Native Trees of California
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
List of native trees of California, including descriptions and pictures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
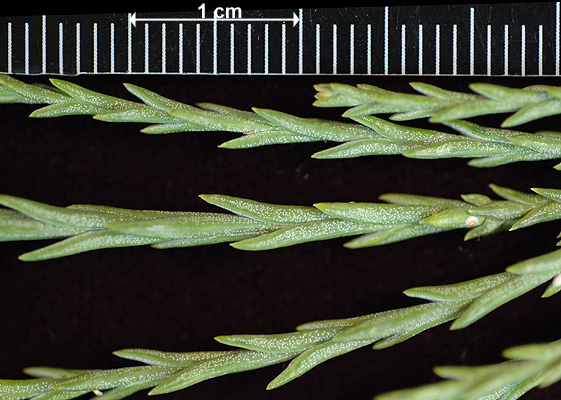
Coast redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) - Cupressaceae
Conifer. Endemic to coastal area of northern California and southwestern Oregon. Evergreen. monoecious, tall at maturity. Bark is reddish brown, hard and furrowed. Leaves are needle-like 0.5-1inch long, flat, spiral, two-ranked, green on the upper surface and have two white stomal bands on the underside of the needles. Cones are small and woody.
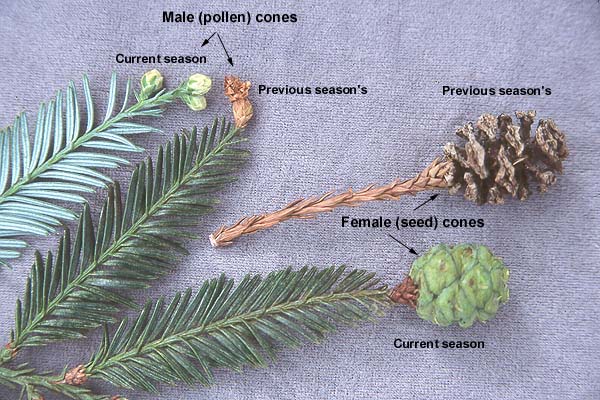

Giant sequoia (Sequoiadendron giganteum) - Cupressaceae
Conifer. Commonly found on the western slope of the Sierra Nevada mountain range. Bark is reddish brown, spongy, ridged and cork like. Fire-resistant bark and self-pruned branches. Leaves are blue-green, scale like, sharply pointed or awl-shaped. Small cones ~2in long form late summer and mature the following summer, oval shaped brown and woody.

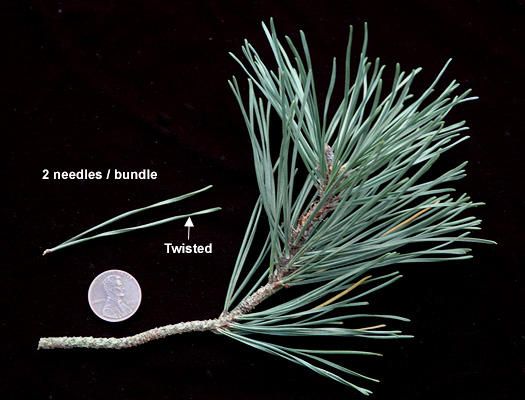
Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) - Pinaceae
Leaves needle-like, 3 needles per fascicle 6-8 inches in length crowded on branchlets. Grows most common in elevations of 4000-85000ft native primarily to mountainous areas in western NA, often growing in pure stands. Bark grayish and scaly but mature trees can have yellowish-brown/cinnamon bark in flat scaly plates. Cones 3” to 6” in length, with stiff scales projecting spine like in matured cones.

Lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) - Pinaceae
Conifer, evergreen. Tall, irregular, twisting young shoots. Broad rounded crown with dark brown bark. Pitch often present on trunk in blobs. Two needles per fascicle, 3-7cm long slightly flattened and often twisted. Cones 2-5cm long, egg shaped and tend to point backwards. Native from northwestern NA to norther California.

Monterey pine (Pinus radiata) - Pinaceae
Conifer. Crown broadly conic, becoming rounded to flattened with maturity. Needles more commonly 3 per fascicle, rarely 2. Bark grey to reddish brown and deeply furrowed. Cones ovoid before opening, broadly ovoid when open 7-15cm long and numerous. Low frost tolerance, hardier to the central to southern regions of California.
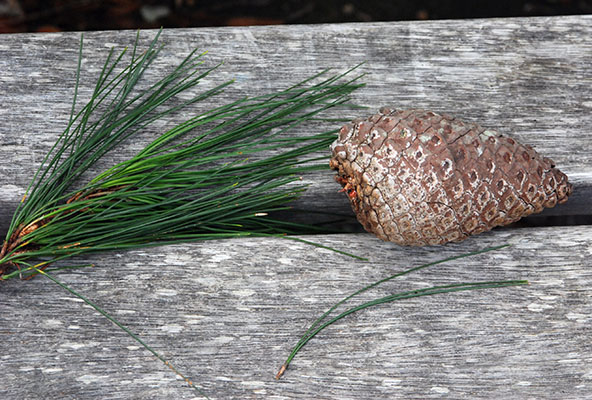

Sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana) - Pinaceae
Conifer. Tallest pine “King of Pines”. Straight trunk free of branches for much of its length, open crown with near horizontal branches. Bark of young trees is thin grayish-green and smooth, on mature trees it is reddish with narrow, broken, scaly ridges separated by deep furrows. Needles 5 per fascicle 5-10cm long, twisted, slender, stiff, sharp-pointed, white lines of stomatal bloom on all surfaces. Cones are large 28-46cm long up to 56cm and cylindrical. Native to North-central Cascade mountains in OR southward through the Sierra Nevada mountains 2000-9000 feet.

Western white pine (Pinus monticola) - Pinaceae
Conifer. Narrow, open, conical crown of horizontal branches. Needles 5 per fascicle 5-10cm long, blue-green with white stomatal lines on inner surface. Can be confused with another species of pine that has 5 needles per fascicle, however this species has white stomatal lines only on the inner surface as apposed to all sides of the needles. Cones are also much smaller 13-23cm long, narrowly cylindrical, pitchy.
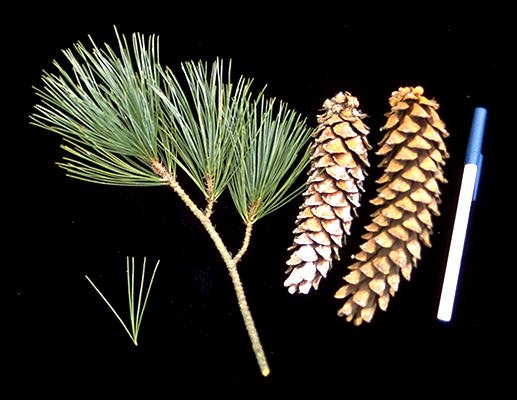

Monterey cypress (Hesperocyparis macrocarpa) - Cupressaceae
Conifer. Narrow or broadly conical when young and broadly spreading with age. Bark red-brown then gray, becoming furrowed with age. Leaves uniform, scale-like, 2-5mm rarely up to 10mm, arranged in 4 appressed (pressed against twig) rows giving the shoots a rounded appearance. Cones globose or somewhat ellipsoid, 2.5-3cm diameter, usually solitary on a short, thick stalk. Native to CA’s Monterey Peninsula along the central coast where only two native stands exist.

Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) - Pinaceae
Conifer. Crown of young trees conical and dense becoming a broad flat top with age. Lower branches drooping with upper ones ascending. Buds oval-conical, apex pointed. Needles flattened and radially arranged (think whorled), rarely appearing 2-3 ranked, bright yellow-green, grooved above with 2 wide stomatal bands on underside. Needles narrowed at base into a slender petiole-like stalk that sits on a stubby leaf cushion (looks like a swollen node). Cones 10cm long with distinctive 3-pronged bracts (“the two back feet and tail of a mouse”), pendant shaped and mature in one season.
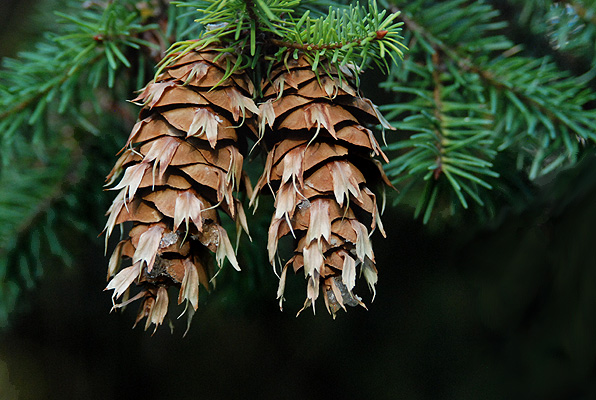

Incense cedar (Calocedrus decurrens) - Cupressaceae
Conifer (but not a true cedar). Stiff or narrowly columnar habit in youth. Branchlets flattebed terminating in dense, fan like sprays. Bark light or reddish-brown. Leaves in 4’s closely pressed forming a “fluted win glass” shape by each outside/lateral pair of leaves. Dark green thoughout year, aromatic when crushed. Female cones 2-2.5cm long composed of 6 flattened and pointed scales resembling duck beaks. Native Range from Western OR to NV, south to California.
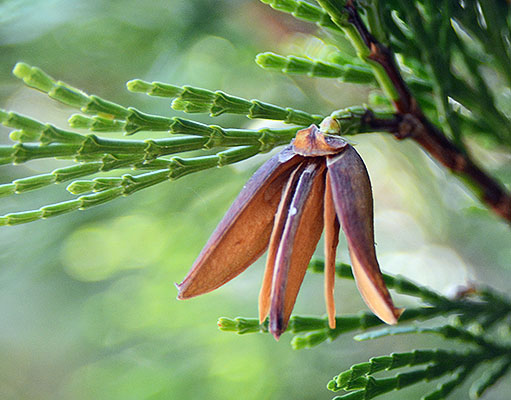

White fir (Abies concolor) - Pinaceae
Conifer, shorter (30-50ft high), conical and branched to base, upper branches tend to point upwards. Leaves needle like and curve outwards and upwards on branches, 4-6cm long, flattened, light green to green-bluish, glaucous (waxy) on both sides and more or less giving a bluish cast. Cones erect, stalked, 8-13cm long, pale green with a purplish bloom and brown at maturity. Native to Colorado, southern Oregon to southern California.
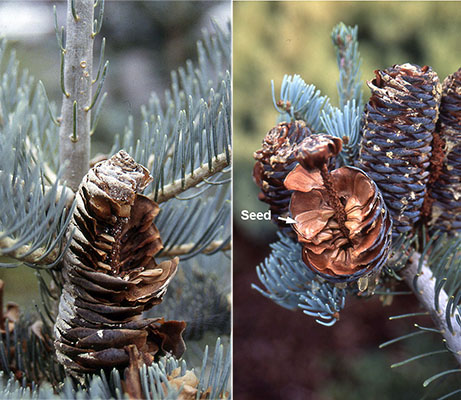

Mountain hemlock (Tsuga mertensiana) - Pinaceae
Conifer. Narrowly conical, branches and twigs thin and nodding, bark grey to reddish brown, scaly and deeply fissured. Needles arranged radially around the stem but densest on the upper side, linear 10-20mm long, stomatal lines on both sides, base attached to the stem via a roundish peg and short petiole,. On short lateral branches the needles are grouped in star-like clusters.Cones oblong-cylindrical, stalkless, 5-8cm long, pendulous, often purple when young.
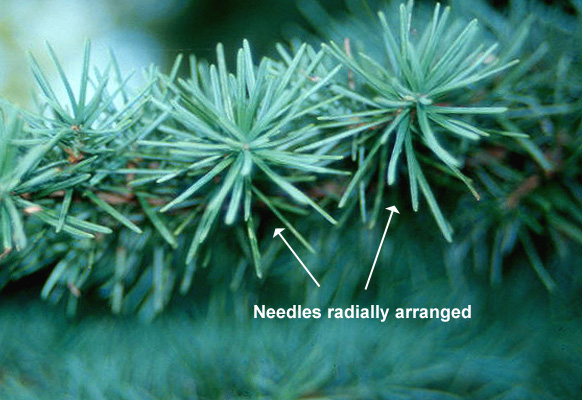

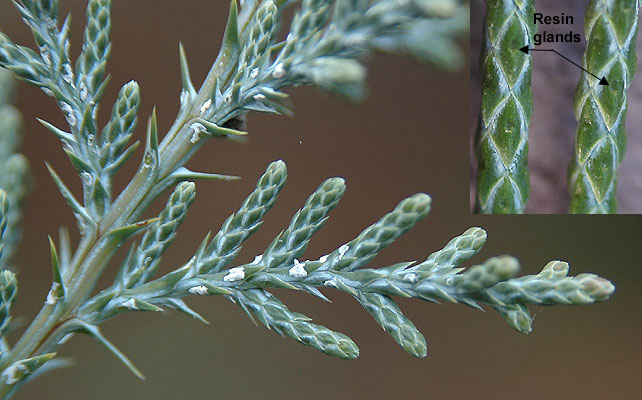
Western juniper (Juniperus occidentalis) - Cupressaceae
Conifer. Tree or shrub 15-30ft high, short trunk with stout spreading branches, ragged and gnarled with age. Scaly, light brown bark. Leaves usually scale-like in whorls of 3 (occasionally opposite), arranged in 6 rows, 3mm long, tightly appressed, gray-green, a distinct gland (dot), juvenile leaves are awl-shaped with tips standing away from the twig. Fruit berry-like, blue-purplish black, soft, juicy, resinous, maturing in second year.

