Macro Notes for AP Test
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
MPS equals
1/MPC
MPC equals
Change in consumption/ Change in Income
MPS
Change in Savings / Change in income
Spending Multiplier
1/MPS
Tax Multiplier
(1/MPS) - 1
Inflation Formula
Nominal % Change - Real % Change
CPI

GDP Deflator Formula
(Nominal/ Real) (100)
Nominal GDP Formula
(GDP Deflator x Real GDP) (100)
***On pyramid nominal is on top and the GDP Deflator and Real GDP are on the bottom
Inflation Rate Formula

Money Multiplier
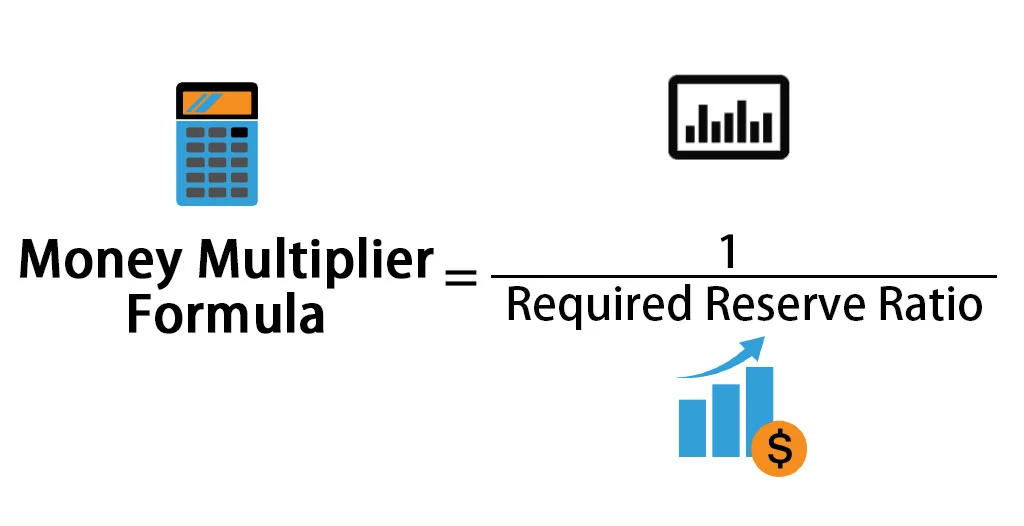
Quantity of Money Theory Formula

A PPC that is concave to the origin is
Bowed Out
For a bowed out PPC as more a good is produced what happens to the opportunity cost?
The opportunity cost increases
Olivia volunteers full time at an animal shelter and will not accept any offers for paid jobs for the next six moths. What best describes the employment position Olivia is in?
Olivia is not in the labor force
**People who are not working AND not actively looking for work are not in the labor force. This includes volunteers, retirees, stay at home parents and discouraged workers
With expansionary fiscal policy what happens to Real GDP and nominal interest rate?
Real GDP increases and nominal interest rate increases because demand for loanable funds increases
Economic Growth is best measured by a sustained increase in which of the following?
(a) Per capita real gross domestic product
(b) Nominal GDP
Explanation:
Economic growth is best measured by a sustained increase in real GDP per capita which accounts for both inflation and population growth
A rise in real per capita GDP means that on average individuals in an economy are producing and consuming more services over time
The measure of Real GDP per capita is superior to Nominal GDP b/c Nominal GDP does not account for inflation.
The measure of Real GDP per capita is superior to just Total Real GDP b/c Total Real GDP does not account for population changes
Assume that a country’s government increases borrowing. What will most likely happen to the prices of previously issued bonds and the price level in the short run?
Bond Price: Decreases
Price Level: Increase
Why does Bond Price Decrease?
When the government borrows more it issues new bonds to finance its spending. This increases the supply of bonds in the market and a higher supply of bonds lowers the price of previously issued bonds
Why does price level increase?
Price Level increases b/c AD increases (shifts right) due to increased government spending
If government spending increases at the same time a country’s central bank conducts monetary policy to increase its policy rate, the interest rate and private investment in plant and equipment will most likely change in which of the following ways?
The interest rate will increase and private investment in plant and equipment will decrease
***When government spending increases the supply of loanable funds decreases which drives up the interest rate
***If policy rates are increased then resource cost will be higher so businesses are less likely to invest in new equipment
In the Long Run a fully anticipated expansion of the money supply will
Increase both the price level and Nominal GDP
Why does Nominal GDP increase and not Real GDP?
