2.3 - government interventions, price floor/ceilling, subsidies, taxes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
reasons for government interventions into the market
to support firms
to promote equity
to collect government revenue
to support poorer households
to correct market failures
methods of government interventions
indirect taxes
subsidies
price controls
price ceilling
price floor
taxes types
direct
income tax
indirect
goods and services tax
direct taxes types
progressive (more you earn more you pay, tax brackets)
flat/ fixed
regressive (more you earn less you pay)
indirect taxes types
general taxes (on all goods and services)
excise taxes
on alcohol
tobacco
sugar
indirect taxes
imposed on government causing supply curve to shift left
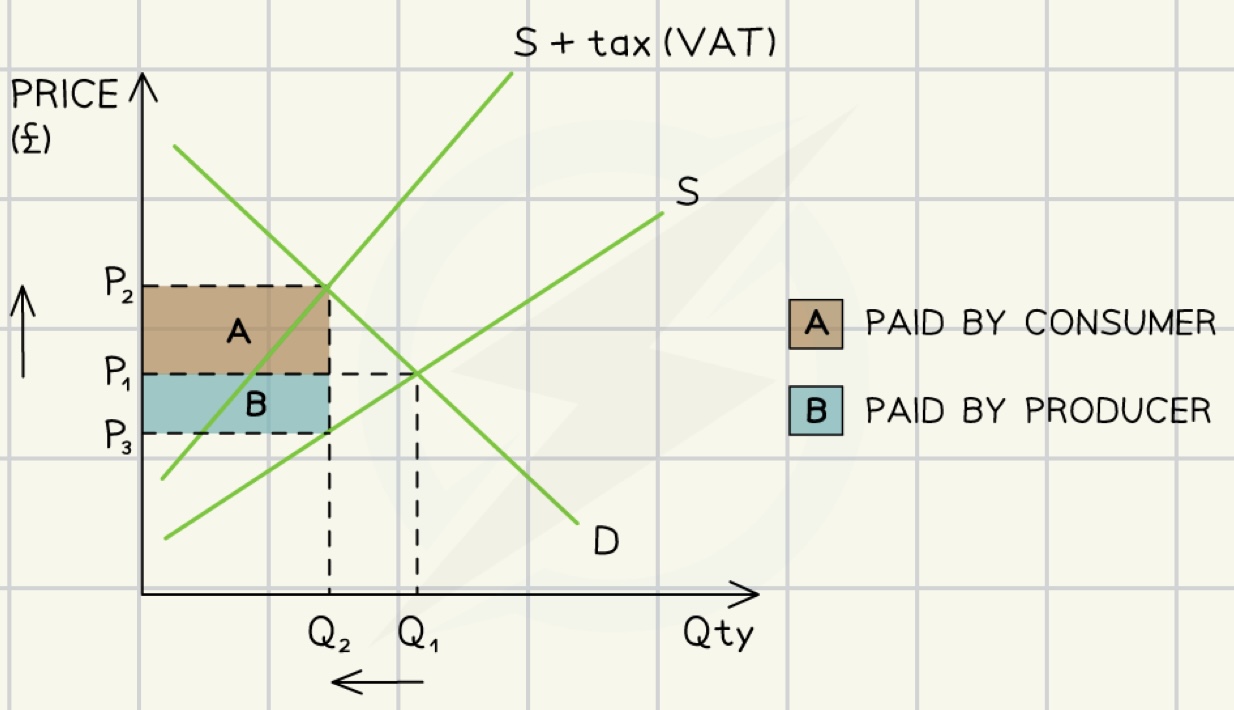
ad valorem VAT indirect tax
amount of good/service↑ = tax↑
specific indirect tax
fixed tax per unit of output
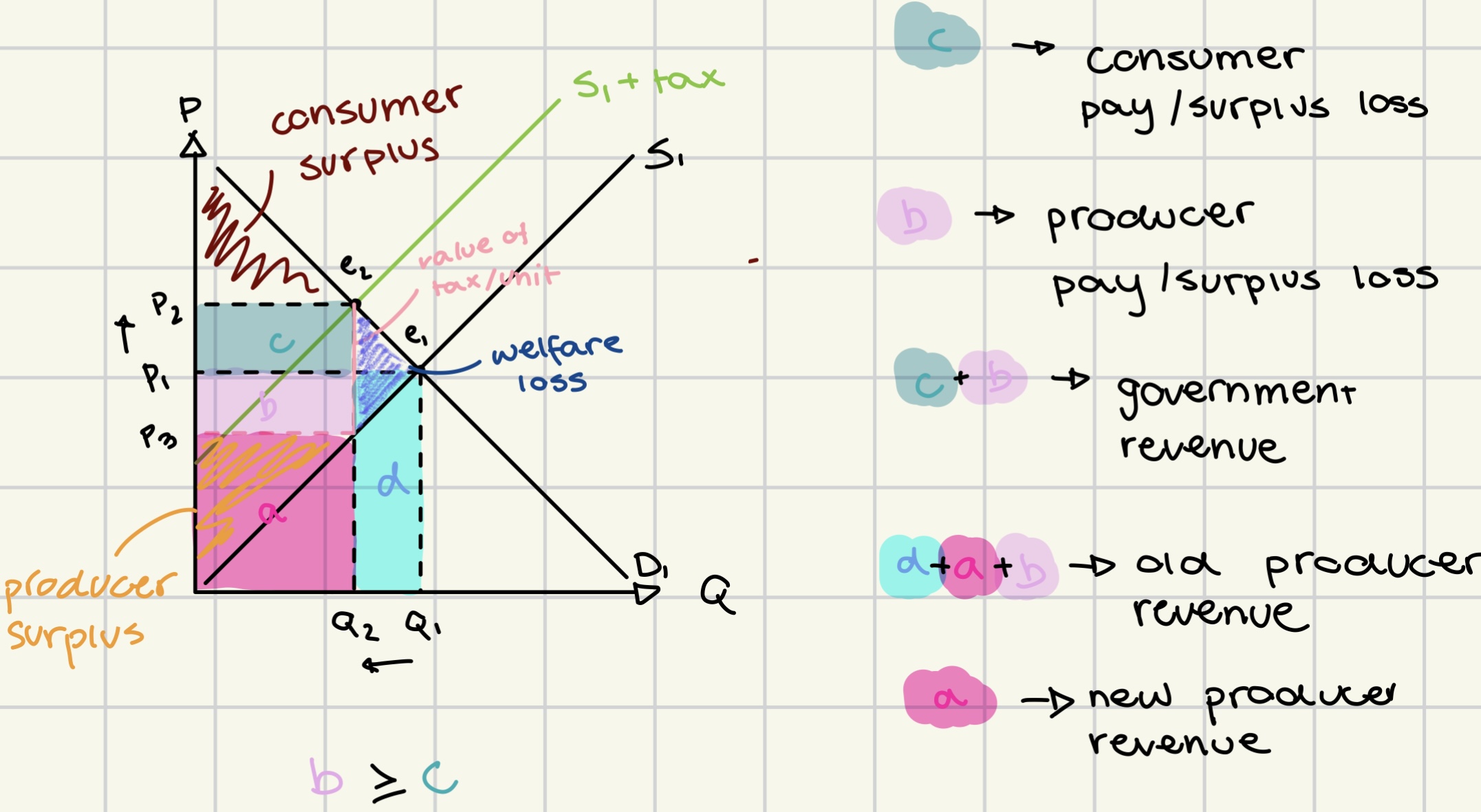
welfare loss
cost to society caused by the lack of efficiency in the allocation of resources
advantages of indirect taxes
raises price and lowers demand for demerit goods
raises revenue for government
