RPD 10 - Metal Alloys & Metal Framework Fabrication (Quiz 5)
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Noble metal
Base metal
What type of metal alloys are used in the fabrication of RPD framework?
gold and platinum
noble metal consist of metals from ___________ and ___________ group, which are highly resistant to oxidation + dissolution in inorganic acids
Noble metals
What type of metal are the following?
Ruthenium (Ru)
Rhodium (Rh)
Palladium (Pd)
Silver (Ag)
Osmium (Os)
Iridium (Ir)
Platinum (Pt)
Gold (Au)
base metal
Define the following:
A metal that readily oxidizes or dissolves to release ions
Base metals
What type of metal are the following?
Chromium (Cr)
Manganese (Mn)
Cobalt (Co)
Nickel (Ni)
Copper (Cu)
Aluminum (Al)
Carbon (C)
Silicon (Si)
Gallium (Ga)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Tantalum (Ta)
Cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr)
Cobalt-chromium nickel (Co-Cr-Ni)
Nickel-chromium (Ni-Cr)
Titanium (Ti)
What are 4 common base metal casting alloys used in RPD?
Beryllium
In base metal casting alloys for removable partial dentures nickel-chromium alloys can be prepared with or without what element?
E. low density
All of the following are important characteristics of ideal RPD metals EXCEPT:
a. corrosion resistant
b. light weight
c. high strength
d. high modulus of elasticity
e. low density
f. low cost
chromium type alloys
What is the principle material used in fabrication of RPD?
Chromium (Cr)
All alloys contain ________ to prevent corrosion + tarnish
passivation
Define the following:
The ability of a metal to prevent corrosion and tarnish
cobalt chromium
What is Vitallium composed of?
Vitalium (a cobalt-chromium alloy - exhibits higher ductility and improved toughness compared to pure chromium alloys)
Chromium (Cr) alloys have an elongation of only 2–3% and are quite brittle. Which alloy allows greater elongation and is less brittle?
60%
for the cobalt chromium alloys, it contains about ___% cobalt
25-30%
for the cobalt chromium alloys, it contains about ___-___% chromium
cobalt
What metal contributes to the hardness of the alloy?
chromium
What metal contributes to the corrosion resistance of the alloy?
hardening and strengthening
Molybdenum, tungsten, + carbon contributes to the ________ and ________ of the alloy
fluidity
Manganese + silicon contribute to the _______ of the alloy
50%
What percent of the cobalt-chromium-nickel is cobalt?
25%
What percent of the cobalt-chromium-nickel is chromium?
19%
What percent of the cobalt-chromium-nickel is nickel?
nickel
chromium
aluminum
beryllium
N C A B
what metals does Nickel-Chromium comprise? (4)
beryllium
In Nickel-Chromium, this metal contributes the following:
- Lowers the melting temperature
- Enhances fluidity
- Improves grain structure
titanium
What metal is lighter than chromium and just as strong?
Type IV gold alloy
what type of gold has been used in RPDs?
higher
the melting temp of the base metal RPD alloys are significantly _________ than those of the gold alloys
Lustrous
Silvery white
What are 2 characteristics of polished Co-Cr and Ni-Cr?
False (Cr alloys are lighter than gold alloys)
t/f: chromium alloys are heavier than gold alloys
True
T/F: Linear casting shrinkage is relatively high for chromium-based alloys
Lighter
___________ weight materials are especially useful for the construction of large and bulky maxillary removable appliances
30%
Chromium-based alloys are _____% harder than type IV gold alloys and they require special equipments for finishing and polishing
tensile strength (ultimate tensile strength: 621-828 MPa)
What property of metals makes it fracture resistant?
yield strength (414-621 MPa)
What property of metals makes it resistant to permanent deformation?
2x
The modulus of elasticity of base based metal alloy is ___x that of gold alloys
2-3%
Co-Cr alloys exhibit elongation of ___-___%
10%
Co-Cr-Ni alloys elongate ___%
less amount of molybdenum + carbon
Why do Co-Cr-Ni alloys elongate more than Co-Cr alloys?
No
Can Co-Cr alloys be improved or controlled by heat treatment?
Yes
Can Ni-Cr alloys strength and ductility be altered by high temperature heat treatment?
corrosion resistance
alloys containing greater than 85% Cr, Co and Ni exhibit a reasonable degree of intraoral _______
Passivation
Chromium-containing alloys resist corrosion through ___________, where a Cr₂O₃ film forms spontaneously in air, creating a protective barrier against oxidation and corrosion.
zirconium oxide (ZrO2)
Chemical coating with ________ reduces Cr release levels in artificial saliva = better corrosion resistance
galvanic corrosion
Repair or modification of a Co-Cr-Mo RPD framework should be done with the same alloy to avoid ________
chromium
________ type alloys are attacked by chlorine, therefore house bleach should not be used for cleaning
phosphate bonded or ethyl silicate (ethyl silicate is preferred)
What is the most common investment materials used in RPD?
phosphate bonded or ethyl silicate
What materials compensate for the high linear casting shrinkage of Co-Cr alloys?
Can produce voids in large casting
What problem can occur during the casting of cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) alloys if gases become trapped in the molten metal?
phosphate bonded investments
ID the type of investment material:
- 80% refractory fillers (silica in the form of cristoballite or quartz)
phosphate bonded investments
ID the type of investment material:
- Contains binder (magnesium oxide and phosphate)
phosphate bonded investments
ID the type of investment material:
- Carbon is added to produce clean casting and facilitate easy removal of castings
phosphate bonded investments
ID the type of investment material based on the following advantages:
- High strength
- Easily withstand temps that reach 1650 F
- Used with high-fusing ceramometal alloys
ethyl silicate bonded investment
ID the type of investment material:
- Binder is silica gel that reverts to silica
ethyl silicate bonded investment
ID the type of investment material:
- Can be heated from 2000-2150 F
ethyl silicate bonded investment
ID the type of investment material based on advantages:
- Ability to cast high temp alloys (base metal alloys)
- Good finish
- Low distortion
- High thermal expansion
casting temp
___________ affects the microstructure + mechanical properties of Cr-Co alloys
high speed lab equipment
What is used to adjust the alloy due to hardness and strength?
Cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) base metal alloys used in RPD frameworks
ID the type of investment material based on disadvantages:
- Cast clasps can break in service even in short period of time, due to fatigue
- Difficult to adjust due to hardness, strength & low elongation
- High hardness can cause excessive wear of restorations or natural teeth that contact the cast framework
nickel
What is the most known metal allergy, with 10-20% incidence?
women
nickel allergies are more common in _______ and can be caused from chronic exposure through jewelry and can be quite severe
false, will not always react (immunological tolerance/possible genetic component)
t/f: individuals that are allergic to Ni will always react to intraoral nickel
true
t/f: nickel ions are documented as mutagens in humans, but no evidence that they are carcinogenic intraorally
true
t/f: Various nickel compounds may contribute to the development of nasal and lung cancers
beryllium
What metal has been associated with the following?
- Occupational hazards as an increase risk of lung cancer and tumors in men
- Revealed a very high leakage which may pose a health risk
- Acidic environment enhances release
Berylloisis
Define the following:
- Chronic allergic type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds
- Condition is incurable, but symptoms can be treated
occupational lung disease
___________ occurs only in individuals with a hypersensitivity to beryllium
1. Survey by retripoding the master cast and outline the partial design on the cast
2. Beading 0.5 mm deep and wide
3. Block out and relief (parallel block out, shaped, arbitrary, relief)
4. Duplication (reversible hydrocolloid)
5. Refractory cast (trimmed, treated with model spray or bees wax)
6. Waxing
7. Major connector and denture base minor connectors
8. Burn out and casting
9. Recovering the casting
10. Finishing and polishing
What are the 10 steps of fabrication of metal framework?
