03 - review of molecular bio
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
what is the role of proteins?
the “doers” in the cell; the ones that make most of the action happen
what do proteins include?
enzymes (catalyze reactions) and structural proteins (contribute to cell structure)
what are proteins?
polymers (polypeptides) of the 20 different amino acids
how many amino acids might an average protein contain? what bonds join those amino acids together?
200-1500 amino acids; amino acids are joined together covalently by peptide bonds to form proteins
what are the components of a polypeptide?
a beginning (“amino-” or “N-terminus”) and an end (“carboxyl-” or “C-terminus”)
what are the different structures of protein?
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
what is denaturation?
disruption of protein structure and its function
what does a primary protein structure look like?
linear amino acid sequence
what made the mice obese vs lean?
the genotype of the mice (obese: ob/ob, and lean: ob/+, +/+)
what does a secondary protein structure look like?
a repeating structure due to hydrogen bonds between amino acid side chains; alpha helix or beta sheet
what does a tertiary protein structure look like?
the 3d structure or “fold” of the protein; depends on hydrogen bonds, electrical charges, and hydrophobic interactions between amino acid side chains; critical for protein function
what does a quaternary protein structure look like?
2 or more independently-folded polypeptides together in a complex; often held together with disulfide bonds
what is a mutation?
a change in a cell’s dna sequence; often results in a change in the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein
what are nucleic acids?
polymers of nucleotides, covalently linked by phosphodiester bonds
what is dna?
the hereditary material that contains genes
what is process is rna involved in?
making protein from the information in genes: rRNA, tRNA, mRNA
what are carbohydrates?
primary main source of energy for many organisms
what elements do carbohydrates contain?
C, H, and O
what is a glycoproteins?
carbohydrates that decorate proteins
where are polysaccharides found?
on the outside of many bacterial cells like a capsule or slime layer
what is a polysaccharide?
polymer (long chain of repeating units) of monosaccharides, which are covalently linked by glycosidic bonds
what is a polymer?
long chain of repeating units
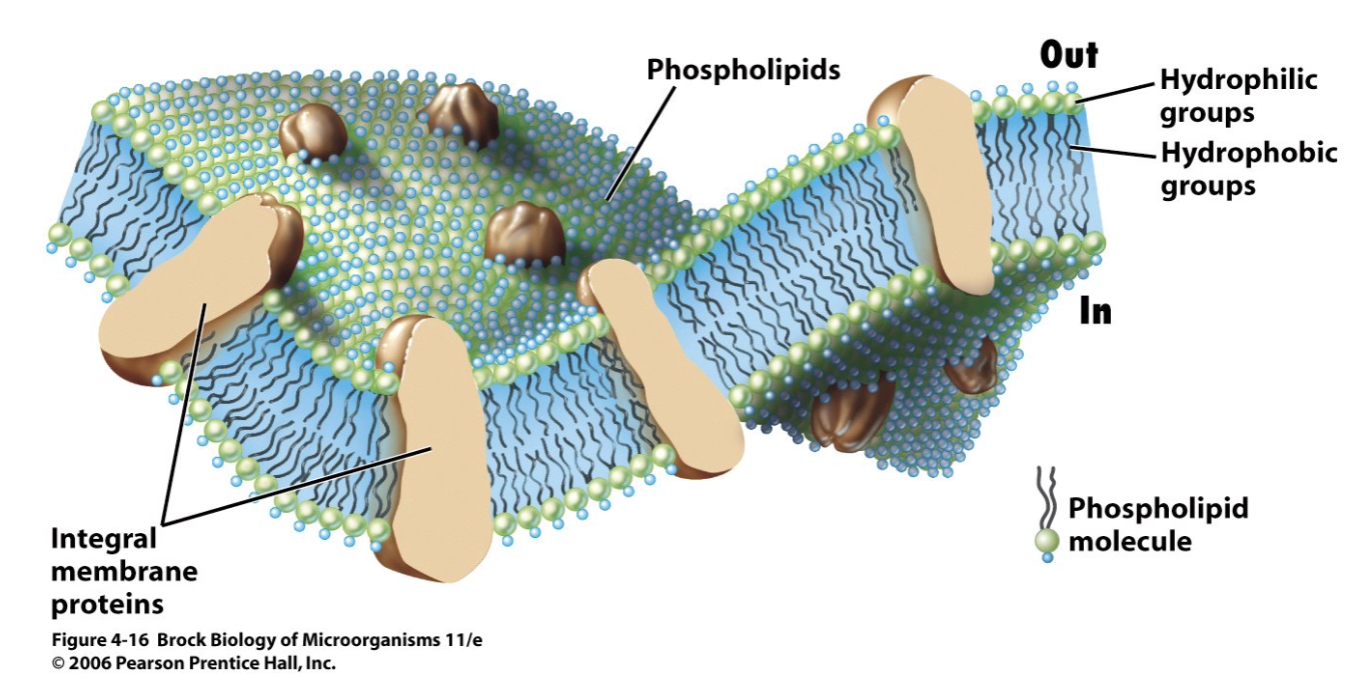
what is the structure of a lipid (phospholipid)?