disadvantages of indirect taxes
tax may be ineffective on demerit goods
helps develop illegal/ grey markets
may lead to staff layover due to lower demand
subsidies
financial assistance given by the government
to increase production
to increase provision of merit goods
to reduce costs
to support employment
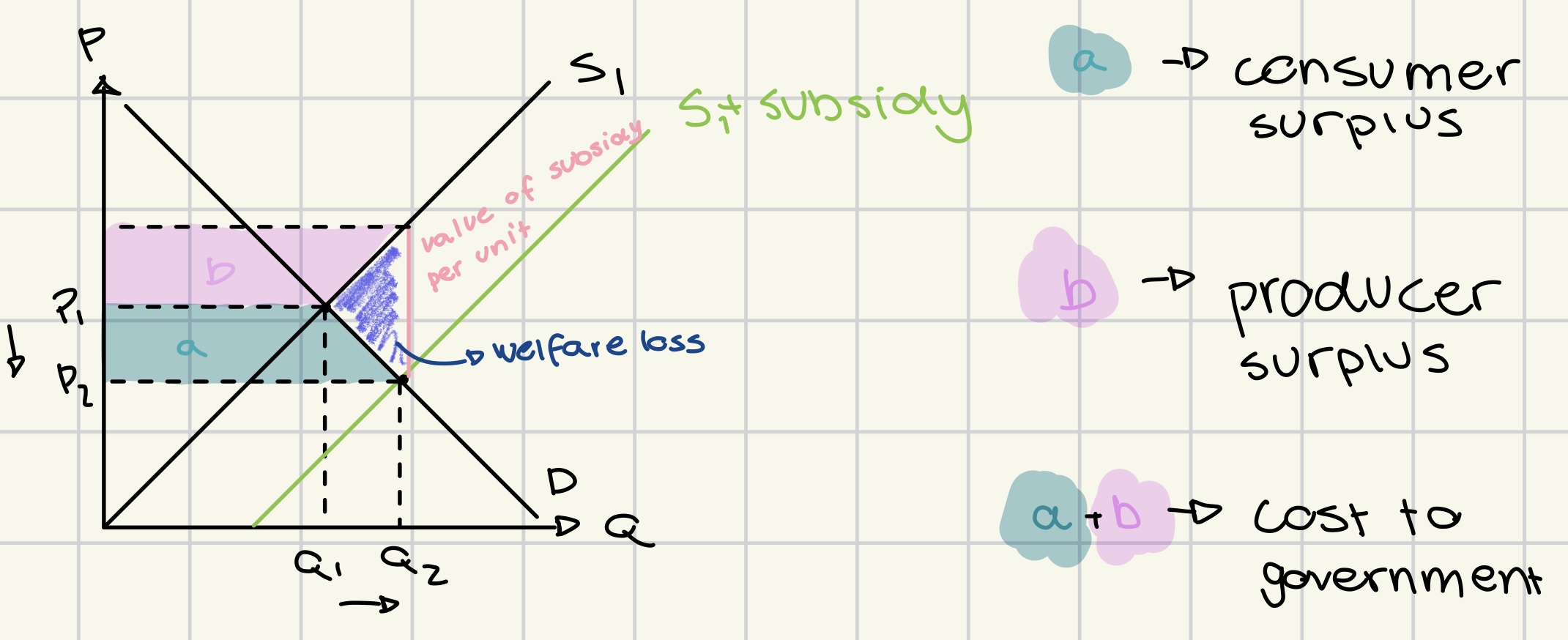
advantages of subsidies
financial benefits for producers
lowers prices for consumers
increases supply of merit goods
wealth redistribution
may benefit lower-income individuals
encourages economic growth.
