Lecture 3 Innate Immunity Part I
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Innate Immunity
-Generalized response
-Has no memory
-Fast-acting, always present
-Born with this system
-Evolutionarily older process
Adaptive immunity
-Specific response
-Has memory
-Slow-acting, must ramp up
-Acquire this system
-Key feature of vertebrates
External Defenses
1st line of defense
includes:
-Physical barriers
-Chemical barriers
-Biological barriers
Immune system mechanism
-Safeguard us from infections
-Surveil our body for intruders
-Maintain protective responses against harmful elements
Physical barriers
keep hazardous organisms and materials outside the body
includes: skin, mucosal membranes, hair, cilia, etc.
skin
physical barrier
Epidermis - outer layer of dead, tightly-packed keratinized cells
-shedding of dead skin cells removes attached microorganisms; Few pathogens can penetrate layers
Dermis - collagen protein fibers give strength and pliability to resist abrasions
mucosal membranes
physical barrier lining respiratory, digestive, urinary, conjunctival, and reproductive
-line all body cavities open to the outside envrioment
-Living epithelial cells tightly packed to prevent pathogen entry
-Continual shedding of cells carries attached microorganisms away
hair
physical barrier
Hair Follicles (Nasal hair, Eyelashes, Eyebrows, Body hair, etc.)
-Trap dirt, debris, and potentially harmful microorganisms
-Eyelashes - Eyelid movement sweeps airborne dirt/debris/microorganisms away from the eye
Cilia
physical barrier
-Beat in concerted waves to propel pathogens and inhaled particles trapped in the mucous layer out of the airways
-Sneezing or coughing ejects mucus and pathogens from the nose and throat
Chemical barriers
Antimicrobial Peptides
found on the skin, mucosal membranes, and in phagocytes
- increases their antimicrobial activity
Examples:
-Defensins
-Lactoferrin
-Dermcidin
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
small, positively charged amino acid sequences naturally found in the innate immune system (a.k.a. antimicrobial enzymes)
Sweat
chemical barrier secreted by sweat glands; contains antimicrobial peptides (Defensins)
-salt inhibits pathogen growth by drawing water from microbial cells (osmosis)
Sebum
chemical barrier secreted by sebaceous (oil) glands; lowers skin pH to inhibit bacterial growth
-helps keep skin pliable and less likely to break or tear
Mucus
chemical barrier that lines mucosal membrane surfaces to trap dirt and microbes
-every day, you swallow and digest about 1 liter of mucus
Lysozyme
chemical barrier that destroys bacterial cell walls
-A primary component of saliva and tears
Tears
chemical barrier that is a heterogenous mixture of water, lipids, mucus, electrolytes, and proteins
-contain antibacterial enzymes (Defensins, Lysozyme, and Lactoferrin) and high quantities of IgA
Urine
chemical barrier that flushes out the organs of the urinary tract
-Bladder epithelial cells secrete antimicrobial compounds into the urine
Saliva
chemical barrier secreted by the salivary glands; regulates oral pH to inhibit bacterial growth
-contains antibacterial enzymes (Defensins, Lysozyme, and Lactoferrin) and high quantities of IgA
Cerumen
chemical barrier that is an oily emulsion that coats and protects the ear
-Traps dust and repels water; maintains a low pH to inhibit bacterial growth
Stomach Acid
chemical barrier with a low pH (2) kills most harmful microbes
Biological barriers
living organisms that help protect the body from pathogens (Microbiome)
-trillions of harmless bacteria, protists, and fungi live on the human skin and in the urinary, reproductive, and gastrointestinal tracts.
-these bacteria use up food and surface space that help prevent pathogenic bacteria from colonizing the body
-Some harmless bacteria also secrete substances that changes conditions of their environment, making them less hospitable to potentially harmful bacteria
-reduce the chances that pathogenic microorganisms can reach sufficient number to cause illness
Internal Defenses
2nd line of defense
includes interferons, immune cells, complement system, and inflammation
Interferons
a group of proteins manufactured by cells in response to viral infections
Abbreviated IFN or IF
Produced by virus-infected cells to signal neighboring cells.