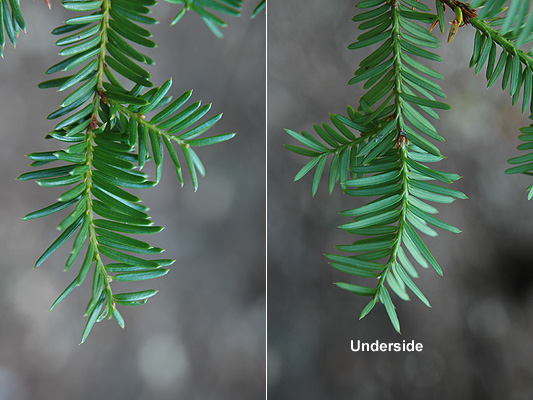
Pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia) - Taxaceae
Conifer. Evergreen tree or shrub, spreading. Understory tree. Bark with thin, dark red-purple scales. Needles arranged radially around stem but appearing more or less 2-ranked, 1-2.5cm long, linear, tapering to a horny point, yellow green above and paler below, short yellow petiole. Dioecious - male and female plants / reproductive parts separated. Cone is a fleshy, scalet, oblong oval enclosing a single seed. Native range from extreme southeastern Alaska to northern California, east to Northeastern Oregon.

Red fir (Abies magnifica) - Pinaceae
Conifer, evergreen, large, 125-200 ft (38-60 m) high, narrow pyramidal crown, short branches. Bark is thick, reddish brown, and deeply furrowed in narrow ridges. Leaves (needles) are linear, 2-3 cm long, spirally arranged but concentrated on the upper side of the twig, pointing upward (needles on the underside are hockey-stick-shaped... i.e., base parallels the twig... similar to A. procera), silvery-green to blue-green, stomatal bloom on all surfaces. Cones 15-22 cm long, cylindrical, purple or purplish-brown then brown at maturity. Native to California, extreme western Nevada and the Siskiyous of southern Oregon. Found in almost pure stands at high altitudes along the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada Mountains of California.
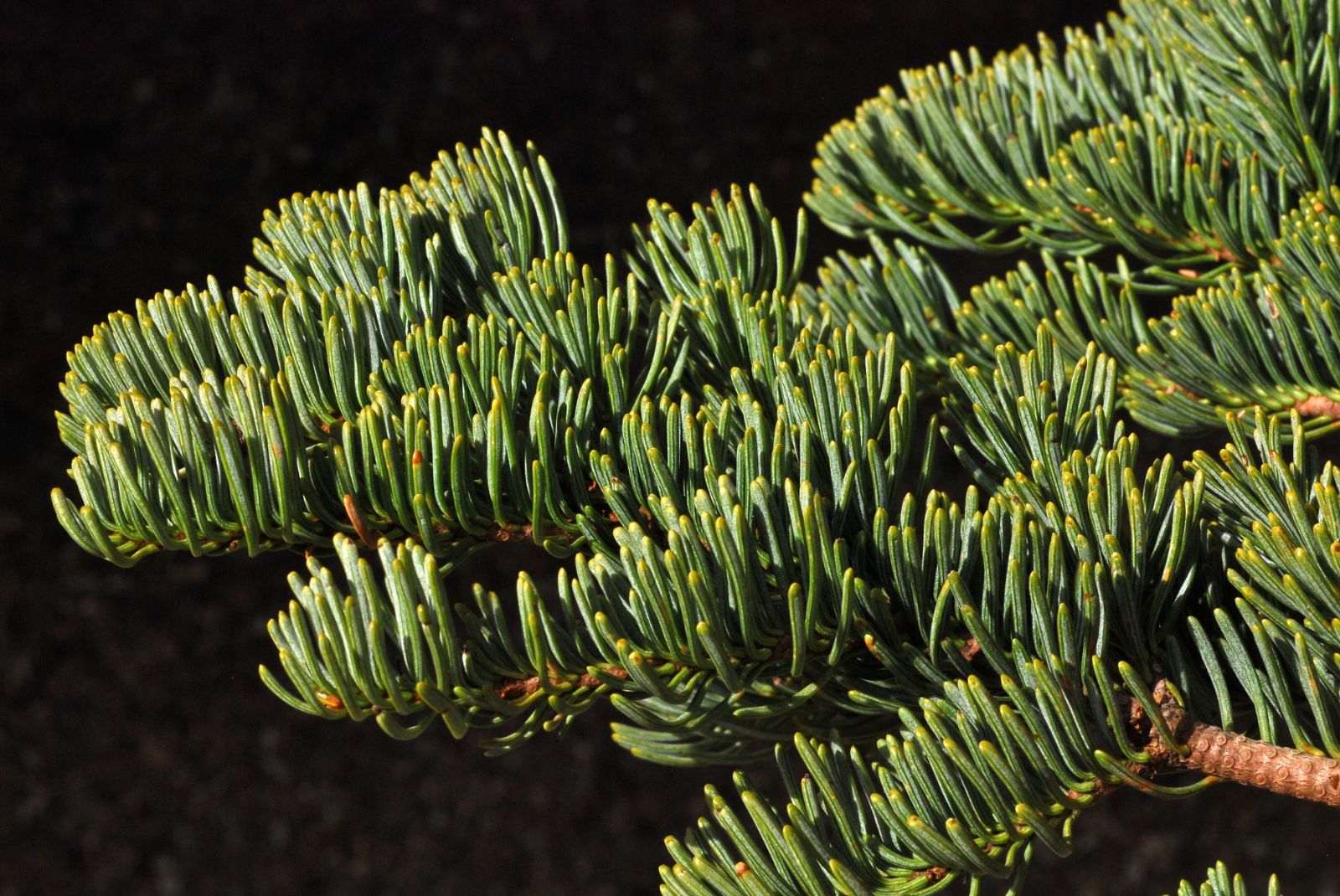

