bio 101 - chapters 4.1-4.3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
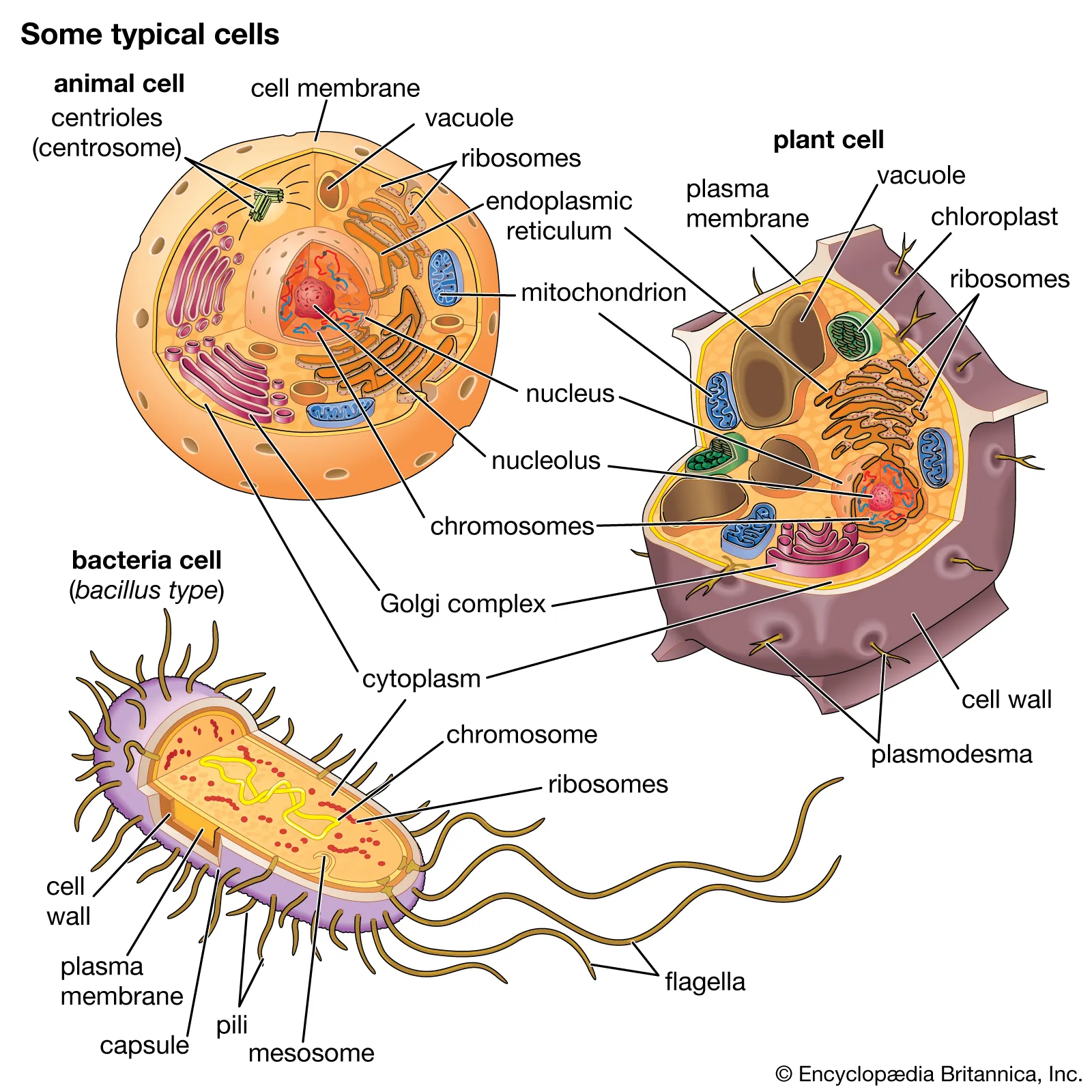
cell
the smallest unit of life that can function independently and perform all the necessary functions of life
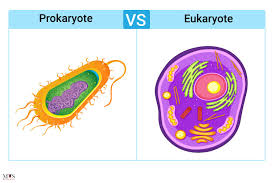
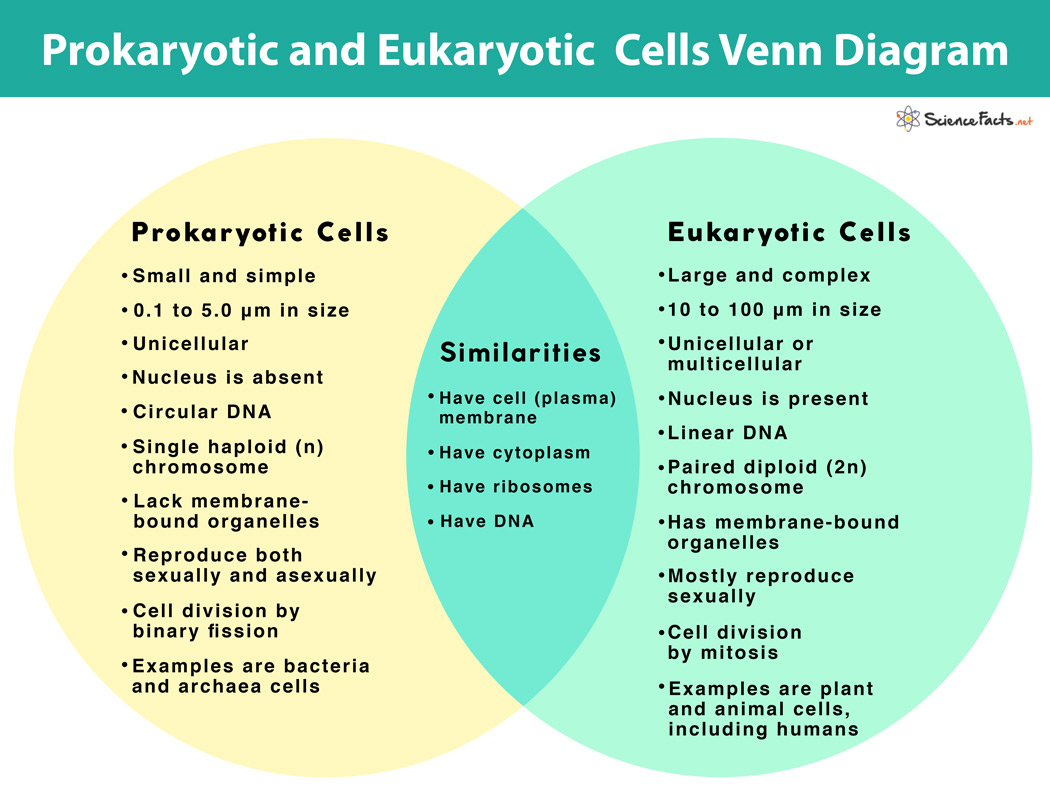
eukaryotic vs prokaryotic
eukaryotic: large, has dna in nucleus