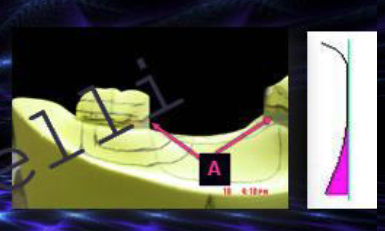
parallel
ID the type of block out at A:
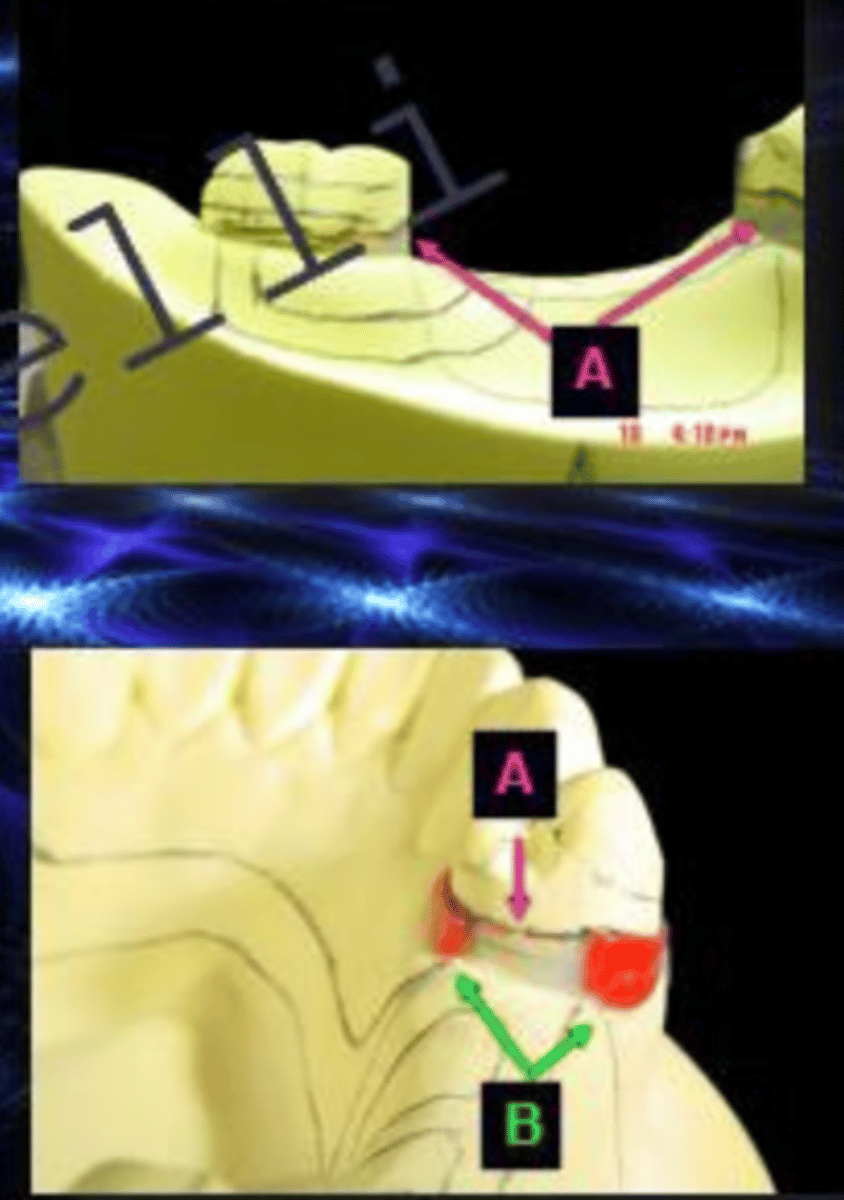
shaped
ID the type of block out at B
arbitrary
ID the type of block out at C:
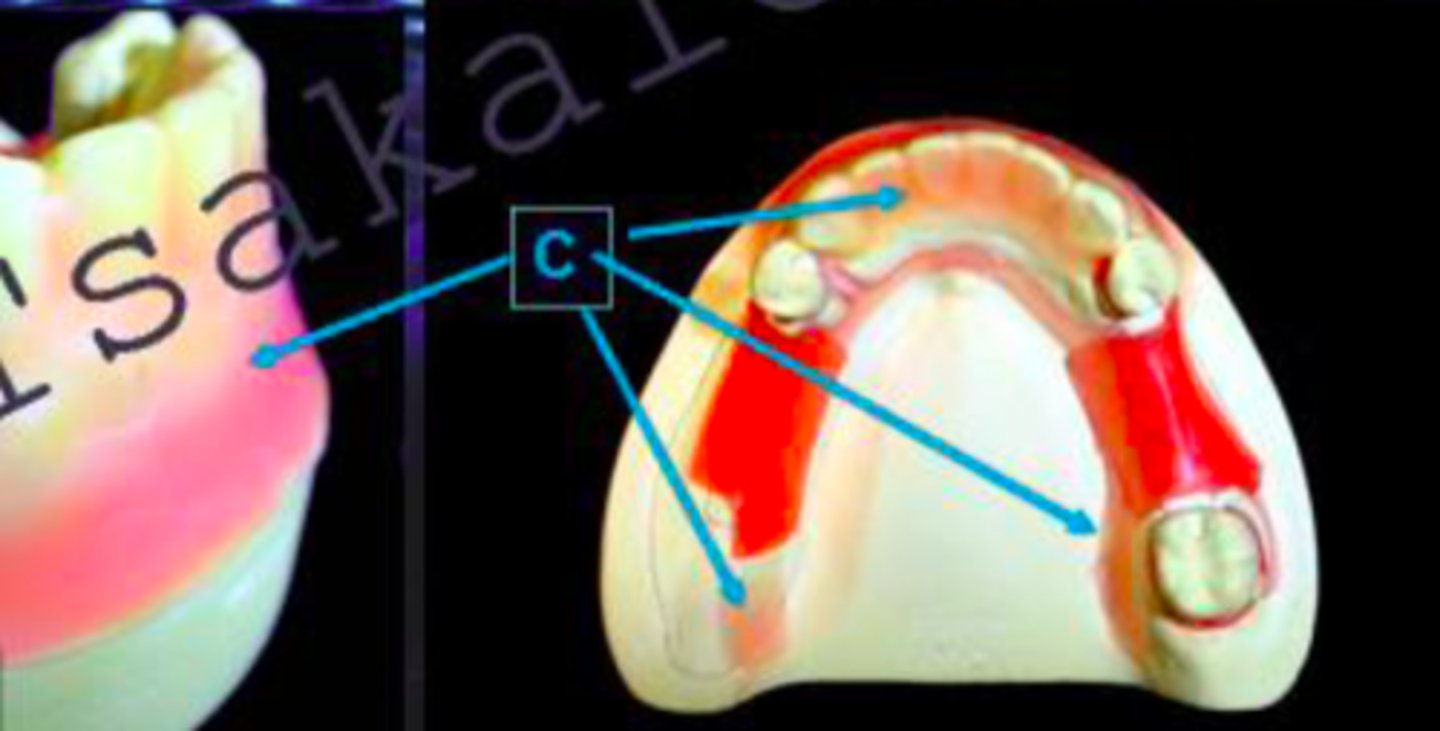
