Unit 2 exam
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
1
New cards
Senate
One of 2 chambers, represents states equally
* 6 yr term
* 100 senators
* more national interest
* 6 yr term
* 100 senators
* more national interest
2
New cards
House of Representatives
One of 2 chambers, equally represents population
* 2 yr term
* 435 members
* more for public interest
* 2 yr term
* 435 members
* more for public interest
3
New cards
Pork barrel
jobs, policies, that benefit specific voters (to help local rep win reelections)
4
New cards
Descriptive presentation
whether a member shares the same ethnic, race, religion, gender as a voter
5
New cards
Substantive representation
whether a member shares the same policy concern/interests of a voter
6
New cards
Trustee model
represents voters’ interest from afar weighin in national, local, moral concern
7
New cards
Delegate model
carries out direct desires of voters
8
New cards
Politico
someone who acts as a delegate towards very important policies but a trust on less complex issues
9
New cards
Incumbent advantage
has a political advantage over challengers at elections
10
New cards
Redistricting
redo of geographic boundaries of legislative districts, occurs every 10 yrs after census to ensure equal representation
11
New cards
Apportionment
dividing the number of house seats to the states after redistricting
12
New cards
Gerrymandering
using the redrawing of districts for a political advantage, protect incumbents, or change the proportion of minority voters
13
New cards
Universalism norm
when benefits are being divided, available to all states and districts
14
New cards
Logrolling
Congress votes on bills they wouldn’t so that they get support for their bills; “if you scratch my back, I’ll scratch yours”
15
New cards
Earmarks
federally funded local projects that are attached to bills
16
New cards
Speaker of the House
elected leader of the House; head of the majority party; Influences legislative agenda, committee assignments, scheduling, and overal party assignments
17
New cards
Majority Leader
elected head of the party holding majority of seats in the House/Senate; House: aids speaker of the house
18
New cards
Whip system
organizes house leaders who work to spread information and promote party unity when voting happens; Three functions - information gathering, spreading info, and building alliance
19
New cards
Minority leader
elected head of the party hold the least amount of seats in the house/senate
20
New cards
Second in command
assistant majority/minority leader
21
New cards
President of the Senate
Vice president; Only duty is to be the tie breaker and preside over proceedings
22
New cards
President pro tempore
presides over senate; senior member
23
New cards
Roll call votes
recorded vote on legislation
24
New cards
Party vote
a vote in which the majority of one party opposes a position of the other party majority
25
New cards
Part unity
members of congress in the same party vote together on same legislations on party votes
26
New cards
Ideological polarization
no overlap in ideals between parties, makes compromise difficult
27
New cards
Conditional Party govt
stronger leadership in congress but conditional on consent of party members
28
New cards
Standing committees
permanent part of house and senate; more authority, get most work done; Draft legislation and oversee how it’s established,
Many committees share jurisdiction
Many committees share jurisdiction
29
New cards
Select committee
address specific topics for a one to two terms; mostly collect information, provide policy option, and be attentive on the issue; can be temporary
30
New cards
Joint committee
have both House and senate members, limited authority; can be temporary
31
New cards
Conference committee
temporary to resolve issues on house/senate version of a bill
32
New cards
Rules Committee
sets rules on the debates in the house, how long can someone talk, type/quantity of amendments in a bill
33
New cards
Multiple referral
sent more than one committee
34
New cards
Markup
debate aspects of the issue or suggest amends to change the bill
35
New cards
Record vote
if 25 members want to vote, all members go on the floor to vote electronically where it’s displayed
36
New cards
Filibuster
talking about a bill for a really long time to kill the bill
37
New cards
Hold
an objection on a time limit
38
New cards
House Rules Committee
rules that govern the bill process
39
New cards
Closed rules
no amendments to bill
40
New cards
Open rules
allow relevant amendments
41
New cards
Modified rules
allow specific amendments
42
New cards
Committee of the whole
every member is present for this legislative meeting, has rules that must be followed; All amendments are considered under a five minute rule (Can be bent with a phantom amendment to add another 5 minutes)
43
New cards
Power of the purse
congress power to control fiscal policy; They can cut funding of a program if it’s not implemented correctly
44
New cards
Fire alarm oversight
wait until there’s a crisis to spring into action
45
New cards
Police patrol
congress has constant vigilance
46
New cards
President’s job description
Head of the executive branch; Vesting clause declares president is the head of the government and head of state, preside over the country
47
New cards
Constitutional authority
powers from constitution
48
New cards
Statutory authority
powers that come from laws
49
New cards
Constitutional enumerated powers
implementation of laws
* Uses their jugdment to input legislative goals into programs
issue orders to govt agencies that make significant policy changes
Appointment power
* Name ambassadors, senior bureaucrats, and members of the federal judiciary
* Controls 8,000 positions
* About 1200 of these appointees require senate approval
1. One limit on presidential power
Commander in chief - control military
* Uses their jugdment to input legislative goals into programs
issue orders to govt agencies that make significant policy changes
Appointment power
* Name ambassadors, senior bureaucrats, and members of the federal judiciary
* Controls 8,000 positions
* About 1200 of these appointees require senate approval
1. One limit on presidential power
Commander in chief - control military
50
New cards
Recess appointment
appointee temporarily holds a position without congress approval
51
New cards
Executive orders
president can change government policy without congressional approval
52
New cards
War Powers Resolution of 1973
limits the president’s ability to send and control the army; here must be notification by the President to the legislative branch within 48 hours of deploying any troops; deployment can be for up to 60 days without a formal Congressional declaration
53
New cards
Treaty Process
Treaty making powers is shared between president and congress; President and staff negotiate terms then send it to congress for approval; Congress isn’t involved at the start which give president unlimited scope of what the treaty can entail; However, since it needs congressional approval, president has to be considerate of congress’s preferences
54
New cards
Executive agreement
agreement between the executive branch and a foreign govt; doesn’t require senate approval
* Can be undone by next president
* Can be undone by next president
55
New cards
President Duties
communicating with foreign leaders, nongovernmental organizations, and citizens
56
New cards
State of the Union address
annual speech given to congress about the current state of the nation
* president can recommend policy here, needs to be sponsored tho
* president can recommend policy here, needs to be sponsored tho
57
New cards
Pocket veto
president can veto a bill by not responding it if congress is not in session within the 10 days
58
New cards
Presidential Pardon
President can pardon people charged with federal crimes or reduce their sentence
59
New cards
Executive privilege
ability to shield themselves and their subordinates from revealing information from the White House from the legislative and Judicial branches
* isn’t absolute ( US v Nixon)
* isn’t absolute ( US v Nixon)
60
New cards
Executive Office of the President (EOP)
immediate staff to the president
1. Has the Office of Management and Budget
1. Develops president's budget proposal and monitors spending in govt agencies
2. Office of the United States Trade Representative
1. Negotiates trade agreements with other nations
help president achieve their policy goals and get reelected
* most staff are presidential appointees
1. Has the Office of Management and Budget
1. Develops president's budget proposal and monitors spending in govt agencies
2. Office of the United States Trade Representative
1. Negotiates trade agreements with other nations
help president achieve their policy goals and get reelected
* most staff are presidential appointees
61
New cards
First Spouse
One of the president’s most important advisors; Is seen as someone that can express president’s opinions to political appointees, members of congress, or media; Represents America in many events; Controversial whether they should decide policy because they weren’t elected to do so
62
New cards
The President’s Cabinet
* Composed of 15 executive departments heads along with other appointees
* Members help implement president’s agenda in their departments
* Appointees monitor the actions of lower-level bureaucrats since they’re often not sympathetic to president’s priorities
* Members are chosen for their loyalty and expertise
* Members help implement president’s agenda in their departments
* Appointees monitor the actions of lower-level bureaucrats since they’re often not sympathetic to president’s priorities
* Members are chosen for their loyalty and expertise
63
New cards
Unilateral Action
Undefined clarity of presidential power enables a president to take unilateral action
1. Change policy without consulting congress
2. They know their action has little chance of being reversed
3. presidents find loopholes, used to justify unilateral action
1. Change policy without consulting congress
2. They know their action has little chance of being reversed
3. presidents find loopholes, used to justify unilateral action
64
New cards
Unitary executive theory
idea that the vesting clause allows the president to issue orders and policy directives that Congress can’t undo unless it’s explicitly said in the Constitution
65
New cards
Signing statement
document issued by the president when signing a bill stating their own interpretation that may differ from Congress to have some influence
1. Influence over implementation of law, telling bureaucracy to follow their interpretation
2. If there’s issues with the bill, court has to take into account the presidents interpretation
1. Influence over implementation of law, telling bureaucracy to follow their interpretation
2. If there’s issues with the bill, court has to take into account the presidents interpretation
66
New cards
Impeachment
strips presidents power
* needs to be started at House (charged)
* trial held by Senate, 2/3 majority
* needs to be started at House (charged)
* trial held by Senate, 2/3 majority
67
New cards
Presidential approval rate
percentage of the public that think they’re doing a good job
1. State of the economy is a factor
2. Certain policies
1. State of the economy is a factor
2. Certain policies
68
New cards
Going public
appealing to american citizens
69
New cards
Bully pulpit
president’s ability to speak directly to the public about policy matters
70
New cards
Census
Every 10 years, it’s used to count population of the country
* helps redistrict for HoR
* helps redistrict for HoR
71
New cards
Enumerated Powers (Congress)
Powers stated in the Constitution
* declare War
* power to tax
* borrow money
* coin money
* post office
* power of the purse
* declare War
* power to tax
* borrow money
* coin money
* post office
* power of the purse
72
New cards
Implied Powers
Powers not stated in the Constitution
* establish national bank (Congress)
* regulate immigration (Congress)
* initiate tax laws and spending bills (House)
* establish national bank (Congress)
* regulate immigration (Congress)
* initiate tax laws and spending bills (House)
73
New cards
Cabinet
Cabinet members are the president's top advisors and are responsible for managing the various departments and agencies within the executive branch
* 15 department heads
* 15 department heads
74
New cards
Ambassadors
responsible for representing the United States in foreign countries and for managing diplomatic relations
75
New cards
White House Staff
responsible for providing support and assistance to the president
76
New cards
Federalist 70
Justification for single president
* One executive can get things done more efficiently and quickly. If there was more than one, it would require debates and compromises which take up a lot of time.
* If power is shared among more than 1 executive, then the ability to maintain and govern the nation will diminish. This can become an issue when an emergency arises and needs to be handled quickly
* Division among executive can occur which can cause a domino effect and cause division within the country
* If the executives were to abuse their power, finding out who is at fault and be held responsible will be nearly impossible whereas if it’s a single executive, we know who it is
* One executive can get things done more efficiently and quickly. If there was more than one, it would require debates and compromises which take up a lot of time.
* If power is shared among more than 1 executive, then the ability to maintain and govern the nation will diminish. This can become an issue when an emergency arises and needs to be handled quickly
* Division among executive can occur which can cause a domino effect and cause division within the country
* If the executives were to abuse their power, finding out who is at fault and be held responsible will be nearly impossible whereas if it’s a single executive, we know who it is
77
New cards
Precedent
A legal decision or set of decisions made in earlier, similar cases that serves as a guide or reference for future cases
78
New cards
Stare decisis
The legal principle that courts should follow precedents set by earlier, similar cases, in order to maintain consistency and predictability in the law
79
New cards
Ideology
\
A set of beliefs, values, and principles that shape an individual's perspective and decision-making
A set of beliefs, values, and principles that shape an individual's perspective and decision-making
80
New cards
Presidential appointment
The process by which the President of the United States nominates individuals to fill federal court vacancies, including those on the Supreme Court, which must be confirmed by the Senate
81
New cards
Jurisdiction
The authority of the Supreme Court to hear and make decisions on certain legal cases
82
New cards
Oral Arguments
The opportunity for both sides of a case to present their arguments and answer questions from the justices in an open session
83
New cards
Briefs
Written arguments submitted by both sides of a case before oral arguments, outlining their positions and evidence
84
New cards
Majority Opinion
The decision reached by a majority of the justices in a case
85
New cards
Dissenting Opinion
A written disagreement with the majority opinion by one or more justices who believe the decision was incorrect
86
New cards
Concurring Opinion
A written agreement with the majority opinion by a justice who agrees with the outcome, but for different reasons
87
New cards
Writ of Certiorari
A formal request by one party to have a case heard by the Supreme Court
88
New cards
Amicus Curiae Briefs
Briefs filed by individuals or organizations who are not parties to a case but have a strong interest in the outcome and wish to offer their expertise and perspective
89
New cards
Public Opinion
Court makes decisions that are perceived as controversial or unpopular, it can lead to public criticism and pressure on the Court to reconsider its decisions
90
New cards
Judicial Activism
more proactive role for the judiciary, where they take a more expansive view of their powers and actively seek to protect individual rights and liberties; approach often leads to decisions that strike down laws or actions of other branches of government as unconstitutional
91
New cards
Judicial Restraint
emphasizes the importance of adhering to precedent and the text of the Constitution, and defers to the decisions of elected branches of government; seeks to limit the role of the judiciary in making policy decisions and to preserve the balance of powers within the government
92
New cards
Independent agencies
these agencies operate outside of the control of any one particular department and have a specific mission or function
* Environmental policy agency
* NASA
* Environmental policy agency
* NASA
93
New cards
Iron Triangle
term used to describe the relationship between interest groups, bureaucratic agencies, and congressional committees, in which each entity has a vested interest in preserving the status quo
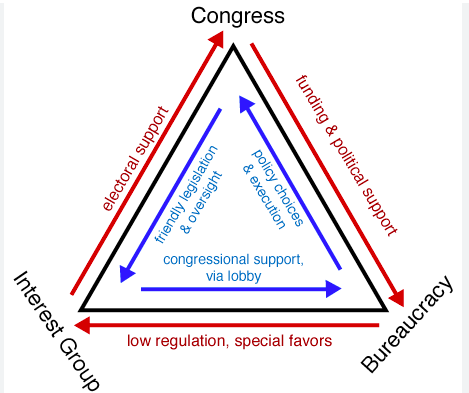
94
New cards
Pendleton Act
government jobs should be awarded on the basis of merit
95
New cards
Hatch Act
act forbids federal workers from taking part in partisan political activities
96
New cards
Discretionary Authority
The power given to an agency to make decisions about the implementation of existing laws, using its discretion and judgment
97
New cards
Rule-making Authority
The power of an agency to create rules and regulations that govern the behavior of individuals and organizations
98
New cards
Agency
A government department, division, or organization responsible for implementing specific policies and regulations