Part 9: Pediatric Solid Tumors- General Info
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is meant by pediatric “solid tumors”
the tumor is a physical mass,
Childhood cancer excluding:
leukemias- not a solid tumor
brain tumors- their own category
“Pediatric” age group
children up to the age of 15
number of pediatric cancers diagnosed/ year
9k/ year
number of pediatric cancer deaths/ year
1500/ year
def. inflammation of the lungs
term. pneumonitis
def. any disfunctions/ diseases of the brain
term. encephalopathies
def. inflammation of the small intestines
term. enteritis
def. anything that is hollow/ honeycomb- shaped
alveolar
Give an example of an alveolar structure
alveoli of the lungs
def. having many shapes
term. pleomorphic
def. loss of the iris
term. aniridia
def. massive fatigue
term. malaise
Pediatric solid tumors epidemiology (4)
cancer is #2 cause of death in children
over ½ childhood cancers are solid tumors
6k solid tumor cases/ year; 1/3 die
Higher incidence in males
What are the most common childhood cancers. Ranked
leukemia (~40% of peds cancers)
CNS tumors
Childhood cancers usually involve ___tissues, while adult cancers generally involve ___ tissues
childhood:
hematopoietic
nervous
connective
Adult:
epithelial (environmentally induced)
How are childhood cancers generally treated? why?
using a multi-disciplinary treatment- due to concerns for late effects
at specialized clinics, rather than local hospitals
Childhood tumors etiology (3)
genetic/ hereditary
Virus (e.g. EBV)
AIDS- Kaposi’s & Lymphomas
RARELY associated with environmental conditions - those have long latent periods
Staging for peds tumros
no generally accepted staging system for pediatric tumors
True or False: We need to keep late effects in mind when determining tx for peds tumors
True
late effects of RTT on children (6)
late carcinogenesis
Retardation of bone/ cartilage growth
intellectual impairments
sterilization (if gonads are in field)
Other organ specific effects
psychosocial effects
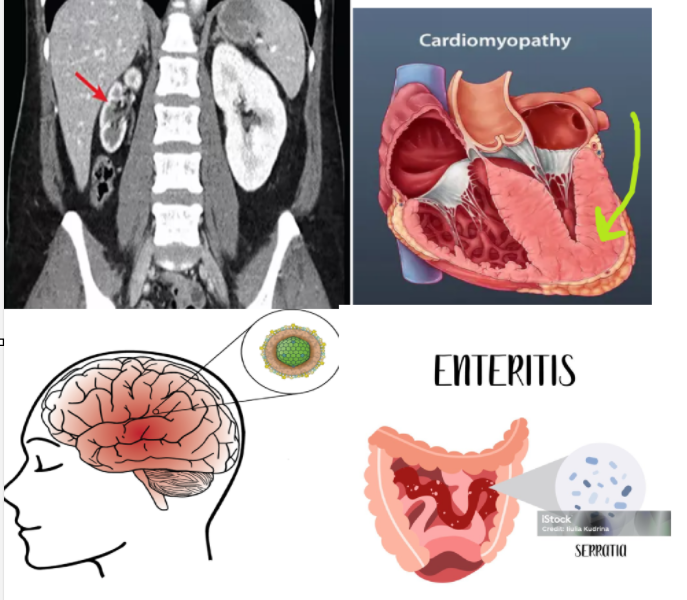
late effects of chemo in children (5)
renal atrophy
cardiomyopathy
encephalitis
enteritis
psychosocial effects
True or False: Late effects on children can be synergistic
True, therefore carful planning is required
Mnemonic for ped tumors discussed
W – Willie
N – Nelson
R – Ran
R – Red
L – Lights
L – Like (an)
O – Outlaw
E – Escaping
G – Gunshots
What pediatric solid tumors were discussed (9)
Wilms Tumor- kidney
Neuroblastoma- neural crest cells that develop into adrenal medulla
Rhabdomyosarcoma- embryonic mesenchyme (soft tissue) that develop into muscle
Retinoblastoma
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis- histiocytic immune system’s Langerhans cells
Lymphoma- HD, NHL, Burkitt’s
Osteogenic Sarcoma (osteosarcoma)- bone
Ewing’s Sarcoma- soft tissue near the bone (not a bone tumor)
Germ Cell Tumors- ovum or sperm cell
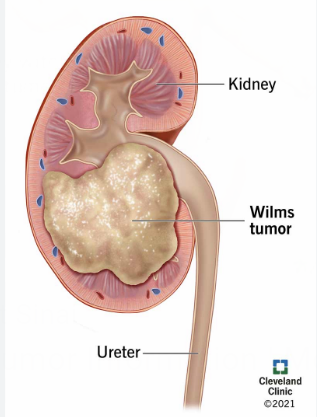
What childhood cancer is this?
