test 3 thorax breats Beam Restriction and Shaping in Radiation Therapy, Radiation Oncology and Drug Administration Overview
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
What does SSD stand for in radiation therapy?
SSD stands for Source to Skin Distance, which refers to how far the radiation source is from the patient's skin.
What is the purpose of setting the SSD for every treatment port?
To ensure accurate treatment delivery by calibrating the radiation source distance for each specific treatment angle.
What does SAD stand for and what does it represent?
SAD stands for Source to Axial Distance, indicating the distance from the radiation source to a fixed point in the patient.
What is the significance of simulation in radiation therapy?
Simulation is crucial for accurately setting up treatment parameters and ensuring that the tumor volume is targeted correctly.
What must be verified before treating a patient in radiation therapy?
The treatment plan must be verified, including parameters like SSD vs. SAD, patient positioning, dose, and consent.
What is included in a radiation treatment prescription?
The prescription includes the dose, bolus requirements, treatment area, energy type, and any necessary boosts or reductions.
What is the role of immobilization devices in radiation therapy?
Immobilization devices are used to keep the patient in the same position for each treatment session to ensure consistency.
What are portal images and why are they important?
Portal images are films taken of the treatment area to ensure accurate alignment with the planned treatment fields.
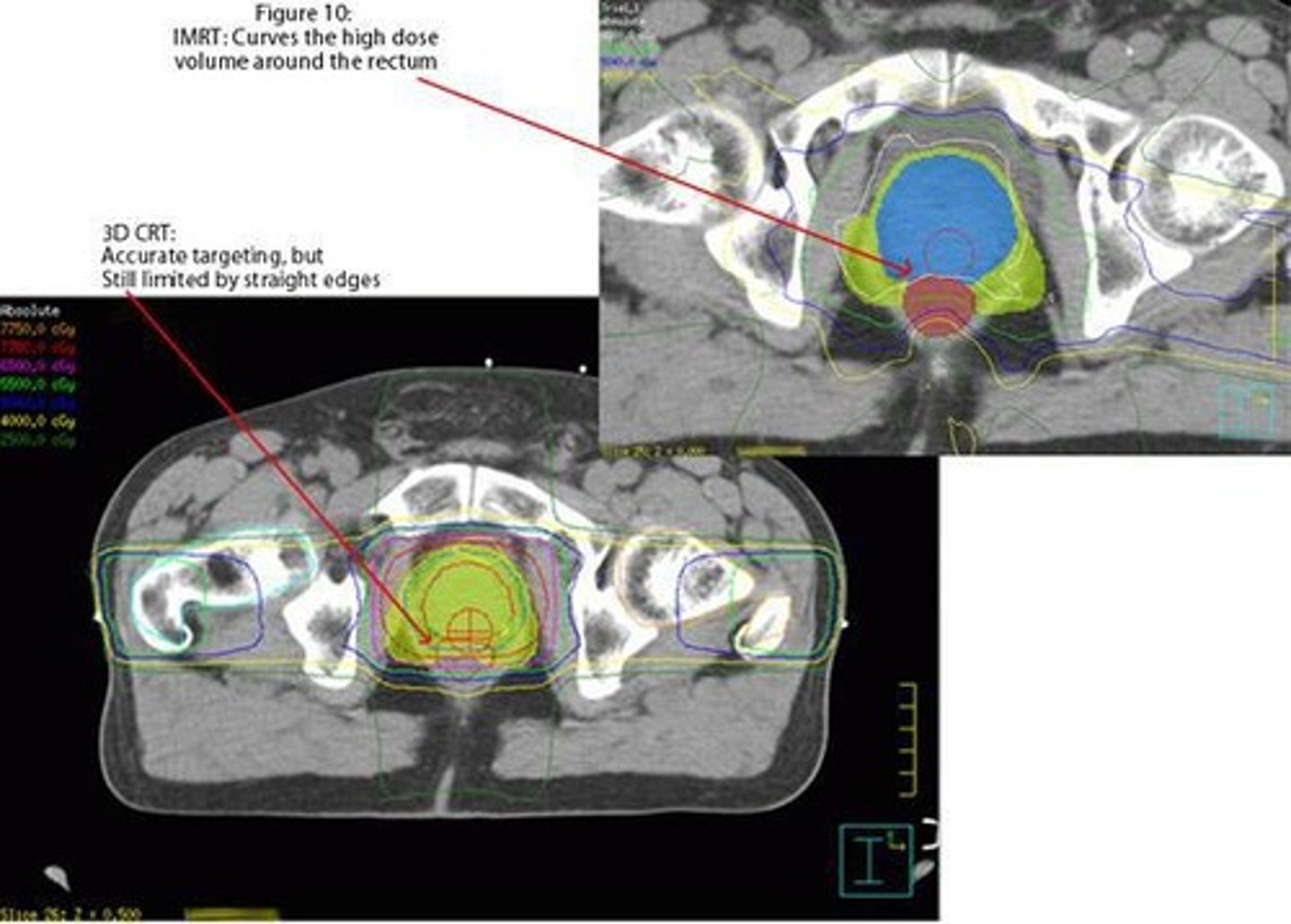
What is the difference between Non-IMRT and IMRT?
Non-IMRT uses open fields with customized MLCs, while IMRT delivers radiation in a non-uniform manner to better spare critical structures.
What materials are commonly used for bolus in radiation therapy?
Common bolus materials include Superflab, Vaseline gauze, wet towels, water bags, and paraffin wax.
What is the purpose of using bolus in radiation treatment?
Bolus is used to increase the skin dose and to even out irregular contours on the patient's body.
