2- Alkanes
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Saturated hydrocarbons - they only contain carbon/carbon and carbon/hydrogen single bonds
What are alkanes?
CnH2n+2
a) C6H14
b) C5H12
c) CH4
Formula for alkanes
a) Hexane
b) Pentane
c) Methane
109.5 - each carbon atom forms a tetrahedral shape
Alkanes bond angle between carbons
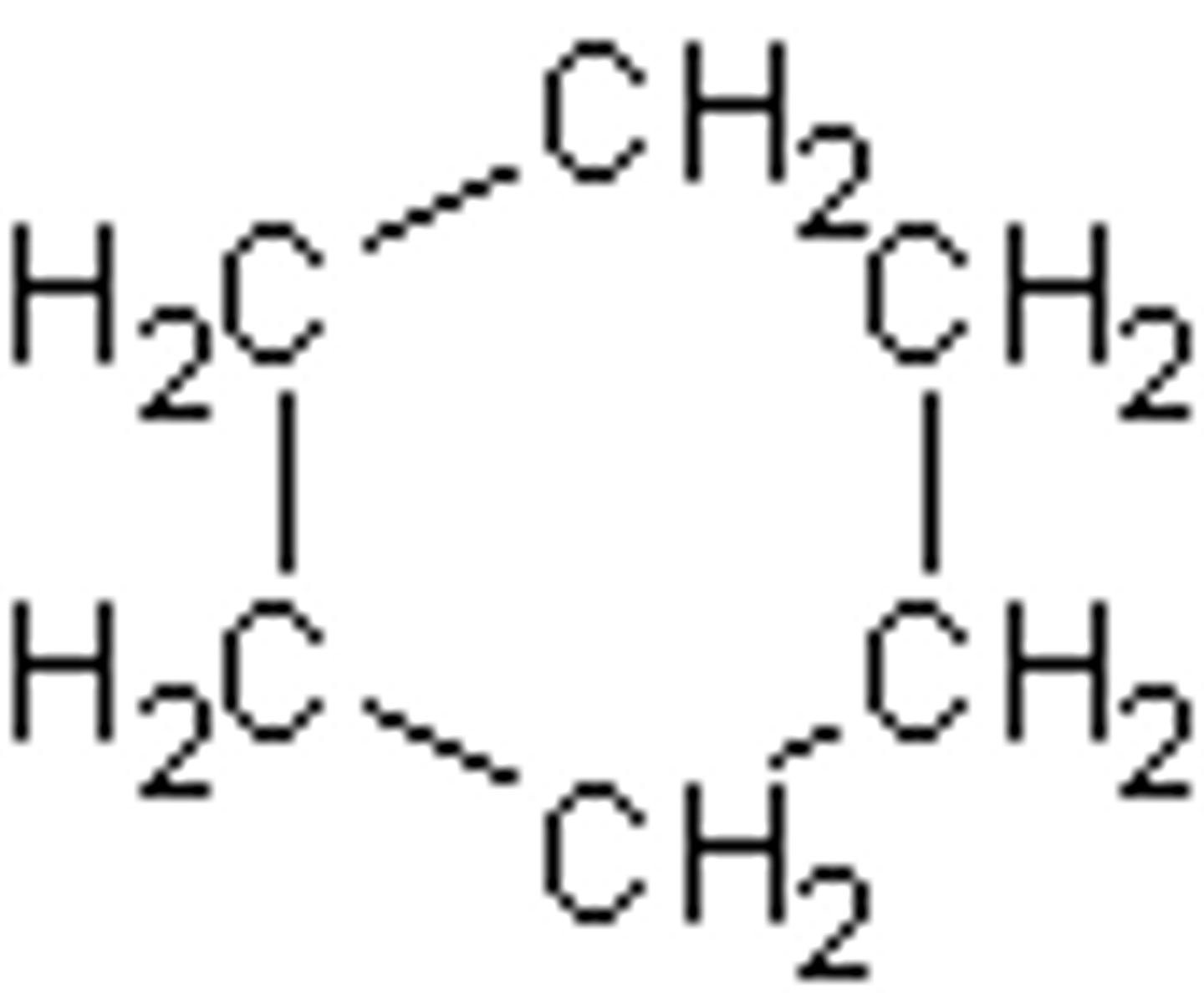
CnH2n - end hydrocarbons are not required
Ring alkanes formula
Alkanes are non-polar because the electronegativities of Carbon and Hydrogen are so similar. The only intermolecular forces between molecules are weak van de Waals, larger the molecule the stronger the van de Waals
Polarity of alkanes
Relatively low boiling points
As alkane chain size increases the boiling point increases due to increased van de Waal forces
Shorter chains - gasses at room temp
Pentane - liquid at room temp
18+ carbons - solid at room temp (waxy feel solids)
Boiling points of alkanes
Even lower boiling point than unbranched, intermolecular forces are weaker as chain cannot pack so closely together.
