Pharmacokinetics Part II
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Debrisoquine is a antihypertensive drug oxidized by which CYP enzyme?
Which ratio can be used to measure how effectively this enzyme metabolizes Debrisoquine?
Does a high value of this ratio mean better metabolism or worse?
2D6
Parent Drug: oxidized metabolite
high value (>10) = poor metabolism
extensive metabolizer= 0.1-10
low value (<0.1) = ultrarapid metabolism
what is the metabolite of oxidation of Debrisoquine by CYP2D6?
4-OH Debrisoquine or
1-OH debrisoquine
which CYP2D6 alleles allow for normal metabolism?
*1 and *2
which CYP2D6 alleles allow for ultrarapid metabolism ?
would you need to take a higher or lower dose of Debisoquine?
duplication of *2
higher dose bc/ drug is getting metabolized extensively
which CYP2D6 alleles allow for intermediate metabolism (less than normal) ?
would you need to take a higher or lower dose of Debisoquine?
*9, 10, 17, 41
lower dose bc/ its not being elminated effectively
which CYP2D6 alleles allow for poor/no metabolism ?
would you need to take a higher or lower dose of Debisoquine?
*3, 4, 5, 6,
lower dose bc/ its not being elminated from body
to remember: they’re just little kids, they cant eliminate effectively
more than ____ variants in the CYP2D6 gene have been identified
75
does *10 have even more reduced metabolism than *9, 17, 41?
YES but not to the extent of 3, 4, 5, 6 which are POOR
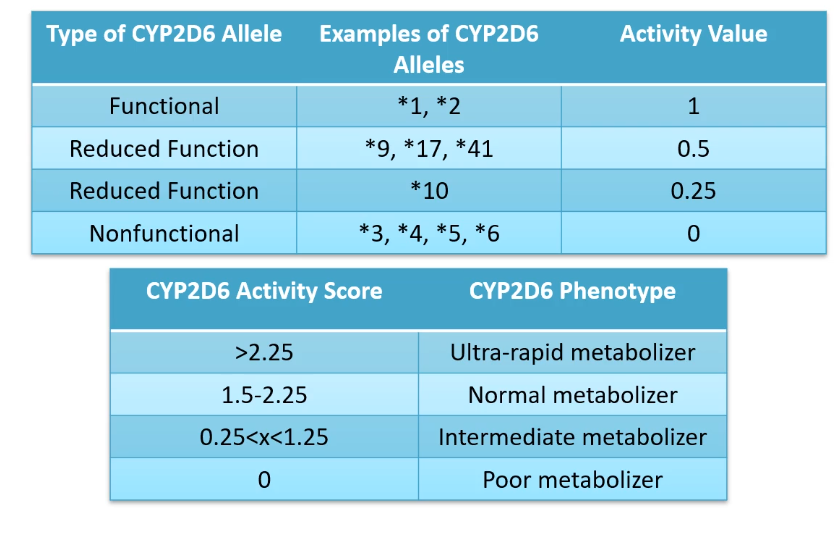
lets say Mark gets diplotype *2 from his dad and *6 from his mom
how well would he metabolize Debisoquine?
would you need to increase or decrease his dose?
*2 = 1
*6 = 0
activity level = 1+ 0 = 1
mark is considered an intermediate metabolizer
he should take lower doses of depisoquine since his body cannot properly eliminate the drug from his system
if a person has poor metabolizer through CYP2D6 would they need a higher or lower dose of codeine?
higher dose bc/ codeine is not being converted to more active morphine through CYP2D6
would you see higher or lower concentrations of morphine in a patient who is a CYP2D6 UM?
what would you expect to see in these patients?
