Ch 10
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what is a bond
a security that obligates the issuer to make specified payments to
the holder over a period of time.
what is face value/par value
the final payment to the bondholder at the maturity.
what is coupon rate?
a bond’s annual interest payment per dollar of par value.
invoice price formula
invoice price = quoted price + accrued interest
accrued interest formula



what is a callable bond
the firm has an option to call back bonds.
does callable bonds have a higher coupon rate than regular bonds?
yes
what are convertible bonds
do they have a lower or high coupon rate than nonconvertible bonds
the buyer has an option to convert bonds into stocks.
lower coupon rate than nonconvertible bonds.
what are puttable bonds
does the bond have lower or higher rate
the buyer has an option to convert bonds into stocks.
lower coupon rate than nonconvertible bonds.
what is flating-rate bonds
coupon rates periodically reset according to some
market rates
what are yankee bonds
Dollar-denominated bonds sold in the U.S. by
non-U.S. issuers
what are samurai bonds
Yen-denominated bonds sold in Japan by non-
Japanese issuers
what are bulldog bond?
Pound-denominated bonds sold in the U.K. by
non-U.K. issuers
what are euroyen?
Yen-denominated bonds selling outside Japan
what are eurosterling
Pound-denominated bonds selling outside the U.K.
what are inverse floaters?
Coupon rate falls when interest rates rise
what are asset-backed bonds
Income from specified assets used to service debt
what are pay-in-kind bonds
Issuers can pay interest in cash or additional bonds
what are catastrophe bonds
Higher coupon rates to investors for taking on risk
what are index bonds
Payments tied to general price index or price of a
particular commodity
what are TIPS
Par value
of bond increases with consumer price index
Nominal Return and Real Return formula

what is bond pricing
calculating the pv of all future cash flow at YTM
what is ytm
universal discount rate for cash flows of any horizons.
bond price formula

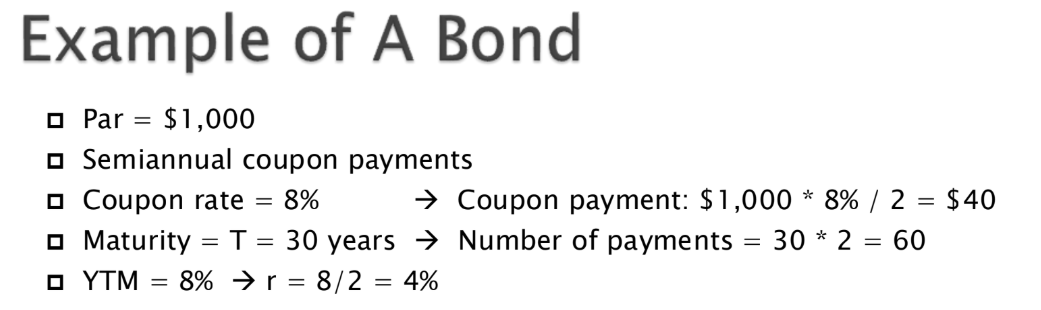
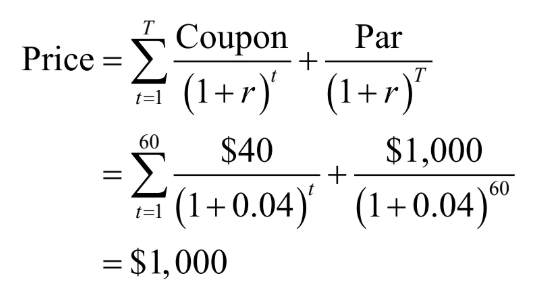

find the price
slide 22 - 24
Par= $1,000
Semiannual coupon payments
Annual coupon rate = 8%
Maturity = T = 30 years
Bond price = PV = $1,276.76
Find Current YIeld
Find APR