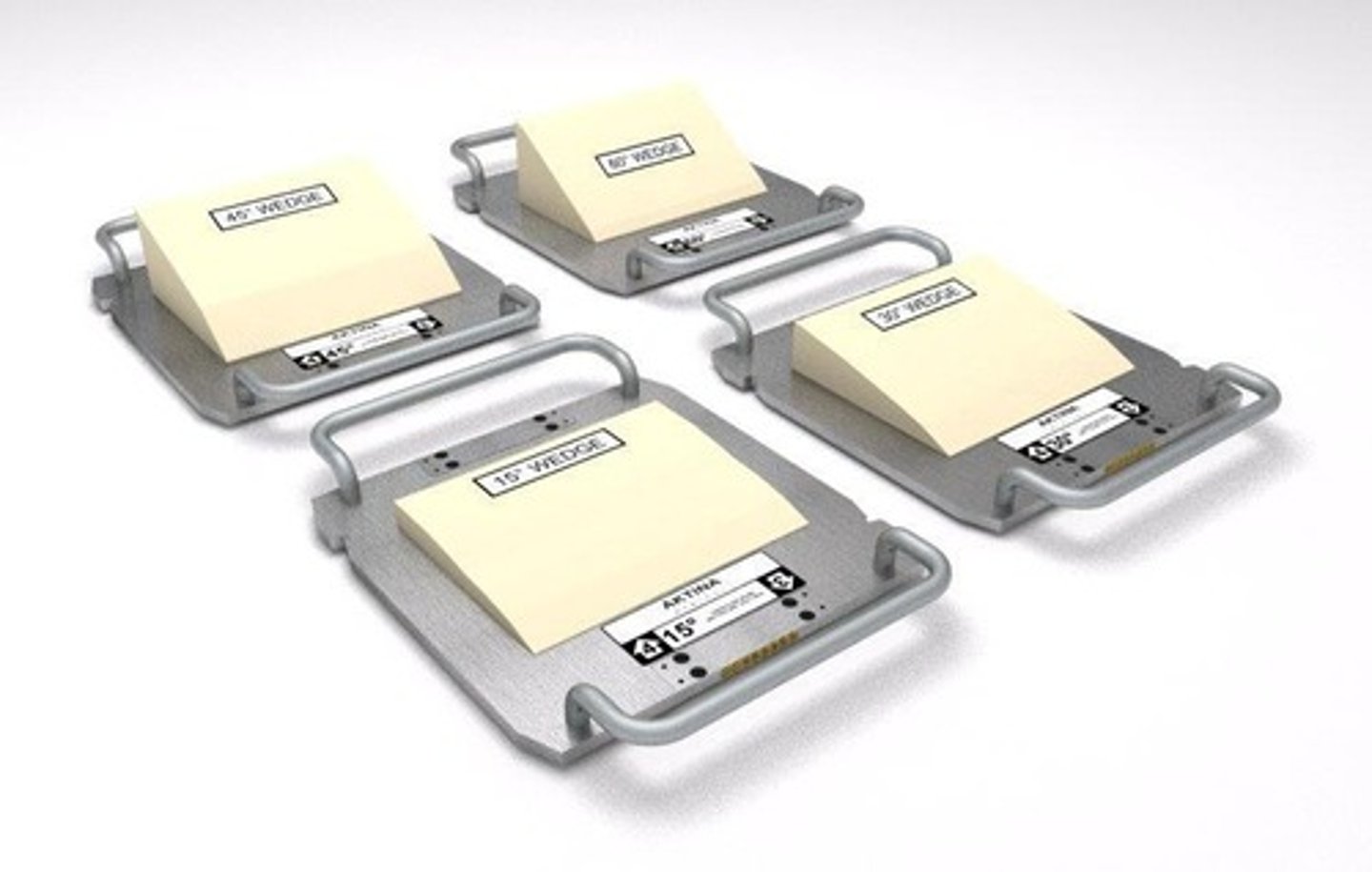
What are hard wedges and when are they used?
Hard wedges are devices that come in various angles (15, 30, 45, 60 degrees) to deliver a homogeneous dose over curved treatment areas.

What is a dynamic wedge?
A dynamic wedge, also known as an electronic dynamic wedge, is a computerized method used to shape the treatment portal instead of using a physical wedge.
What is the purpose of boost fields in radiation therapy?
Boost fields deliver a high dose to a small volume, specifically targeting the gross tumor volume while excluding regional lymph nodes.
What is the significance of the patient's first day of treatment?
It involves verifying consent, proper immobilization, and ensuring that all treatment parameters are correctly set before proceeding.
What is the function of Multileaf Collimators (MLCs) in radiation therapy?
MLCs are used to shape the treatment field dynamically within the gantry head, reducing the need for poured blocks.
What is the composition of Cerrobend used for radiation shielding?
Cerrobend is composed of bismuth (50%), lead (26.7%), tin (13.3%), and cadmium (10%).
What are the potential side effects of IMRT compared to Non-IMRT?
IMRT has greatly reduced patient side effects by allowing for better sparing of critical structures during treatment.
What is the importance of verifying the treatment plan before patient treatment?
It ensures that all aspects of the treatment are correct and that the patient is receiving the intended therapy safely.
What is the role of the therapist in the treatment process?
The therapist is responsible for verifying the treatment plan, ensuring informed consent, and preparing the patient for treatment.
What are the typical angles for hard wedges used in radiation therapy?
Hard wedges typically come in angles of 15, 30, 45, and 60 degrees.
What is the purpose of using a prescription in radiation therapy?
The prescription outlines the treatment parameters, ensuring that the therapy is delivered according to the physician's orders.
What is the significance of the patient's tattoos in radiation therapy?
Tattoos are used as reference points for accurate positioning and alignment during treatment.
What is the effect of bolus on skin reactions during radiation therapy?
Bolus can cause skin reactions by bringing the radiation dose closer to the skin, which does not promote skin sparing.

What is the purpose of the Radiation Oncology Treatment Chart?
It remains in the radiation oncology department, contains the patient's treatment history, serves as a legal document, and is part of the QA program.
What ethical responsibility do therapists have regarding patient records?
Therapists must maintain the patient's privacy and right to confidentiality.
What are some components included in a patient's chart in Radiation Oncology?
A patient's chart may include an ID photo, treatment field photos, progress notes by MD and Nurse, treatment summary, follow-up visits, history and physical, pathology reports, lab values, treatment planning, treatment records, and patient prescription.
What does 'fraction' refer to in Radiation Prescription?
Fraction refers to the individual treatment dose.
What is meant by 'protraction' in the context of Radiation Prescription?
Protraction is the time period over which the treatment will be given.
What are 'elapsed days' in Radiation Oncology treatment?
Elapsed days refer to the total time over which treatment is protracted.
What information is contained in the treatment record?
The treatment record contains the patient's ID, a signed prescription, treatment planning data, portal films, SSDs, the delivery of treatments, administration of daily and cumulative treatments, and elapsed days.