Valley oak (Quercus lobata) - Fagaceae
Broadleaf, deciduous, medium to large tree, at maturity from 30-90 ft tall. Branches have an irregular, spreading and arching habit. The trunk is usually short and stout; bark is light gray and in time segments into rectangular, alligator-like, patches. Leaves are simple, alternate, obovate, 5-10 cm long, base wedge-shaped, 6 to 10 rounded or blunt lobes, separated by deep clefts (greater than ½ distance from lobe tip to midrib); dark green above and paler green below and covered with a fine pubescence. Inconspicuous male and female flowers appear in spring and are borne on the same tree (monecious). Male flowers are in yellow-green catkins about 2.5 to 5 cm long whereas the small female flowers are usually in clusters of 2-3 in axils of leaves. Fruit, an acorn, is brown, slender, 3-6 cm long, pointed "shaped like a pointed cartridge shell", 1/3 of which is enclosed in a deep cup with light brown scales; matures in first year. Native range is limited (endemic) to and widely distributed in California; it is common in the Central Valley and found in many smaller valleys and also in the coastal hills and mountain ranges. It tolerates cool wet winters and hot dry summers.
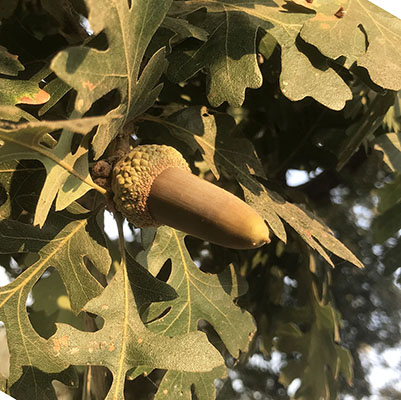

California black oak (Quercus kelloggii) - Fagaceae
Deciduous tree, 40-80 ft (12-24 m), open, rounded crown, may be a shrub at high elevations, to 15 ft (4.5 m). Bark dark gray or black, smooth on young trees and broad, irregularly plated ridges. Leaves alternate, simple, 8-15 cm long, sharply cut into 7-11 lobes, which toothed, each tooth ending in a bristle, base often obtuse or wedge-shaped, upper surface glossy green, paler below, both surfaces of young leaves sometimes pubescent and dusty rose or soft pink, autumn color is yellow or yellow orange. Fruit (acorn) 2-3.5 cm long, cup encloses about half the nut; acorns mature in the second year.
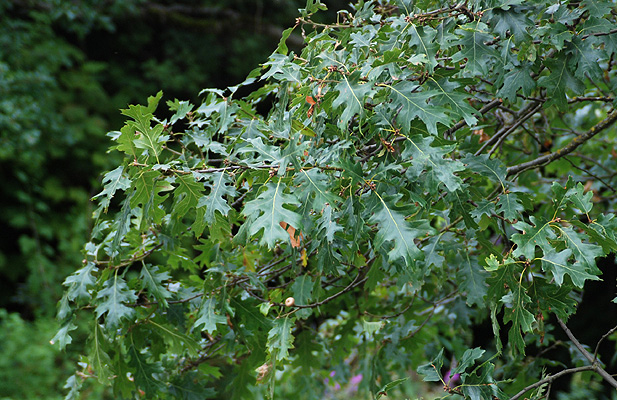

Canyon live oak (Quercus chrysolepis) - Fagaceae
Broadleaf evergreen tree/shrub, 20-60 ft (6-18 m) high, short trunk, spreading horizontal branches, sometimes shrubby. Leaves alternate, simple, elliptical to oblong, 2.5-7.5 cm long, 1.2-4 cm wide, often with spiny teeth, some entire, thick, leathery, shiny green above and yellowish or gray below. Male catkins. Acorns egg-shaped, variable in size, 2-5 cm long, with a golden-scaled (chryso - gold, lepis - scale) turban-like cap; requires two seasons to mature. Native to southwest Oregon, California, Nevada, Arizona.
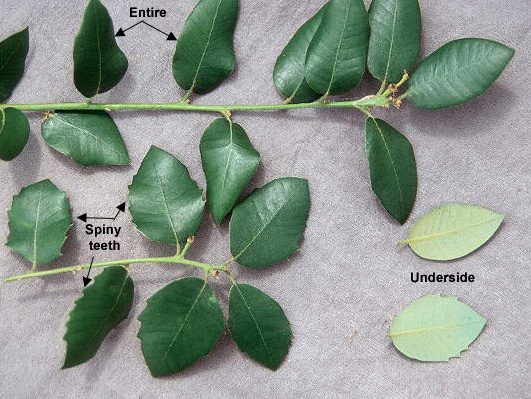
California Scrub oak (Quercus berberidifolia) - Fagaceae
Evergreen shrubs or small trees 3-15 ft tall; bark gray, scaly. Twigs usually gray or yellowish, sometimes reddish, densely packed twigs and leaves can form an almost impenetrable barrier. Leaves simple, alternate, leathery, obovate to elliptic, 1.5-3.0 cm long, base of leaf truncate or rounded, apex rounded or acute, margins irregularly toothed or spiny, upper surface green, flat to wavy, lower surface grayish green and slightly hairy; petiole 2-4 mm long. Fruit (acorns) solitary or paired, brown, egg-shaped, 1-3 cm long, cup hemispheric or turbine like, 8-15 mm deep, enclosing 1/3 to 1/2 of the nut. Native to California, found in the Coast Range and Sierra Nevada and southern California mountains and into Baja California.
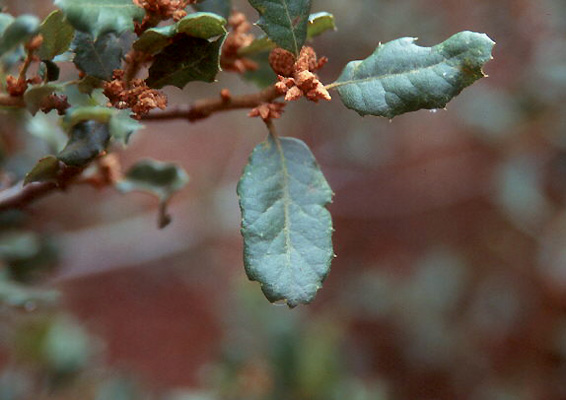

Coast live oak (Quercus agrifolia) - Fagaceae
Broadleaf, evergreen tree, to 30-80 ft (9-24 m) tall, often with a greater spread, broadly rounded form, dense foliage, short trunk, may have a shruby form in chaparral habitat. Bark dark gray or brown, smooth at first, finally thick, deeply furrowed. Leaves simple, alternate, oblong to oval, 2-6 cm long and 1.2-4 cm wide, thick, leathery, rounded or heart-shaped at base, tip rounded, margins turned under (cupped like basil) and bearing spiny teeth (holly-like), glossy green above, below pale green, and with tufts of hair in the axils close to the petiole. Fruit (acorn), nut is brown, narrowly egg-shaped, 2.5-4 cm long, about a fourth enclosed by a thin cup. Native mostly to the coast side of California's Coast Range, and along streams draining into the Central Valley, ranges from the Mendocino County in the north to Mexico's Baja California.
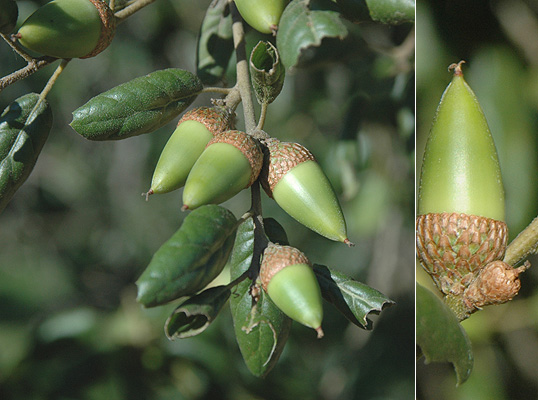