increased concentrations of morphine bc/ CYP2D6 is ultrarapid leading to higher conversion of codeine to morphine
may experience side effects such as CNS and respiratory depression bc/ of enhanced analgesic
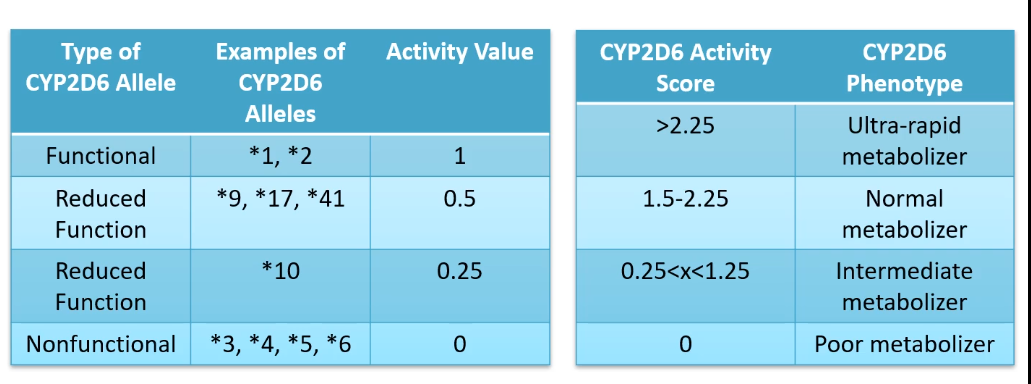
Mark’s mom has a diplotype of *9/*3
Mark’s dad has a diplotype of *4/*5
Mark inhereted *3/*4
how does each person in the family metabolize through CYP2D6?
mom = 0.5 + 0 = 0.5 (intermediate metabolizer)
dad= 0 + 0 = 0 (POOR metabolizer)
mark = 0+0 = 0 (POOR metabolizer)
what is the indication for Tamoxifen and which enzyme is it metabolized by?
tamoxifen is a SERM
selective estrogen receptor modulator for ER+ breast cancer
metabolized by CYP2D6
tamoxifen is a prodrug
what is its activated metabolized form?
which enzymes allow it to react its activated form?
active metabolite = N-desmethylTAM and endoxifen (100x stronger)
tamoxifen —> N-desmetylTAM (using CYP3A4/5) —> endoxifen (CYP2D6)
OR
tamoxifen —> 4 hydroxytam (CYP2D6) —> endoxifen (CYP3A4/5)
what are the two ways tamoxifen can get metabolized into its active form?
tamoxifen —> 4- hydroxyTAM (CYP2D6) —> endoxifen (CYP3A4/5)
tamoxifen —> N-desmethylTAM (CYP3A4/5) —> endoxifen (CYP2D6)

explain why you would see higher endoxifen concentrations in patients with diplotype *1/*1 compared to *1/*varient and varient/varient
*1/*1 is the extensive metabolizer (normal) of tamoxifen giving greatest endoxifen levels in the plasma
Are ER+ breast cancer relapse times shorter and outcomes worse for those who are poor CYP2D6 metabolizers or ultrarapid CYP2D6 metabolizers?
POOR CYP2D6
tamoxifen must be metabolized by CYP2D6 to be effective
what is recommended before initiating tamoxifen treatment in ER+ breast cancer patients ?
genetic testing to see if they have the diplotype alleles that makes them poor CYP2D6 metabolizers
if they do have poor CYP2D6 metabolism then you should consider prescribing them aromatase inhibitor such as letrozole instead of tamoxifen
would you recommend an aromatase inhibitor instead of tamoxifen to a CYP2D6 ultrarapid metabolizing patient or a CYP2D6 poor metabolizing patient?
CYP2D6 poor metabolizing patient bc/ they wont be able to convert tamoxifen to its active form endoxifen
which CYP2D6 metabolizers would you start with the standard dose of tamoxifen?
ultrarapid metabolizers and
normal(extensive) metabolizers
the following recommendation would be given to which CYP2D6 metabolizer:
consider aromatase inhibitor or use higher tamoxifen dose
intermediate CYP2D6 metabolizer
they can still metabolize to active form so you can try increasing the dose still
the following recommendation would be given to which CYP2D6 metabolizer:
consider aromatase inhibitor (letrozole, anastrozole)
CYP2D6 poor metabolizers
upping the dose of tamoxifen would not increase your chances of having higher endoxifen bc/ your body is not metabolizing tamoxifen unliek intermediate
should you prescribe moderate/strong CYP2D6 inhibitors if prescribing tamoxifen?
NO bc/ you need CYP2D6 for tamoxifen to be activated
Which diplotypes would lead to poor metabolism by CYP2C19?
would you increase or decrease the dose of drugs metabolized by CYP2C9?
which population is most often seen with this diplotype?