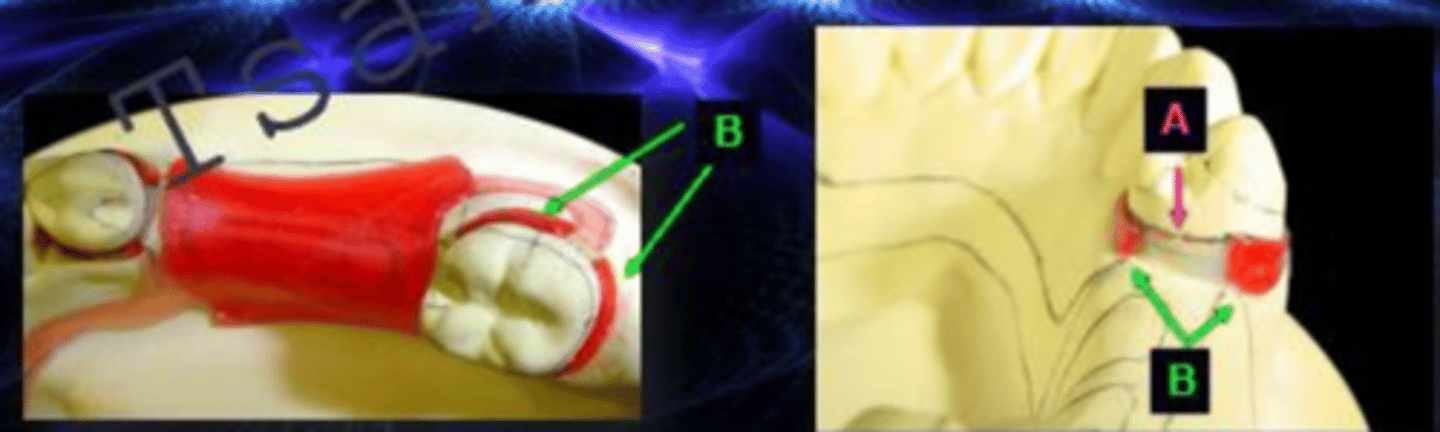
relief
ID the type of block out at D:
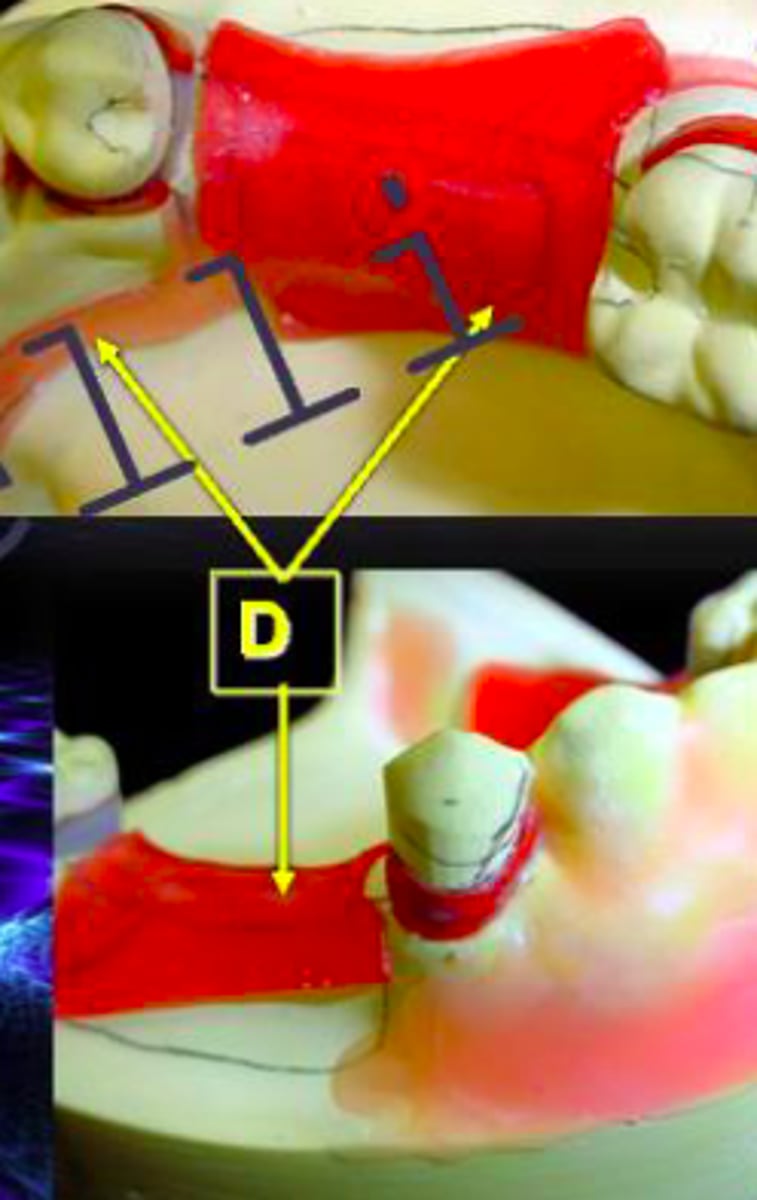
Relief
ID the type of block out at D:
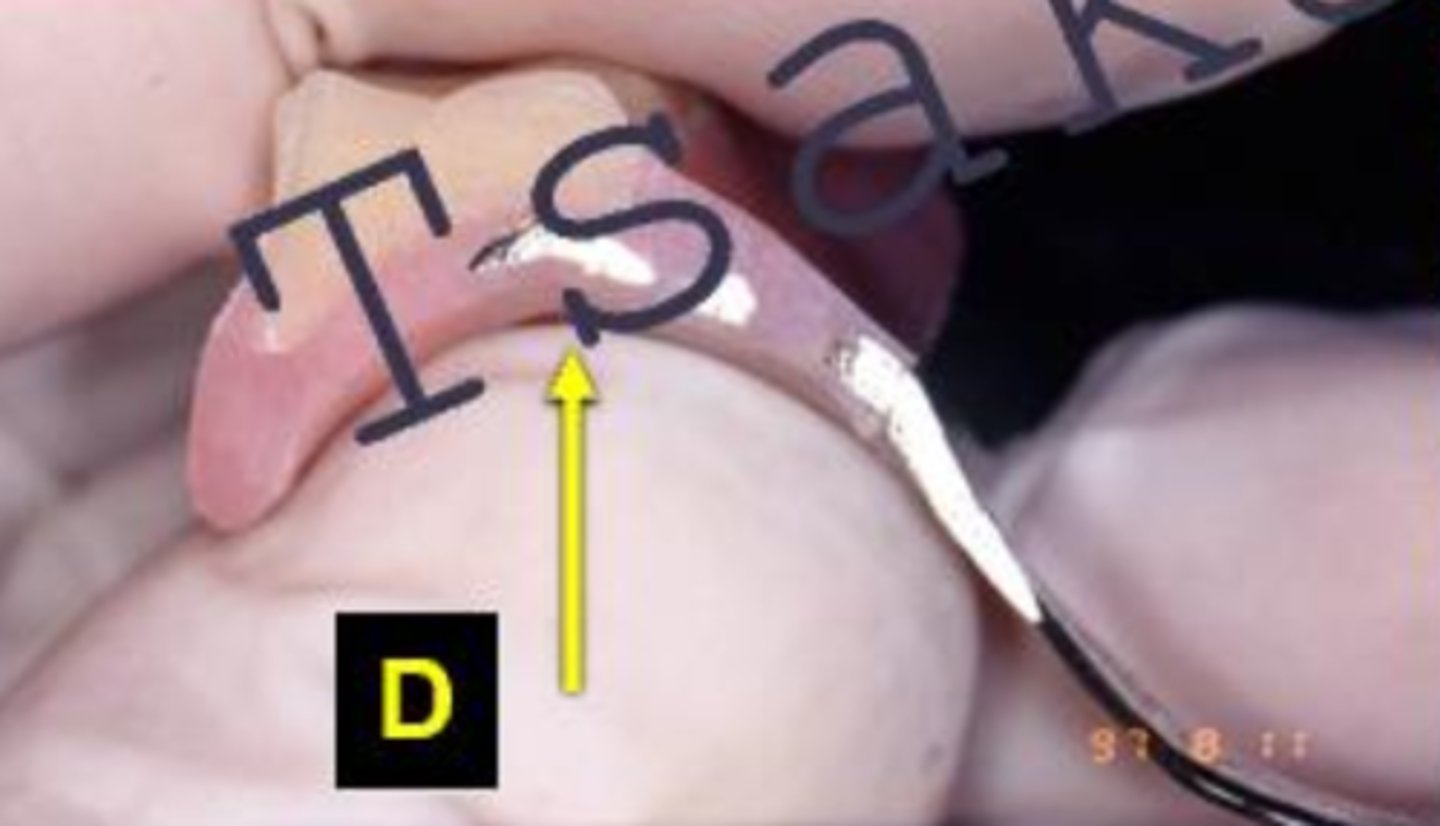
Tissue stops
What is the arrow pointing to?
