Speech & Language Networks
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Receptive language
Auditory and reading comprehension
Expressive language
Spoken and written expression
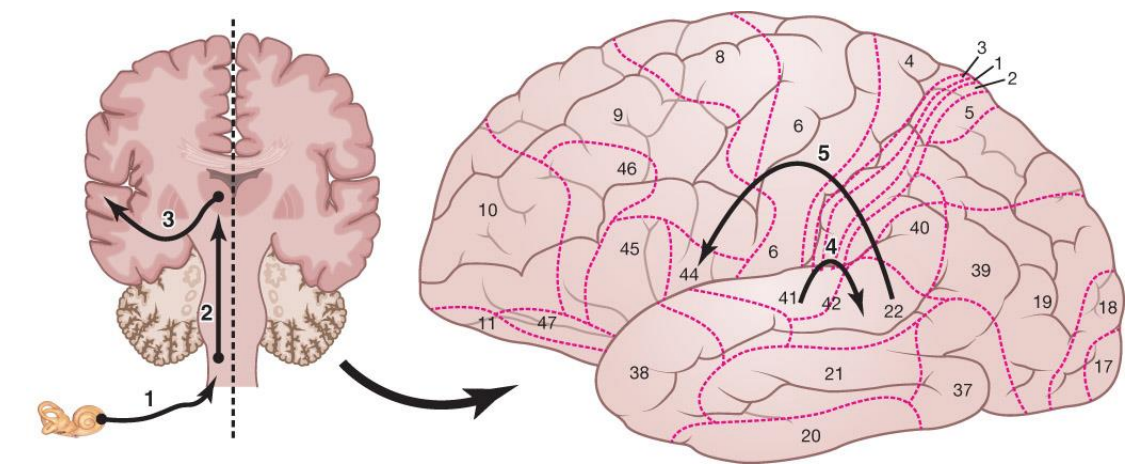
Auditory comprehension of language
ear converts acoustic energy into electrochemical energy and transmits it to the brainstem via cranial nerve VIII
The brainstem sends this information to the thalamus
The thalamus relays the information to the primary auditory cortex (A1=BA41/BA42) for signal processing
A1 routes to Wernicke’s area (BA22) for meaning attachment
Wernicke’s area projects to Broca’s area (BA44/BA45) for higher-level syntactical processing
Auditory comprehension of language cont.
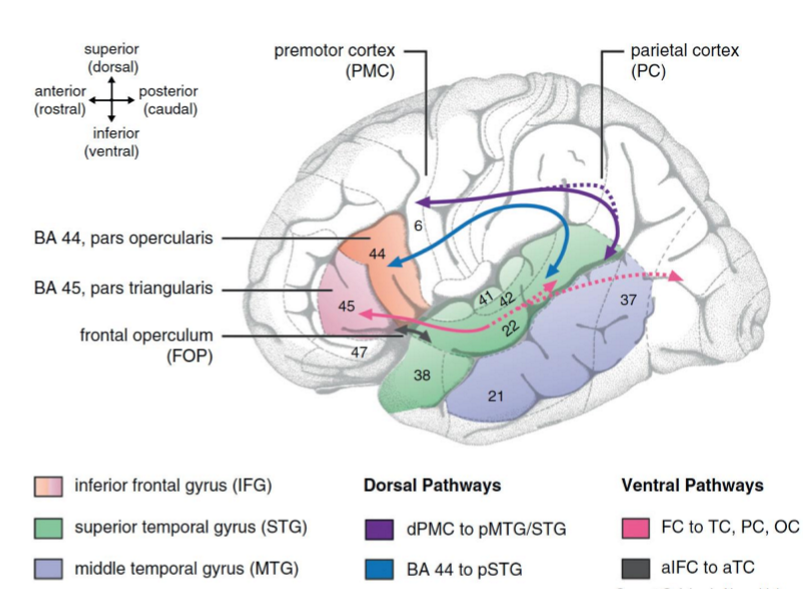
2 dorsal pathways (blue & purple)
Auditory-to-motor mapping via SLF
Syntax processing of complex sentences via AF
2 ventral pathways (pink & grey)
Semantic and basic syntactic processing via Inferior frontooccipital fasciculus & Uncinate fasciculus
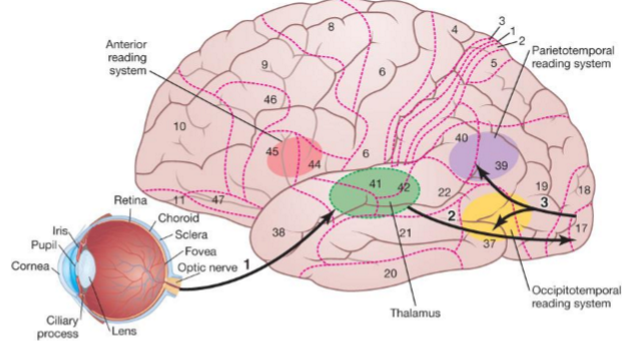
Visual comprehension of language (reading)
Visual information is projected to the thalamus (green in picture, under BA 41/42) via the optic tracts
Thalamus projects to the occipital lobe’s visual areas (BA 17– 19) for visual processing via the optic radiations (geniculocalcarine tract)
The visual areas project a dorsal stream of vision (i.e., the “where” of vision) and a ventral stream of vision (i.e., the “what” of vision). When reading, the anterior, parietotemporal, and occipitotemporal reading systems activate
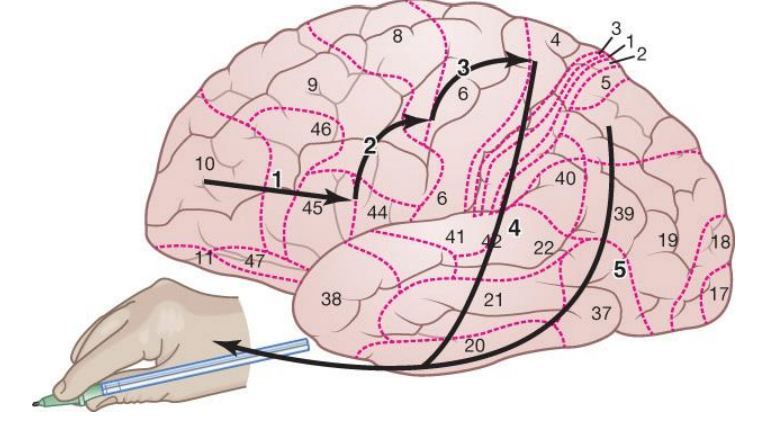
The oral production of language