Surface area of contact isn't as good, van de Waals not as effective
Boiling point of branched alkanes
Insoluble in water
Water is polar, alkanes are non-polar
Non polar substances don't dissolve well
Solubility of alkanes
Unreactive due to strong carbon-carbon and strong carbon-hydrogen bonds
Do not react with acids/bases/oxidising agents etc but they do burn, reactive with halogens under certain conditions
Reactivity of alkanes
Formed millions of years ago by the decomposition of plant/animal remains at high temps and pressures, reforms at a very slow rate (non-renewable)
Why is crude oil a fossil fuel?
Mixture of hydrocarbons - particularly alkanes (branched/unbranched), also contains sulfur
What does crude oil consist of?
It is unrefined, too many substances with different boiling points
Why is crude oil alone not useful?
Fractional Distillation - a physical process (no covalent bonds broken)
1. Crude oil is heated in a furnace
2. Mixture of liquids/vapours passes into the tower with temperature gradient (cooler at top than at bottom)
3. They rise up the tower, condensing at their boiling points
(the shorter chain hydrocarbons condense nearer the top as they have lower boiling points)
4. Thick residue at the bottom is called bitumen, petroleum gas at the top
Describe the process of converting crude oil into useful products
-Lower boiling points
-More volatile (liquid to gas at normal temperatures)