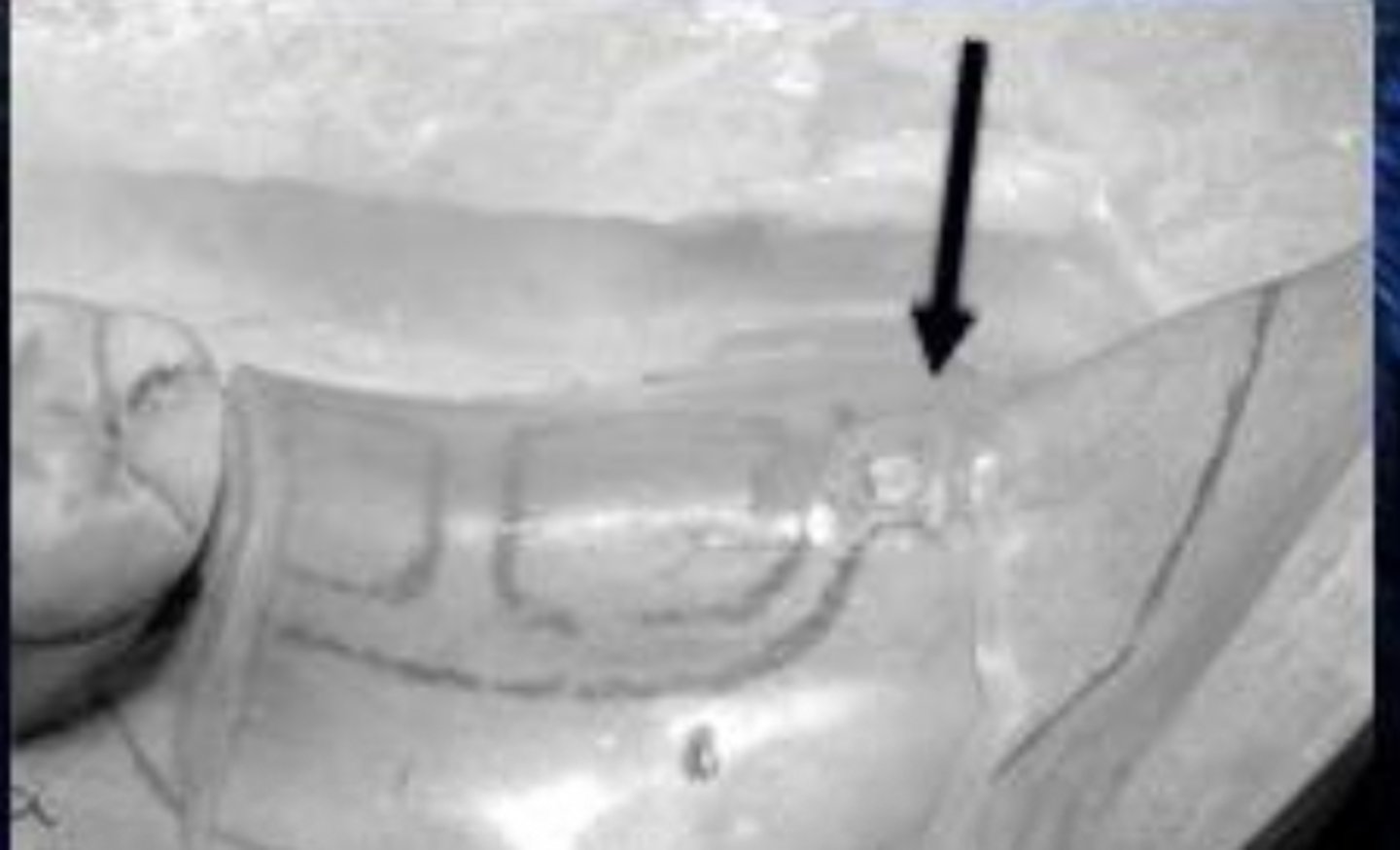
C. Parallel block out
Which type of block out is used to eliminate undercuts along the path of insertion before duplicating the master cast?
A. Arbitrary block out
B. Shaped block out
C. Parallel block out
D. Relief block out
A. Arbitrary block out
Which type of block out is used to prevent metal impingement on soft tissue or to relieve undercuts not used for retention?
A. Arbitrary block out
B. Shaped block out
C. Parallel block out
D. Relief block out
B. Shaped block out
Which type of block out is used to provide relief around soft tissue contours like gingival margins?
A. Arbitrary block out
B. Shaped block out
C. Parallel block out
D. Relief block out
D. Relief block out
Which type of block out is most commonly used on the mandible only?
A. Arbitrary block out
B. Shaped block out
C. Parallel block out
D. Relief block out
Reversible hydrocolloid (agar)
During the duplication step in metal framework fabrication for an RPD, which material is most commonly used?
refractory cast
What cast is made to withstand high temperatures?
