Ch. 12 and 13 Review
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What was Frederick Griffith's experiment about, and what key observation did he make?
Griffith was studying how bacteria cause pneumonia. He observed that a mixture of heat-killed S strain (which did not cause disease) and live R strain (which also did not cause disease) caused pneumonia and death in mice. He also found live S-strain bacteria in these mice, leading to the discovery of transformation.
What is the genetic material that causes transformation?
The genetic material that causes transformation is DNA.
Describe the basic structure of a DNA molecule.
A DNA molecule can be thought of as a twisted ladder called a double helix. The sides of the ladder are made of deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups. The rungs of the ladder are made of nitrogenous bases.
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA, and how do they pair?
•Adenine (A)
•Guanine (G)
•Cytosine (C)
•Thymine (T)
They pair in a specific way:
•Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T).
•Guanine (G) always pairs with Cytosine (C). These pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds.
State Chargaff's Rule.
Chargaff's Rule states that the amount of Adenine (A) is always roughly equal to the amount of Thymine (T), and the amount of Guanine (G) is alway s roughly equal to the amount of Cytosine (C). This is represented as [A] = [T] and [G] = [C].
![<p><span>Chargaff's Rule states that the amount of </span><span style="color: #ceabf6"><strong>Adenine (A)</strong></span><span><strong> is always roughly equal to the amount of </strong></span><span style="color: #f063ff"><strong>Thymine (T)</strong>,</span><span> and the amount of </span><span style="color: #be5ef3"><strong>Guanine (G)</strong></span><span><strong> is alway s roughly equal to the amount of </strong></span><span style="color: #fb84f5"><strong>Cytosine (C)</strong></span><span>. This is represented as </span><span style="color: #ee97fe"><strong>[A] = [T] and [G] = [C]</strong></span><span>.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cabf8a96-130a-4687-b470-ae2b014f9112.jpg)
Explain why Chargaff's Rule works.
Chargaff's Rule works because of complementary base pairing. For every adenine on one strand of DNA, there must be a thymine in the corresponding position on the other strand, and similarly for guanine and cytosine.
Describe the process of DNA replication.
The DNA molecule unzips down the middle at replication forks.
• Each separated strand acts as a template.
• DNA polymerase, an important enzyme, moves along each template strand and adds new nucleotides to create a new complementary strand.
Why is DNA replication called semi-conservative?
DNA replication is called semi-conservative because each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly made strand.
What is the role of DNA polymerase during DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in linking individual nucleotides into DNA molecules during replication. It moves along the template strands, adding new nucleotides to create a new matching strand. It can also proofread the new DNA strands and correct errors.
What are the three main types of RNA and what are their general roles in protein synthesis?
•Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries the instructions from DNA to the ribosomes.
•Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): A key structural component of ribosomes (the protein-building factories).
•Transfer RNA (tRNA): Acts as a delivery truck, bringing amino acids to the ribosome based on the mRNA code.
Describe the process of transcription.
•RNA polymerase finds the promoter, a start signal on the DNA.
•RNA polymerase unwinds a small section of the DNA.
•RNA polymerase uses one strand of the DNA as a template to build a new mRNA molecule by adding complementary RNA nucleotides. Uracil (U) is used in RNA instead of thymine (T).
•Once the gene is transcribed, the RNA polymerase detaches, and the DNA rewinds.
•The mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosomes.
How does base pairing differ in transcription compared to DNA replication?
In transcription:
•Adenine (A) on the DNA template pairs with Uracil (U) on the mRNA.
•Guanine (G) on DNA pairs with Cytosine (C) on mRNA.
•Cytosine (C) on DNA pairs with Guanine (G) on mRNA.
•Thymine (T) on DNA pairs with Adenine (A) on mRNA.
In DNA replication, Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C).
Describe the process of translation.
•mRNA arrives at the ribosome.
•The mRNA message is read in three-letter codons.
•Translation begins at a start codon (AUG).
•Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid and having a complementary anticodon, bind to the mRNA codons.
•The ribosome joins the amino acids together via peptide bonds, forming a growing polypeptide chain.
•This continues until a stop codon is reached.
•The polypeptide chain is released, folds into a protein, or joins with other polypeptides.
What is a codon, and what is its role in translation?
A codon is a group of three nucleotide bases in messenger RNA (mRNA). Each codon specifies a particular amino acid to be added to the protein chain or acts as a start or stop signal during protein synthesis.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a delivery truck, bringing the correct amino acids to the ribosome.
Each tRNA molecule has a specific anticodon that is complementary to a codon on the mRNA, ensuring the amino acids are placed in the correct order.