prokaryotic: small, no nucleus
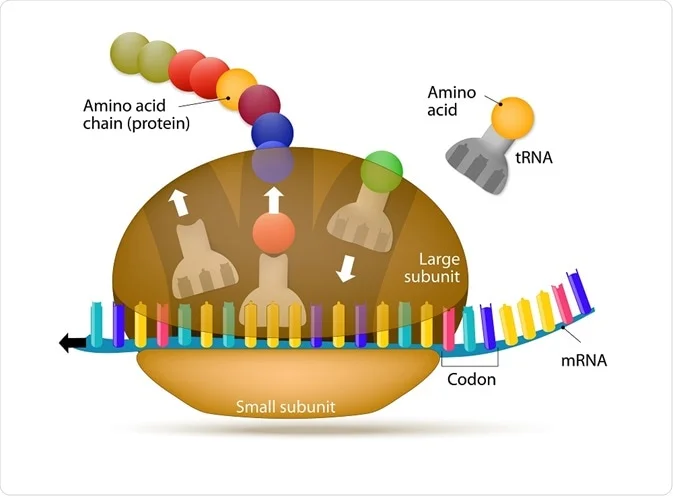
ribosome
granular body in the cytoplasm that converts genetic info into protein
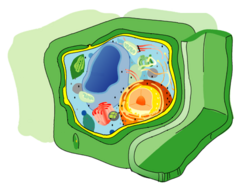
cell wall
protects and gives shape to the cell
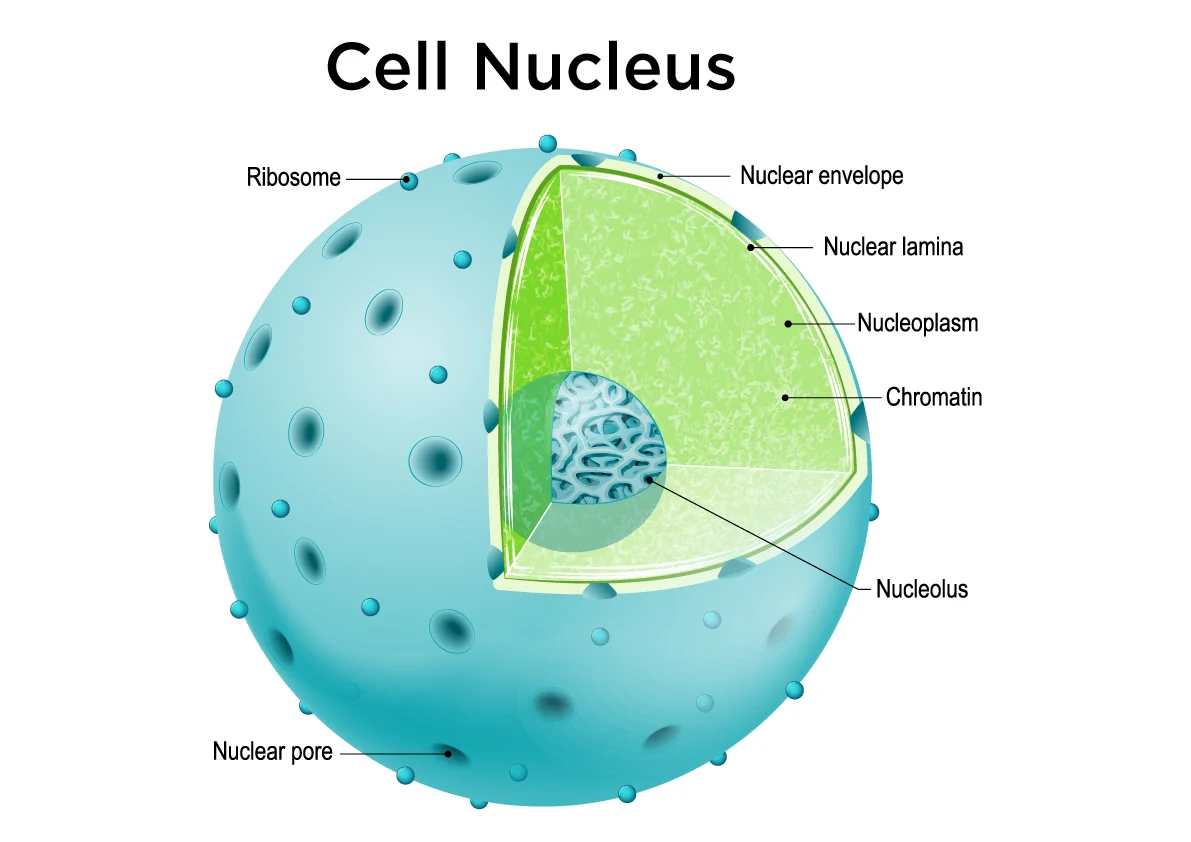
nucleus
a membrane-enclosed structure that contains linear strands of dna
