Fundamentals of Programming - Quiz 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Program
a set of step-by-step instructions that directs the computer to do the tasks you want it to do and produce the results you want.
Defining the problem
It consists of identifying what you know (input-given data) and what you want to obtain (output-the result).
Planning the solution
Two common ways of planning the solution to a problem are to draw a flowchart and to write pseudocode, or possibly both.
Coding the program
To express your solution in a programming language. You will translate the logic from the flowchart, pseudocode, or another tool to a programming language
Testing the program
Eventually, after coding the program, you must prepare to test it on the computer. This step involves three phases.
Desk checking
An informal, non-computerized, or manual process for verifying the programming and logic of an algorithm before the program is launched.
Translating
A translator is a program that checks the syntax of your program to ensure the programming language was used correctly, giving you all the syntax-error messages, called diagnostics, and then translates your program into a form the computer can understand.
Debugging
A term used extensively in programming, it is for detecting, locating, and correcting bugs (mistakes), usually by running the program.
Documenting the program
A detailed description of the programming cycle and specific facts about the program.
Machine Languages
It represents data and program instructions as 1s and 0s-binary digits corresponding to the computer’s on and off electrical states.
Assembly Languages
To replace the 1s and 0s used in machine language, this uses mnemonic codes and abbreviations that are easy to remember: A for Add, C for Compare, MP for Multiply, S.T.O. for storing information in memory, and so on.
High-Level Languages
Programs were written in an English-like manner, thus making them more convenient to use.
Very High-Level Languages
Often known by their generation number. They are called fourth-generation languages or, more simply, 4GLs.
Natural Languages
They resemble the English-like standard language. It means human-like. Instead of being forced to key correct commands and data names in the proper order, a programmer tells the computer what to do by keying in his or her own words.
Algorithm
It is a step-by-step procedure to solve a problem and carries a set of instructions. It can be designed using a flowchart or a pseudocode.
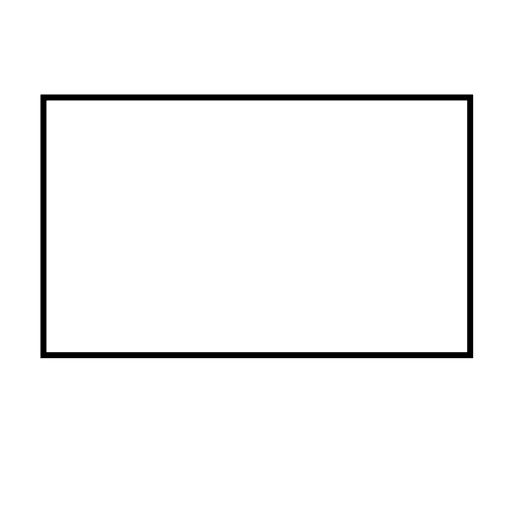
Flowchart
Visual representation of the step-by-step solution.
Pseudocode
Text representation of the step-by-step solution.