What should be reviewed before starting treatment in Radiation Oncology?
Before starting treatment, the chart should be reviewed, including the patient's picture, consent form, and simulation notes.
What is the significance of simulation notes in patient treatment?
Simulation notes detail how the patient is set up for treatment.
What is the role of progress notes in a patient's chart?
Progress notes document the patient's ongoing treatment and response by the MD and Nurse.
What is included in the treatment planning data?
Treatment planning data includes the strategies and methods for delivering radiation therapy to the patient.
What is the importance of a signed prescription in the treatment record?
A signed prescription is a legal requirement and confirms the treatment plan authorized by the physician.
What is the QA program in the context of Radiation Oncology?
The QA program ensures the quality and safety of radiation treatments provided to patients.
What is the purpose of the pathology reports in a patient's chart?
Pathology reports provide critical information regarding the diagnosis and characteristics of the patient's condition.
What is a dosimetry plan?
A treatment plan that includes the use of wedges, bolus, and blocks, and is signed by a medical doctor.
What does the daily treatment record document?
The course of the treatment's implementation and directs each subsequent treatment.
What information is included in the daily treatment record?
Treatment number, recorded SSDs, addition or deletion of fractions delivered, elapsed days, total dose, and notations regarding port films.
Who must sign or initial all treatment deliveries?
The treating therapist.
What must the therapist monitor during treatment?
The radiation delivered and doses to critical structures.
What is the maximum dose to the spinal cord that a therapist must be aware of?
4500 cGy.
What are some common side effects a therapist should expect from treatment?
Erythema, dry desquamation, moist desquamation, xerostomia, esophagitis, dysphagia, temporary hair loss, and permanent hair loss.
What is the biggest error in written charting?
Math errors.
What are Record and Verify systems?
Radiation treatment interfaces that comprise a computer network, containing the patient's electronic treatment chart and communicating with treatment machines.
What are two examples of Record and Verify systems used in clinics?
IMPAC (Mosaic) owned by Elekta and ARIA owned by Varian Medical Systems.
What types of drugs may a technologist or therapist administer?
Sedation, pain management, contrast media, and emergency drugs for contrast reactions.
What is the ASRT perspective on drug administration by radiologic technologists?
They are permitted to perform venipuncture and administer contrast media, radiopharmaceuticals, and IV medications where allowed by state statutes and institutional policy.
What is the role of pharmacology in radiation therapy?
Therapists need a basic understanding of medications and their common side effects as part of patient overall care.
What types of medications specific to radiation therapy may therapists administer?
Contrast media (ionic vs. non-ionic), anesthetics, eye drops before eye shields, and IV fluids.
What is the difference between a chemical name and a generic name of a medication?
The chemical name states its chemical composition and molecular structure, while the generic name is usually suggested by the manufacturer.
What is the official name of a drug?
Usually the same as the generic name.
What is the brand or trade name of a drug?
The drug's name in official publications.
What are legend drugs?
Medications that require a prescription and have a written legend on the prescription.
What is the chemical name of diazepam?
7-chloro-1, 3-dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2h-1.
What is the generic name of diazepam?
Diazepam.
What is the official name of diazepam according to USP?
Diazepam, USP.
What is the brand name of diazepam?
Valium®.
What is pharmacokinetics?
The way the drug travels through the body to their appropriate receptor site.
What are the four main processes involved in pharmacokinetics?
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion.
What is pharmacodynamics?
The way in which drugs affect the body.
What is the significance of a drug's molecular structure?
Each drug has a unique molecular structure enabling it to interact with a specific enzyme or corresponding cell type.
What are the principles to consider in pharmacology?
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion.
What variables affect patient response to drugs?
Age, weight and physical condition, gender, personal and emotional requirements.
What are some non-therapeutic reactions to drugs?
Allergic reactions, tolerance, cumulative effect, idiosyncratic effects, dependence, drug interactions, iatrogenic disease.
What are the Seven Rights of Medication Administration?
Right patient, right medication, right dose, right time, right route, right documentation, right reason/indication.
What is required for radiation therapy treatments?
A prescription.
What are some routes of drug administration?
Oral, sublingual, buccal, mucous membrane, topical, rectal, parenteral, intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, IV, chest tubes and lines, central venous lines.
What are the legal aspects of drug administration?
Documentation and informed consent.
What is the function of the bony thorax?
It protects organs and aids in respiration.
What structures form the borders of the bony thorax?
Thoracic vertebrae (posterior), sternum (anterior), ribs (lateral), and costal cartilages.