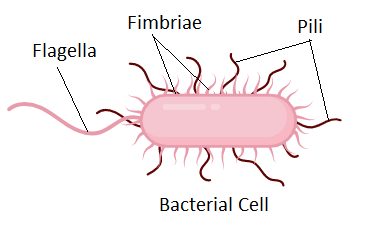
pili
hair-like projections that help prokaryotes attach to surfaces and then exchange dna with other cells
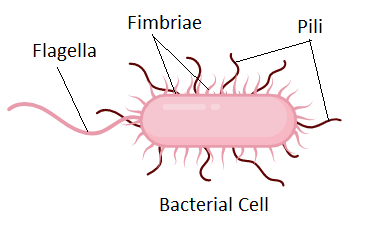
flagellum
a long, thin, whip-like appendage that projects from the cell; like a propellor
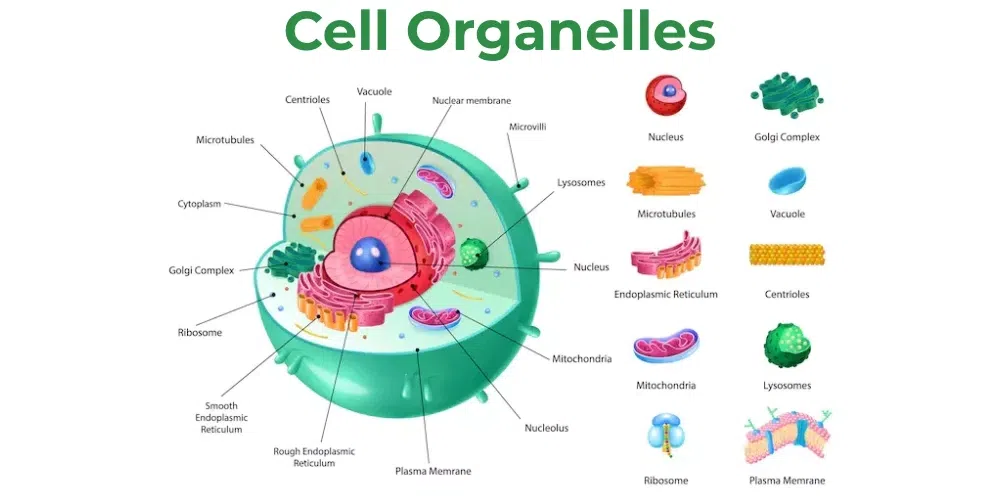
organelle
