota?
A potential increase in microbes producing pro-inflammatory molecules like LPS, and a decrease in microbes that support tight junctions
causing low grade intestinal inflammation
Peritonitis
microbes seep into admoninal space and cause infection
Why are individuals at higher risk of infection after experiencing diarrhea from infections like dysentery or norovirus?
Because diarrhea reduces gut microbial diversity, weakening microbiome and making the host more susceptible to further infections for several weeks.
Gnotobiotic animals
animals with a known and defined microbiota, including germ-free animals. They are expensive to manage but are extremely valuable for microbiome research.

Germ free animals
Germ-free animals have abnormal physiology:
Poorly developed immune systems
Lower cardiac output
Need more calories to maintain body weight
Thin intestinal walls with stunted villi
Enlarged, abnormal ceca
Misshapen (crescent-shaped) mitochondria
Odd behavior (e.g., aggression or extreme timidity)
These traits show that the gut microbiota is essential for normal immune, metabolic, and even behavioral development, and that there is communication between the microbiome and mitochondria.
Boy in the bubble
SCID patient, born with impaired immune system. Lived for 12 years in completely sterile enviornment.
only case of “germ free human”
he died after he got transfusion from sister who unknowlingly has Epstein Barr