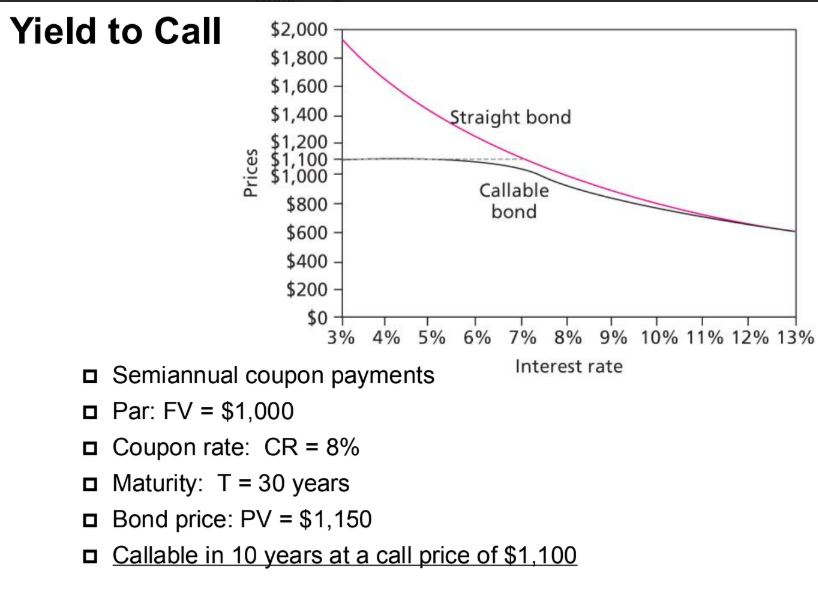
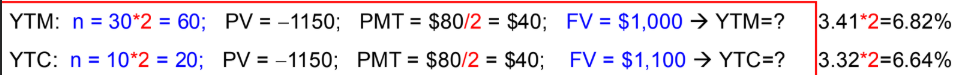
if the interest rate (YTM) is constant over the life of the bond,
would the bond price still varies over time?
Answer: the bond price still
varies over time unless it’s
sold at the par (CR=YTM).
Separate Trading of Registered Interest and
Principal of Securities (STRIPS)
• Oversees creation of zero-coupon bonds from
coupon-bearing notes and bonds
Determinants of Bond Safety
coverage ratios
leverage ratios
liquidity ratios
profitability ratios
cash flow to debt ration
what is a bond indenture
contract between issuer and holder
what is a sinking fund
periodic repayment of bonds
what is a subordination clause (bond indenture)?
restric additional borrowing
senior bondholder get paid first
what is collateral
asset for possible default
what is debenture
not backed by collateral
what is credit default swaps
Insurance policy on default risk of corporate
bond or loan
(Designed to allow lenders to buy protection
against losses on large loans)
what is term structure of interest rates