Palmer oak (Quercus palmeri) - Fagaceae
Broad leaf tree. Leaves evergreen and leathery, wavy-edged with holly-like appearance. Alternate, simple, pinnately veined with spiney teeth. Monoecious with a catkin inflorescence. Found in dry slopes and ridge tops more commonly found in southern California and Arizona

White alder (Alnus rhombifolia) - Betulaceae
Deciduous tree, mature trees are generally 50-80 ft (15-24 m) tall, record trees reach over 100 ft (30 m), the crown is open, broadly rounded in shape, branches slender and nodding at the ends. Mature forest trees often have several trunks arising from a single clump. Winter buds about 13 mm long, slender, dark red, covered with a pale pubescence. Bark is light gray, whitish, smooth or slightly rough on young trees but becomes plated and reddish-brown at maturity. Leaves alternate, simple, elliptic to rhombic, 6-10 cm long, 4-5 cm wide, rounded or acute at the apex, gradually or abruptly narrow and wedge-shaped at the base, singly or doubly serrate, somewhat undulating margins, dark green and glossy above, often minute glandular dots on the midrib, yellow-green below. Male (pollen) catkins in groups of 2-7, each about 10-15 cm long and 0.5 cm wide at pollination (early spring). Female flowers short, erect catkins small clusters, they emerge in winter, mature seed catkins (cones), are woody, barrel-shaped, 10-15 mm long. ative range extends along the Pacific Coast from southern British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, California and Baja California, eastward along the main tributaries of the Columbia River into eastern Idaho. Generally found on moist sites along streams and on lower mountain slopes. Fast growing, tolerant of heat and wind, susceptible to tent caterpillars and borers in its native range. Tolerates infertile soil because it forms an association with a small soil bacteria, Frankia, resulting in root nodules that transform the tree into a nitrogen fixer.
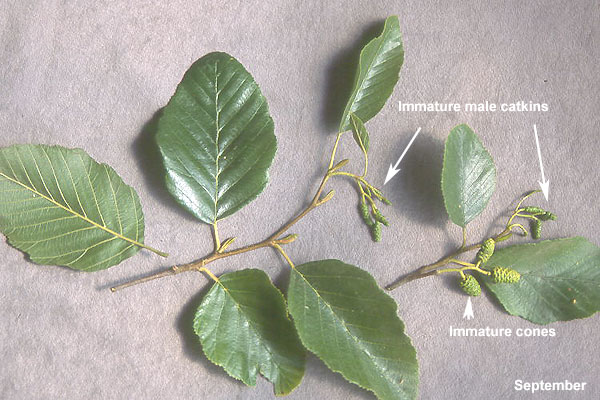
Quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides) - Salicaceae
Broadleaf deciduous tree, 40-50 ft (12-15 m), pyramidal and narrow when young, long trunk and narrow, rounded crown when mature. Bark is thin, smooth greenish white to cream colored, furrowed dark brown or gray in old age. Leaves alternate, simple, thin, ovate to orbicular, 4-7.5 cm long, finely glandular serrate, lustrous dark green above, glabrous below. Fine yellow color in fall. Laterally flattened petioles allow leaves to flutter in the slightest breeze (to " quake"). Typically dieocious, male and female flowers on separate plants and in long slender catkins that appear before the leaves. Male catkins are at first about 3 cm long and lengthening to 8 cm before falling off, the small flowers are tiers of red stamens mixed with long, silky hairs. The female flowers are in slender, pendulous catkins that lengthen to 10 cm and develop into a string of green fruit capsules, each about 6 mm, containing 10 minute seeds embedded in cottony fluff which aids in wind dispersal of the seeds. Forms clones connected by a common parent root system. Since trees are typically dieocious (i.e., male and female flowers on separate plants), a given clone may be either male or female. The most widely distributed tree in North America.
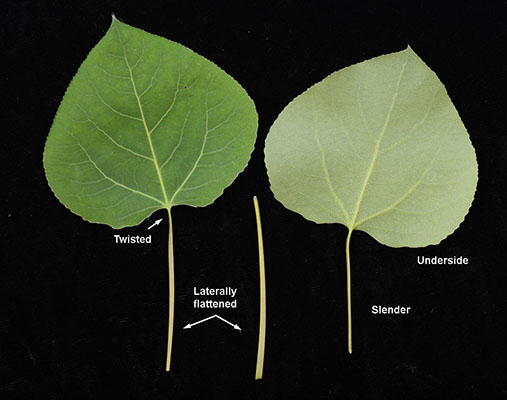

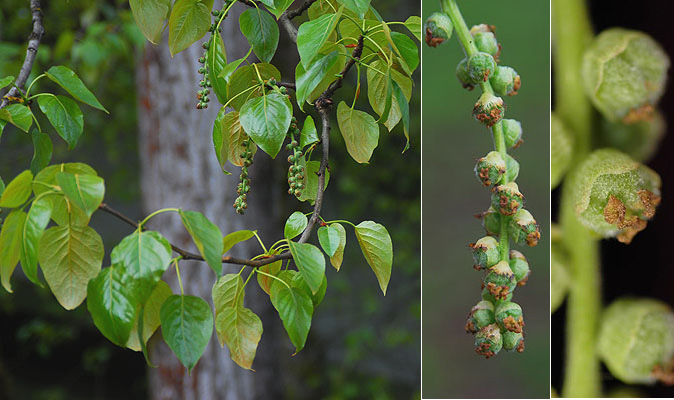
Black cottonwood (Populus trichocarpa) - Salicaceae
Deciduous tree, to 40 ft (12 m) in 15 years, finally to 150 ft (45 m), trunk long and straight, narrow crown. Bark dark gray-brown with age, in flat-topped ridges alongside V-shaped grooves. Winter buds round or slightly angled, about 2 cm long with 6-7 scales, long pointed, orange-brown, very resinous and fragrant (balsam odor); apparently the fragrance is especially pronounced in the spring as the leaves unfold. Leaves alternate, simple, broadly ovate, 7-12 cm long, base usually rounded (sometimes wedge- or heart-shaped), finely toothed, dark green above, silvery green below, often with brown resin blotches, petiole round, not flattened. Flowers in long catkins, male (pollen) catkins 4-5 cm; female (seed) catkins 6-8 cm long, extending to 12-15 cm prior to seed release. The seed catkins bear nearly spherical capsules, about 4 mm, which split into 3 parts to release silky tufts ("cotton") with attached small seeds (about 2 mm long). Terminal buds 17-20 mm long with 6-7 visible scales, lateral buds parallel to twig. Sun, prefers moist situations, but tolerates poor and dry soils. Wood very brittle. Female trees release a substantial amount of "cotton", which some consider a nuisance. Native range from southern Alaska to southern California, east to the Rocky Mountains.

California bay laurel (Umbellularia californica) - Lauraceae
Leaves very aromatic. Broadleaf evergreen tree/shrub, 25-30(70) ft (7.6-9(21) m) high, loose foliage in shade, but a round, gum-drop habit when in the open. Leaves alternate, simple, elliptical or lance-shaped, 5-13 cm long, thick and leathery, margin entire and slightly thickened and revolute (turned under), shiny dark green above and dull and lighter below; very aromatic. Clusters of small, creamy white flowers in early spring, but thereafter may flower sporadically for several months. Fruit about 2 cm long, elliptical to nearly round, greenish to purple, maturing in late autumn. Native to southwest Oregon, south along Coast Range, and in Sierra Nevada, to southern California.

Pacific madrone (Arbutus menziesii) - Ericaceae
Broad-leaved evergreen tree, 20-65 ft (6-20 m), mature bark reddish brown, exfoliating, bark on stems smooth and reddish. Leaves alternate, simple, oval, broad, 3.5-10 cm long x 4-7.5 cm wide, thick and leathery, base subcordate to broad-cuneate, apex obtuse or somewhat acute, margin entire, lustrous dark green above. Flowers white, urn-shaped, about 1 cm long. Fruit ellipsoid or obovoid, orange-red, 10-13 mm. Native to Pacific Northwest and California, narrow belt along the Pacific Ocean. Sheds leaves and bark irregularly.
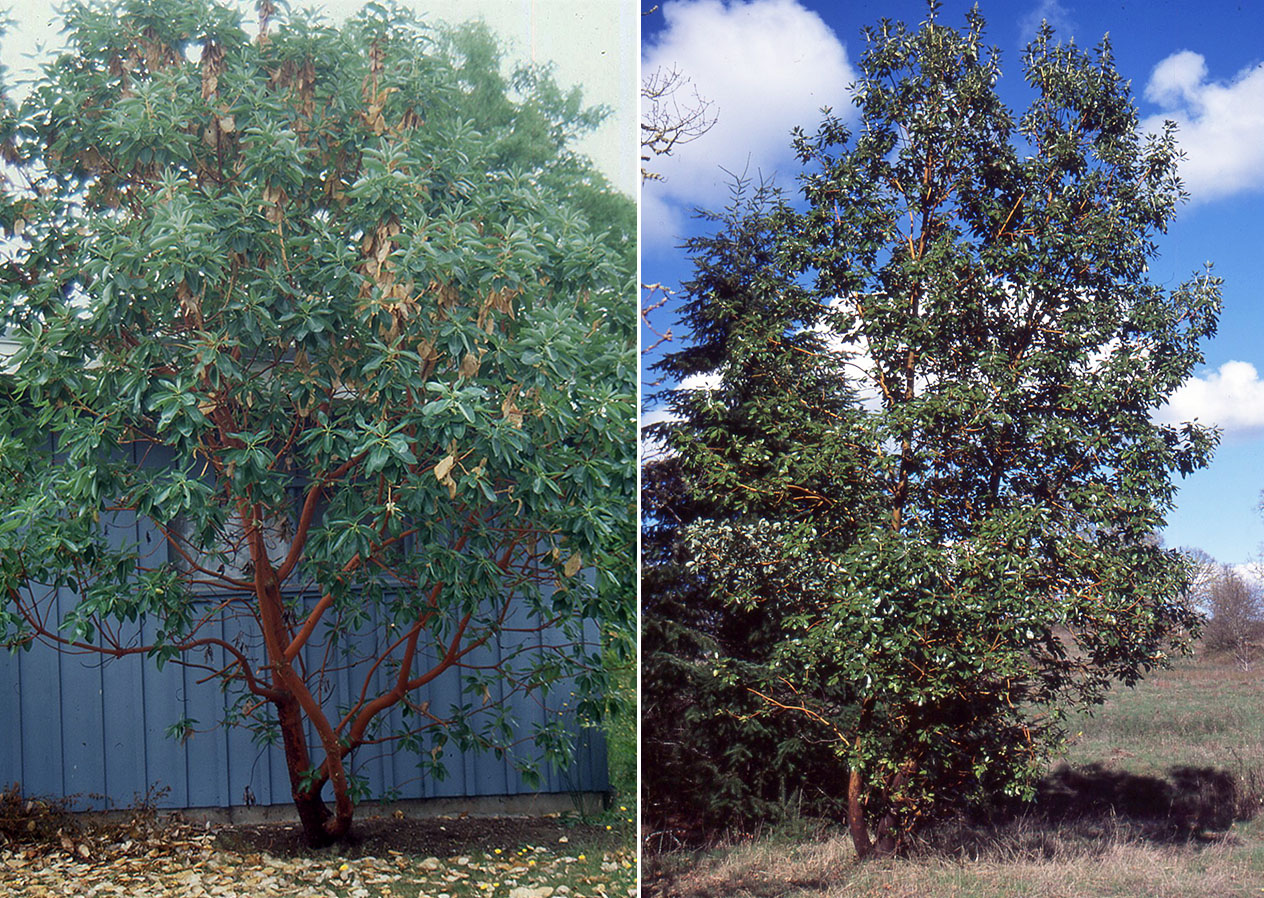