paint on investment
ID the type of investment:
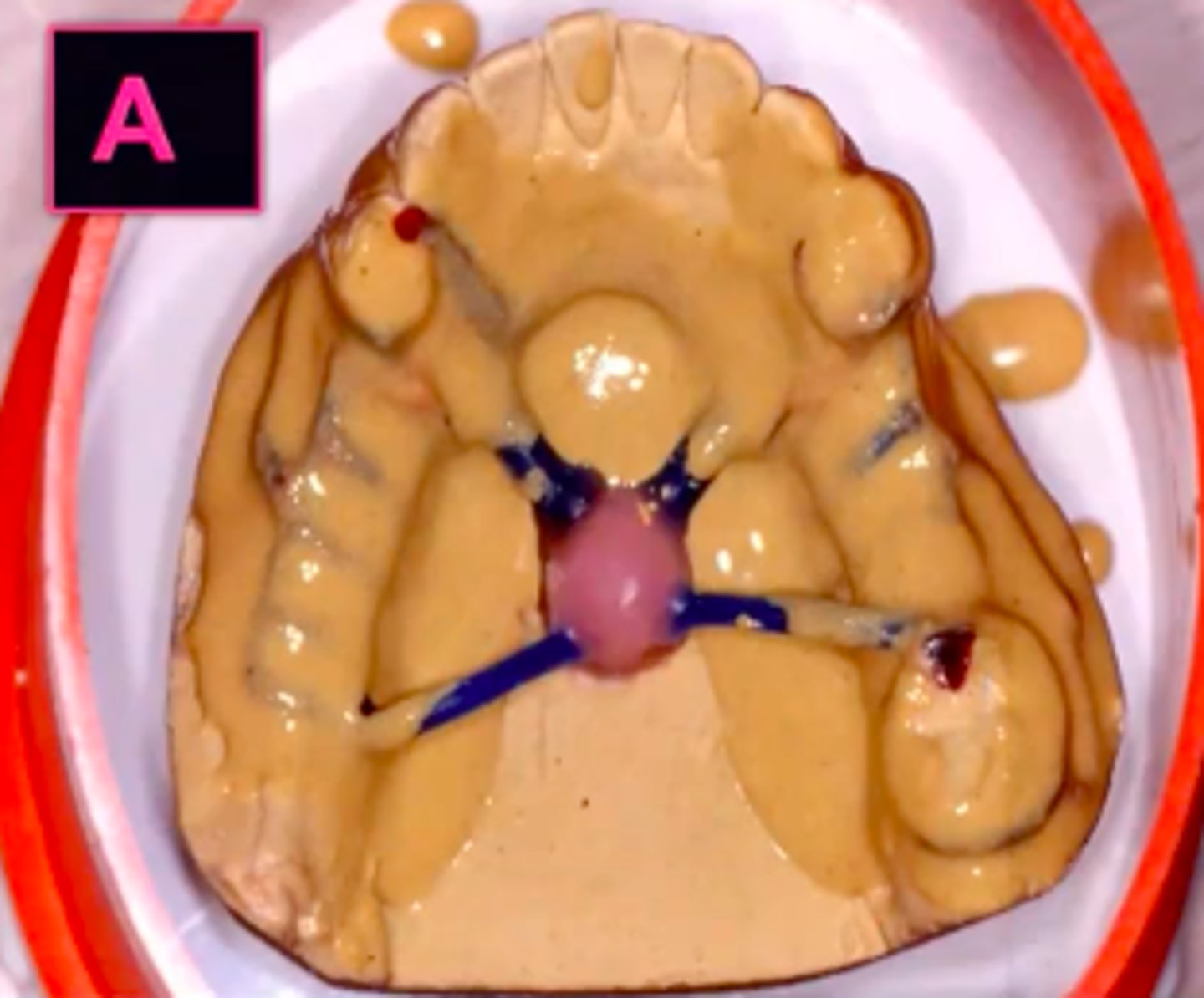
outer investment
ID the type of investment:
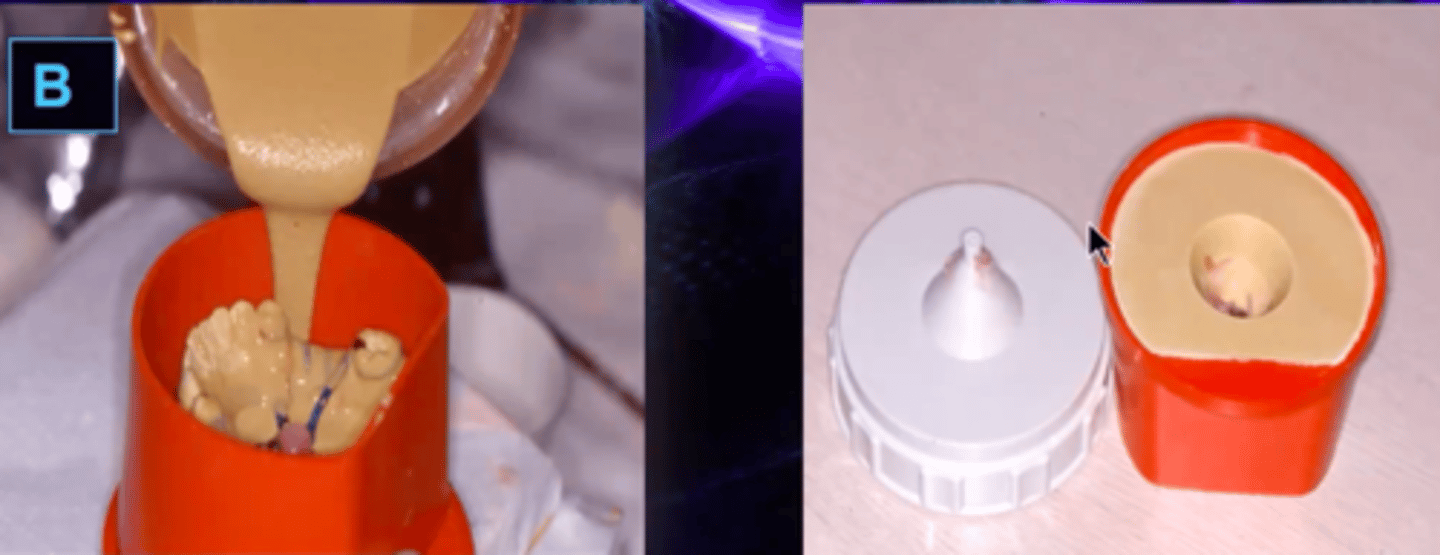
casts alloy clasps
What type of clasp is a part of the framework?
WW clasps
What type of clasp should be soldered to the framework?