YTM and term to maturity relationship
what is expectations hypothesis
YTM based on future short-term interst rates
what are the three explaination of the yield curve
expectations theory
liquidity prefernce throry
synthesis
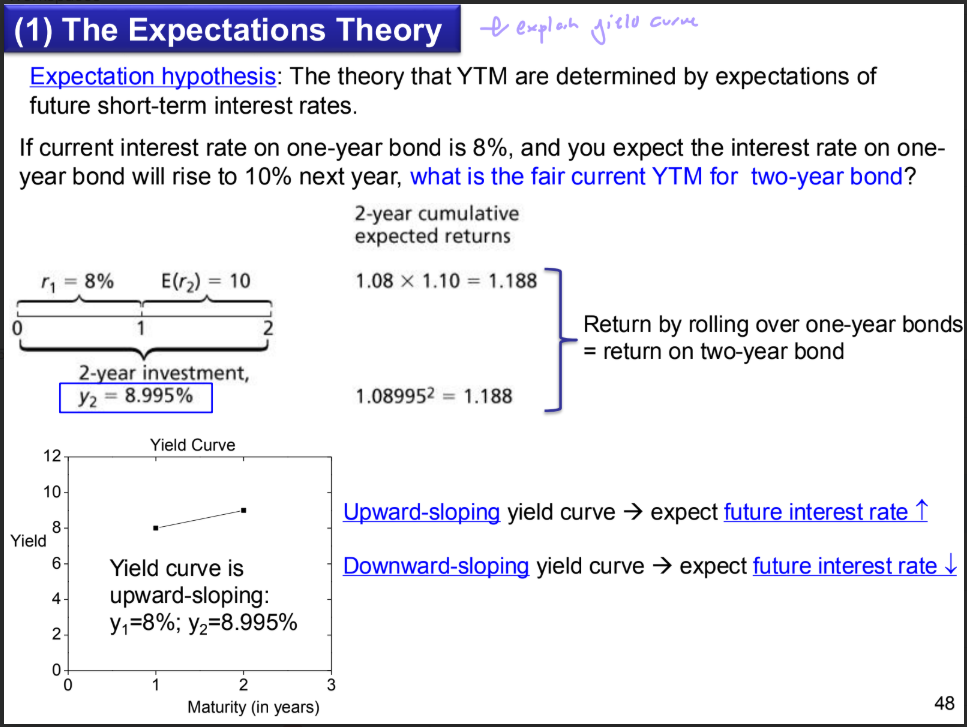
what is the expectation hypothesis
The theory that YTM are determined by expectations of
future short-term interest rates.
If current interest rate on one-year bond is 8%, and you expect the interest rate on one-year bond will rise to 10% next year, what is the fair current YTM for two-year bond?
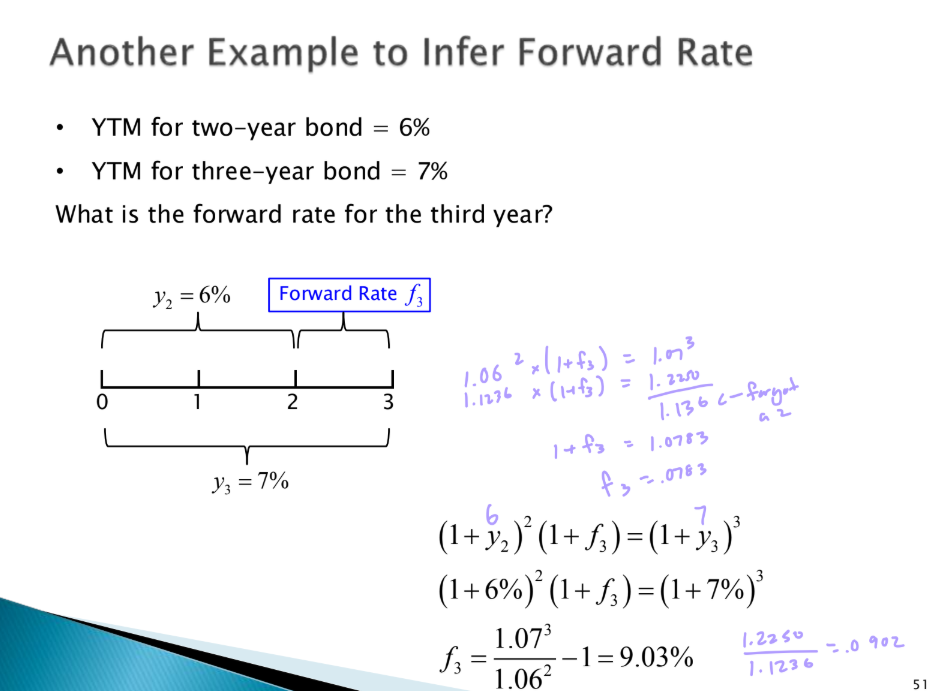
what is forward rate
Inferred short-term ROI for future period,
makes expected total return of long-term bond
equal to that of rolling over short-term bonds
We observe y1=8% and y2=8.995%, we can infer one-year forward rate:
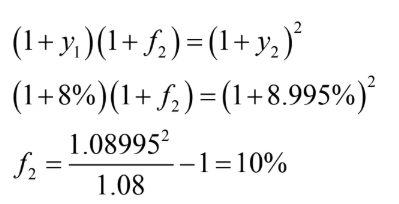

what is the liquity preference theory
The theory that investors demand a risk premium
on long-term bonds.
The yield curve will be upward-sloping even in the absence of any expectation
of future increases in interest rates.