Food supply, plant growth, and productivity
1/48
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Food security
The ability of human populations to access food of sufficient quality and quantity
Why is there a concern for food security?
There is a growing human global population which increases the demand
What two things must food production be?
Sustainable and not degrade the natural resources in which agriculture depends on
Sustainability
Something that’s guaranteed over a long period of time
Where does most human food come from?
A small number of plant crops
What four crops does most human food come from?
Cereals
Legumes
Potatoes
Roots
What is food production (agriculture) dependent on?
The factors that control photosynthesis and plant production
What is the solution to the problem - the area to grow crops is limited?
Replace existing crop plants when higher yielding cultivars
What is the solution to the problem - shortage of mineral elements or water?
Increase the supply of fertilisers or use a sprinkler system
What is the solution to the problem - pests (eg. fungi or Insects)?
Use fungicides or insecticides
What is the solution to the problem - competition from weeds?
Use herbicides
What four things do plant breeders seek to develop in their crops?
Ability to thrive in particular environmental conditions
Disease and pest resistance
High nutritional values
Physical characteristics suited to harvesting and rearing
Why is food production (agriculture) dependent on photosynthesis?
Produces obtain their energy from the sun and this is then passed onto animal consumers along the food chain
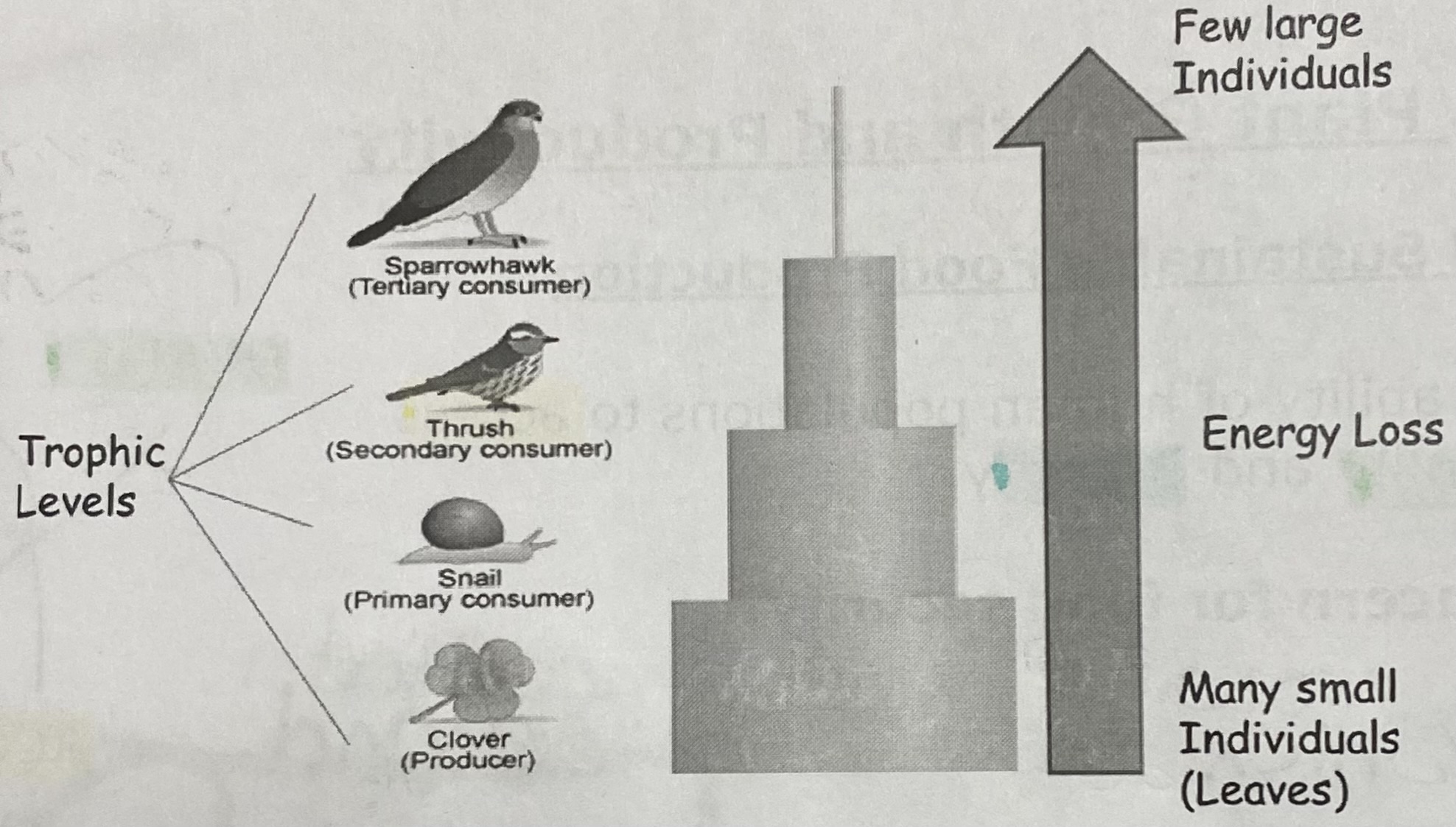
Diagram: food chain
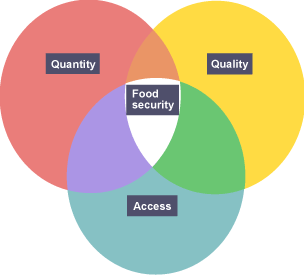
Diagram: food security
Why do livestock produce less food per unit area than plants?