disadvantages of subsidies
opportunity cost
over-dependency
stifle innovation
stifle improvements
fairness concerns
mis-allocation of resources
fossil fuel subsidy may discourage investment in green energy
environmental and social impacts
price controls
government regulations that set maximum or minimum prices for goods and services to stabilize the economy.
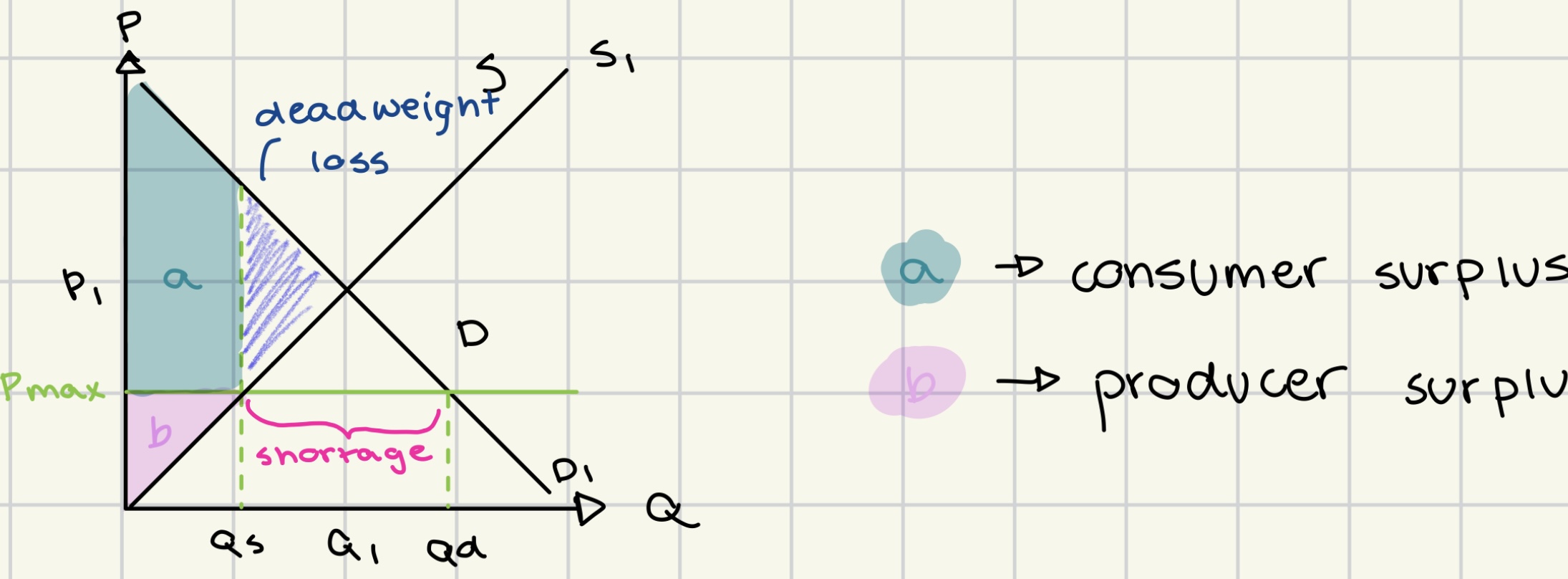
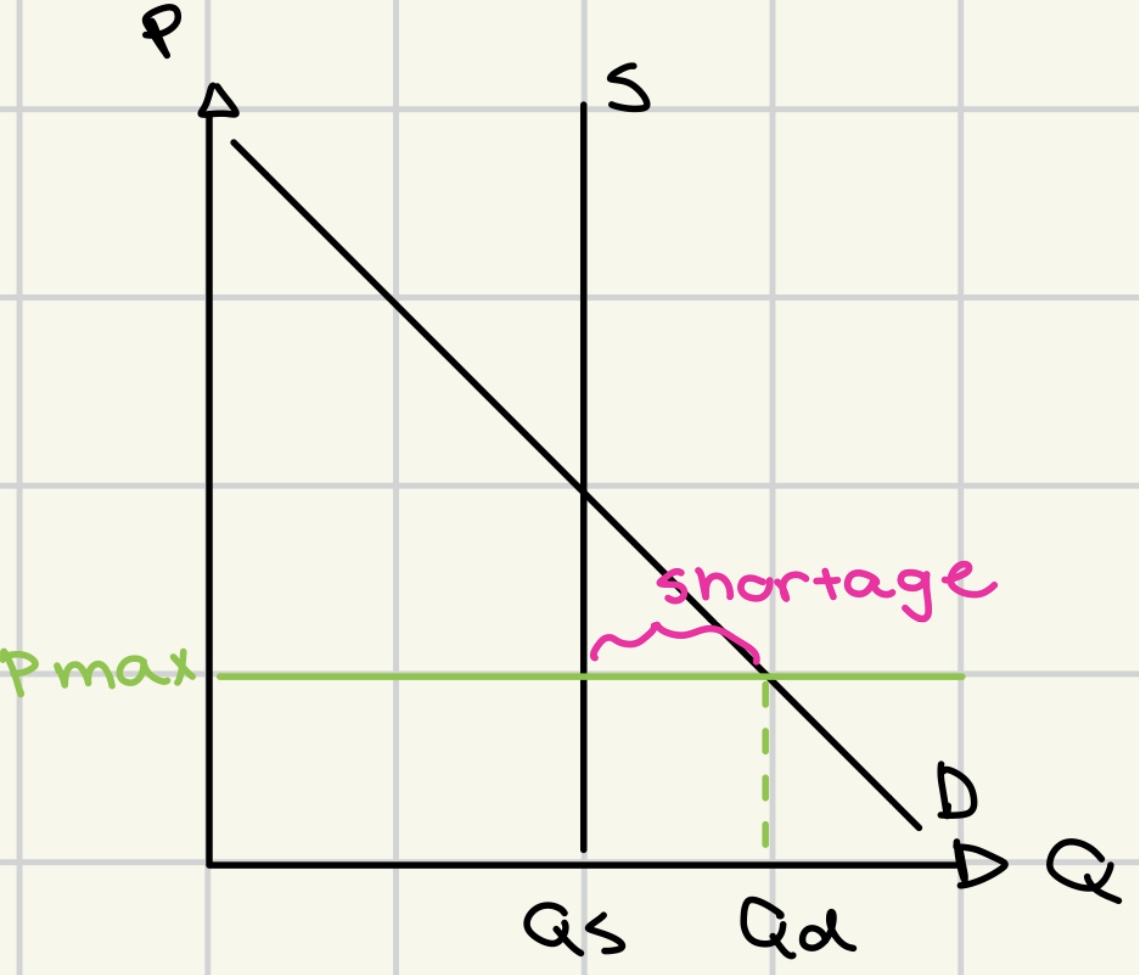
price ceiling
government-set maximum price that can be charged for a good or service
to protect consumers from excessively high prices.