-Real GDP does not change in the LR b/c it is determined by factors like technology, labor, and capital not the money supply
-In the LR money supply affects nominal variables like nominal GDP and price level but does not change real variables like Real GDP or real wages
Assume the MPC is 0.75, net exports decrease by 10 billion and government spending increases by 20 billion. The equilibrium gross domestic product can increase by a maximum of
net change in spending: 20-10=10 billion
1/0.25=4
10×4= 40 billion
The demand curve for money (MD) shifts to the right when
the nominal gross domestic product increases
***When nominal GDP increases it means that the total value of goods and services produced (measured in current prices) has risen. This leads to
Higher Income Spending
Greater Demand for money
If the required reserve ratio is 10% what is the maximum change in the money supply from John’s deposit of $50,000 cash into his checking account?
$450,000
(1/0.1)=10
50,000(10)=500,000
500,000-50,000=450,000 b/c they can’t loan out the amount he deposited
More discouraged workers leads to a
decrease in rate of unemployment and decrease in labor force participation rate
In the country of Pierce, government spending decreased while the level of private savings increased. How will these changes affect the real interest rate and interest sensitive spending in the short run?
Real interest rate will decrease and interest sensitive spending will increase
**Gov spending decrease —→ Reduces demand for loanable funds which decreases interest rate
**Private Savings increase —→ More savings increase supply of loanable funds which pushes interest rates down
Why does CPI does not measure the true cost of inflation?
Improvements in the quality of goods and services are not fully reflected
What happens to output in demand pull inflation and cost push inflation?
Output increases during demand pull inflation but decreases when there is cost push inflation
Bond prices and interest rates have a
inverse relationship
GDP deflator in base year
is 100
What happens during the expansionary phase of business cycle?
Employment increases, interest rates decrease
Deflation leads to
increased real value of fixed incomes
What is a defining characteristic of a fractional reserve banking system?
The fact that banks retain an amount of bank reserves that is less than the amount of customer demand deposits
Which of the following would decrease the United States net exports to South Korea?
South Korean computer companies sell more computers to the US.
***This counts as an increase in imports for the US so that means net exports would decrease for the United States
An increase in the purchases of newly constructed houses will result in which of the following?
Aggregate Demand will increase as a result of an increase in investment spending
**Newly constructed homes are counted under capital goods in macroeconomics not consumer spending. That is because housing is a capital investment not like a good you consume like groceries.
CPI=
(Cost of Market Year 2/ Cost of Market Basket Base Year) x 100
Pat deposits a portion of her wages into a personal savings account every week. The saved money can be considered to be primarily a
Store of Value
****A store of Value means money can be saved now and still used later. It holds value over time so it can be used for future purchases
Means of Payment/Medium of Payment
When money is used to buy something immediately
Unit of Account
When money is used to value or set prices
(This costs $10)
Banks expand the money supply when they
make a loan
***Each loan adds to the total money supply because the same original money is showing up in multiple accounts; this is called the money multiplier effect
The economy is currently in long run equilibrium. If the central bank increases the money supply what will happen to price level and real output in the long run?
Price level will increase and output will remain at the full employment level
***In the long run money is neutral, it only affects price level not output
When interest rates rise the opportunity cost of holding cash
increases because the cash you are holding is not making interest in the banks.
Competition makes prices more
flexible rather than sticky b/c firms in highly competitive markets must adjust prices to stay relevant.
Sticky Prices or Wages
prices or wages don’t adjust quickly when economic conditions change
A bank has $200 million in demand deposits and $150 million in reserves. The reserve ratio is is 20 percent. What is the maximum amount of loans the bank can make from its reserves?
0.2(200)=40 million
150 million - 40 million= 110 million in excess reserves so that is how much the bank can loan out
Opportunity Cost
The value of all forgone benefits of the next best alternative
Trade Off
all the alternatives that are sacrificed when a choice is made- not just the next best one
When nominal income is less than the inflation rate then
real income decreases because prices are rising faster than your income is increasing so your purchasing power falls
In the factor market government and businesses
buy resources while households provide resources such as workers
In the product market
government an households are purchasers of goods and services while businesses provide
For the actual PPC curve to shift rather than just the point then
there must be a negative or positive change in net investment (differing unemployment shifts the point only)
SRAS self corrects in an inflation
Because resource cost is too high meaning that workers will demand higher wages leading to higher input costs for businesses
Income taxes and transfer payments are
automatic stabilizers
What decreases during crowding out?
Investment spending decreases which decreases the growth rate of the economy
Gross Investment=
Purchases of physical capital
Foreign Goods purchased by the US are ______ from GDP
subtracted b/c they are imports
Economic Expansion in the United States causes the dollar to _____ on the foreign exchange Market
depreciate b/c there is more of it available on the foreign exchange market
Which of the following combinations of monetary and fiscal policies will cause the largest increase in growth rate?