-More flammable
-Less viscous (gloopy/thick)
-Less coloured
Properties of shorter alkanes
Long chain alkanes are not as useful, high demands for shorter alkanes which are useful for products such as naphtha/petrol
Why is cracking useful?
The breaking down of long-chain alkanes into alkenes and shorter-chain alkanes
What is cracking?
-Shorter, more useful chains are produced (petrol)
-Alkenes produced, which are more reactive than alkanes
Two useful results of cracking
C18H38 ---> C2H4 + C3H6 + C13H28
For the other product, calculate how many C and H are left
C18H38 is cracked into ethene, propene and one other product. Give the symbol equation for this reaction
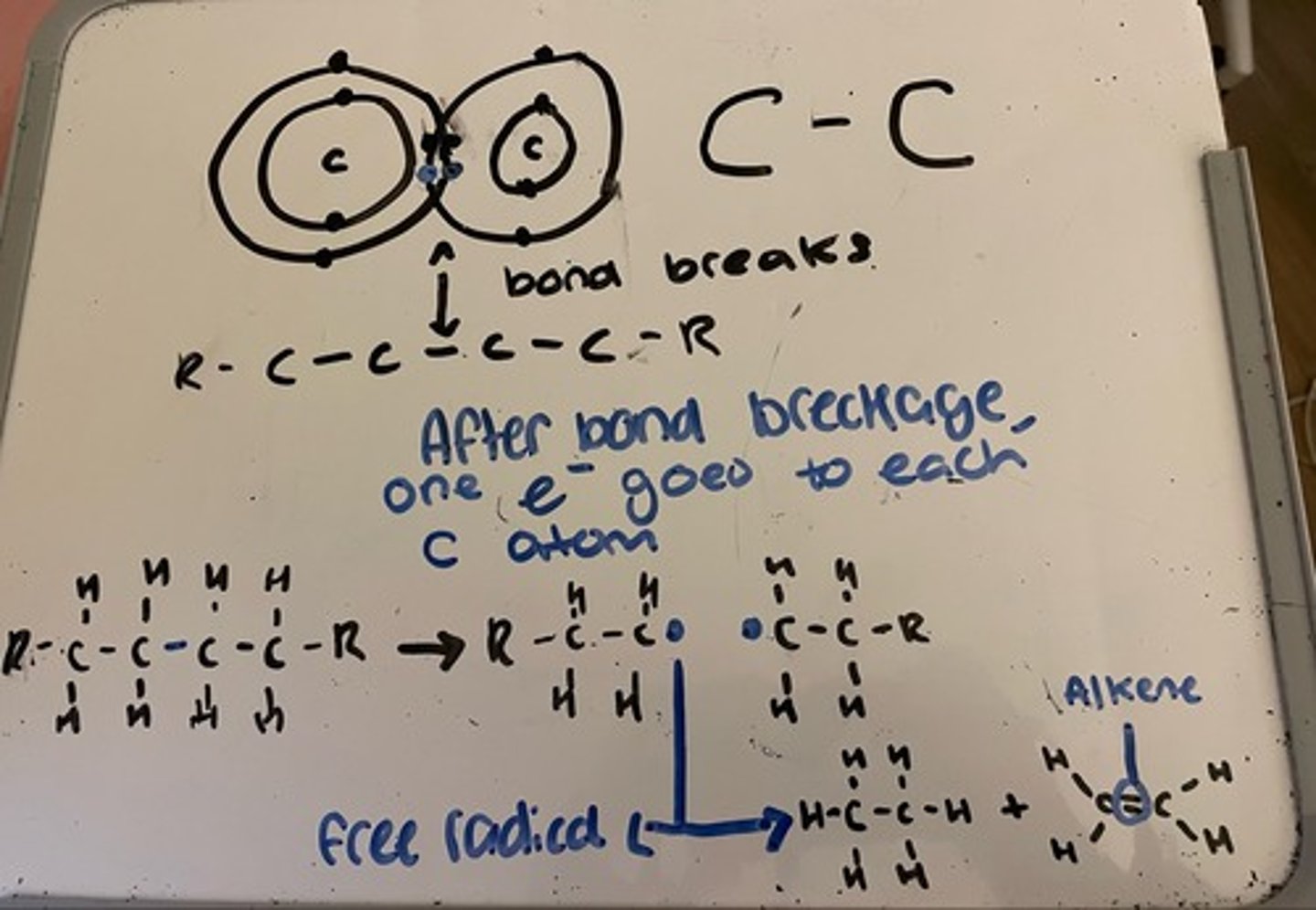
Carbon-carbon bond breaks, so that one electron from the pair goes to each carbon atom, so initially two short chains are produced
The unpaired electron (blue dot) is a free radical, these are highly reactive
These react in numerous ways, but there are not enough hydrogens to produce two alkanes, one of the new chains must have a C=C, so an alkene is formed
NOTE: any number of c-c bonds may break, hydrogen may also be formed
Process of thermal cracking
a) -High temperature (700-1200K)
-High pressure (7000kPa)
b) Alkanes are kept in these conditions for a very short amount of time (1 sec), this limits decomposition (to C and H)
a) Conditions for thermal cracking
b) How can we control thermal cracking?