government use of price ceiling
long period of time
rent control
medicine for chronic conditions
short period of time
to stabilize markets that have increased prices due to unusual context
advantages of price ceiling
increased consumer surplus
benefit from lower prices
can protect vulnerable consumers during disasters
can prevent monopolies from setting excessively high prices
disadvantages of price ceiling
shortages
decreased producer surplus
reduces quality
wastage/ over-consumption/
inefficient allocation of scarce resources
creation of illegal/ grey markets
government provision
fixed supply and price ceiling (concert tickets)
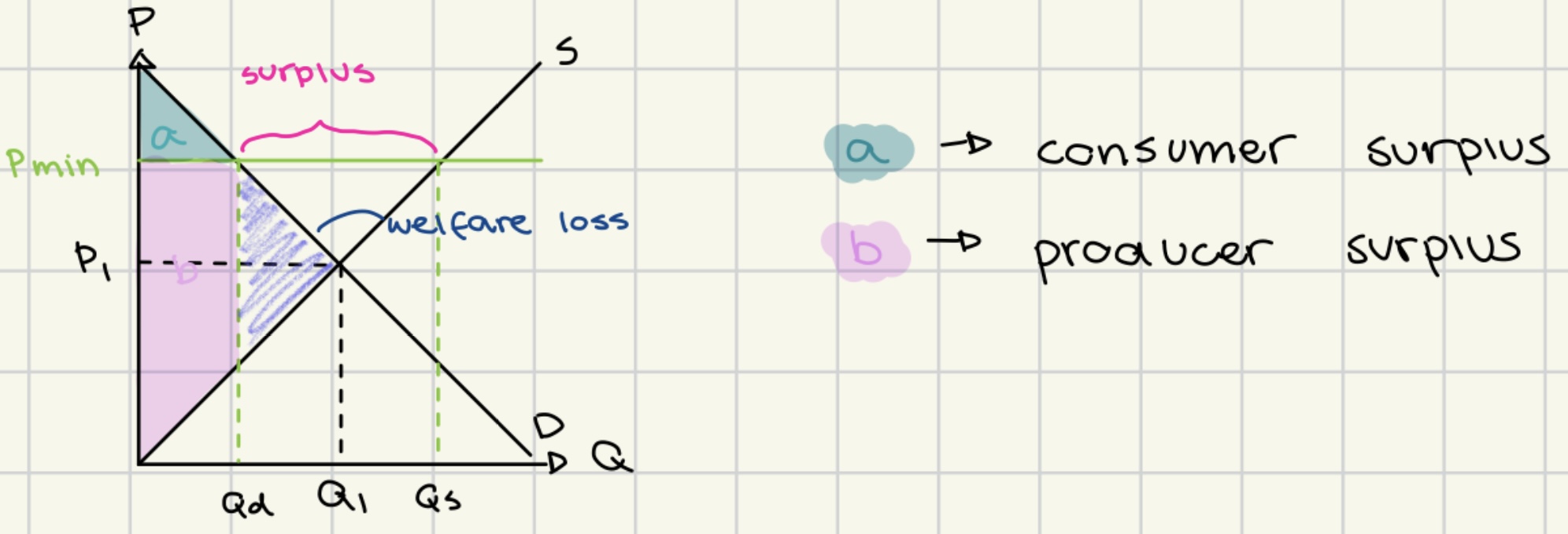
price floor
a minimum price set by the government to prevent prices from being too low
to ensure producers have a fair price
often applied in agricultural markets
government use of price floor
help producers earn more in times of crisis
decrease consumption of a demerit good
to protect workers from wage exploitation
minimal wage
advantages of price floor
increased producer surplus
minimal compensation secured for suppliers
prevention of price fluctuations and market stability
disadvantages of price floor
supply surplus
decreased consumer surplus
potential unemployment
increased prices for consumers
black markets may emerge.
