APUSH: Colonial America
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Period 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
mercantilism
An economic policy where the colonies provided raw materials to Britain and bought back finished goods to enrich the mother country
Ben Franklin urged the 13 colonies not to agree with it through the cut up snake cartoon
Name the 13 colonies
New York, New Hampshire, New Jersey (New), Virginia, Georgia ,Maryland (sisters), North Carolina, South Carolina (twins), