PT 856 lecture 3: resistance training
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Resistance training details
- Effective intervention strategy to enhance muscular performance via muscular and neural adaptations
Basic elements of muscle performance (3)
- Strength
- Power
- Endurance
Muscle strength (muscle vs neural adaptations)
- Muscle: increased cross-sectional area or hypertrophy, selective hypertrophy of fast twitch type 2
- Neural: increased recruitment and rate-coding
What motor units are recruited first (hennemans size principle)
- Small motor units then large
Spatial vs temporal summation
- Spatial: increase in force by increasing the number of motor units recruited
- Temporal: increased in force by increasing the firing rate
Increases in muscle strength are driven by what in the first 8 weeks.
- Neural adaptations
Muscular adaptations to lead to increased endurance
- Increased capillarization
- Increased mitochondrial density
- Increased oxidative capacity
What is most effective in eliciting tendon adaptations
- High intensity loading
What do ligaments adapt to?
- Mechanical stress
o Less than tendons
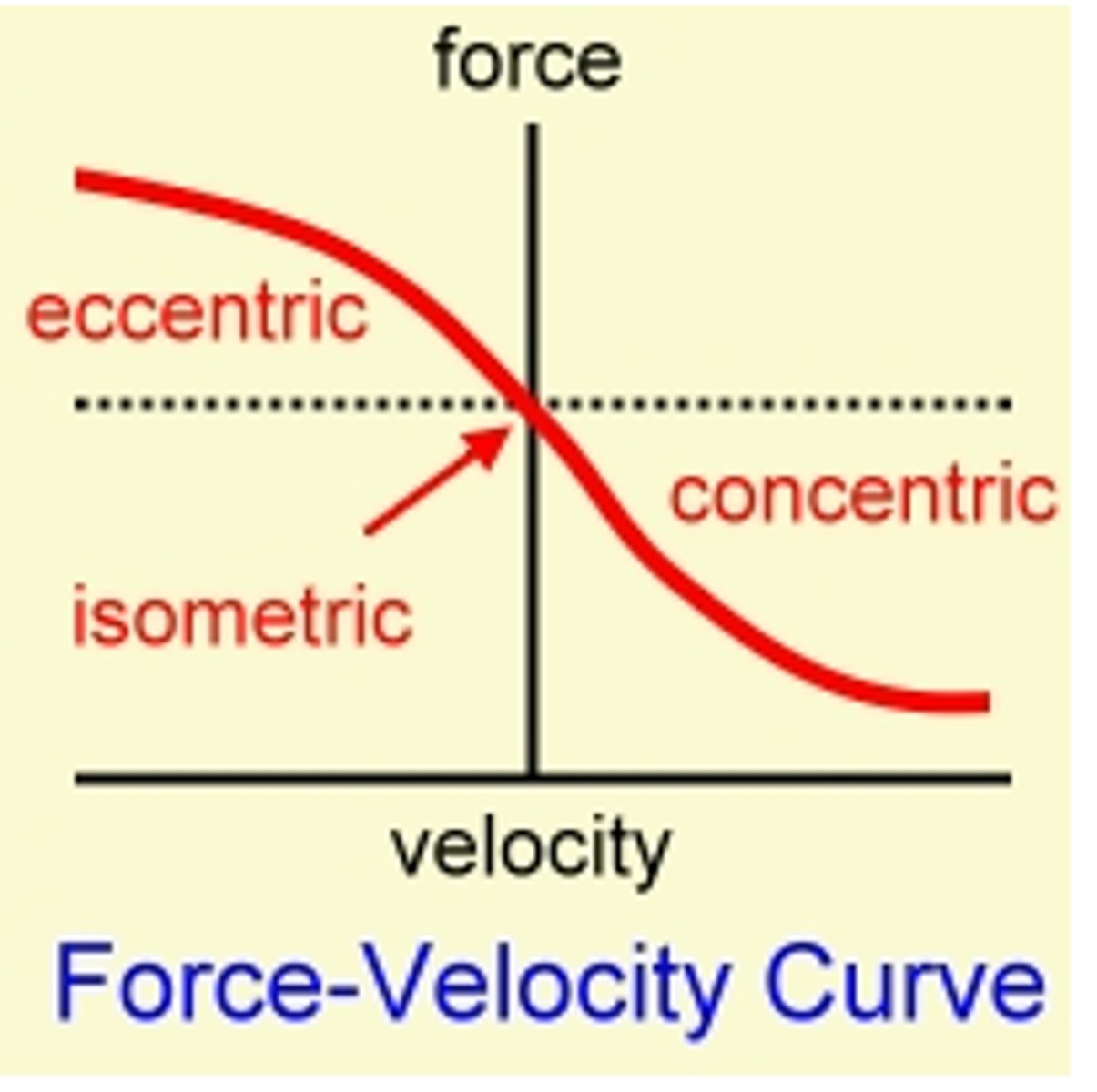
Force velocity curve details (eccentric vs concentric)
- Eccentric:
o Slower: decreased force
o Faster: increased force
- Concentric
o Slower: increased force
o Faster: decreased force
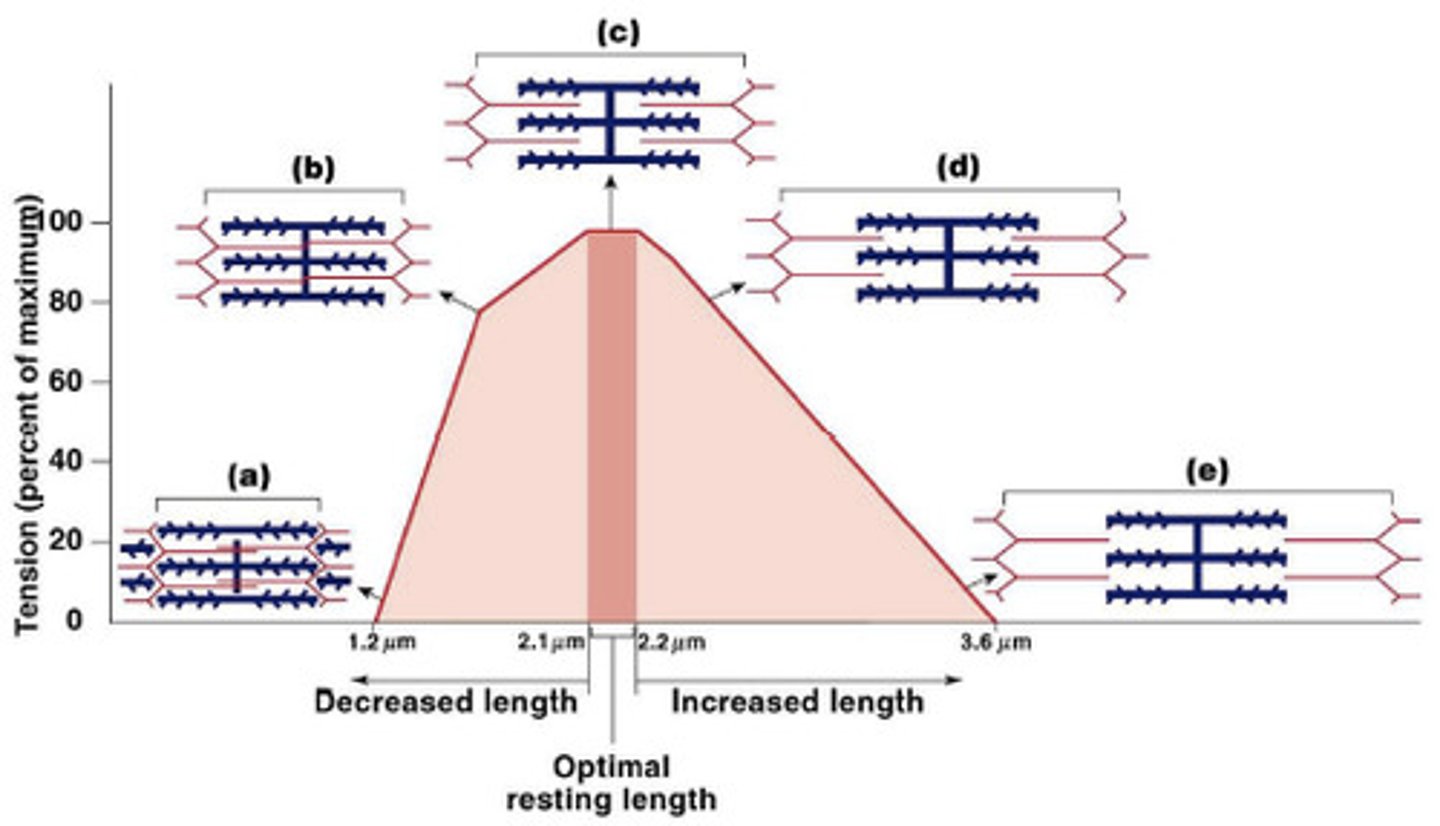
Force- length relationship
- Optimal length is in midrange -> more overlap and more force generated
Three energy system
- ATP-PCR
- Anaerobic glycolysis
- Oxidative
When are the three energy systems used?
- ATP-PCR: rapid max effort (second)
- Anaerobic glycolysis: brief moderate- high intensity (minutes)
- Oxidative: endurance (multiple mins - hours)
What is a one rep max
- Maximal weight an individual can lift for only one rep
What is the gold standard for assessing strength
- Isokinetic dynamometer
An isokinetic dynameter can test what types of contractions
- Isokinetic: resistance against an angular velocity
- Isometric: resistance against fixed surface
Power measures
- Chair rise test
- Vertical jump
- Single arm shotput
- Wingate test
Endurance measures
- 6 min walk test
- Isokinetic dynamometry
What is progressive overload
- The gradual increase of stress placed on the body during resistance training
Effects of targeting single joint of multi joint muscles
- Single joint: less skill dependent and may target muscle groups better
- Multi joint: may be tailored to more specific task
When to use isometric, concentric and eccentric movement
- Isometric: early post op and tendinopathy
- Concentric: power and strength adaptations
- Eccentric: tendinopathy
Exercise order guidelines
- Large muscle groups before small
- Multi joint before single joint
- High intensity before low intensity
Muscle strength progressive overload
- 1-3 sets, 1-12 reps at 80-100% of 1 rep max
- 2-3 mins rest
Muscle power progressive overload
- 1-3 sets, 3-6 reps, 30-40 % of 1 rep max
- 2-3 mins rest
Muscular endurance progressive overload
- 1-3 sets, more than 15 reps, 40-60 % 1 rep max
- Short periods of rest (less than 90)
2 for 2 rules
- If the patient can perform 2 or more reps over the assigned goal for at least 2 consecutive sets, add weight