Bigleaf maple (Acer macrophyllum) - Aceraceae
Deciduous tree, 50-75(100) ft [15-23(30) m], ascending, becoming rounded, shallow root system. Leaves, opposite, simple, large (20-30 cm across, the largest leaves of all the maples), lustrous dark green above, pale beneath, 3-5 toothed lobes, petiole yields milky sap when detached. Flowers in early spring usually before leaves appear, the flowers are small, 10 mm across, greenish-yellow, fragrant, in drooping clusters, 10-15 cm long, male and female flowers occur in the same cluster. Fruit (double samara), large, 4 cm long, hang down in racemes, seeds very pubescent. Foliage yellow to gold or brown in fall. Native from southwest British Columbia to southern California, from sea level to 5,500 ft (1,650 m). Because the bark of this tree retains moisture, in the Pacific Northwest its trunk and large branches are often covered with mosses, liverworts, and ferns (especially the licorice fern, Polypodium glycyrrhiza). Its sap has a high sugar content.
![<p>Deciduous tree, 50-75(100) ft [15-23(30) m], ascending, becoming rounded, shallow root system. Leaves, opposite, simple, large (20-30 cm across, the largest leaves of all the maples), lustrous dark green above, pale beneath, 3-5 toothed lobes, petiole yields milky sap when detached. Flowers in early spring usually before leaves appear, the flowers are small, 10 mm across, greenish-yellow, fragrant, in drooping clusters, 10-15 cm long, male and female flowers occur in the same cluster. Fruit (double samara), large, 4 cm long, hang down in racemes, seeds very pubescent. Foliage yellow to gold or brown in fall. Native from southwest British Columbia to southern California, from sea level to 5,500 ft (1,650 m). Because the bark of this tree retains moisture, in the Pacific Northwest its trunk and large branches are often covered with mosses, liverworts, and ferns (especially the licorice fern, <em>Polypodium glycyrrhiza</em>). Its sap has a high sugar content.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9dde0bfc-1b79-4619-b9d9-a432d09670cb.jpg)
Blue elderberry (Sambucus cerulea aka Sambucus nigra spp. cerulea) - Caprifoliaceae
Broadleaf deciduous (nearly evergreen mild climates) tree or large shrub,15-30 ft (9-15 m) high, may form a thicket, has pithy stems. Leaves opposite, pinnately compound, 15-25 cm long, 5-7(9) leaflets, each 5-15 cm long and 1-5 cm wide, narrowly ovate or lanceolate, unequal at base, coarsely serrate, bright green (a variable species). Leaf petioles opposite nearly connect with each other, and petiole base covers buds. Flowers yellowish-white, 5-lobed, 6 mm wide, in many branched, flat clusters in a flat-topped umbel-like cyme. Fruit 6 mm, dark blue with whitish bloom, edible, but not very palatable fresh. Native from British Columbia east to Montana and Utah, south to California and New Mexico. Shrubs in this genus are the only ones found in the Pacific Northwest forests that have both opposite and pinnately compound leaves.
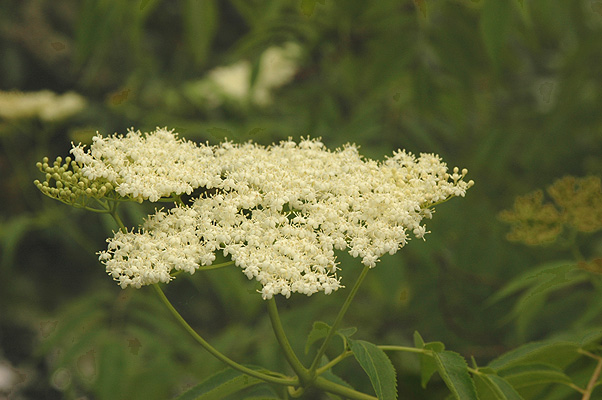

California buckeye (Aesculus californica) - Sapindaceae
Broadleaf deciduous tree or large shrub, single or multistemmed, 12-30ft (3.5-9 m) tall, flat topped to rounded and very broad; trunk short, with many ascending branches, bark grayish white. Leaves opposite, palmately compound, 5 leaflets, occasionally 7, each 7.5-15 cm long, elliptic-oblong to lance-oblong, base narrowed or rounded, tip acuminate, margin sharply serrate, dark green above, paler below with hairs on veins; petiole 1-2.5 cm long. Flowers showy, white to rose-colored, fragrant, about 2.5 cm long, in dense, narrow clusters, 8-20 cm long; stamens long-exerted, petals of equal length. Fruit somewhat pear shaped, 5-7 cm long, usually contains 1 large seed, 2-5 cm, they are glossy brown and poisonous. Native to California, found in the woodlands and valleys of the Coast Range, Sierra Nevada and Tehachapi Mountains.
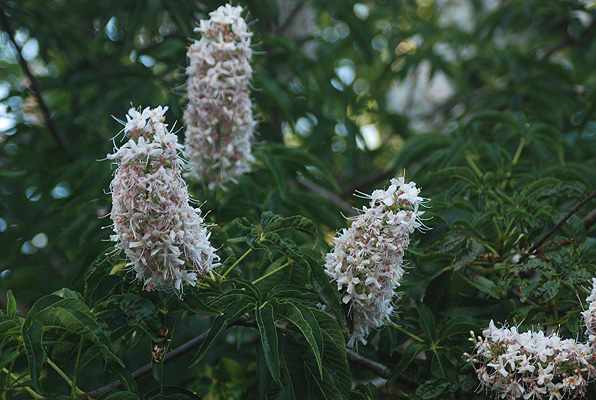