What are the two main steps in getting proteins from DNA?
The two main steps in getting proteins from DNA are:
•Transcription: Copying the DNA instructions into RNA.
•Translation: Using the RNA instructions to build the protein.
What is a point mutation, and what are the three types of point mutations?
A point mutation is a small change in the DNA code that happens at a single spot.
The three types are:
• Substitutions: One base is replaced by another.
• Insertions: An extra base is added to the sequence.
• Deletions: A base is removed from the sequence.
What are chromosomal mutations?
Chromosomal mutations are large-scale changes to the DNA code that affect whole chromosomes or large chunks of them, rather than just a single letter.
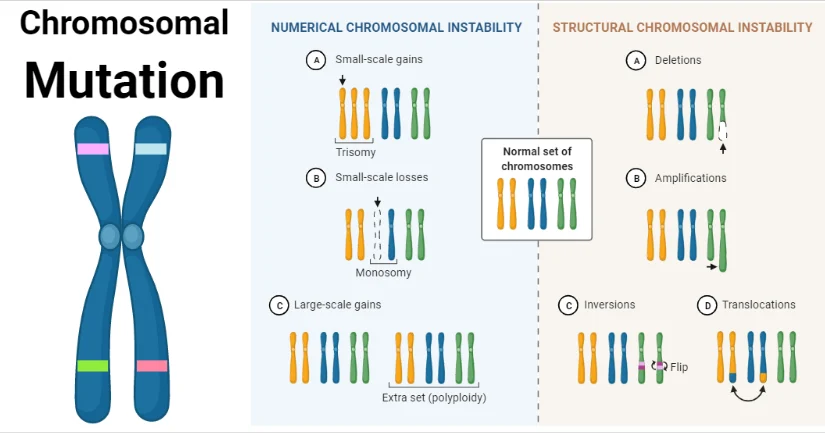
Name and briefly describe four types of chromosomal mutations.
• Deletion: Losing a section of a chromosome.
• Duplication: Having an extra copy of a section of a chromosome.
• Inversion: A section of a chromosome gets flipped or reversed.
• Translocation: A piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to a different chromosome.
What is a carcinogen? Give some examples.
A carcinogen is anything that can cause cancer. Examples include too much ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun (linked to skin cancer) and certain chemicals found in things like tobacco smoke and pollution (chemical mutagens).
Define the term "transformation" in the context of genetics.
Transformation is the process by which one strain of bacterium is apparently changed into another strain, as observed in Griffith's experiments.
What is a bacteriophage?
A bacteriophage is a type of virus that infects and kills bacteria. It is composed of a DNA core and a protein coat.
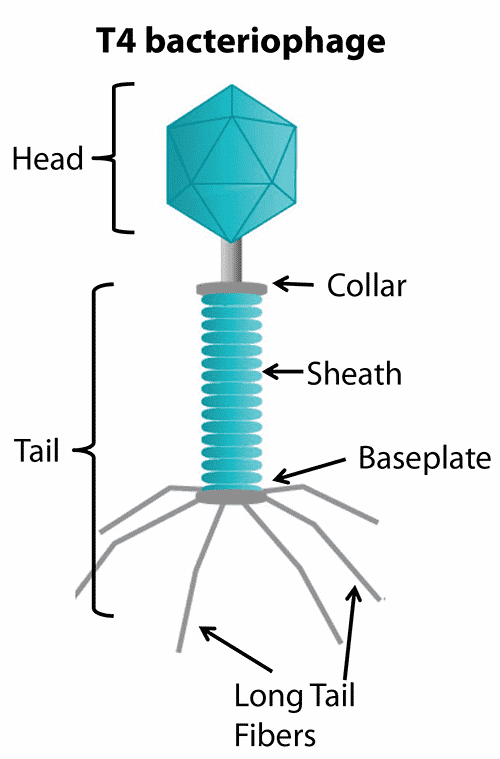
Define "replication" in the context of DNA.
Replication is the process before a cell divides when its genetic information (DNA) must be copied. The double-helix structure of DNA makes this process possible.
What is RNA, and how does it differ from DNA in terms of structure and bases?
RNA is a nucleic acid that is generally single-stranded, contains ribose sugar, and has the base uracil (U) in place of thymine (T). DNA is typically double-stranded and contains deoxyribose sugar and thymine (T).
Define "mutation" in the context of genetics.
Mutation refers to changes in DNA sequences that affect genetic information.
Mutations can be gene mutations (like point mutations) or chromosomal mutations. They can involve changes in a few nucleotides or large changes in chromosomes