Topic 2: Measuring the Macroeconomy (ECON1102)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
National income accounting
Provides a systematic method of aggregating the production of diverse goods into a single measure of overall economic activity.
What does national accounting allow us to analyse?
The state of an economy at a given time, the changes over time, and differences across countries.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The market value of the final goods and services produced in an economy over a certain period.
Circular Flow
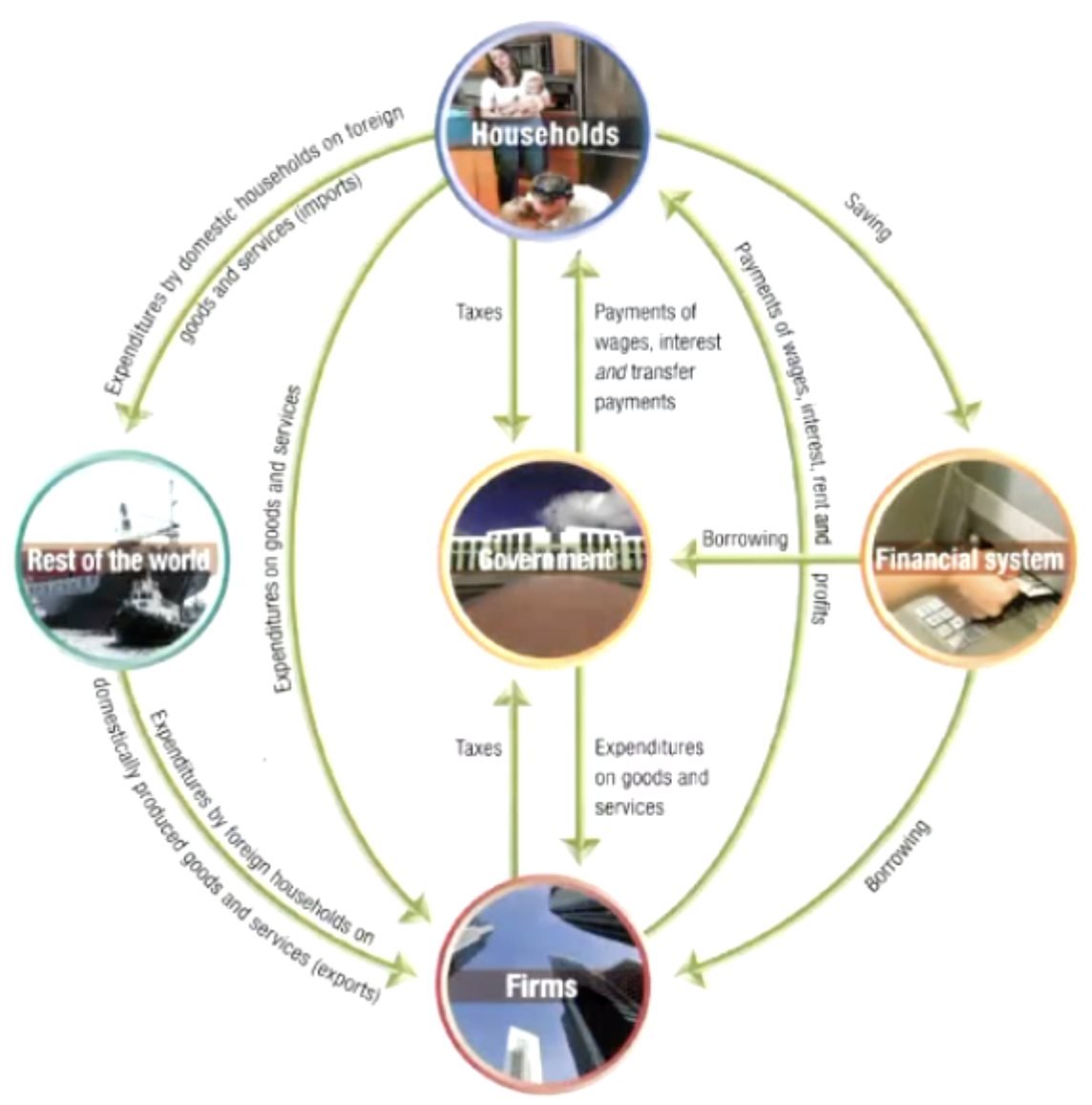
True or False: Production = Expenditure = Income
True
What does the production measure of GDP count?