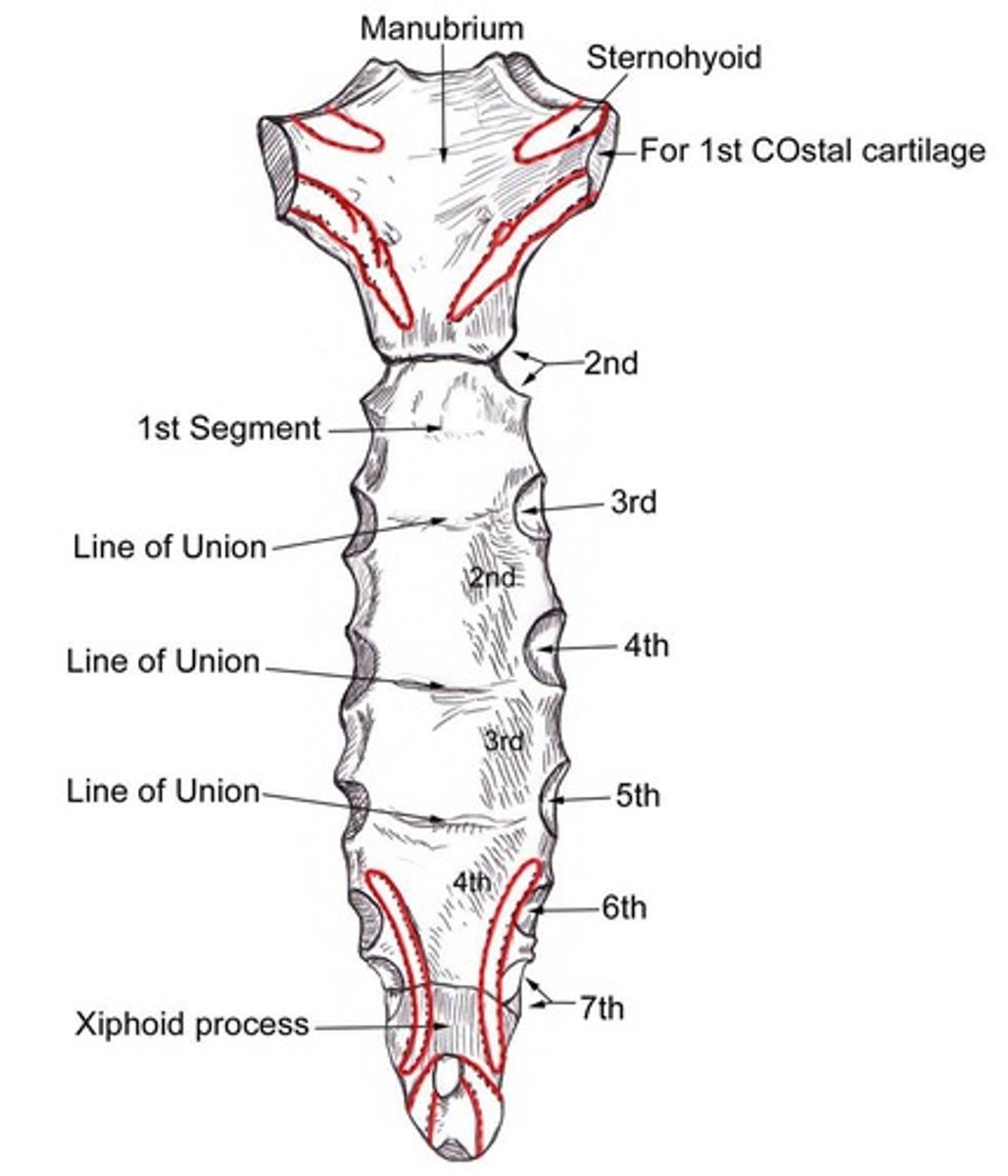
What is the most superior portion of the sternum?
The manubrium.
What does the manubrium articulate with?
The first two pairs of ribs and the clavicles.
What is the significance of the angle of Louis?
It is the articulation of the body and the manubrium, located at T4-T5.
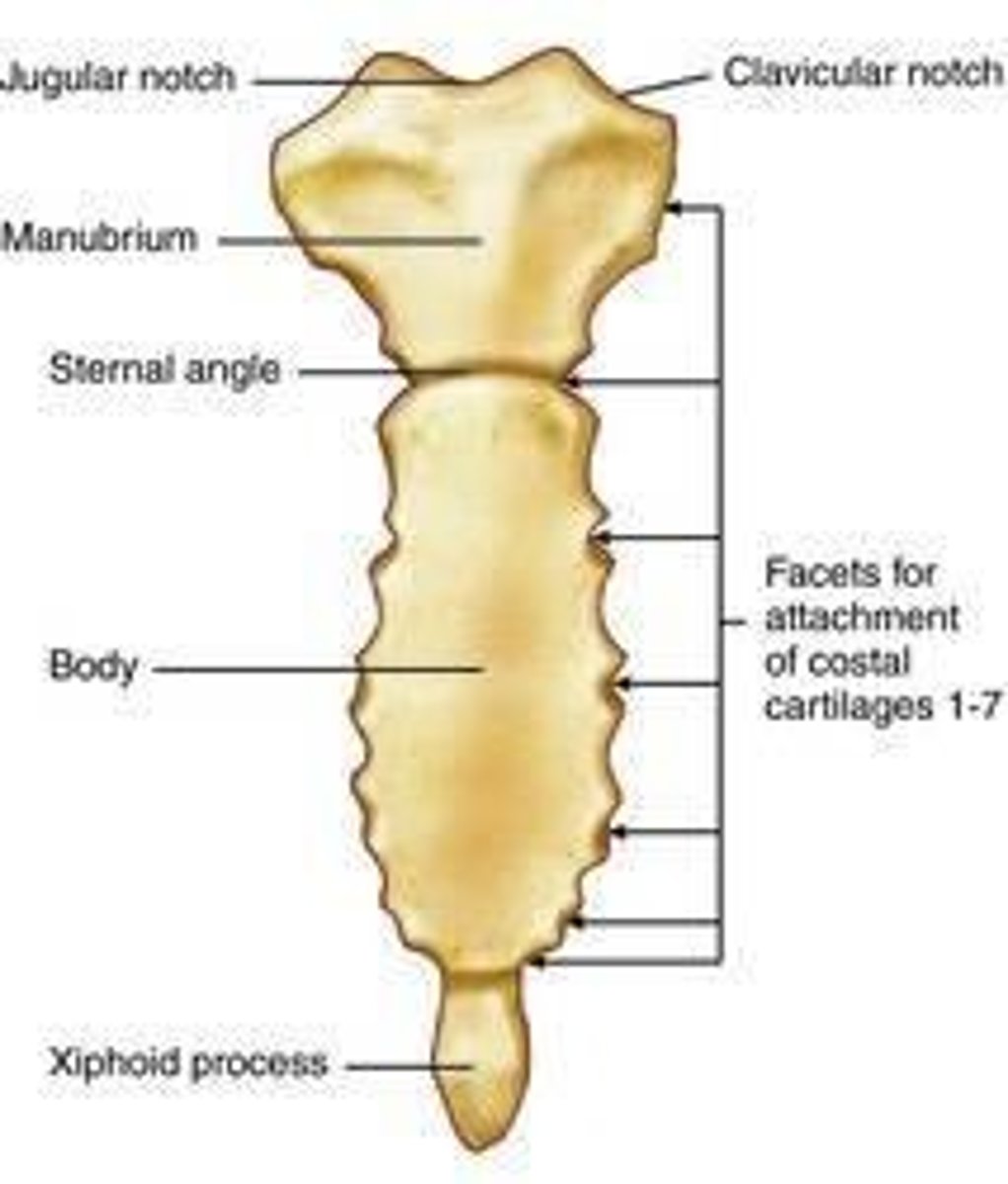
What ribs does the body of the sternum articulate with?
The 3rd through 7th ribs.