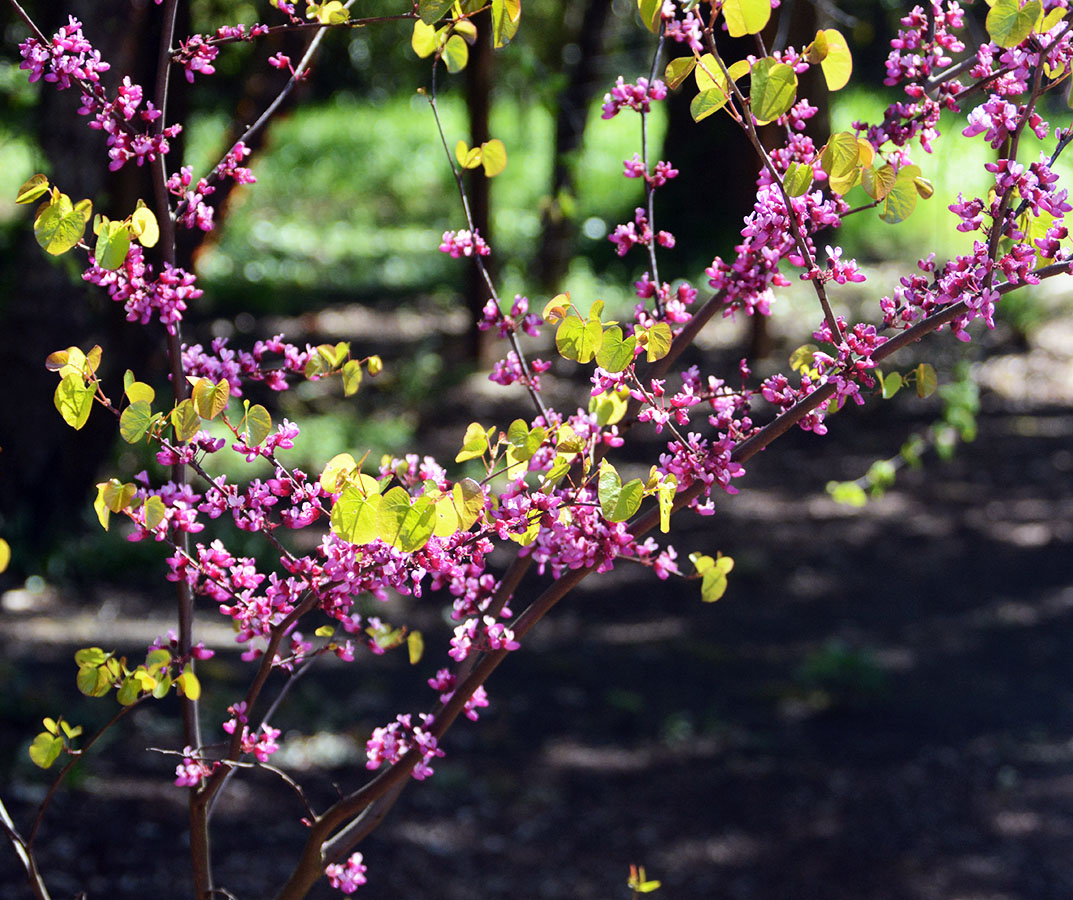
Western redbud (Cercis occidentalis) - Fabaceae
Broadleaf deciduous shrub, or small tree, to 16 ft (5 m) tall, often multistemmed, rounded crown. Twigs slender, angled, smooth, brown bark with lighter lenticels. Leaves alternate, simple, 4-9 cm long, may be somewhat wider, nearly round to kidney shaped (reniform), 7-9 veins from the cordate (heart shaped) base, shallow notch (emarginate) or rounded at the apex, mostly hairless, dark green above and paler below. Flowers pea-like, 12 mm long, purplish-pink, appear before leaves, blooms February-April. Fruit pod-like, flat, 5-9 cm long, narrowly oblong, brown or purplish, maturing in late summer, may hold brownish pods in winter. Native range includes Utah, Arizona (common in the Grand Canyon National Park), and especially California.

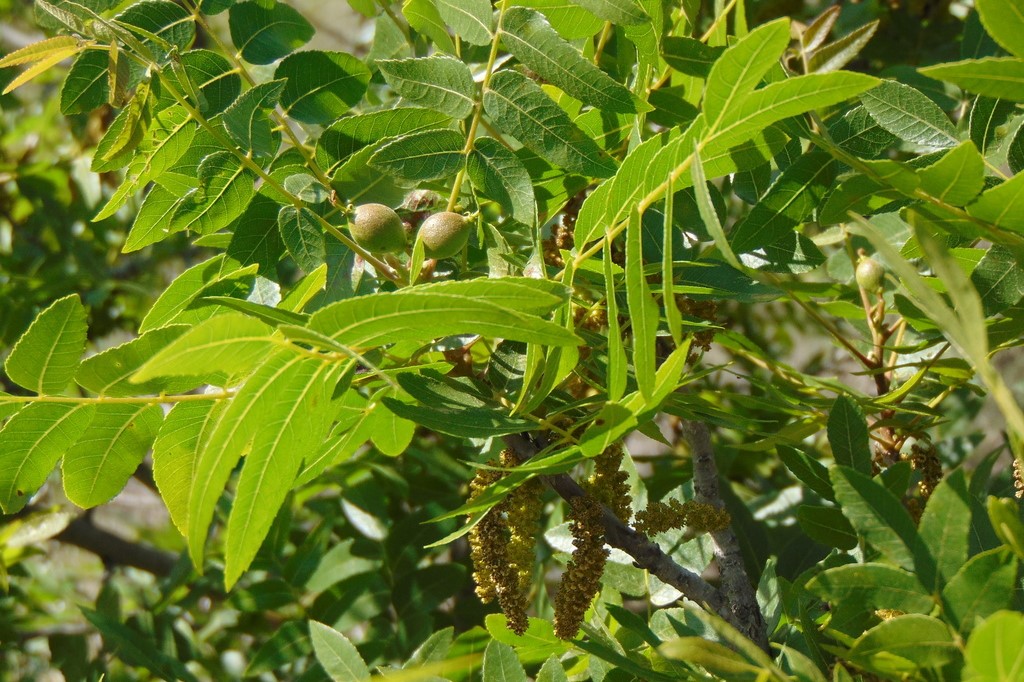
California black walnut (Juglans californica) - Juglandaceae
Deciduous tree, small to medium sized tree, to 40 ft (12 m) tall, may be shrub-like when forked near base, short trunk, rounded crown. Leaves alternate, pinnately compound, 15-23 cm long, odd number of leaflets, 11 to 15, each leaflet oblong to lanceolate, 2.5-6 cm long, margin finely serrated, apex long or short pointed, upper surface glossy green, paler below with tufts of hairs along the veins; fall color yellow or brown. Male flowers small, each with 30-40 stamens, in catkins 5-7.5 cm long; female flowers rounded, 2-3 yellow styles about 12 mm long. Fruit globose, 8-12 mm diameter, thin dark-colored husk. Southern Native, approximately from Santa Barbara to San Diego.

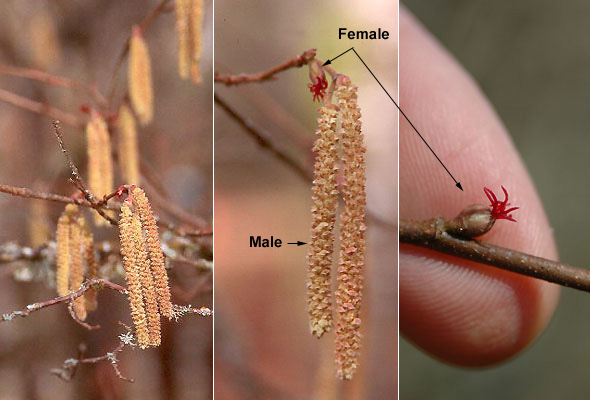
California hazelnut (Corylus cornuta var. californica) - Betulaceae
Deciduous shrub, open, spreading, multistemmed, 5-12 ft (1.5-4 m) high. Twigs brown, slender, zigzag; trunk bark gray and smooth. Leaves alternate, simple, 4-10 cm long, ovate to obovate, base cordate, coarsely toothed margin, pubescent below. Male flowers in pendent catkins, grouped on the ends of the previous season's twigs, they are 2.4-5 cm long. The female flowers are small, appear as rounded buds with bright red stigmas. Fruit (nut) covered with a involucre (husk), much longer (beak) than the nut it encloses. Native range from British Columbia, south along the Coast Range and Cascades and finally further south into the Sierra Nevada of California.