structure in cytoplasm that’s enclosed separately; the cell’s ‘organs’
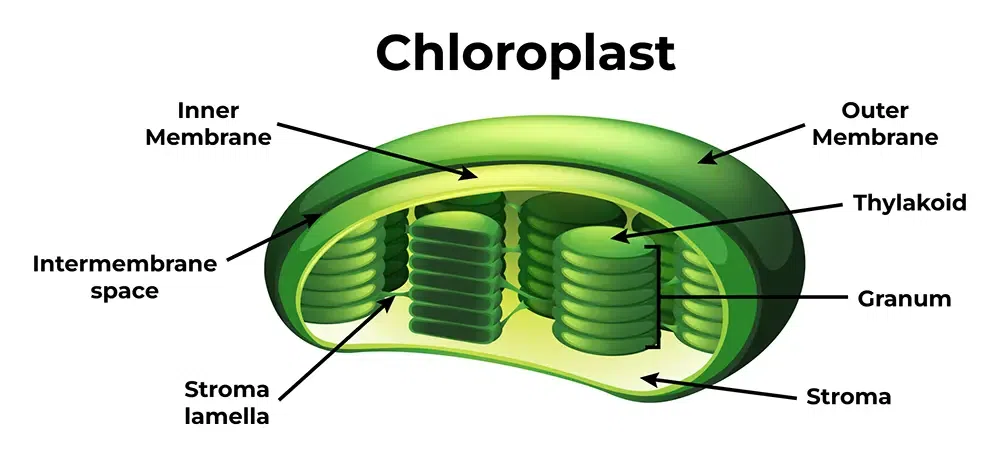
chloroplast
organelle in plant and eukaryotic algae cells in which photosynthesis occurs
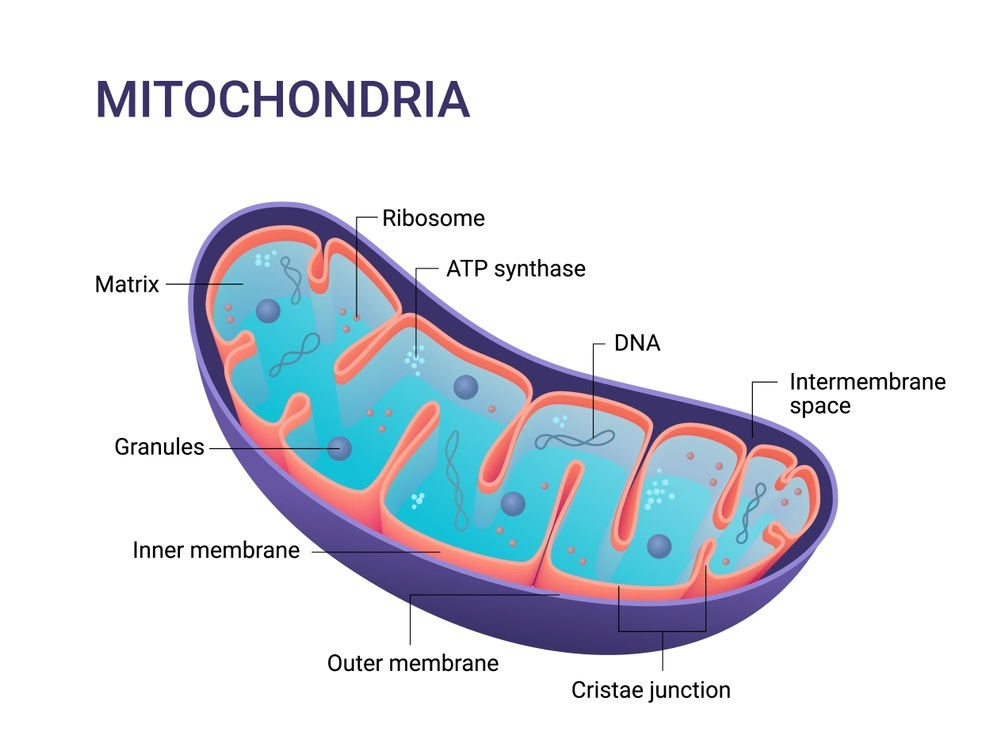
mitochondria
organelle in plant and animal cells that converts the energy stored in food into a form usable by the cell; the powerhouse!