Wilms Tumor- kidney
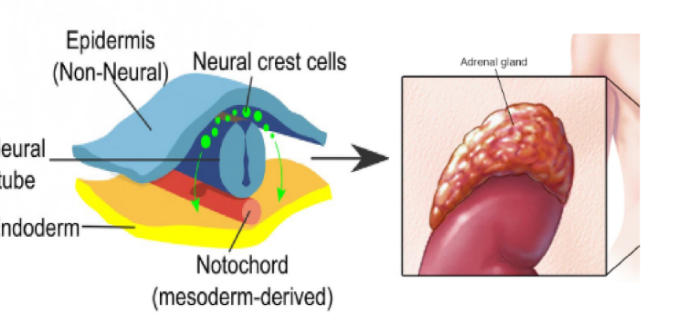
What childhood cancer is this?
Neuroblastoma- neural crest cells that develop into adrenal medulla
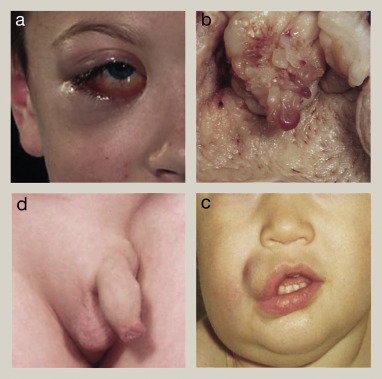
What childhood cancer is this?
Rhabdomyosarcoma- embryonic mesenchyme (soft tissue) that develop into muscle
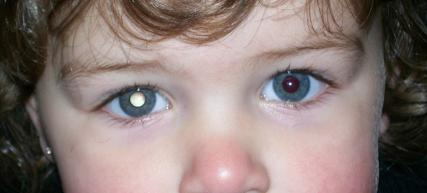
What childhood cancer is this?
Retinoblastoma
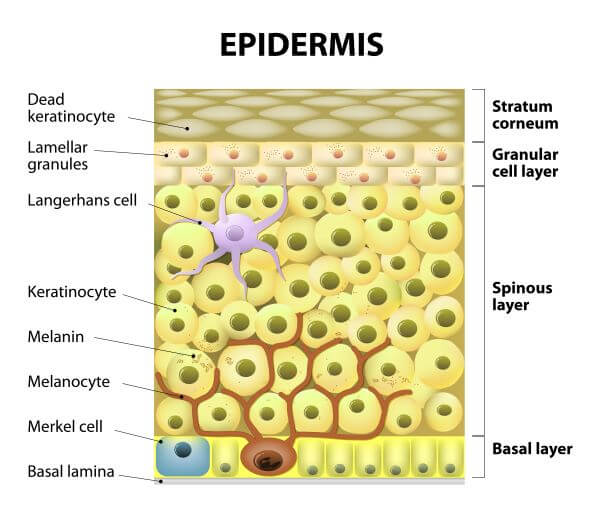
What childhood cancer is this?