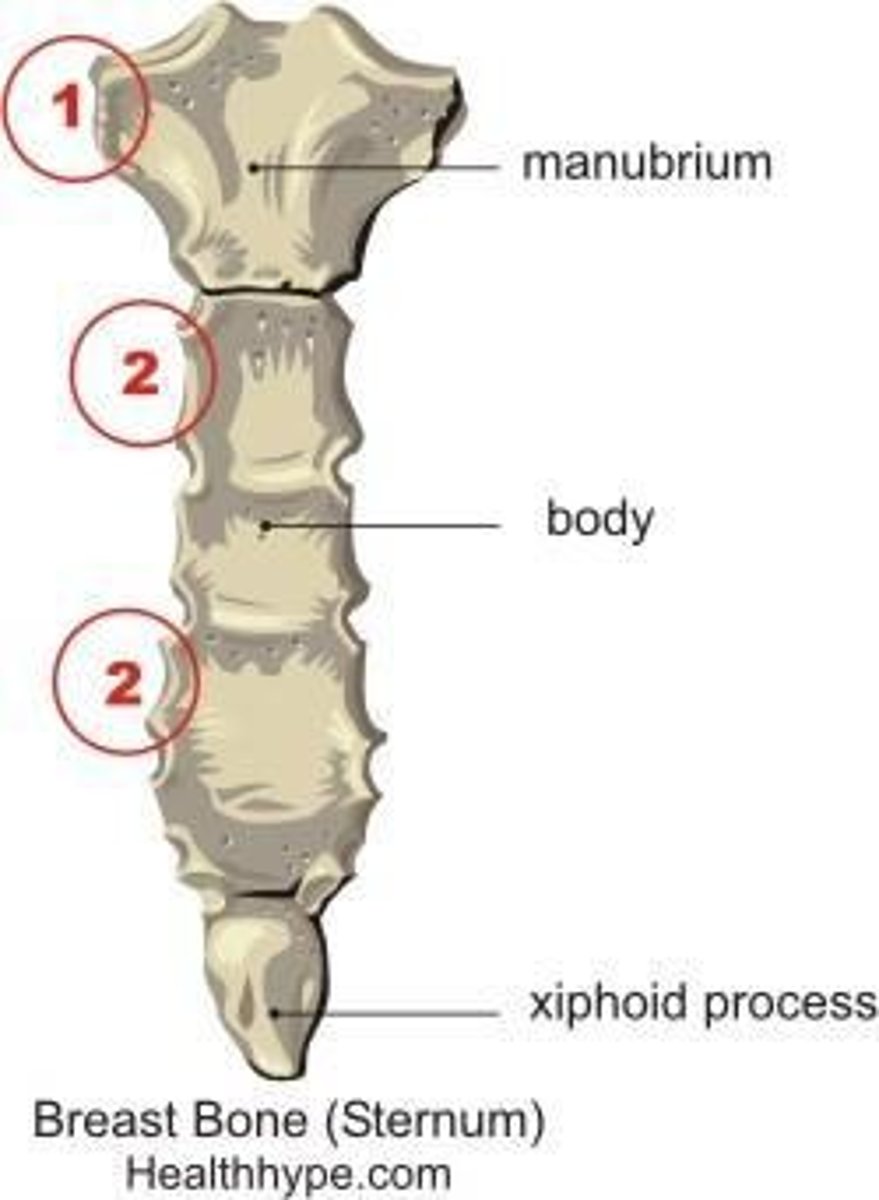
What is the xiphoid process and where is it located?
It is the inferior part of the sternum, located at T9-T10, and serves as a site for muscle attachment.
How many pairs of ribs are there, and how are they categorized?
There are 12 pairs of ribs: 7 true ribs and 5 false ribs (8th to 12th pairs do not articulate with the sternum).
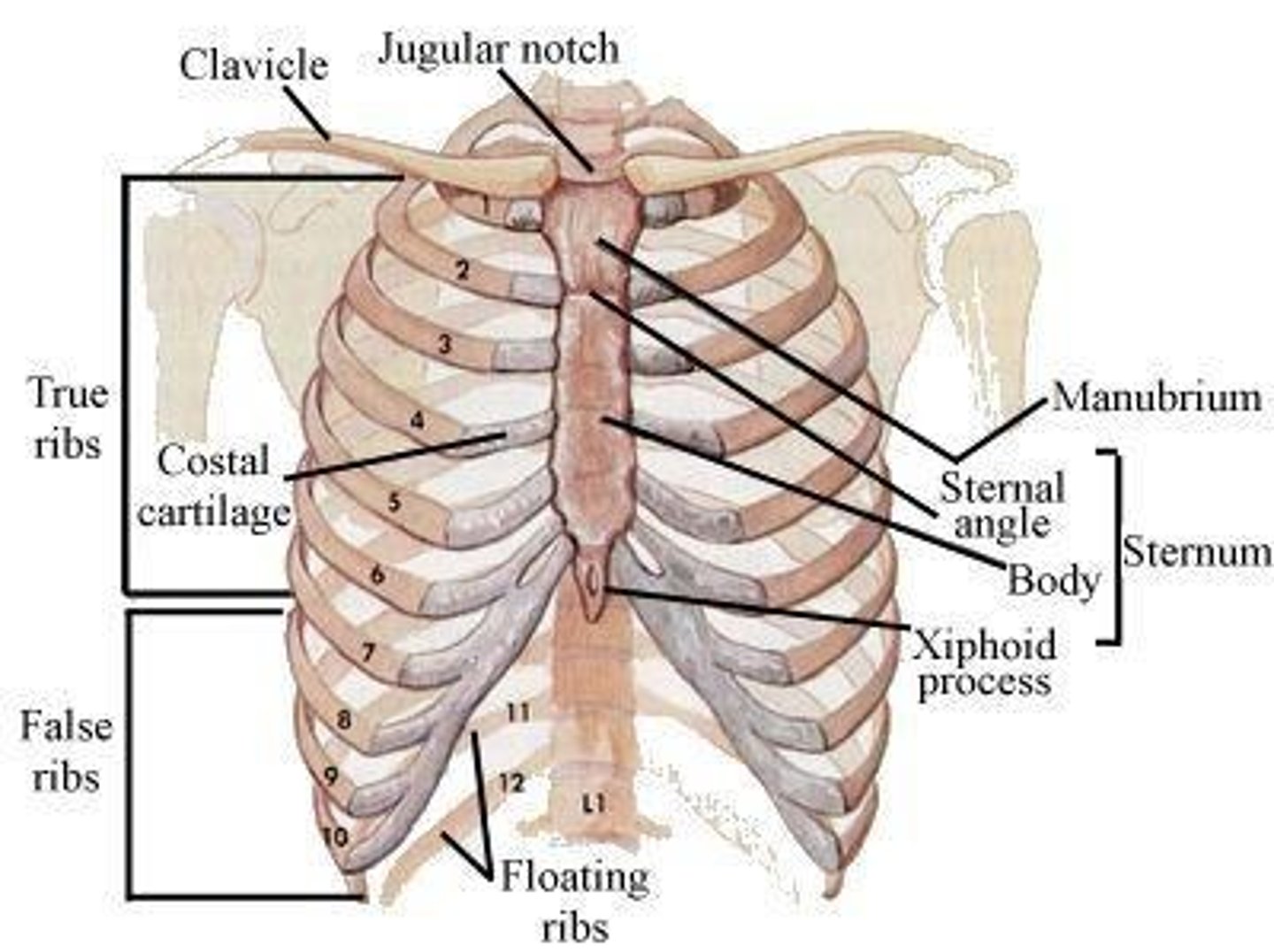
What are the floating ribs?