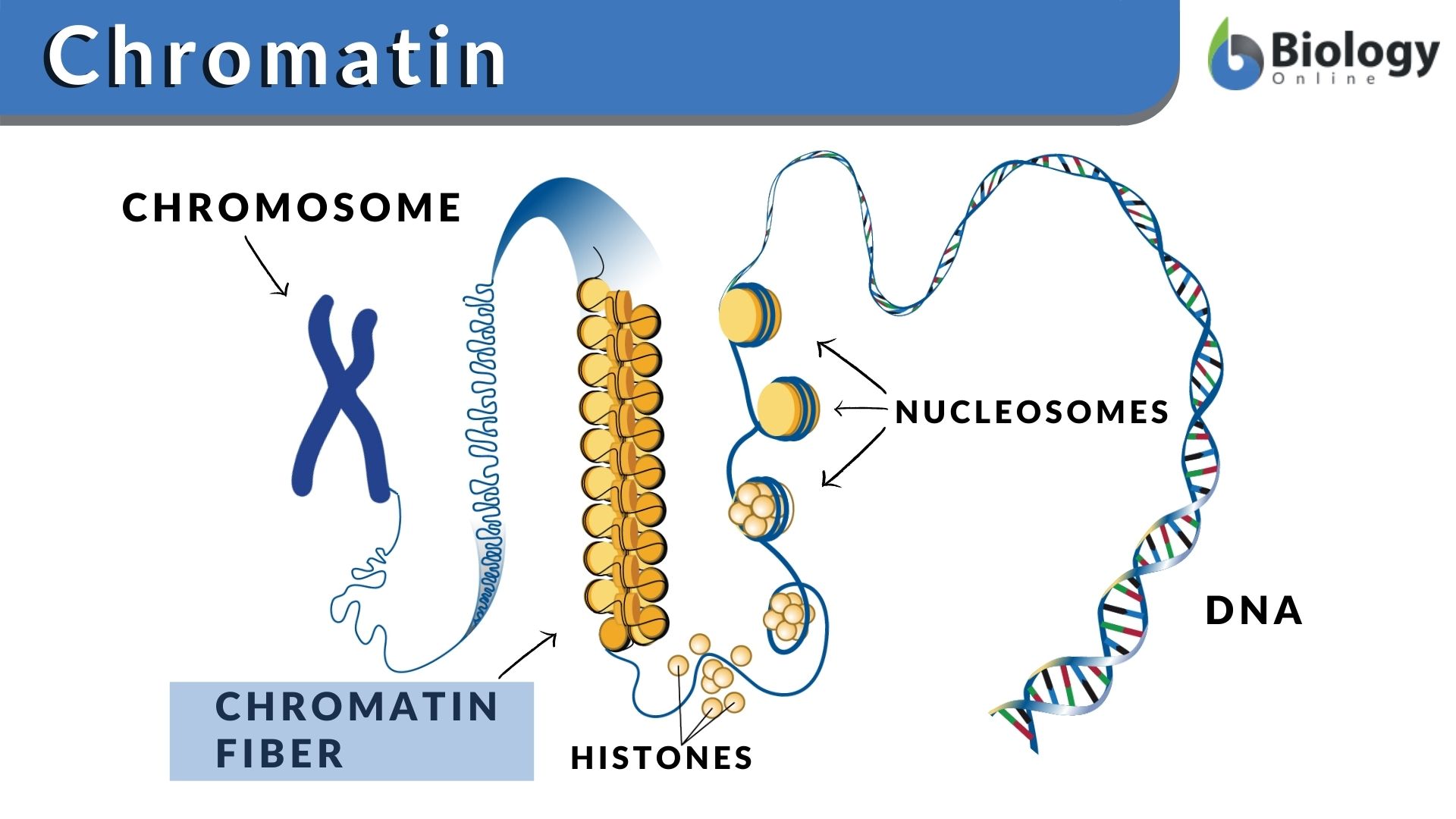
chromatin
the fibers of dna, which carry all hereditary information
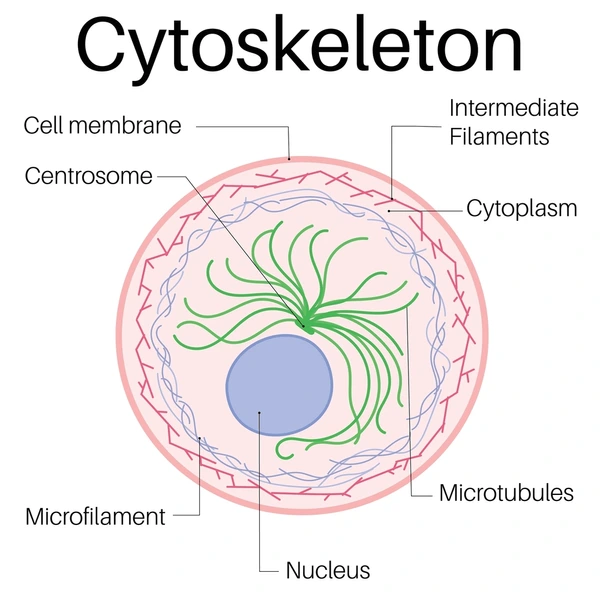
cytoskeleton
the inner scaffolding of the cell made from proteins
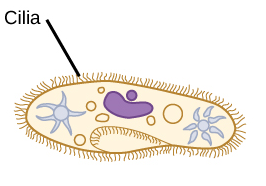
cilia
short projections often found in large numbers on a single cell; can either move a cell or move particles along cell’s surface