* the purple cell
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis- histiocytic immune system’s Langerhans cells
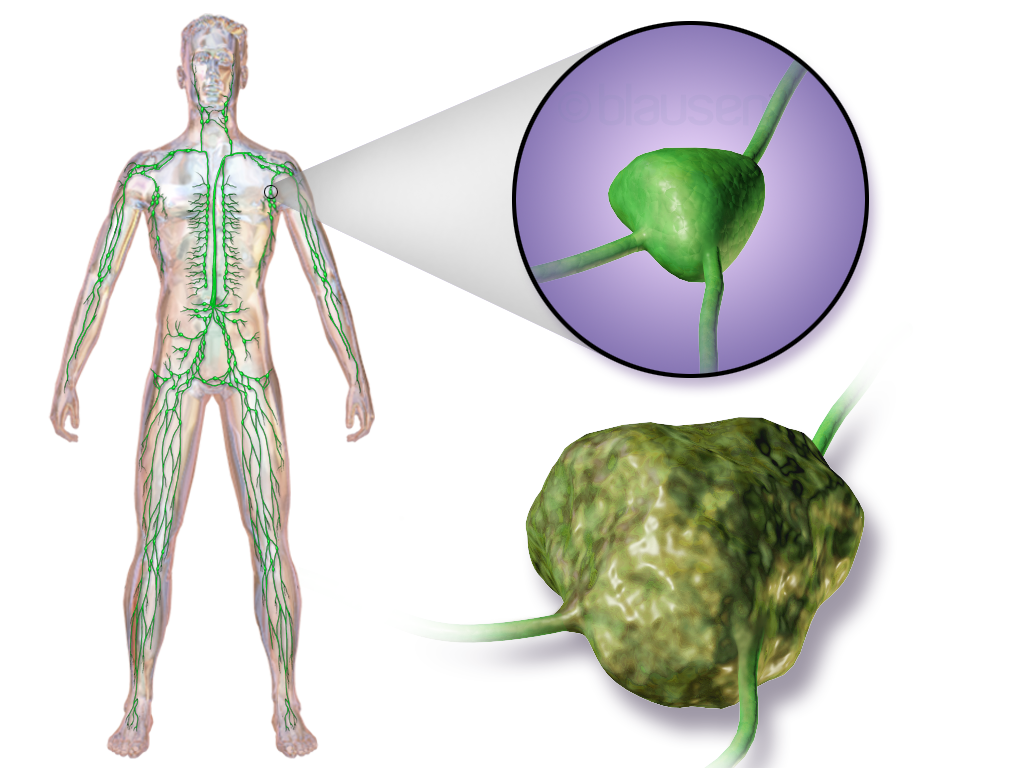
What childhood cancer is this?
Lymphoma- HD, NHL, Burkitt’s
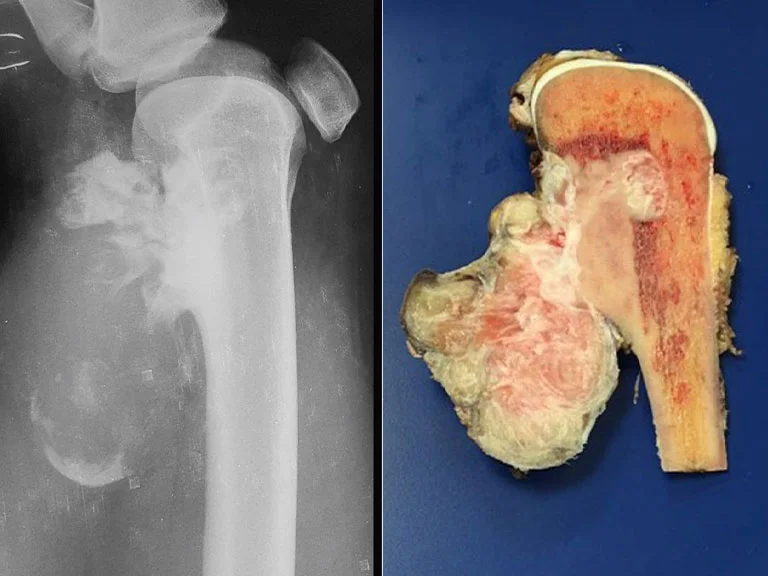
What childhood cancer is this?
Osteogenic Sarcoma (osteosarcoma)- bone
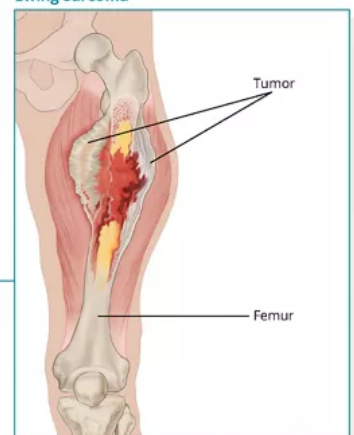
What childhood cancer is this?
Ewing’s Sarcoma- soft tissue near the bone (not a bone tumor)
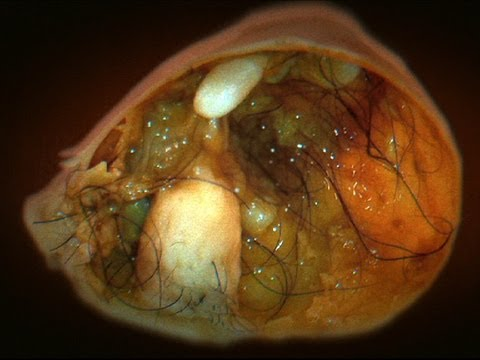
What childhood cancer is this?
Germ Cell Tumors- ovum or sperm cell e.g. teratoma