-interfere with viral replication
-Enhance phagocyte activity
-Stimulate antibody production
-Enhances NK cell killing power
-Slow cell division and tumor growth
Innate Immune cells
derived from myeloid precursors
"Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas!"
-Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophil, and Basophil
Antigen-Presening cells
present antigen (i.e., pieces of phagocytized bacteria) to T-cells in the adaptive immune system
-Macrophages, Dendritic cells, and Select B-cells
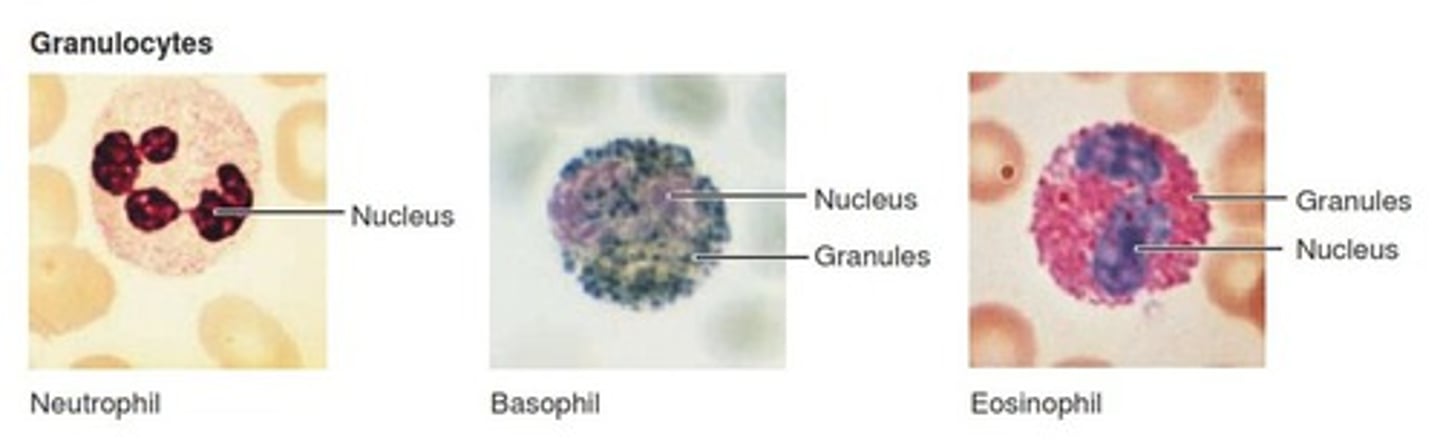
Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
Also known as granulocytes
-Short-lived phagocytic cells
-Contain lysosomes to break down infectious microorganisms
-Produce peroxide, superoxide radicals, and nitric oxide (toxic to cells)
-Defects in PMN cell function result in chronic/recurrent infection
Macrophage
phagocyte that engulf/break down trapped materials and take up antigens, process them, and present them to T-cells