-Heat alkanes at lower temperature and pressure than thermal cracking, using a zeolite catalyst (consists of silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide)
This produces mostly branched alkanes, cycloalkanes and aromatic compounds (such as benzene shown in diagram)
Products obtained from catalytic cracking are mainly used for motor fuels, can also be separated by fractional distillation
Process of catalytic cracking
-High temperature (720K)
-Low pressure (slightly above atmospheric, 1-2atm)
-Zeolite catalyst (consists of silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide, honeycomb structure with enormous surface area, small amount of catalyst needed allows cost reduce)
Conditions for catalytic cracking
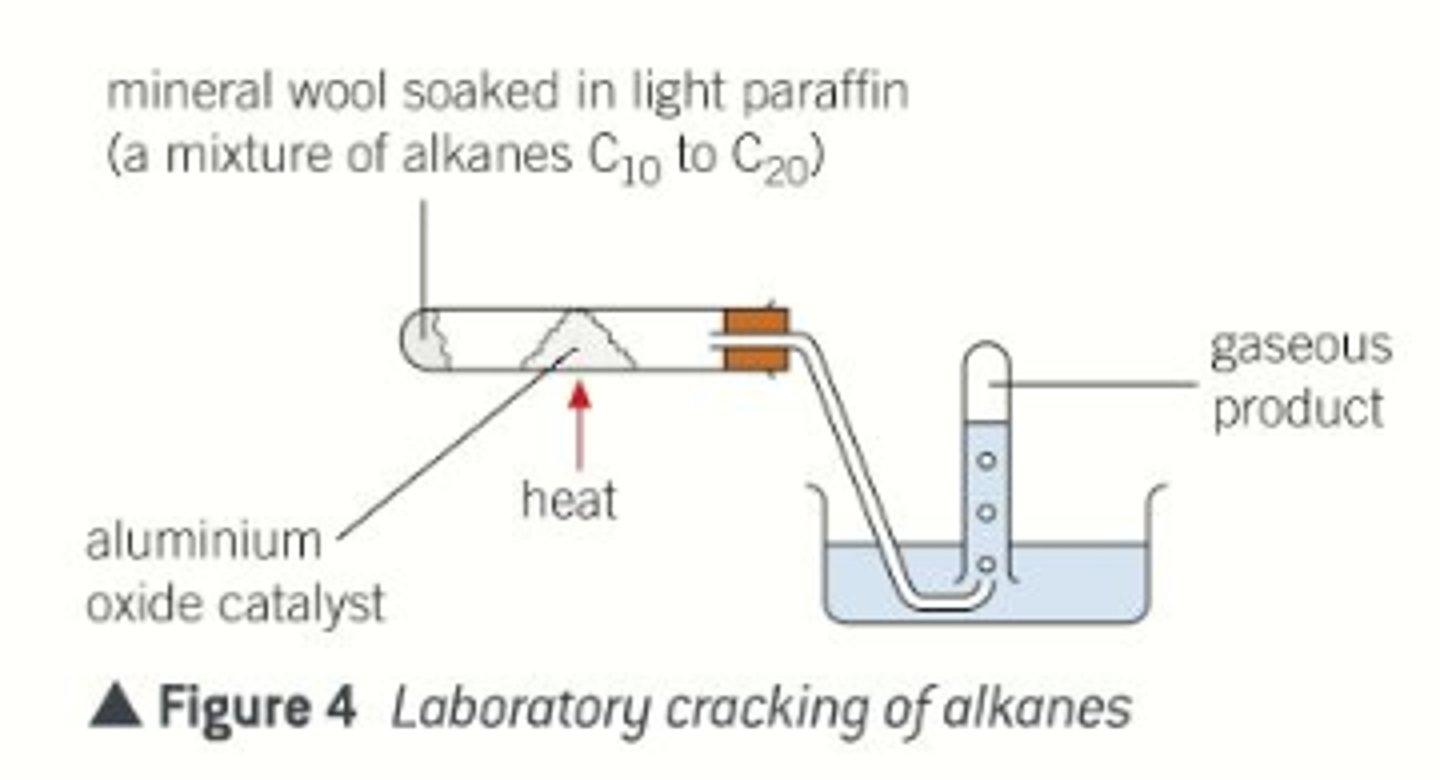
Set up apparatus shown in the diagram
Paraffin inside tube (mixture of alkanes)
Heat aluminium oxide catalyst, alkane vaporises and moves across catalyst and rises through water as bubbles
Bubbles displace the water so that it moves downward
Can test for the presence of alkenes as the gaseous mixture will decolourise (from yellow-brown) bromide solution
How can we carry out catalytic cracking in the laboratory?
a) burning of hydrocarbons in excess oxygen
b) burning of hydrocarbons in limiting oxygen
What is meant by
a) complete combustion
b) incomplete combustion
Clean flame - shorter alkane
Sooty flame - larger alkane
How are different flames from combustion related to the alkane size
Carbon dioxide and water
Products of complete combustion
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) ---> CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
For balancing leave oxygen until the end
Complete combustion of methane equation
C2H6 (g) + 3 1/2 O2 (g) ---> 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l)
Complete combustion of ethane equation
Heat, combustion reactions will have large negative enthalpies.