*2/*2 , *2/*3, *3/*3
use alternative therapy overall
south asians
which diplotypes would lead to ultrarapid metabolism by CYP2C19?
would you increase or decrease the dose of drugs metabolized by CYP2C9?
*17/*17 and *1/*17
should be able to administer standard dose
which diplotypes would you see in an individual who has normal metabolism (extensive) through CYP2C19?
*1/*1
which diplotypes would you see in an individual who has intermediate metabolism (extensive) through CYP2C19?
would you increase or decrease the dose of drugs metabolized by CYP2C9?
*1/*2 or *1/*3
give alternative therapy
omeprazole and lansoprazole are ___________ _____ _________ that __________________ and _____________
used to treat _____ ______ __________
inactivated by ________
proton pump inhibitors
reduce stomach acid secretion and increase pH
ussed to treat peptic ulcer disease
inactivated by CYP2C19
are omeprazole and lansoprazole activated or deactivated by CYP2C19 ?
DEACTIVATED
what effect does poor metabolism by CYP2C19 have on the efficacy of proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole and lansoprazole?
poor metabolism of CYP2C19 is favored as it allows the action to last longer since drugs are not being deactivated through metabolism
do patients with CYP2C19 UM or PM have higher PPI drug levels, AUC, better pH changes, and enhanced ulcer cure rates?
CYP2C19 PM
antiplatelet drug used as secondary prevention of atherothrombotic events following an MI, stroke, and peripheral artery disease
clopidogrel
is clopidogrel activated by or inactivated by CYP2C19 ?
activated
clopidogrel is a prodrug
patients with a loss of function CYP2C19 SNP are at an increased risk of ________ _______ events
why is this the case?
MI (myocardial infarction)
CYP2C19 is used to activate clopidogrel. those with poorer metabolism( 2/3 2/2 3/3) are at increased risk since activated clopidogrel is meant to prevent MI events through its antiplatelet activity
nonnucleoside RT inhibitor to treat HIV
Efavirenz
high levels of Efavirenz (due to poor metabolism) may increase risk of ___________ (_______, ________)
low levels of Efavirenz (due to high metabolism) may lead to ______ _________
high concentration (poor metabolism) = neurological disease (hallucinations, sleep disorders)
low concentration (high metabolism) = virologic failure
which enzyme deactivates Efavirenz (HIV treatment)
what is the name of the deactivated drug?
CYP2B6 metabolizes efavirenz into inactive 8-hydroxyefavirenz
which enzyme is used to inactivate the glucuronide conjugate of Efavirenz ?
UGT N-glucuronidation
There is an additional category for CYP2B6 metabolism which is________ _______
Which diplotypes fall under this new category?
rapid metabolizer (not as rapid as ultrarapid metabolizer)
*1/*4 or *1/*22
which diplotypes lead to CYP2B6 ultrarapid (UM) metabolism?
should you increase or decrease the normal 600mg//day dose of Efavirenz?
*4/*4 or *22/*22
don’t need to adjust dose of Efavirenz
which diplotypes lead to CYP2B6 nromal/ extensive metabolism (EM/NM) ?
should you increase or decrease the normal 600mg//day dose of Efavirenz?
*1/*1
don’t need to adjust dose of Efavirenz
which diplotypes lead to CYP2B6 intermediate metabolism (IM)?
should you increase or decrease the normal 600mg//day dose of Efavirenz?
*1/*6 *1/*18
*4/*6 *4/*18
*22/*6 *22/*18
Decreased the dose of Efavirenz as intermediate metabolism will allow efavirenz to accumulate in the blood leading to neurological defects such as hallucinations and sleep disorders
which diplotypes lead to CYP2B6 Poor Metabolsim (PM)?
should you increase or decrease the normal 600mg//day dose of Efavirenz?
*6/*18 *6/*6 *18/*18
lower dose to avoid toxic levels of efavirenz in the blood leading to neurological disorders such as hallucinations and sleep disorders
Which enzyme inactivates NSAIDs?
CYP2C9
what is the MOA of the Non Steroidal Ani-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) ?
inhibits cyclooxygenases (COX) which normally converts Arachidonic Acid into Prostaglandin
What can toxicities in NSAIDs (due to poor metabolism by CYP2C9) lead to?
GI, renal, cardiovascular toxicity
CYP2C9 SNPs impact PK of
slightly different guidelines for
________, ________, and __________
intermediate/poor metabolizers are at greater risk for toxicity
ibuprofen
flurbipofen
celecoxib
lornoxicam
different for meloxicam, piroxicam, tenoxicam
What are the reference diplotypes for CYP2C9 ?
What is the activity score?
*1/*1
1+1 = 2
What are the diplotypes for the intermediate metabolizer (IM)?
what are the activity scores for each of the diplotypes?
what should the doses be?
*1/*2 (1+0.5) = 1.5 (normal dose)
*2/*2 (0.5+0.5) = 1 (lowest starting dose)
*1/*3 (1+0) = 1 (lowest starting dose)
What are the diplotypes for the poor metabolizers?
what are the activity scores for each of the diplotypes?
what should the doses be?
*2/*3 (0.5+ 0) = 0.5
*3/*3 (0+0) = 0
Give 25-50% of the lowest recommended starting dose OR alternative therapy not metabolized by CYP2C9, including aspirin, ketorolac, naproxen, and sulindac
which medication is widely used as an immunosuppressive medication used to prevent transplant rejection
tacrolimus
tacrolimus binds to ________ ________ ( ______ binding protein) and inhibits _________ which is responsible for dephosphorylating ________ transcription factor
This reduces the transcription of IL-2 and prevents T cell activation
immunophilin FKBP12 (FK506 binding protein)
Inhibits calcineurin, which dephosphorylates NFAT
Tacrolimus has a narrow therapeutic index and large interpatient PK variability
Tacrolimus is metabolized by ________ and ________
What is their method of metabolism?
Polymorphisms in ________ influence phenotypic variation
tacrolimus is metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5
demethylation and hydroxylation
CYP3A5
what are the three different modes of CYP3A5 metabolism?
extensive metabolizer (EM)
intermediate metabolizer (IM)
poor metabolizer (PM)
What is the diplotype for extensive/normal metabolism of tacrolimus metabolism by CYP3A5?
what dose is recommended for individuals with this diplotype?
*1/*1
increase starting dose (1.5-2x recommended dose)
What is the diplotype for intermediate metabolism (IM) of tacrolimus metabolism by CYP3A5?
what dose is recommended for individuals with this diplotype?
*1/ *3
*1/ *6
*1/ *7
increased starting dose (1.5-2 starting dose)
What is the diplotype for intermediate metabolism (IM) of tacrolimus metabolism by CYP3A5?
what dose is recommended for individuals with this diplotype?
*3/*3 *3/*6 *3/*7
*6/*7 *7/*7 6*/6*
start with standard recommended dose and then TDM
CYP3A5 ___ and ____ have decreased trough concentrations of tacrolimus and compared with those who are CYP3A5 ____, possibly delaying acheivement of target blood concentrations
HOWEVER starting dose should never exceed ______mg/kg/day
Extensive Metabolizers and Intermediate Metabolizers of CYP3A5 require heightened 1.5-2 times recommended starting dose
normal dose needed for Poor Metabolizers of CYP3A5
0.3
fluoropyrimidines are used for treating ______ ________
5-fluorafacil and its prodrug _________
10-40% of patients develop severe and sometimes life-threatening toxicities such as _________, ______, _______, ________, ________, and _________)
solid tumors
capecitabine
neutropenia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis, mucositis
Fluropyrimidines and DPYD:
Capecitabine —> 5” DFCR (using ____________)
5”- DFCR ——> 5’ DFUR (using ____________)
5’DFUR—→ 5-FU (using ___________)
carboxyl-esterase
cytidine deaminase
thymidine phosphorylase
_________________ ___________ (______) is encoded by _____ gene
1st and rate limiting step in metabolising 5-FU—→ _________
Reduced _____ activity
increases t1/2 of 5-FU due to reduced clearance
dose related toxicities
Recommendations
______ reduce dose by 25-50%
_____: use a different drug
dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) encoded by DPYD gene
dihydroflouracil (DHFU)
DPD
IM
PM
The UGT2A locus encodes for ___ UGT1A proteins
There are also ___ pseudogenes in the locus (nonfunctional DNA that resembles functional DNA)
9
4
exon ___ is unique for each of the 9 UGT1A proteins
exons ___-____ are the same for each of the 9 UGT1A proteins
1 is unique
2-5 are the same
DISPOSITION OF BILLIRUBIN:
Outside of the sinusoid, unconjugated bilirubin is bound to ________
Within the space of ________ unconjugated billirubin is freed from _______ and enters the hepatocyte
In the hepatocyte, the unbound unconjugated bilirubin gets conjugated using ________
It then undergoes further _________ by __________
NOW it is able to get into the bile through MRP2!
albumin
disse albumin
GST
glucoronidated UGT1A
inherited genetic disease that results from (near) complete or complete loss of UGT1A1 due to mutation in the coding sequence
Criglet-Najjar Syndrome
which type of Crigler-Najjar Syndrome is due to highly deficient UGT1A
which type of Crigler-Najjar Syndrome is due to NO UGT1A
Type 2= highly deficient
Type 1= COMPLETEY deficient (MORE SEVERE)
why is the loss of UGT1A so critical as seen in Crigler-Najjar SYndrome?
UGT1A glucoronates bilirubin and allows it to enter the bile
if Billirubin is left unconjugated it is able to reach the blood-brain barrier, where it can lead to neurotoxicity (Kernicterus)
If unconjugated bilirubin due to Crigler-Najjar Syndrome reaches the BBB then there is a potential for kernicerus, which leads to
__________
increased/decreased muscle tone
______ and _______ disabilities
lethary
increased muscle tone
motor and intellectual
how has Crigler - Najjar Syndrome been treated?
certain wavelengths of blue light (430-490) convert billirubin to water soluble forms to be eliminated
Gilbert’s Syndrome occurs when ___ copy of UGT1A1 gene has a mutation
The most common polymorphism is ____________
Is Gilbert’s syndrome more or less severe than Crigler-Najjar Syndrome
____% increase in serum bilirubin levels
often ______ descent
1
less severe than Crigler-Najjar
60%
asian
antiretroviral protease inhibitor against HIV infection that inhibits the UGT1A1 glucuronidation of bilirubin
Atazanavir
a patient’s plasma concentrations is tested and they have increased serum levels of bilirubin, patient tests negative for hepatotoxicity ,what is a possible explanation?
patient is on Atazanavir which decreases their UGT1A1 levels. UGT1A1 usually removed bile from blood and into bile duct but with low levels of this enzyme patient now experiences hyperbilirubinemia
________(CPT-11) is a prodrug used in the chemotherapy of solid tumors
What activates this enzyme, and what is the enzyme activated into?
What does the activated form of this drug do?
Irinotecan
carboxylesterases activate irinotecan into SN-38
inhibit the topoisomerase I of cancerous cells
what role does UGT1A1 have in Irinotecan action?
what happens if there is a UGT1A1 deficiency?
UGT1A1 inactivates the activated form of Irinotecan (SN-38) turning it into SN-38 glucoronide
if UGT1A1 is deficient then there will be toxic levels of SN-38 leading to leukopenia, neutropenia, intestinal cell damage (diarrhea)
explain how a patient on Irinotecan with Gilbert’s syndrome could experience dramatic decreased neutrophil counts
irinotecan is converted into its activated form SN-38 using carboxylesterase
Gilbert’s syndrome decreases UGT1A1 levels causing increased toxic levels of SN-38
SN-38 can be drained into the small intestine from the bile duct and come back into the blood stream from the intestine
increased SN-38 in the blood leads to neutrophil death
what specific UGT1A1 mutation decreases its activity leading to higher levels of neutrophil death?
if there are more or less than 6 ATA repeats of the TATA box in the promotor region of the UGT1A1 gene
__________ variant results from (TA)7TAA rather than (TA)6TAA
this is relevant when taking which medication?
UGT1A1*28
Irinotecan
Yuji, a Japanese patient was diagnosed with tuberculosis
His pharmacist accidently typed that he he needed to take his isoniazid 3 times daily instead of once a day
Yuji however does not experience any isoniazid toxicity, why is that?