90% of energy is lost at each tropic level, whereas only 10% is passed along
Which food chains are more efficient?
Shorter ones
What two things explain why livestock is sometimes farmed rather than crops?
The climate might be too harsh and the landscape might not be suitable
Example: why is livestock sometimes farmed rather than crops?
If the environment is too hilly or rocky
What must a plant do to be productive?
Photosynthesis as rapidly as possible
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants absorb light energy to make glucose
Why is the rate of photosynthesis of crop plants important?
The greater the rate of photosynthesis, the greater the rate of plant growth and therefore the higher the yield of the crop
What are two factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis of a plant?
The concentration of pigments in the leaves and the size of the leaf
What is the first thing to happen in photosynthesis?
Light is absorbed by the plant leaves
Visible light
The name given to the light from the sun or light bulbs that is made up of all the colours of the rainbow
What are the three fates of light when hitting a leaf?
Absorption
Reflection
Transmission
A pigment
A substance which absorbs visible light
What determines the colour of pigments?
The light/wavelength they don’t absorb
What are the four pigments in plant leaves?
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll B
Carotene
Xanthrophyll
What determines colours?
Wavelengths of lights
What is the technique that separates photosynthetic pigments?
Chromatography (TLC)
What is an advantage of plants having carotenoids?
The total quantity of light absorbed is greater than it would have been if only one pigment was absorbed
What do carotenoids do?
They extend the range of wavelengths absorbed and pass the energy to chlorophyll (A and B) for photosynthesis
What are the two pigments known as carotenoids?
Carotene and xanthrophyll
Absorption spectrum
This shows how much light of each wavelength is absorbed by the different plant pigments
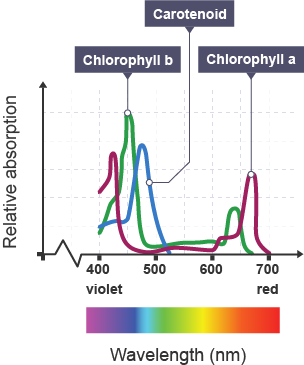
Diagram: absorption spectrum
What apparatus is used to measure the degree of absorption by the different plant pigments?
A spectrometer
Action spectrum
This shows the effectiveness of different wavelengths of light at brining about photosynthesis
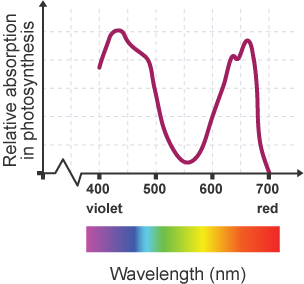
Diagram: action spectrum
What does the close correlation between the action and absorption spectrum show?
The leaf pigments absorb the wavelengths of light that are the most effective at bringing about photosynthesis
What is stage one of photosynthesis?
The light dependent stage
What is stage two of photosynthesis?
The Calvin cycle
What are the four stages of the light dependent stage?
Light energy, absorbed by pigments, excited electrons in the pigment molecules
These high-energy electrons are transferred through an electron transport chain and pump hydrogen ions across the membrane. The return flow of hydrogen ions drives ATP synthase
Rotation of ATP synthase produces ATP
Energy is also used to split water into hydrogen ions and oxygen (photolysis). Oxygen is evolved (removed) and hydrogen ions bind to the coenzyme NADP to form NADPH
What two things are required for the Calvin cycle from the light dependent stage?
ATP and the hydrogen ions held in the coenzyme NADP
What are the three stages of the Calvin cycle?
Carbon dioxide enters the cycle and binds to RuBP (Ribulose Biphosphate). This reaction is controlled by the enzyme RuBisCO
The intermediate produced (3-phosphoglycerate/3PG) is phosphorylated by ATP and combines with hydrogen ions (from NADPH). This forms glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
G3P is used to synthesis glucose and to regenerate RuBP
Phosphorylation
When molecules have a phosphate added to them they become energy rich and more reactive, cellular respiration provides the energy for this and ATP turning into ADP + Pi provides the additional phosphate
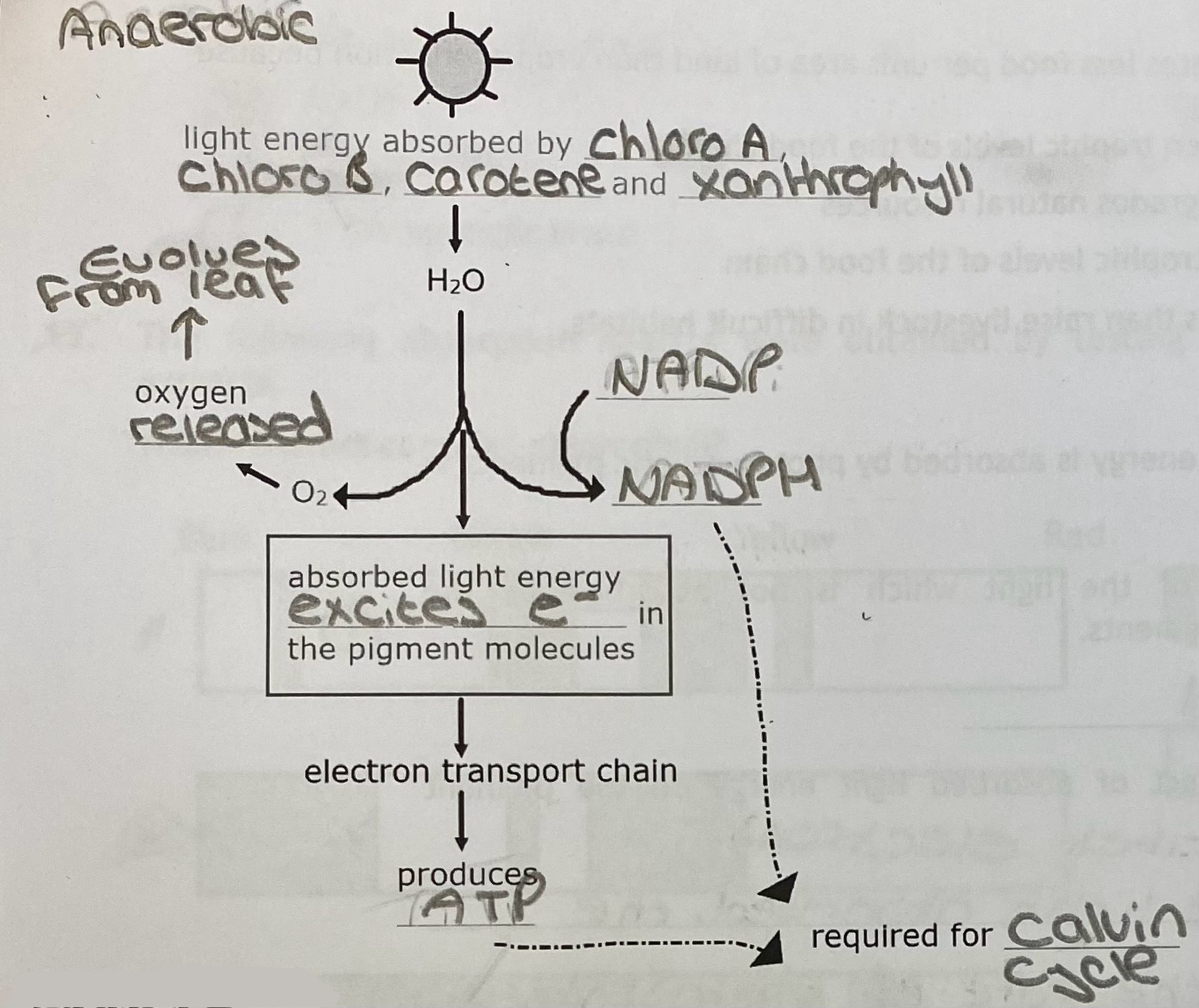
Diagram: the light dependent stage
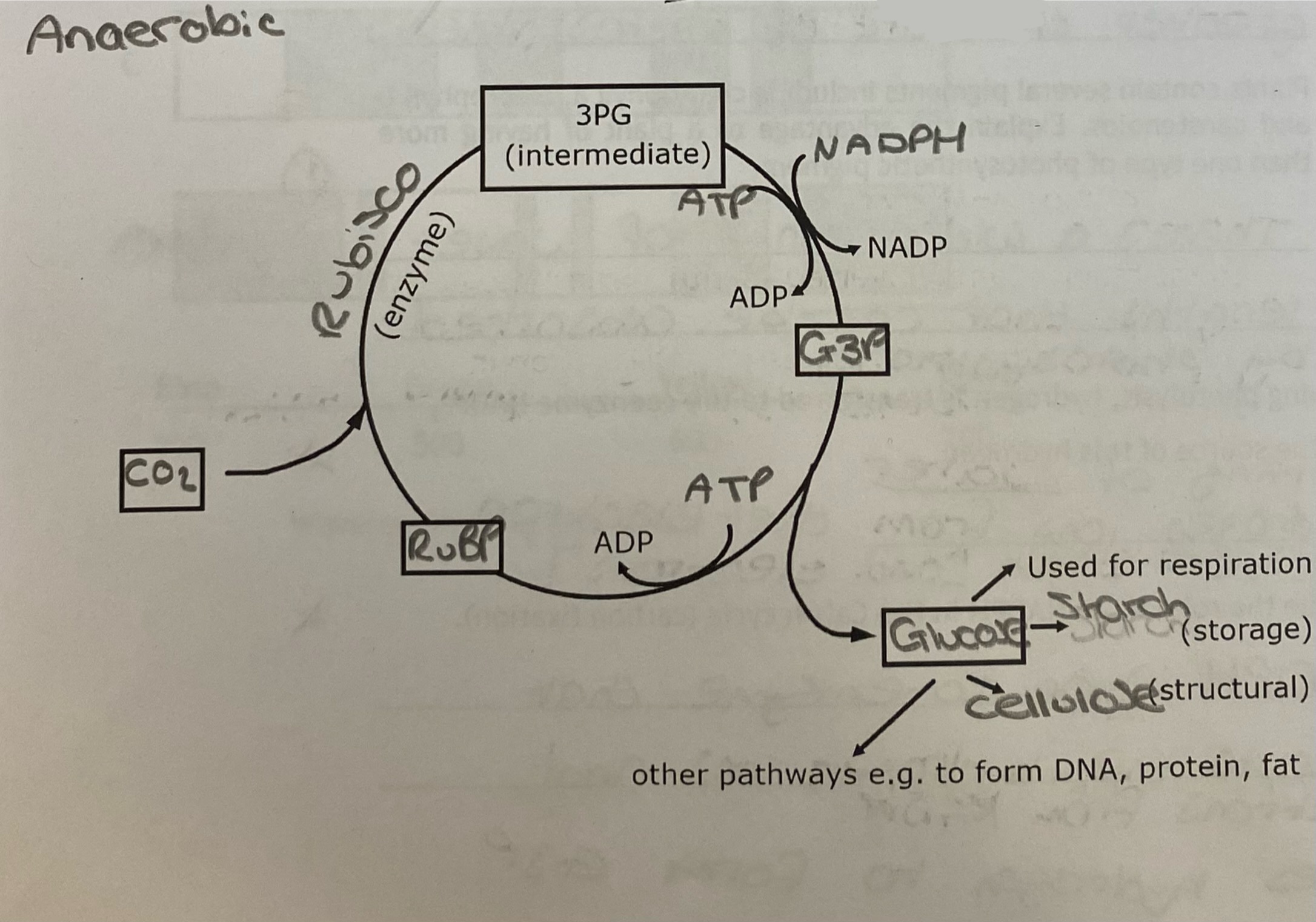
Diagram: the Calvin cycle
What are the four possible fates of glucose at the end of photosynthesis?
Respiration
Synthesised into cellulose as a structural carbohydrate
Synthesised into starch as a storage carbohydrate
Other pathways (to form DNA, fat, proteins, etc)