The more carbons present, the larger the heat output. They store a large amount of energy for a small amount of weight
What do combustion reactions give off?
Methane, propane, butane, petrol, paraffin
Examples of alkane fuels
Carbon monoxide, carbon and water
Products of incomplete combustion
Soot (carbon alone)
C3H8 (g) + 2O2 (g) ---> 3C (s) + 4H2O (l)
What is produced during incomplete combustion when even less oxygen is present? Give an equation for this using propane as an example
C3H8 (g) + 3 1/2 O2 (g) ---> 3CO (g) + 4H2O (l)
Incomplete combustion of propane equation
Bunsen burner used with a closed air hole, flame is yellow and a black sooty deposit appears on apparatus
Example for incomplete combustion
Carbon monoxide (CO)
What is produced from incomplete combustion and is a poisonous gas?
Carbon particulates (soot)
What pollutant worsens asthma and can cause cancer?
Carbon dioxide
What is a greenhouse gas produced from complete combustion?
Water vapour
What is another greenhouse gas that is a product of combustion?
Sulfur dioxide
What pollutant contributes to acid rain and is represented by SO2?
Nitrogen oxides (NOX)
What occurs in a petrol engine at high temperatures and pressures and contributes to acid rain?
Nitrogen oxides (NOX)
What can react with acid to form nitric acid and contributes to photochemical smog?
Unburnt hydrocarbons
What pollutant contributes to photochemical smog and causes health issues?
Generate electricity by burning fossil fuels such as coal or natural gas, these fuels contain sulfur.
Combustion of these fuels therefor results in SO2, which causes acid rain by combining with oxygen and water in the atmosphere to form sulphuric acid
SO2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) + H2O (l) ---> H2SO4 (l)
How do power stations contribute to acid rain?
Gas given off by power stations (SO2) are called flue gasses.
A slurry of calcium oxide (lime) and water is sprayed into the fuel gas which reacts with the calcium oxide and water to form calcium sulfite, which can be further oxidised into calcium sulfate (gypsum)
CaO (s) + 2H2O (l) + SO2 (g) ---> CaSO4 (s) + CO2 (g)
Gypsum produced, can be sold :)
An alternative process used calcium carbonate (limestone) rather than calcium oxide (lime)
CaCO3 (s) + 1/2 O2 (g) + SO2 ---> CaSO4 (s) + CO2 (g)
Co2 produced, bad for environment :(
Process of flue gas desulfurisation
Catalytic converters can help remove the three main pollutants from vehicle exhausts (nitrogen oxides, unburnt hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide).
Converter is a honeycomb coated with platinum and rhodium metals (these are catalysts)
What is a catalytic converter?
-NOX, CO and unburnt hydrocarbons enter the converter
-Honeycomb shape provides a large surface area, maximises opportunity for collision between gasses and catalyst (also means a little of the expensive catalysts goes a long way)
-Gasses react with each other to form less harmful products
For example:
Carbon monoxide + nitrogen oxide -> nitrogen + carbon dioxide
Hydrocarbons + nitrogen oxide -> nitrogen + carbon dioxide + water
How does a catalytic converter reduce exhaust emissions?
2CO (g) + 2NO (g) ---> N2 (g) + 2CO2 (g)
Symbol equation for carbon monoxide in catalytic converter
N2, CO2, H2O (water vapour and carbon dioxide still greenhouse gasses but less harmful)
Products of catalytic converter
Carbon dioxide traps infrared radiation so that the earths atmosphere heats up, this is important to sustain life as it keeps the earth warm
Level of CO2 rising, earths temperature therefor rises and is seemingly causing global warming
If temperature increases there will be more water vapour (greenhouse gas), more global warming
Greenhouse effect
The total amount of greenhouse gasses (CH4, CO2, H2O) released to the atmosphere over the full life cycle of a product, service or event.
What is meant by carbon footprint?
Activities which produce no carbon emissions overall to the atmosphere
For example: CO2 in during photosynthesis, CO2 released when burnt
CO2 in = CO2 out
What is meant by a carbon neutral activity?