a charged (hydrophilic) head and an uncharged (hydrophobic) tail
what is the main component of cell membranes?
phospholipid bilayers
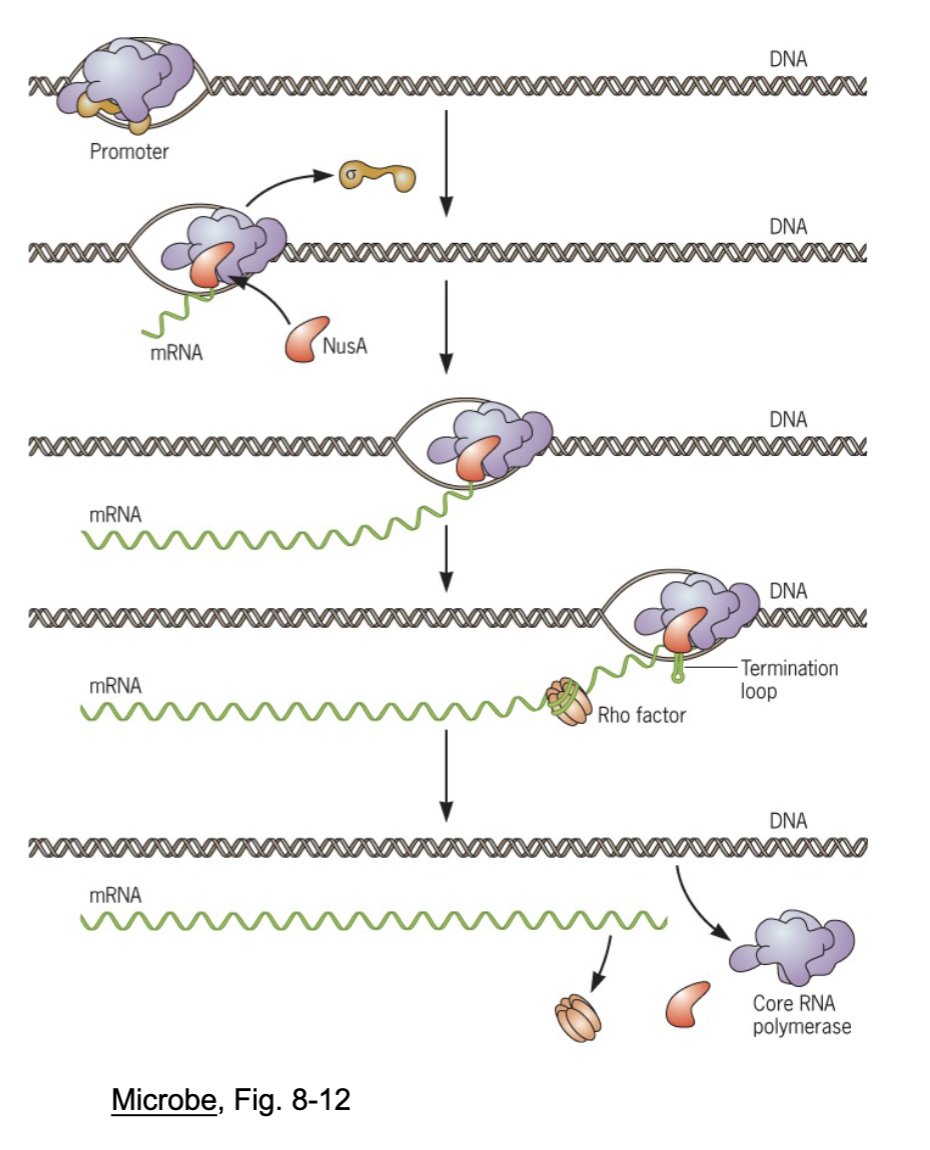
what is the process for gene expression of a typical bacterial gene that encodes a protein
the gene must be transcribed into mRNA and then translated into a protein
what is the process for gene expression of a typical bacterial gene that encodes a rRNA or tRNA
the gene must be transcribed into RNA
what is a gene? what does it encode for?
