Lithium and Bipolar- Joshi
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is bipolar disorder?
just recognize
chronic cyclic mood disorder characterized by recurrent fluctuations in mood, energy, and behavior
includes hypomania, mania, major depression, and mixed episodes
What symptoms characterize mania?
extreme mood elevation: euphoria, extremely optimistic
mood abnormality: irritability, distractibility, agitation
behavioral changes: increased energy, hypersexuality
Major depression is a depressed mood daily for a minimum of __ weeks.
2
Etiology of bipolar disorder?
UNKNOWN!!!
genetics—> CACNA1C, ANK3
NT dysregulation
Secondary causes of bipolar disorder?
medical conditions
CNS disorders, infections, electrolyte/metabolic abnormalities, hormones
drugs
alcohol, drug withdrawals, antidepressants, hallucinogens, weed, DA drugs
environmental triggers
traumatic brain injury, stressful childhood events, etc.
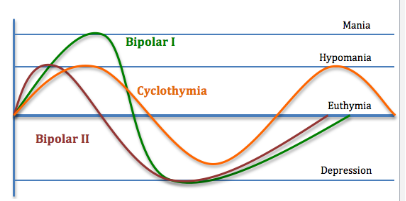
What are the 2 types of bipolar disorder?
how many manic/depressive episodes in each?
Bipolar I: 1 or more manic episodes ± depressive episodes
Bipolar II: 1 or more episodes of hypomania + depression ± manic and mixed episodes
List the drugs used for bipolar disorder:
LITHIUM
antiepileptics: LAMOTRIGINE, valproic acid, carbamazepine
antipsychotics: LURASIDONE, olanzapine, aripiprazole, chlorpromazine
antianxiety: BZDs
Lithium can be used in…
a. bipolar I
b. bipolar II
c. both
c.
MOA of lithium:
not 100% known but…
inhibits inositol monophosphates = inhibits hydrolysis of IP1 and IP2
inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) = reduces phosphorylation of b-catenin, modulates energy metabolism, provides neuroprotection/plasticity
inhibits depolarization-evoked release of DA and NE
inhibits bisphosphate 3’ nucleotidase (BPNT-1)
KNOW THE BOLDED 3
Lithium mimics and replaces what electrolyte in the body?
Na+
How is lithium eliminated?
unchanged in the urine (~95%)
ADRs of lithium:
GI (n/v/d, bloating)
CNS (confusion, lethargy, fatigue, HA, memory impairment, tremor, muscle weakness)
increase WBCs
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (decreases ADH)
polyuria, polydipsia, xerostomia
hypothyroidism
derm ADRs
note: GI and CNS MOST COMMON
Can lithium be used in pregnancy? category? why/why not?
C/I IN PREGNANCY
category D
associated w/ down syndrome, club foot, fetal goiter, abnormalities
C/I of lithium:
Pregnancy
sick sinus syndrome
renal disease
D/I with lithium
diuretics (may increase reabsorption)
NSAIDs, ACEis, ARBs (lithium retention)
insulin/sulfonylureas (lithium enhances hypoglycemia)
succinylcholine, pancuronium (associated with paralysis with lithium)
antipsychotics (risk of serotonin syndrome)
CCB, phenytoin, carbamazepine (neurotoxicity)
Why must lithium be monitored closely?
with what levels does toxicity occur?
NARROW THERAPEUTIC WINDOW
requires therapeutic monitoring
>1.5 mEq/L—> MILD/MOD TOXICITY
>3.0 mEq/L—> SEVERE TOXICITY