STS - QUIZ
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
One Health-Human & Animal Environment
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
One Health Approach
Concept created in 2004
Design and implement programs, policies, legislation, and research in which multiple sectors work together to achieve better public health outcomes (WHO, 2017)
This are the main working organizations:
World Health Organization (WHO)
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
World Organization for Animal Health (OIE)
and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
(SDG 3 - GOOD HEALTH AND WELL BEING) Health
A state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (WHO, 1948)
(SDG 3 - GOOD HEALTH AND WELL BEING) Wellbeing
In contrast to states of human health, describes a situation in which people are free to choose to do and be what they value (Sen 1999)
Good Health and Wellbeing co-determine each other (Gatzweiler et al., 2017)
Wellness
holistic integration of physical, mental, and spiritual well-being
fuels the body, engages the mind, and nurtures the spirit
Health hazards
____ are wellness risks which are usually expressed as probabilities/chances
Probability of suffering harm from an agent that can cause injury, disease, death, economic loss, or damage.
Chemical hazards
from harmful chemicals in air, water, soil, food, and human-made products
Natural hazards
such as fire, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, and storms.
Cultural hazards
such as unsafe working conditions, unsafe highways, criminal assault, and poverty.
Lifestyle choices
such as smoking, making poor food choices, drinking too much alcohol, and having unsafe sex.
Biological hazards
from more than 1,400 pathogens that can infect humans (pathogen is a biological agent that can cause disease in another organism)
• Bacteria
• Viruses
• Parasites
• Protozoa
• Fungi
Zoonoses
diseases or infections that are naturally transmissible from animals to humans (WHO, 2020)
Biological Hazards through Zoonoses and Emerging Diseases
• health risks through deep interconnections of human, animal and environmental health
• ~60% existing human infectious diseases are zoonotic
• ~75% of emerging infectious diseases (including Ebola, HIV, influenza, COVID19) have an animal origin
Infectious disease ( Human to another)
when a pathogen such as a bacterium, virus, or parasite invades the body and multiplies in its cells and tissues (e.g. Tuberculosis, flu, malaria, measles).
Bacteria ( Human to another)
single-cell organisms that are found everywhere. Most are harmless or beneficial. A bacterial disease results from an infection as the bacteria multiply and spread throughout the body.
Viruses ( Human to another)
smaller than bacteria and work by invading a cell and taking over its genetic machinery to copy themselves. They then multiply and spread throughout one’s body, causing a viral disease such as flu or AIDS.
Viral
Systemic, meaning it spreads throughout the body.
It is Contagious
Can’t be treated with Antibiotics
Ex: common colds, flu, chicken pox.
Bacterial
Usually localized, meaning it stays in one part of your body such as ear or throat.
Sometimes contagious.
Treatable with antibiotics.
Ex: Strep Throat, Pneumonia, Urinary Tract Infections.
Antibiotic Resistance:
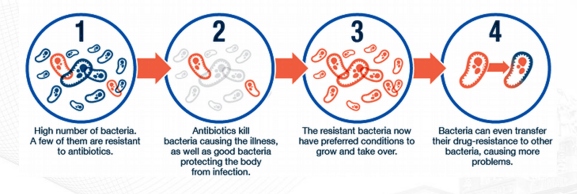
Transmissible disease
infectious bacterial or viral disease that can be transmitted from one person to another. “communicable”
Non-transmissible disease
caused by an agent/event other than a living organism and does not spread from one person to another. “noncommunicable” (e.g. cardiovascular (heart and blood vessel) diseases, most cancers, asthma, and diabetes)
Epidemic
A large-scale outbreak of an infectious disease in an area
Pandemic
A global epidemic such as tuberculosis or AIDS
Disease Name: Coronavirus Disease 2019 or COVID-19
Virus taxonomy (name): Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus or SARS-CoV-2
Role of Thomasian Scientists in Providing Clarity on COVID-19 pandemic in the Philippines
UST CoV-2 Model
• Epidemiological model that predicts the future behavior of a viral pandemic by examining how it has spread in the past.