The 11th and 12th pairs of ribs that do not attach to the sternum.
What is the apex of the lungs?
The apex is located above the level of the first rib.
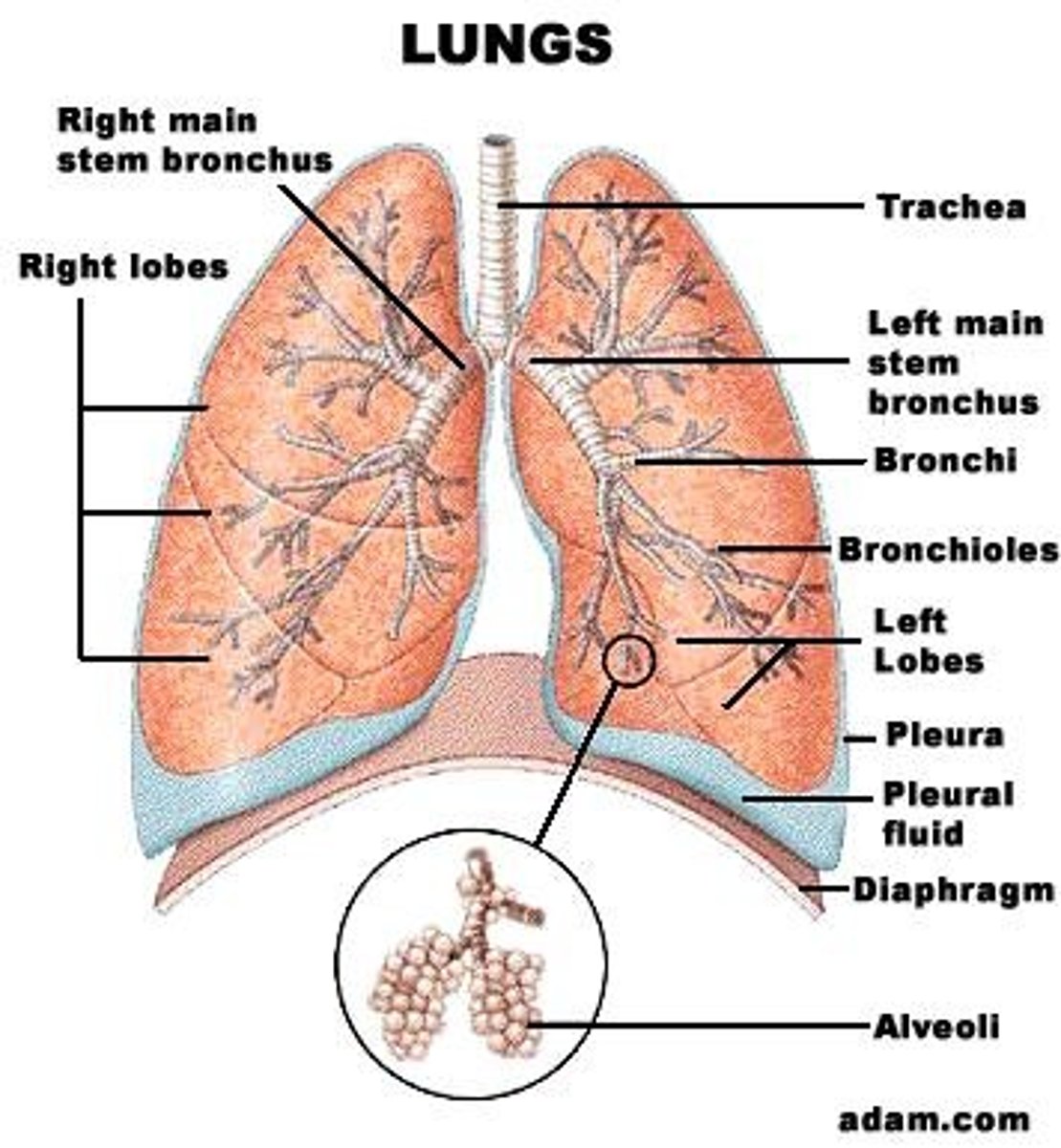
What is the cardiophrenic sulcus?
The medial angle of the lung.
What is the costophrenic sulcus?
The lateral angle of the lung.