The number of goods produced in the economy.
What does the expenditure measure of GDP count?
The total purchases in the economy.
What does the income measure of GDP count?
All the income earned in the economy.
What does the national income accounting identity state?
Y = C + I + G + NX
Y = GPD in dollars, C = Consumption, I = Investment, G = Government, NX = Net exports.
Consumption (C)
Spending by households on goods and services.
Investment (I)
Spending for the purpose of additional production.
Government spending (G)
Goods and services that the government buys.
Net exports (NX)
Spending on exports (X) minus spending on imports (M).
What does a trade deficit indicate? (Expenditure Approach to GDP)
That the country is borrowing goods from the rest of the world. This deficit must be repaid in the form of trade surpluses in the future.
What are transfers? (Expenditure Approach to GDP)
Government payments to individuals (e.g., social security, Medicare, unemployment benefits, etc.).
Are transfers included in GDP? (Income Approach to GDP)
No, because they do not involve the production of goods.
Capital (Income Approach to GDP)
The inputs into production other than labour that are not used up in the production process.
How can firms increase capital? (Income Approach to GDP)
Through investment.
Depreciation (Income Approach to GDP)
The deterioration of the capital stock due to wear and tear.
If we subtract depreciation from gross domestic product, what do we get? (Income Approach to GDP)
Net domestic product
Net domestic product (Income Approach to GDP)
NDP = C + I + G + (X-M) - depreciation
Is there “double counting” in GDP? (Production Approach to GDP)
No. Only the final sale of goods and services count.
Value added (Production Approach to GDP)
The amount each producer contributes to GDP; the revenue generated by each producer minus the value of intermediate products.
Two ways of eliminating double counting (Production Approach to GDP)
Calculate only final output (goods and services purchased for final use).
A firm would report how much it sold to consumers and how much it sold to producers (intermediate goods).
Follow the value added approach.
Value added: increase in value that a firm contributes to a product or service.
Calculated by subtracting intermediate goods (the cost of materials that a firm uses to produce a good or service) from the value of its sales.
What is included in GDP?
Only goods and services that are transacted through official (and legal) markets.
Examples that are counted towards GDP
Value added by a used car dealer.
Commissions paid to stock brokers.
What does GDP not include?
A measure of the health of a nation’s people.
Changes in environmental resources.
Other intangibles people value (crime rates, traffic congestion, etc.).
Value leisure.
Examples that are not counted towards GDP
Value of resale goods.
Sale of stocks or bonds.
Government transfer payments.
Work of house-spouses.
Gross National Product (GNP)
The aggregate final output of citizens and businesses of an economy in one year. It is the output produced by a country’s citizens.
GNP = GDP + Net foreign factor income
Net foreign income
The income from foreign domestic factor sources minus foreign factor income earned domestically.
Gross National Income (GNI)
The total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country. It is equal to (GDP) plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents (thus referring to income residents earn from their labour (L) and capital (K) contributions, minus income earned in the domestic economy by non-residents.
What is Gross National Income (GNI) meant to capture?
How much a country’s residents in a given period are actually earning from their economic activity.
Wealth account
A balance sheet of an economy’s assets and liabilities and it is a stock concept.
Real wealth
The value of the productive capacity of the assets of an economy measured by the goods and services it can produce now and in the future.
Nominal wealth
The value of those assets measured at current market prices.
What can ‘per capita GDP’ be used for?
To compare relative standards of living among various countries.
Why may ‘per capita GDP’ be a misleading measure of living standards?
Because of differences in non-market activities and differences in product prices.
Purchasing power parity
Adjusts for relative price differences before making comparisons.