recrystallization
Excessive heating of the WW clasp should be avoided during casting or soldering because it will cause ________, compromising the wires mechanical properties
decrease
If a WW clasp is overheated, it will ________ the flexibility
soldered
WW should be _________ to the framework at some distance from the retentive terminal reducing the likelihood of overheating during soldering procedure
18-20 gauge
WW retentive clasps are available in ___-___ guage thickness
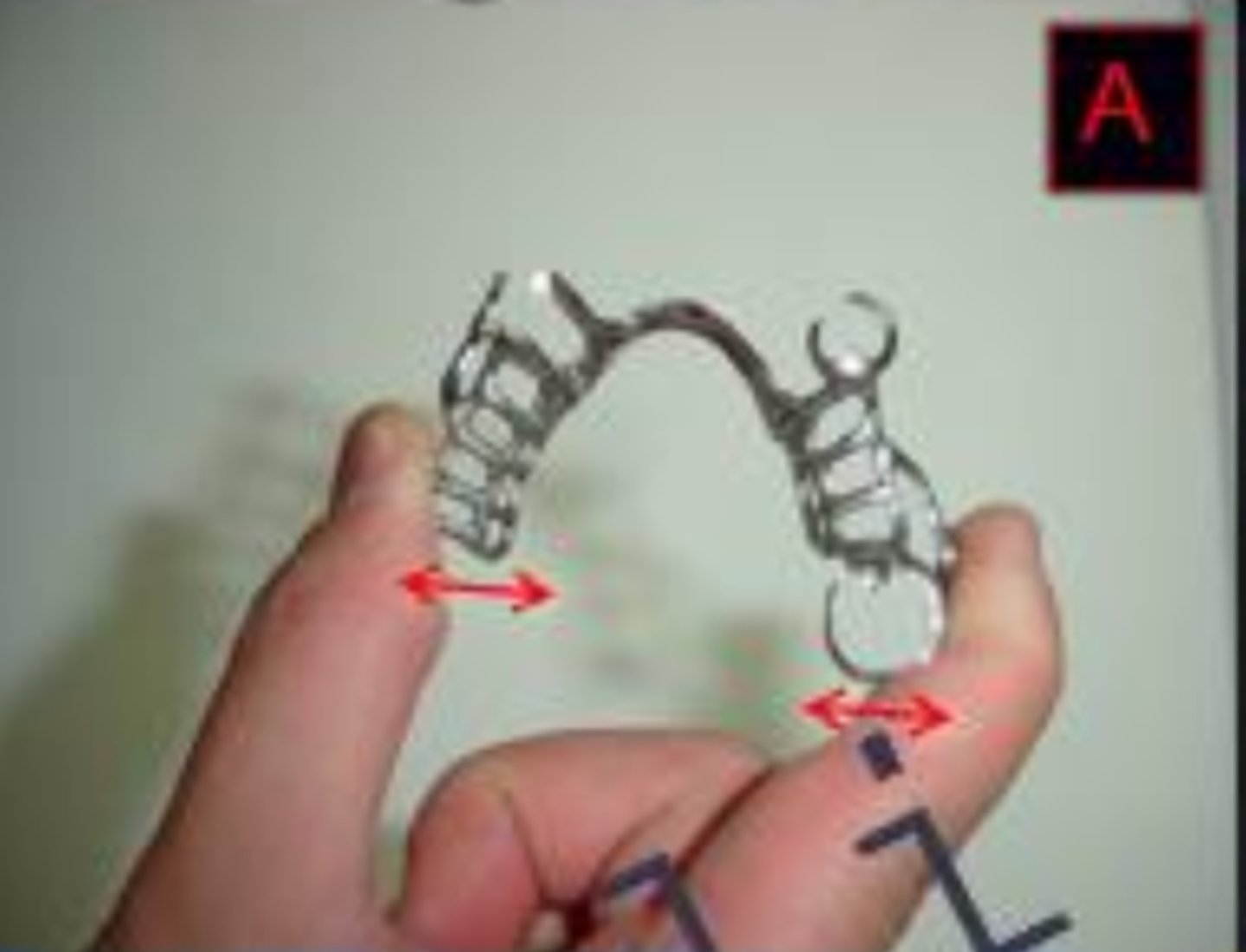
Using a WW retentive clasp
All of the following are advantages of what?
- Flexible in any direction
- Used for greater undercuts (0.02")
- More esthetic
- Minimal tooth contact
- Less fatigue failure
Using a WW retentive clasp
All of the following are disadvantages of what?
- Extra steps in fabrication
- Distortion by patient carelessness
- Distort with function
- Positive bubbles or nodules