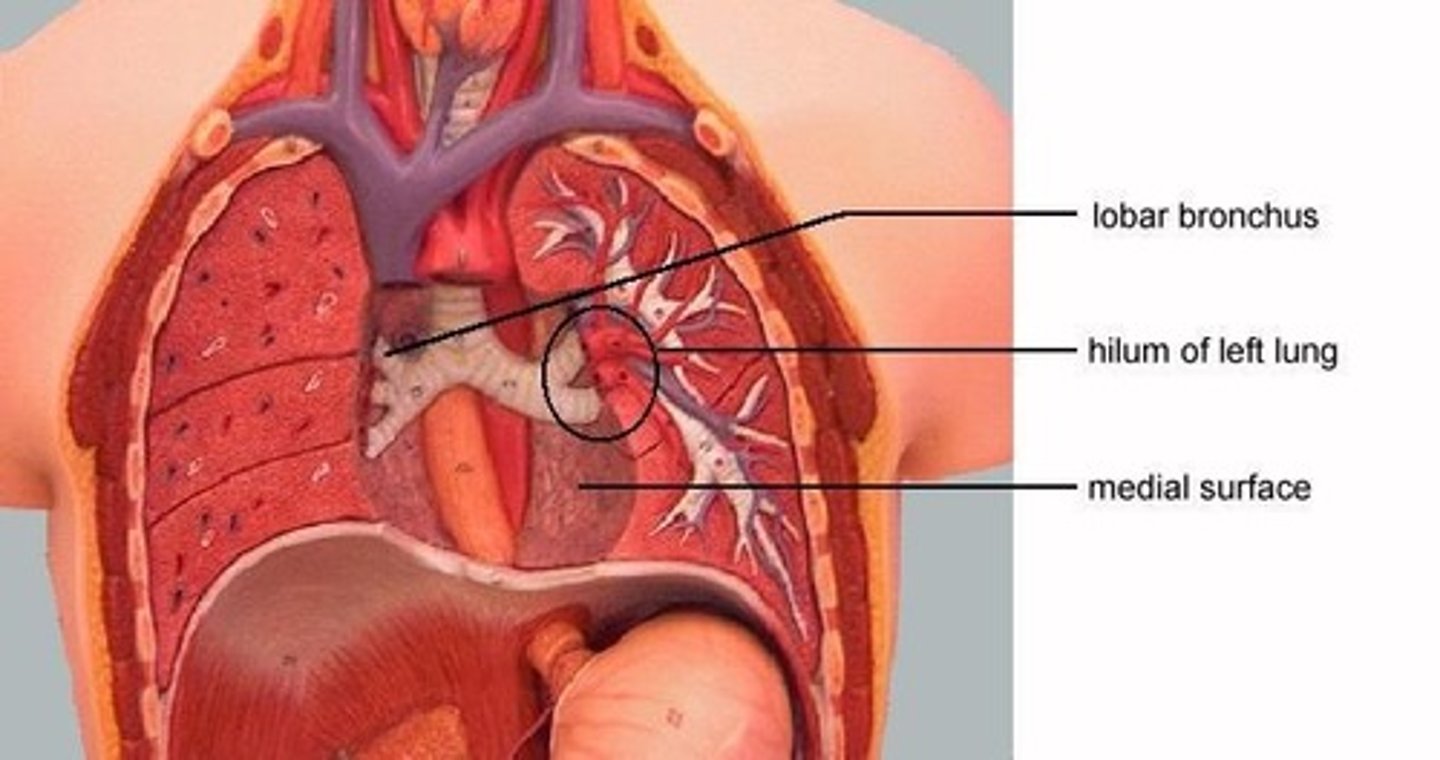
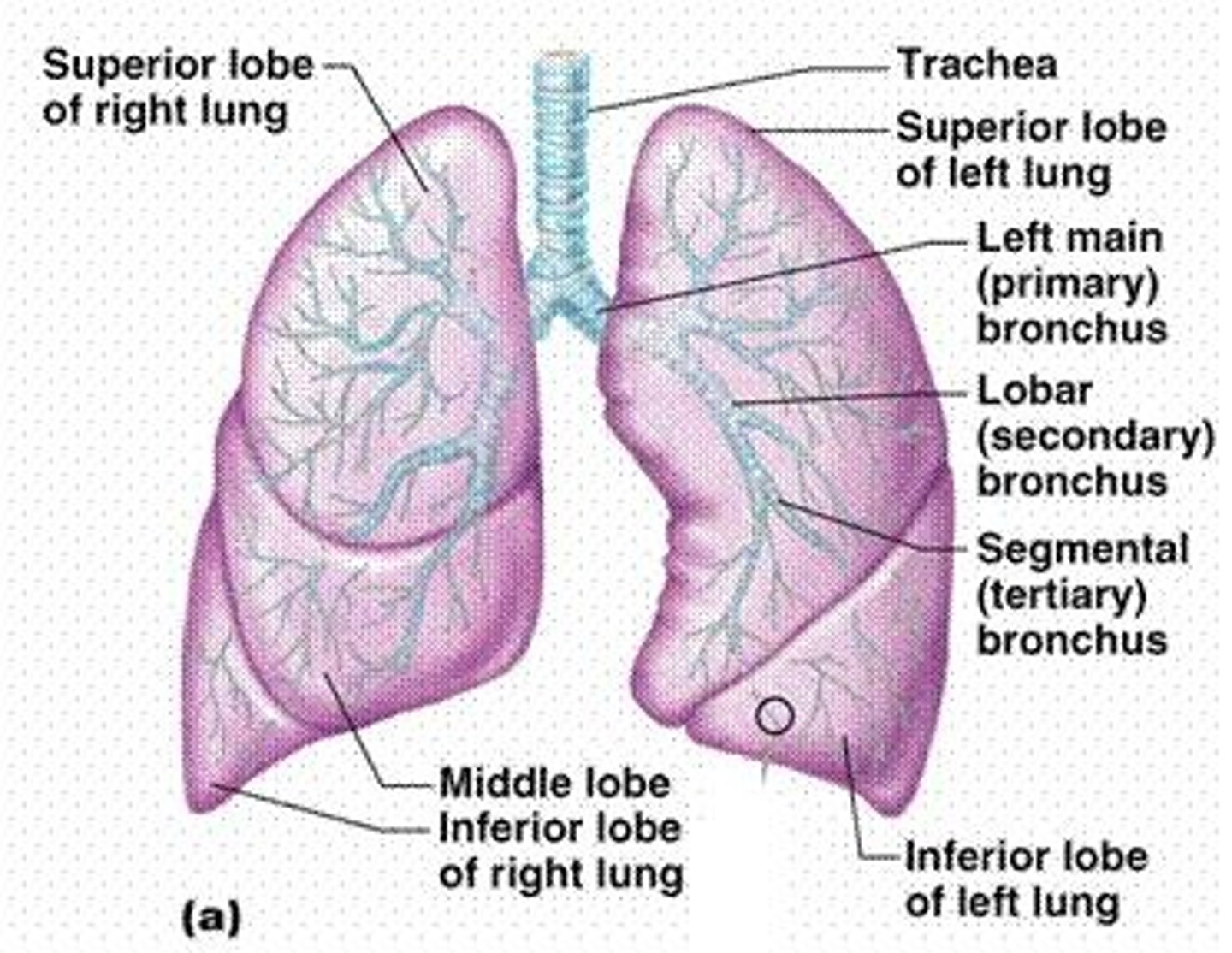
What is the hilum of the lung?