• NCR - over a tenth of the country’s population live - by far, the epidemiological epicenter of the Philippine pandemic
Important aspect of animal health and welfare is the protection of biodiversity
• Variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or for entire Earth.
• Used as a measure of the health of biological systems.
• Current biodiversity is the product of nearly 3.5 billion years of evolution
Levels of Biodiversity
Ecosystem Diversity different habitats, niches, species interactions
Species Diversity different kinds of organisms, relationships among species
Genetic Diversity different genes and combination of genes in species
How much do we know about the world’s biodiversity
• Approximately 1.7-2 million species are named and discovered.
• Estimated total: 100 million species
• The majority are yet to be discovered
How did biodiversity emerge and where can we find them?
Different physiochemical and climatic conditions brought about unique and diverse habitats.
Diverse habitats drive evolution and contribute to species endemicity.
Importance of sustaining biodiversity
• Provides necessary ecosystem services to sustain human life and ecosystem balance.
• Ecosystem services include:
• Supporting
• Provisioning
• Cultural and Aesthetics
• Regulating
Threats to Biodiversity
Anthropogenic impacts bring about population size reductions and species extinctions.
Hunting and overharvesting
Habitat loss
Pollution
Invasive Species
Climate Change
Popular Native Plants Group Affected by the Covid-19 Pandemic Plant Craze
Aroids
Ferns
Palms
Carnivorous Plants
Hoyas and allies
Medinilla
Some Native Trees
Ant plants
Biodiversity Loss Consequences
• Nutrition and food production
• Health research and traditional medicine
• Emergence of infectious diseases
• Climate change
Animal Health and Diseases and Pandemics
Zoonotic diseases due to close contact with Wildlife:
• Rabies
• Salmonella infection
• West Nile virus infection
• Q Fever (Coxiella burnetii)
• Anthrax
• Brucellosis
• Lyme disease
• Ringworm
• Ebola
• COVID-19
The World Organisation for Animal Health
formerly the Office International des Epizooties
The organization ensures transparency in global animal disease situations, collects and disseminates veterinary information, promotes international solidarity, safeguards world trade, improves veterinary services, and ensures animal welfare through scientific evidence.
Philippine Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
Programs
Integrated Approach in the Management of Major Biodiversity Corridors in the Philippines
Maintaining Ecosystem Flows, Mainstreaming Biodiversity and Restoring Degraded Forestlands and Enhancing Carbon Stocks through an Integrated Landscape Approach
Capacity Building for the Ratification and Implementation of the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-Sharing in the Philippines
Combatting Environmental Organized Crime in the Philippines
Carbon-Resilient, Low-Carbon and Sustainable Cities
Environment and One Health
Poor environmental quality has its greatest impact on people whose health status is already at risk.
Lack of ”safe and livable space”.
Poor air and water quality contributes to cancers, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, gastrointestinal problems, neurological problems, etc.
Built environment affects lifestyle (transportation, parks, recreational areas) and primary society services (hospitals, schools, etc.)
Urbanization
the process by which large numbers of people become permanently concentrated in relatively small areas, forming cities.
Poor business environment
Weak infrastructure, land management and access to markets
Low demand for innovation and skill match
Limited access to finance and business support
Insufficient economic planning
Resource Mismanagement
Resource Mismanagement
Energy poverty as the real energy crisis
Land governance crisis leads to congestion in cities and ‘urban nightmare”
Climate Change
used to describe the complex shifts now affecting the planet’s weather and climate systems - National Geographic
National Environmental Health Action Plan
Programs
• Drinking-water supply, Sanitation (e.g excreta, sewage and septage management)
• Zero Open Defecation Program (ZODP)
• Food Sanitation
• Air Pollution (indoor and ambient)
• Chemical Safety
• WASH in Emergency situations
• Climate Change for Health and Health Impact Assessment (HIA)