Asking Questions about Spatial Data
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Queries
Analysis technique/method used to extract certain records from a map or table.
Aspatial queries
All parcels with value greater than $100,000
Spatial queries
All parcels that lie completely within the flood plain
Selecting features of interest
For example, selecting aspen stands from a forest vegetation layer.
Exploring patterns
For example, are aspen stands randomly scattered or clustered? Do they occur in partictular portions of the forest? What are the distributions of stand densities?
Isolating for more analysis
For example, are there any mature stands with large trees and open crowns? where ate they?
Exploring spatial relationships
For example, what fraction of stands are intersected by roads? What types of trees are adjacent to aspen stands?
Queries involving surfaces
Over what range of elevations do aspen occur? Do aspen occur above 1500m elevation?
Interactive query
User visually identifies the desired features in a map or records in the table
Ex. States west of the Mississippi River
Attribute query
An expression is used to find records with values meeting a specified condition
Counties with more than 100,000 people
Spatial query
A spatial relationship between two layers is evaluated
Cities within 50 miles of a major earthquake
Operators
Act on objects to produce a result.
Arithmetic operators
Act on numbers (+−×÷^)
Ex. 3 + 5
Logical operators
Test conditions and return true or false ( = > < ≥ ≤)
Ex. STATE= NJ, GPA >3.0
Boolean operators
Test pairs of conditions and return ture or false (AND OR XOR NOT)
Ex. MAJOR = Geography AND GPA ≥ 3.5
Spatial operators
Test spatial relationships between features ( intersect contains proximity)
Ex. Cities within 50 miles of a volcano
Attribure queries
Use expressions applied to a table to find records that meet one or more conditions.
Structured query langyage (SQL)
Expressions are executed using…
Multiple conditions must be tested
Boolean operators are used when…
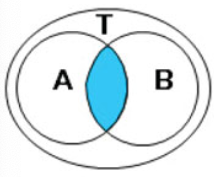
AND
Returns true if both conditions are true
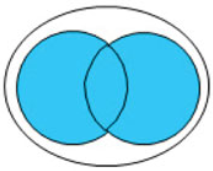
OR
Returns true if either or both conditions are true
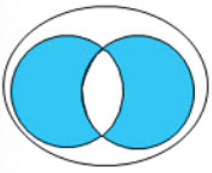
XOR
Returns true if one condition is true and the other is false (doesn’t matter which one is the true one)
NOT
Returns true if the first condition is true and the second condition is false.

Venn diagrams
Help visualize how boolean operators work.
Order of precedence
Multiple conditions are evaluated from left to right unless parentheses are used to change the order.
Intersect
Tests whether features touch
Contains/within
Tests whether a feature is inside another
Proximity
Tests whether features are within a specified distance of another
Contains operator
Permits the feature to lie on the edge of (share a boundary with) the containing feature.
Completely contains operator
Does not permit a shared boundary.
Target layer
The one from which the features will be selected.
Source layer
The one that the target features are compared to.
Select Layer by Location tool
A way to conduct a spatial query.
Logical consistency
How well a data set reflects real-world relationships.
Buffers
A type of spatial query that delineate the area (or boundary) of the region within a specified distance of a set of features.
Dissolve buffers
Used to generate a single, clean buffer region.
Clip and Erase
Extraction functions:
Clip
Works like a cookie cutter to extract features that lie inside the boundary of another data set.
Erase
Keep features outside of the boundary and remove the ones within the boundary.
Extraction functions
May change the lengths or areas of features that cross the boundary.
Interactive selection
User visually picks the desired features form a map.
Selection type
A parameter that determines what happens to an existing selection if another query is performed on the same layer.