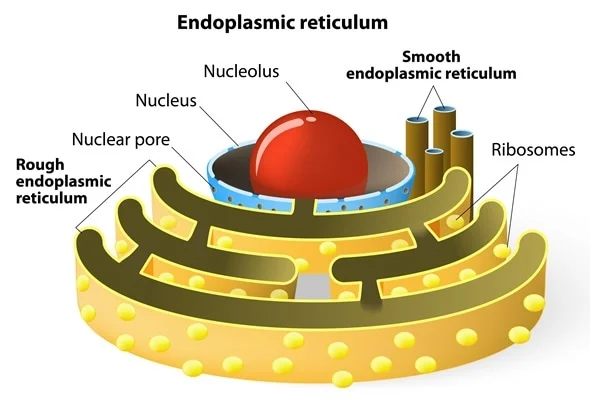
endoplasmic reticulum
a vast network of membranes within eukaryotic cells responsible for synthesizing, folding, and transporting proteins and lipids
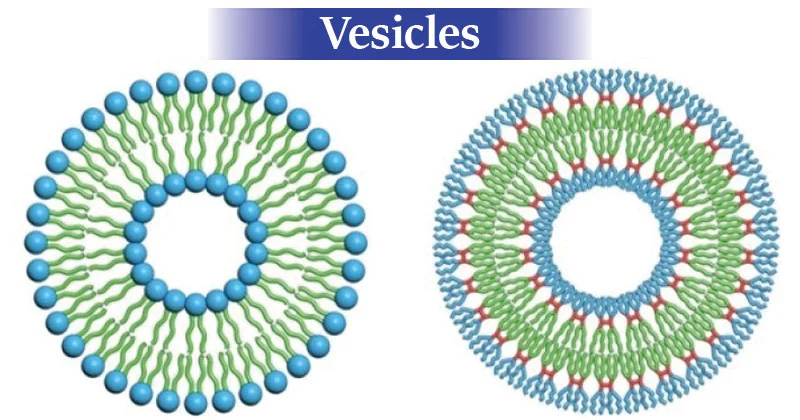
vesicle
a small-pocket like sac that moves and stores proteins, hormones and chemicals