Desire and thoughts to communicate originate in the prefrontal cortex and are sent to Broca’s area for language encoding and speech planning
Broca’s area projects to the supplementary motor area (SMA; top of area 6), which activates speech plans
SMA relays now active plans to the primary motor cortex
Primary motor cortex sends plans to the speech muscles for execution
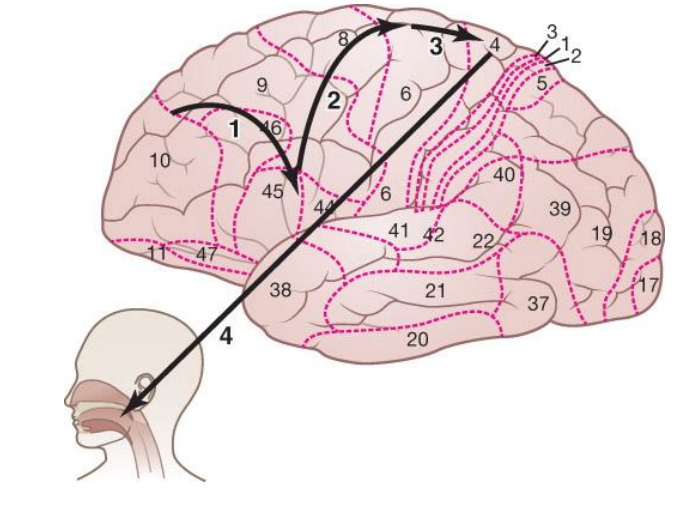
Neural basis of speech
Motor plan => motor program
Plan: high-level representation: the abstract sequence of movements needed to produce a specific utterance, before the execution begins.
Program: the detailed set of muscle-specific instructions that are carried out to execute the motor plan.
Involved in execution of motor program
Motor pathways (descending) - Direct & Indirect pathway
Sensory pathways (ascending)
Neural basis of speech cont.
Direct (pyramidal) pathway
Corticobulbar/corticospinal
Voluntary system
Control of gross motor movement
Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathway
Involuntary movements - Posture, muscle tone, reflexes, movement modulation
Motor control circuits - Basal ganglia & Cerebellum
Initiation and executive of speech involves minimal network of speech production’
motor areas, premotor areas, cerebellum, basal ganglia
The written expression of language
Desire and thoughts originate in the prefrontal cortex, which is sent to Broca’s area for language encoding
Language-encoded thoughts sent to premotor cortex (BA 6) for handwriting motor planning
Motor plans sent to the primary motor cortex
Primary motor cortex sends writing motor plans to the dominant hand
The superior parietal lobe coordinates the visuospatial elements of writing