Expansionary monetary policy, tax increase and gov spending decrease
If more people choose to hold their assets as money then what will happen to nominal interest rate?
Nominal interest rate will increase because demand for money will shift right
In an inflation what happens to real wages?
Real wages decrease
Specialization and trade cannot its normal benefits when
the OPC of making two goods are the same in two countries
Why do automatic stabilizers cause taxes to rise and government spending to fall during a recession?
Automatic stabilizers provide people with stimulus checks and give people higher income allowing income taxes to increase and gov spending to decrease
A rise in real GDP is caused by an increase in
output NOT price level
An Italian company has a shoe factory in America does its profit count towards American GDP or Italian GDP?
American GDP. It does matter where a country has its headquarters. GDP counts production within a nation’s borders.
What is not included in GDP?
Imports
CPI is only affected by
Changes in consumer goods not changes in industrial goods such as forklifts
An increase in demand for money results from a
higher price level
Crowding out leads to a
decrease in investment spending
Shortages
drive up price level so if the quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied prices will be driven upward to restore equilibrium
If products are produced in one year (for example 2006) but sold in the next year (2007) in which year is GDP allocated and why?
The products still count towards 2006 GDP b/c they are counted as inventory and inventory is investment spending
During contractionary phases of the business cycle what kind of fiscal and monetary policies should be used?
Expansionary monetary and fiscal policies
A change in government spending will have a greater impact when the MPC is
larger
Real GDP equals
Current Year Quantities x Base Year Prices
GDP measures
a country’s level of production and income
When will potential GDP fall?
When a country’s retirement age is lowered
How can an economy return to full employment in a recession in the long run?
Nominal Wages AND price level must decrease
Why wages?
As wages fall, production costs for firms decrease encouraging them to hire more workers and produce more stimulating the economy to return to full employment
When the government is increasing its budget surplus then
The supply of loanable funds increases
How is a barter economy different from a money economy?
A barter economy involves higher costs for each transaction due to the need for a double coincidence of wants, whereas a money economy uses currency as a medium of exchange, facilitating easier transactions.
As investment becomes more responsive to changes in interest rate monetary policy becomes
more effective at changing real GDP
How are tariffs different from import quotas?
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, which raise their prices and generate revenue for the government, while import quotas are limits on the quantity of specific goods that can be imported, restricting supply directly.
Why are savings accounts not included in M1?
They are not a medium of exchange
If money supply grows faster than Real GDP that leads to
inflation
If money supply grows slower than Real GDP that leads to
deflation
If economic agents perfectly anticipate policy changes and if all prices including wages are completely flexible which of the following will be true in the long run?
The there be no trade off between inflation and unemployment (Long run Philips Curve)
When will changes in nominal interest rate and real interest rate be the same (both increase or both decrease)
when price level is constant
The federal funds rate decreases when
money supply increases such as through buying bonds due to banks having more reserves, making borrowing easier and lowering the federal funds rate.
unexpected inflation helps
borrowers
unexpected inflation hurts
lenders and people on fixed incomesand those with fixed-rate loans.
National Debt
Accumulation of all budget deficits over time
Budget Deficit
When government expenditures exceed its revenues in a given period.
Long run Aggregate Supply shows that
in the long run price level increase but real output does not change. It reflects the economy's potential output when all resources are fully employed.
M1(Highest Liquidity)
-Currency in circulation
-Checkable bank deposits (checking accounts)
-Traveler’s checks
M1 is money you can spend immediately
M2
All of M1 plus savings accounts, certificate of deposits, and money market mutual funds
M2 includes money that’s not as liquid as M1, but can still be converted fairly easily into cash or checking deposits.
Commodity Money
Something that performs the function of money and has intrinsic value , such as gold or silver, which can be used for trade and has value in itself.
3 shifters of money supply
Reserve Requirement, The Discount rate, and Open Market Operations
Higher Inflation in your country leads to a greater demand of another country’s cheaper goods which causes what of the following changes in the value of the other country’s currency?
An appreciation of the other country's currency.
In the long run changes in the money supply can only cause changes to
inflation not permanent changes in Real GDP
In the short run
-Unemployment can rise or fall
-Wages and prices don’t adjust instantly
Investment Tax Credit
A GOOD THING. It makes investments cheaper for firms encouraging them to invest more in capital goods (economic growth)
Maximum Loans Formula
Initial Deposit (1-RRR)
Max increase in Money Supply
Initial Deposit (1/RRR)