- Voids or porosities
When checking an RPD returned from the lab, what defects do you look out for?
- Reproduction of anatomy
- Smooth and round transition
When checking an RPD returned from the lab, what are 2 characteristics of continuity to look for?
Rigid and strong
When checking an RPD returned from the lab, the major connector should be what?

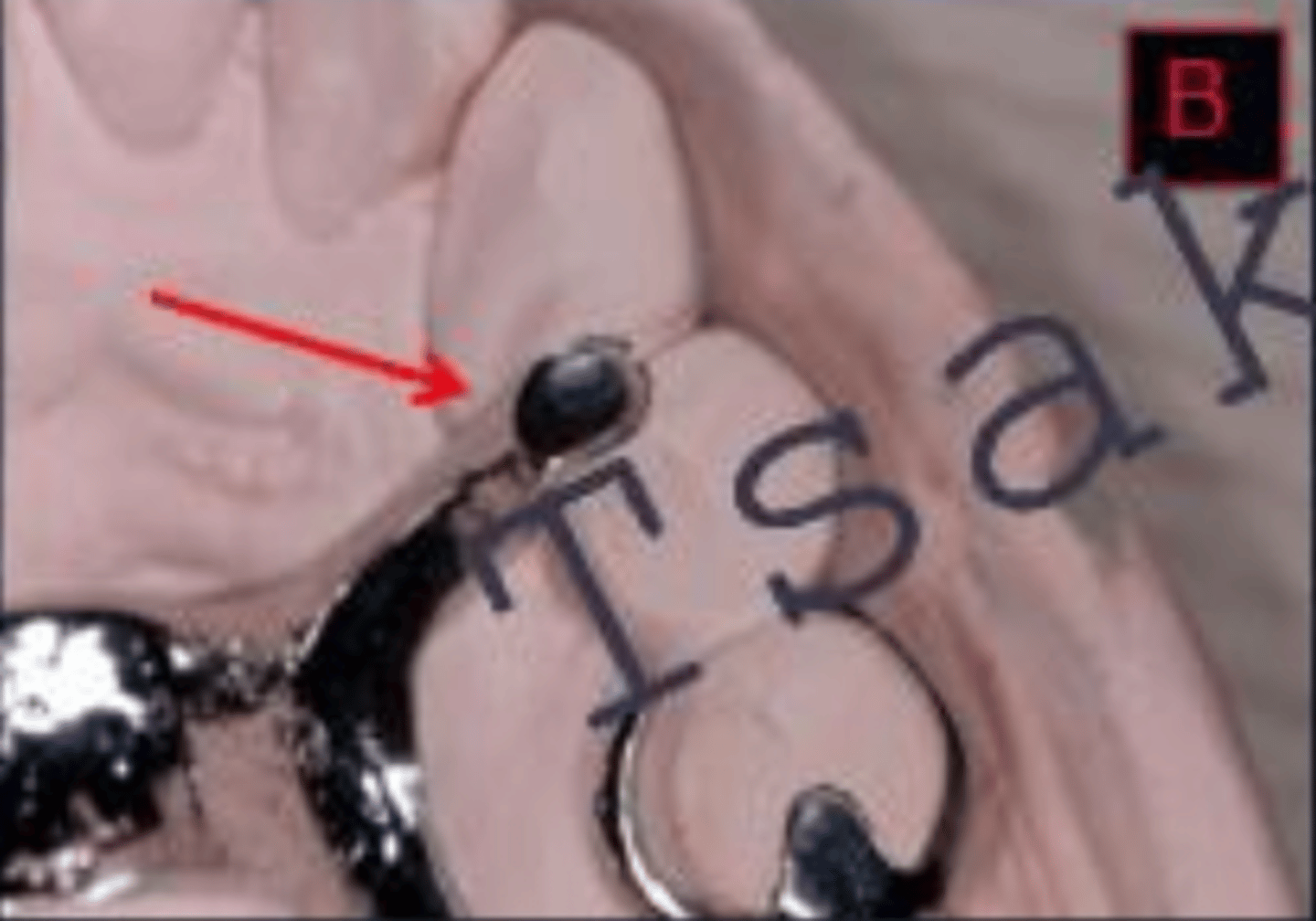
1.5mm
When checking an RPD returned from the lab, the rest should be a minimum of ___mm at the junction

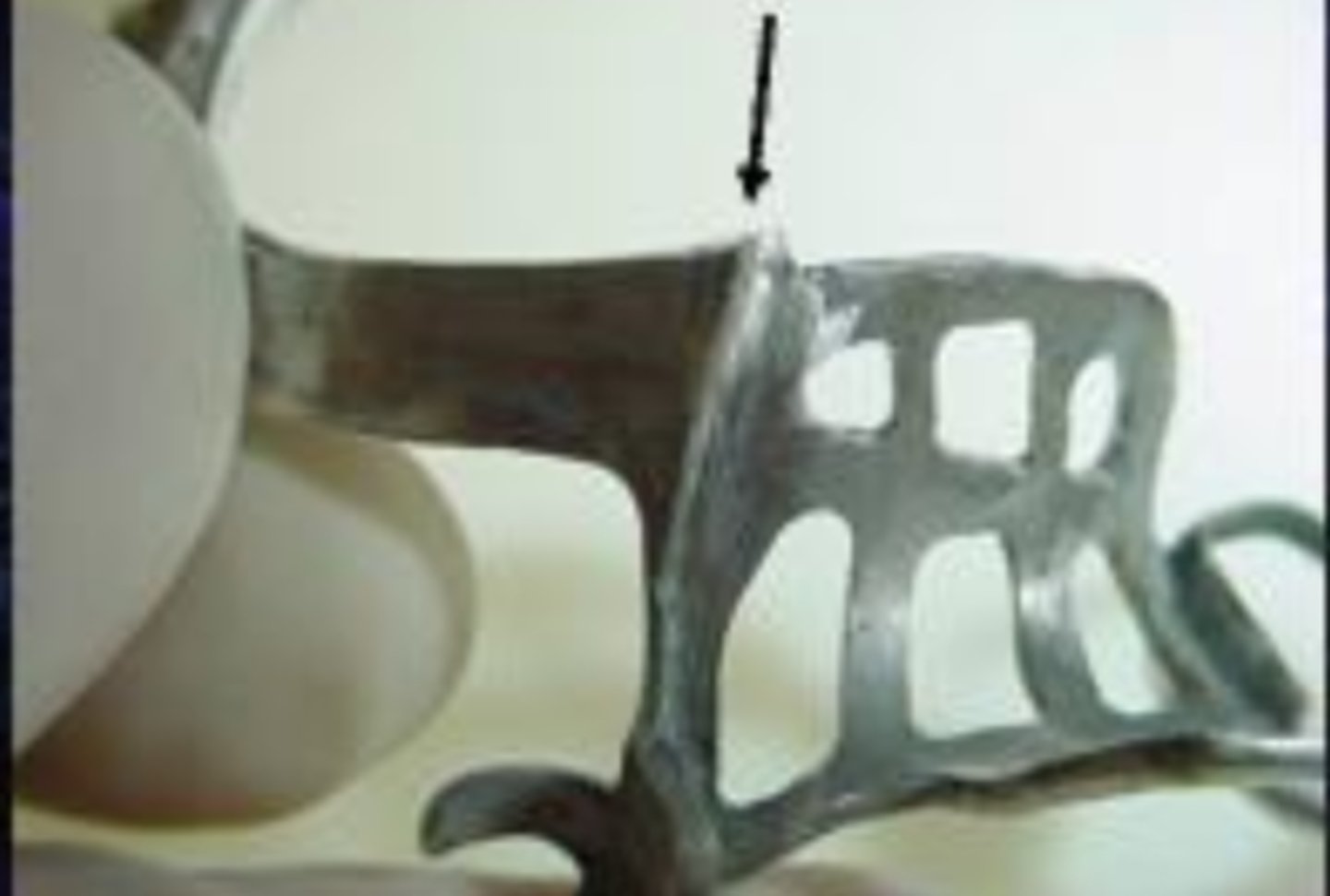
uniformly tapered
When checking an RPD returned from the lab, the clasp should be what?
- Staggered finish line
- Less than 90 degrees
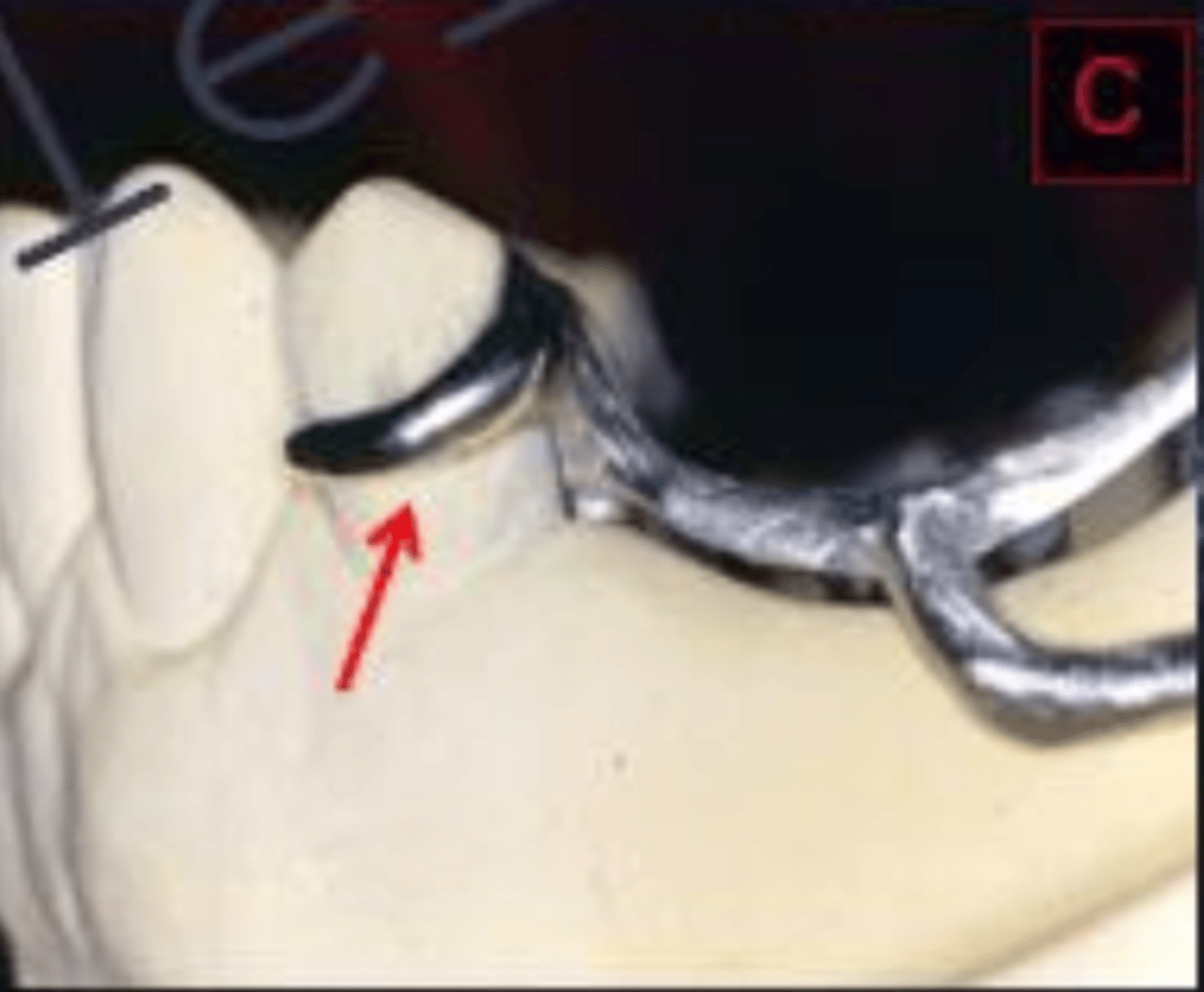
When checking an RPD returned from the lab, finish lines should have what 2 characteristics?
External finish line
What is the box in red pointing to?
Internal finish line
What is the box in blue pointing to?