a genetic unit of function; may encode a protein or a non-translated RNA (ie: rRNA or tRNA
what is genetic expression?
the process by which a gene is made
what is transcription?
the synthesis of rna from a dna template by rna polymerase
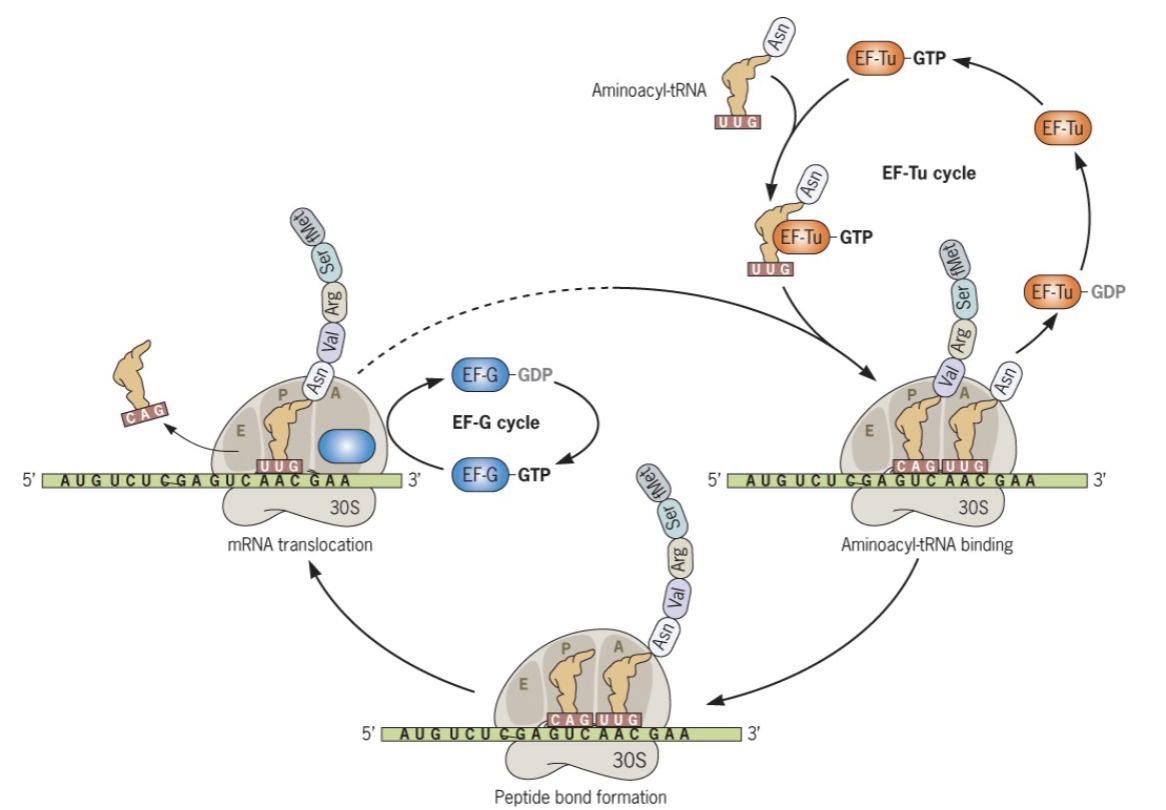
what is translation? what does it involve?
the assembly of amino acids into polypeptides using the genetic information encoded in mRNA molecules; involves ribosomes, tRNA, amino acids, and mRNA
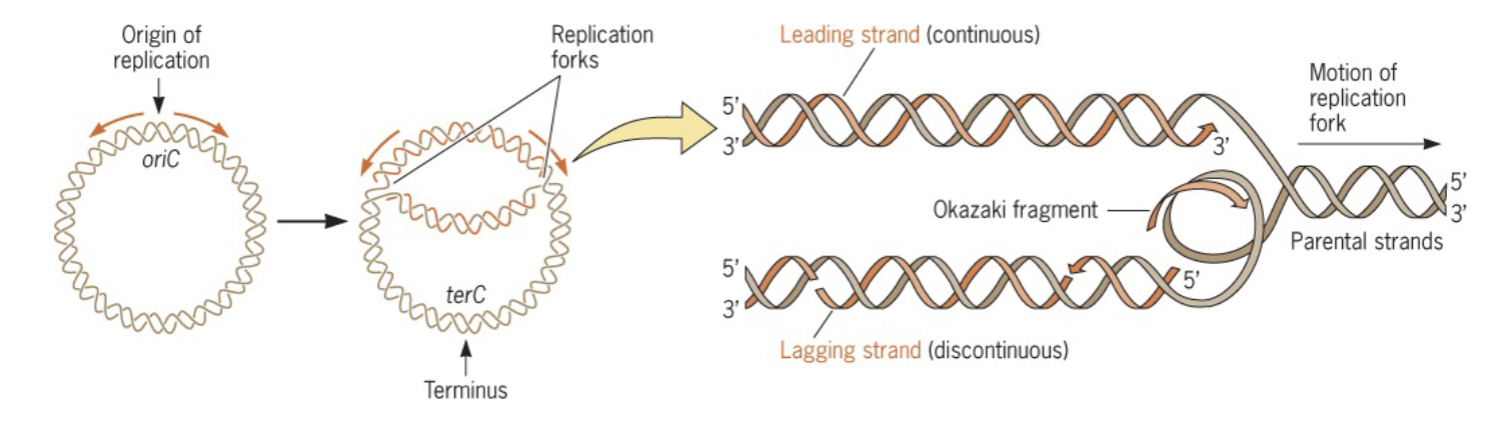
what happens when cells divide in the context of daughter cells?