The area where blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerves enter and exit each lung.
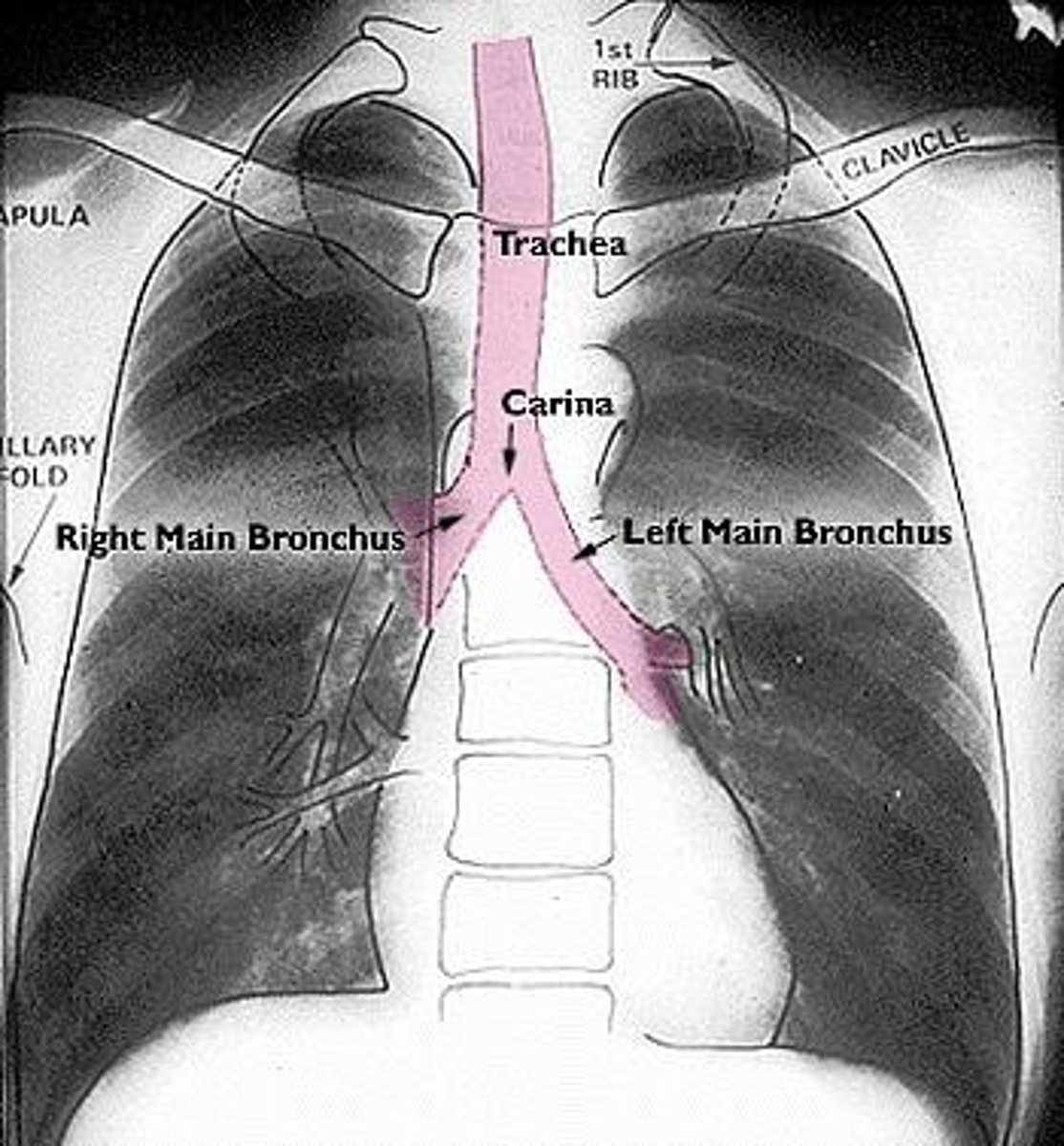
What is the carina and where is it located?
The bifurcation of the trachea at T4-T5.
What are the components of the bronchial tree?
Trachea, carina, main bronchi, secondary or lobar bronchi, segmental (terminal) bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli.
What structures are found in the mediastinum?
Thymus, trachea, esophagus, lymph nodes, thoracic duct, heart, and great vessels.
What is the thymus and its function?
It is located in the superior portion of the mediastinum behind the manubrium and is involved in T-lymphocyte maturation.
Where does the trachea run in relation to the esophagus?
The trachea runs anterior to the esophagus.
What is the diaphragm and its location?
A dome-shaped muscular sheet located at T9-T10.
What are the two anatomical planes of the breast?
The sagittal plane (between the 2nd and 6th rib) and the axial plane (from the sternochondral junctions to the midaxillary line).
What is the average diameter of the breast at its base?
10 to 12 cm, with a thickness of 5 to 6 cm.
What are the three layers of breast tissue?
Subcutaneous layer (skin and fat), mammary layer (glandular tissue and ducts), and retromammary layer (muscle and connective tissue).
What are Cooper's ligaments?
Connective tissue in the breast that helps maintain structural integrity.
What are the two views used in breast imaging?
MLO view and CC view.
What is the function of ligaments in relation to the breast?
Ligaments are firmly attached to the dermis of the skin and anchor the breast.
What bones make up the shoulder girdle?
Clavicle, scapula, and humerus.
What is another name for the clavicles?
Collar bones.
What does the sternal end of the clavicle articulate with?
The clavicular notch of the sternum (SC Joint).
What does the acromial end of the clavicle articulate with?
The acromial process of the scapula (AC Joint).