Since Yuji is Japanese he is able to rapidly metabolize isoniazid through acetylation by NAT2 enzyme
Yuji needs a higher dose anyways because of how rapifly his body eliminates isoniazid through NAT2 enzyme
rapid acetylators may need higher/lower doses of isoniazid
higher —> acetylation through NAT2 deactivates drug
which populations would need higher doses of Isoniazid to treat their tuberculosis?
why is this the case?
eskimos
japanese
latin americans
they are very rapid acytelators so you need more of the drug since much of it will be acytelated by NAT2
Adverse toxicities in slow acytelators:
Isoniazid-induced ______ ________
Procainamide (antiarrhythmic) and Hydralazine (antihypertensive) induced __________
Dapsone (antimicrobial) induced________ ________
LOWER DOSES OF THESE DRUGS SHOULD BE ADMINISTERED BC/ OF SLOW ACCELERATION, WHICH WILL KEEP TOXIC LEVELS IN THE BODY LONGER
peripheral neuropathy
lupus erythematosus
hemolytic anemia
lupus erythematosus may be seen in individuals will slowed NAT2 acytelation taking which drugs?
procainamide (antiarrhythmic) and hydralazine (antihypertensive)
hemolytic anemia may be seen in individuals will slowed NAT2 acytelation taking which drugs?
dapsone (antimicrobial)
peripheral neuropathy may be seen in individuals will slowed NAT2 acytelation taking which drugs?
how can this be combated to prevent toxicity of the drug?
isoniazid
vitamin B6 (pyroxidine)
NAT2 metabolizes Isoniazid into which two inactive metabolites?
acetylhydrazine and isonicotinic acid
which medications does TPMT (ThioPurine S- Methyl Transferase) metabolize?
6-mercaptopurine
6-thioguanine
azathioprine
TPMT is used to metabolize medications
6-mercaptoPURINE
6-thioGUANINE
Azathioprine
What are the indications for these medications?
leukemia (acute lymphoblastic)
Inflammatory bowel disease
transplant
We can measure TPMT activity in ____ _____ _____ (surrogate for drug-metabolizing tissues)
not reliable in people receiving _____ transfusions in the last ___-___ days
red blood cells
30-60
where can TPMT be found?
red blood cells
azothioprine is the prodrug for __________ which is further metabolized by TPMT into ___________
does the metabolism by TPMT activate or inactivate the drug?
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) —> 6-methyl-mercaptopurine (using TPMT)
INACTIVATE
SEQ inactivation pathways for 6-mercaptopurine
6- mercaptopurine —> 6-methyl-mercaptopurine (using TPMT)
6-mercaptopurine —> 6-thiouric acid (using Xanthine Oxidase)
6-mercaptopurine —> 6-thiosinic acid (usinh HGPRT)— 6-thioguanine nucleotides —> thiouric acid
SEQ activation of azathioprine
azathioprine —> 6-mercaptopurine—> 6-thionosinic acid (USING HGPRT) —> 6-thioguanine nucleotides
6-mercapturicpurine which is inactivated by TMPT has a narrow therapeutic index associated with ______________
myelosuppression
_______ is associated with 6-mercapturicpurine efficacy and toxicity
TPMT
TPMTH (high activity TPMT) is associated with which alleles?
*1 and *24
TPMTH (low activity TPMT) is associated with which alleles?
*2, 3A, 3B, 3C, 4
what is the most common TPMTL (low activity TPMT) variant in Caucasians ?
Why do they have such low levels of TPMTL?
*3 (5% heterozygous frequency 0.3% homozygous null)
increased protein degradation is the cause of low levels of TPMTL
which patients would you give the highest dose of azathiopurine (prodrug of 6MP) to?
V/V (*2, 3A,B,C,4 / *2,3A,B,C, 4)
W/W (*1/*1,*24/*24, *1/*24)
V/W (*2, 3A,B,C,4 / *1 or 24)
give highest dose to W/W bc/ they will rapidly deactivate 6-MP
lowest dose to V/V bc/ they will poorly metabolize 6-MP, leading to myelosuppression
SEARCH STUDY was the Study of Effectiveness of ________ _______ in ___________ and ______________
Study of Effectiveness of Additional Reductions in Cholesterol and Homocysteine
SEARCH was a study with 12,064 patients with prior myocardial infarction
half of the patients were on _____mg other half was on ____mg
out of 6,031 patients on ____mg only 90 suffered from myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
half of 81mg half on 20mg
80mg—> myopathy and rhabdomyolysis