new daughter cells must receive a copy of the genome
what is replication? where does it begin? what is it catalyzed by?
the process of duplicating a dna molecule; begins at the origin of replication; catalyzed by dna polymerase
what is a genome?
all the genes in a cell or organism
what is recombination?
genetic exchange resulting from a crossover between two different dna molecules or different regions of a dna molecule
what is homologous recombination? what process is it done by?
a recombination event that occurs between two homologous (very similar) dna molecules; done by crossing over
what is transmission EM (TEM)
make thin slices of sample so electrons can pass through
what is scanning EM?
coat sample with a think layer of heavy metal
during which process(es) is/are new phosphodiester bonds formed?
transcription where rna is being synthesized and replicaiton where dna is being synthesized
during which process(es) is/are new peptide bonds formed?
translation where proteins are being synthesized
in living cells, how often do the processes of transcription and translation occur (all of the time, some of the time, or never?)
all of the time
in living cells, how often does the process of replication occur? (all of the time, some of the time, or never?)
in the production of new cells (ie: mother cells making daughter cells)
would you expect a fast-growing bacterial cell to have more, fewer, or the same number of ribosomes as a slowly growing bacterial cell? justify your answer.
fast growing cells will have more ribosomes because for cells to grow they have to synthesize more proteins
what is the role of dna?
store the genetic information of the cell in a stable, heritable form
what is the role of rna?
act as the working copy of genetic information (mRNA), helps build proteins (tRNA, rRNA), and can regulate gene expression
what is the role of polysaccharides?
provide energy storage and structural support
what is the role of phospholipids?
form the structural basis of biological membranes, creating a barrier that separates the cell from its environment and regulates transport
which of these is not a polymer (a covalently-linked chain of repeating subunits): dna, rna, polysaccharides, phospholipids, or protein?
phospholipids
what does it mean for a gene to be expressed?
the information it encodes for in its dna sequence is used to mae a functional product like a protein
who are the main players in transcription? of the players you mentioned, indicate which ones are enzymes and which ones are regions on DNA or RNA.
rna polymerase → enzyme, promoter → dna region start site, terminator → dna region stop site, transcription factors → proteins, mRNA → rna product (transcript)
who are the main players in translation? of the players you mentioned, indicate which ones are enzymes and which ones are regions on DNA or RNA.
ribosome → enzyme complex (rRNA +proteins), catalyzes peptide bonds; mRNA → rna region, carries codons; tRNA → rna molecules, bring amino acids and match codons; start stop codons → mRNA regions, signal begin/end; aminoacyl - tRNA synthase → enzymes, attach amino acids to tRNAs
when does replication need to occur?
before cell division (S phase of interphase)
who are the main players in replication? of the players you mentioned, specify which ones are enzymes and which ones are regions on DNA or RNA.
origin of replication → dna region (starting site); helicase → enzyme (unwinds the dna), primers → enzyme (lays rna primers); dna polymerase → enzyme (synthesizes new dna); ligase → enzyme (seals the okazaki fragments); rna primer → rna region (starting point for polymerase)
what is the role of rRNA?
forms the core and helps maintain shape of the ribosome and acts as the catalyst of the ribosome
which type of microscopy will we be doing in lab?
light microscopy; you can see most bacteria but not viruses
how does electron microscopy differ from light microscopy?
electron microscopy uses a beam of electrons rather than light which gives much higher resolution and allows for visualization