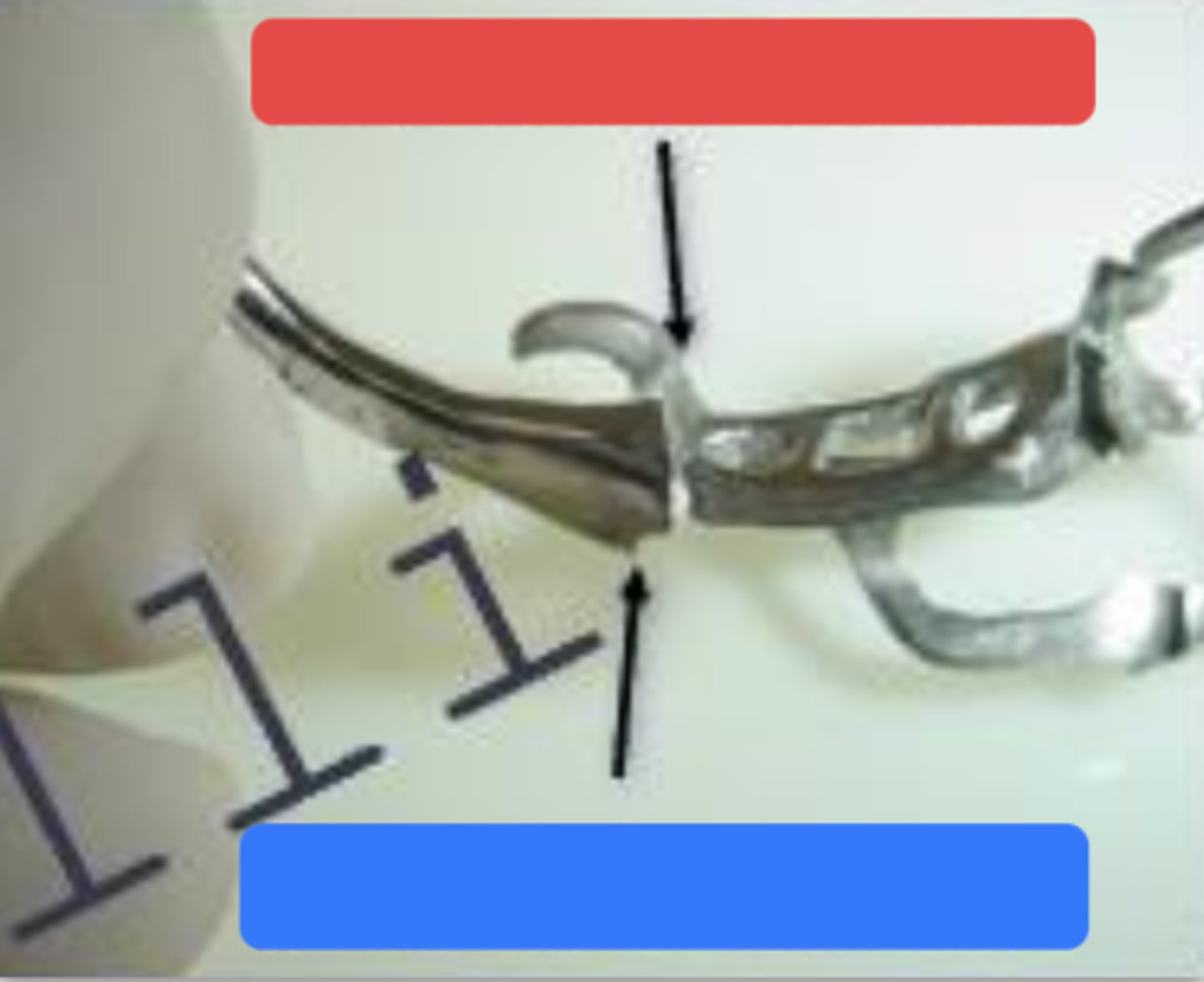
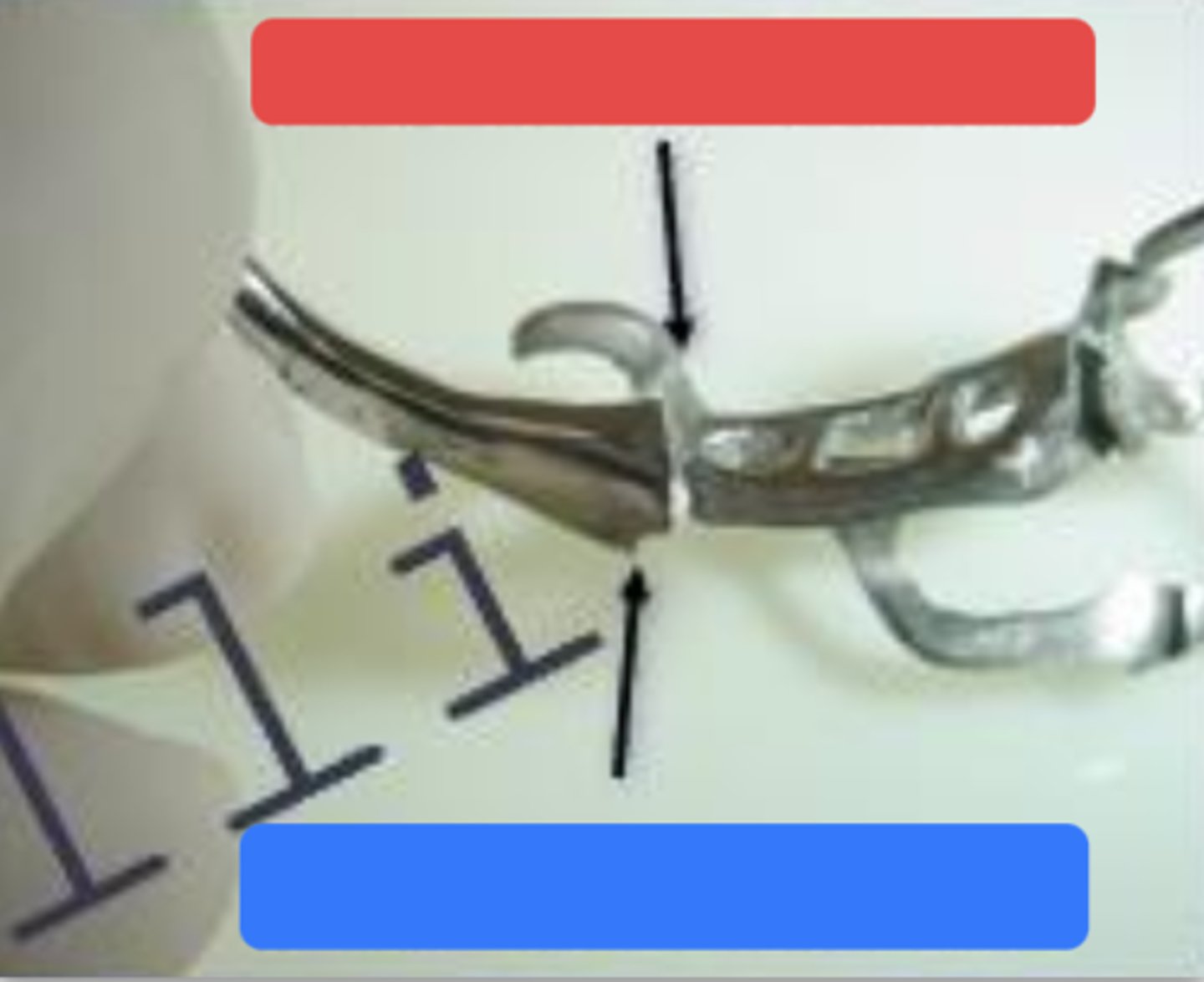
External finish line
What is the arrow pointing to?

Internal finish line
What is the arrow pointing to?

false -- not highly polished for intimate adaptation
t/f: the tissue surface of the maxillary major connector should be highly polished for intimate adaptation