-following tissue migration, undergo additional differentiation based on location
-Members of the reticuloendothelial system
Dendritic cells
specialized white blood cells that patrol the body searching for antigens that produce infections
-phagocytes
-Most efficient APCs
-varying cell lines (myeloid and lymphoid varieties)
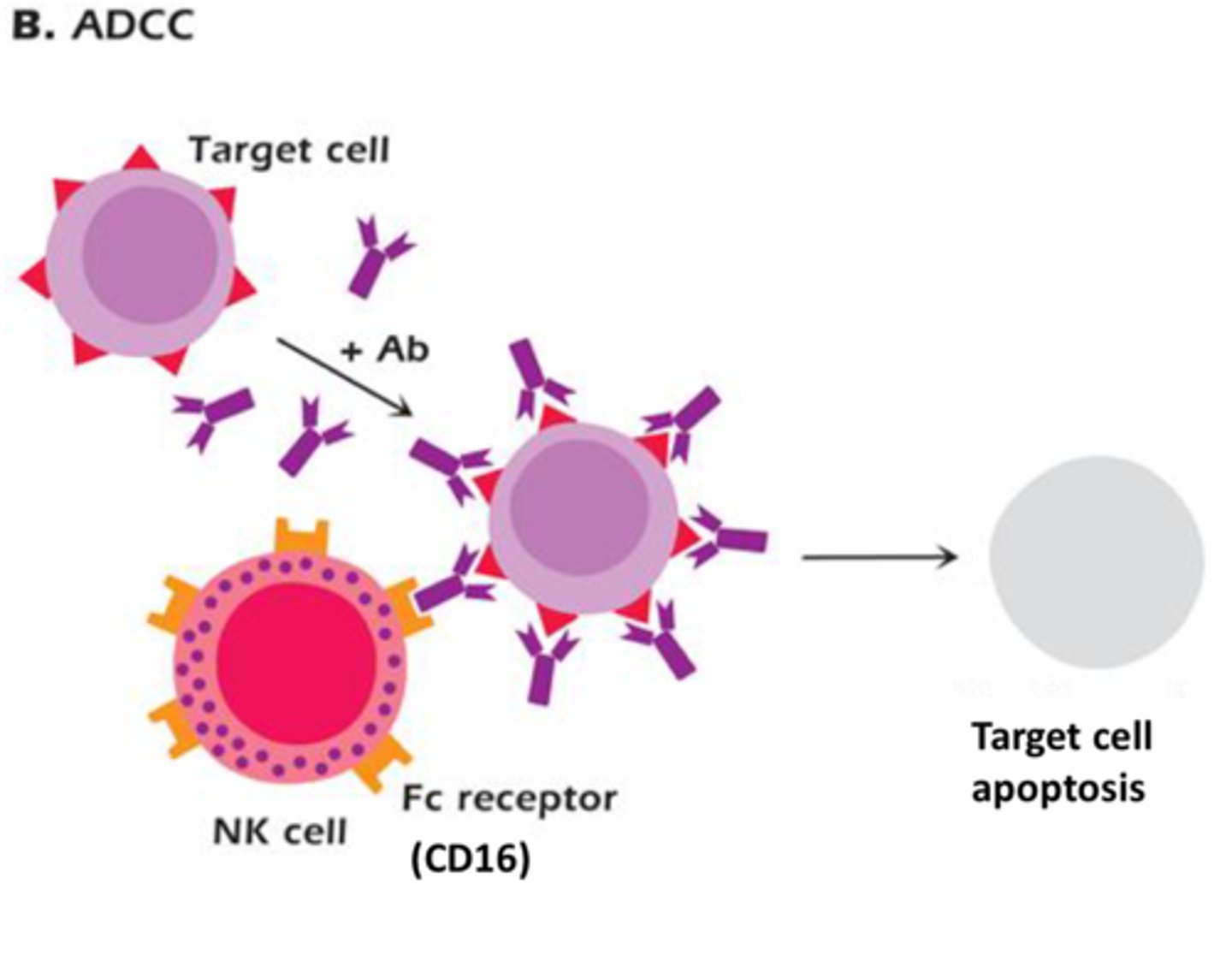
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
play an early role in terminating viral-infected cells or tumor cells
-in between innate and adaptive
Two receptors control whether NK cells will eliminate host cells:
-Inhibitory Receptor = Major Histocompatibility complex (MHC) Class I
-Activating Receptor = Killer-Cell Inhibitory Receptors (KIRs)
Viral-infected cells and tumor cells DO NOT express sufficient MHC class I molecules to prevent termination
-NK cell releases perforin and granzymes to cause cell lysis
Innate Lymphoid cells
come from lymphoid tissue
Various subsets have different roles and different locations.
Act in early stages of immune response as it transitions to adaptive response.