minimum wage
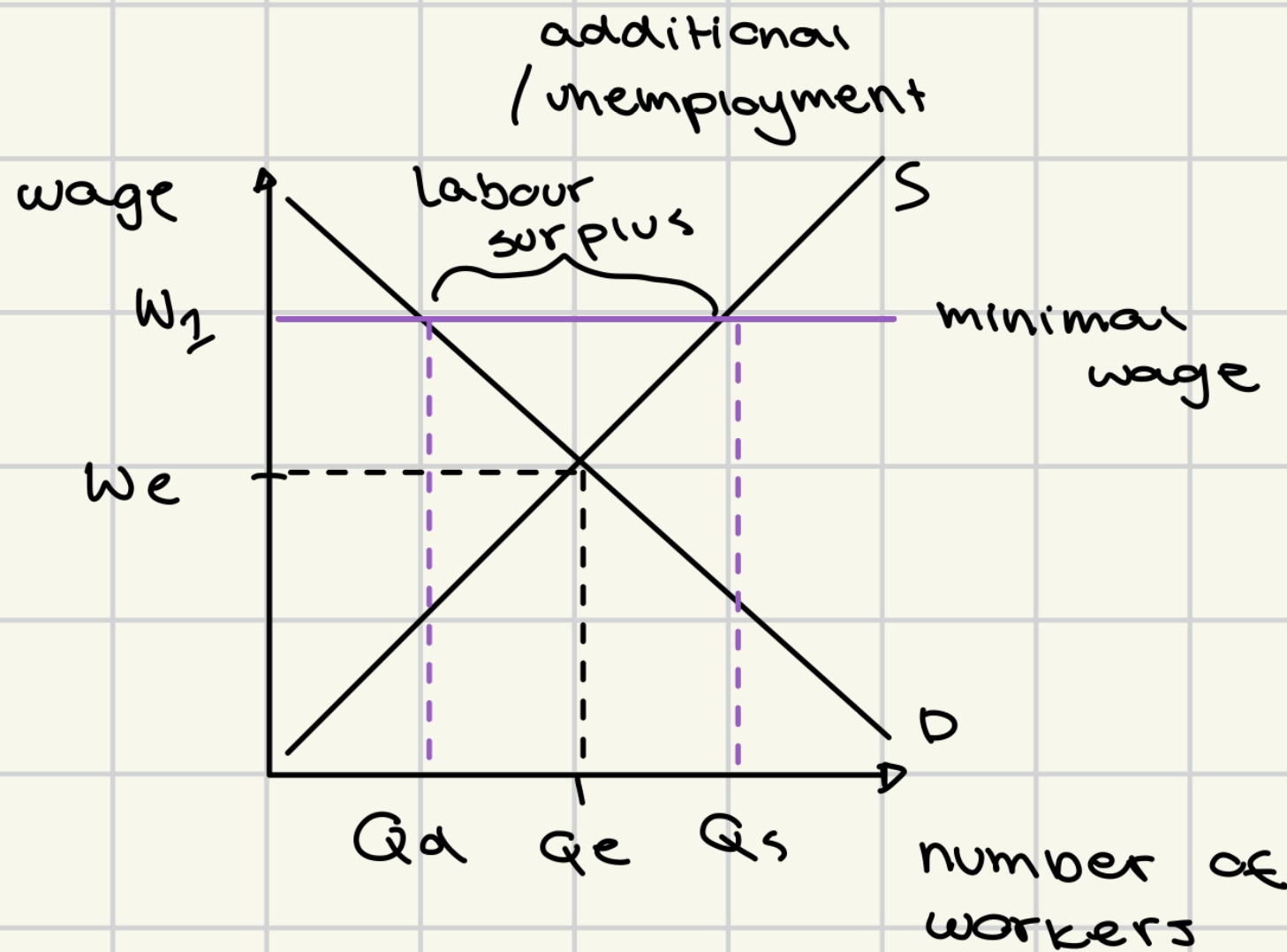
advantages of minimum wage
increased income for workers
reduction of poverty
improved worker productivity and morale.
disadvantages of minimum wage
potential job loss
higher costs od production
reduced demand for low-skilled labor