Moles SO2 = 6490000x10^6/64.1 = 1.012x10^9
Mass Cao = 1.012x0^11 x 56.1 = 5.68x10^9 (kg)
In 1970, the total UK emissions of sulfur dioxide were 6.49 million tonnes (1 tonne=1000kg)
Calculate the mass, in kg, of calcium oxide needed to react with this mass of sulfur dioxide.
CaO + SO2 --> CaSO3
Ethanol has hydrogen bonding where has ethanethiol only has weak van de Waals. Hydrogen bonding is stronger than VDW
Explain why ethanethiol (C2H5SH) contains a lower boiling point than ethanol (C2H5OH) (2)
Thermal cracking
State the type of cracking which produces high proportions of ethene and propene
C16H34 + 16.5O2 ---> 16CO + 17H2O
If a boiler for a central heat system is faulty, a poisonous gas may be produced from the combustion of C16H34
Write an equation that forms this poisonous gas and one other product
polypropene/propanal/propanone
Suggest one important substance manufactured on a large scale from propene (1)
Cl2
Dodecane can be converted into halododecanes.
Deduce the formula of a substance that could be reacted with dodecane to produce 1-chlorododecane and hydrogen chloride only.
a) Not enough oxygen
b) Methane is a greenhouse gas
There is a risk of gas explosions in coal mines. This risk is mainly due to the presence of methane. If the percentage of coal-mine methane (CMM) in the air in the mine is greater than 15%, the explosion risk is much lower. CMM slowly escapes from the mine into the atmosphere.
a) Suggest one reason why there is a much lower risk of an explosion if the percentage of CMM is greater than 15%.
b) State why it is beneficial to the environment to collect the CMM rather than allowing it to escape into the atmosphere.
2NO + 2CO ---> 2CO2 + N2
Catalytic converters are used to remove the toxic gasses NO and CO, write an equation for the reaction of these two gasses that occurs in a catalytic converter when these two gasses are removed
Different boiling points
State the physical property of alkenes that allows it to be separated from a mixture
Fruit ripening/making plastics/make polymers
Use of ethene
C5H12 + 3O2 ---> 5C + 6H2O
Write an equation for the incomplete combustion of pentane to form a solid pollutant
-Same functional group
-Similar chemical reactions
-Same general formula
State characteristics of a homologous series
-Prevents release of toxic CO
-More energy efficient
Give two reasons why boilers are designed to ensure complete combustion
Aluminio silicate (zeolite)
Hexane can be cracked in the presence of a catalyst to produce hydrocarbon Z and methane, give a catalyst for this reaction
Sell HCl
How to boost profit of a reaction that produces undesired HCl
Cl2
Deduce the formula of a substance that could be reacted with dodecane to produce 1-chlorododecane and HCl
Hydrocarbons have different boiling points/bp depends on size/temperature gradient IN THE COLUMN/higher bp hydrocarbons at the bottom
Outline the essential features of fractional distillation of crude oil that enable the crude oil to be separated into fractions (4)
1. Mineral oil (lubricating oil)
2. Gas oil (diesel)
3. Kerosine
4. Naptha
5. Petrol
Order of the fractionating column from bottom to top
NO formed from reaction between O2 and N2 in the air/spark in engine provides/sufficient energy to break N(((N bonds
Explain why NO is formed in petrol engines but not readily formed when petrol burns in air (3)
N2 + O2 -> 2NO
Equation for the formation of nitrogen monoxide
State the meaning of the term 'fraction' relating to fractional distillation
Mixture of compounds with similar boiling points
C=O vibrates at infrared frequency
Give one reason why CO2 absorbs infrared radiation
The energy stored in fuels can be compared using energy density values measured in kJ dm–3
Calculate the energy density of butan-1-ol.
Enthalpy of combustion of butan-1-ol = –2676 kJ mol–1
Density of butan-1-ol = 0.810 kg dm–3
Relative molecular mass (Mr) of butan-1-ol = 74.0
Amount of butan-1-ol in 1dm3 = 810/74 = 10.95
Energy from 1dm3 10.95 x 2676 = 29300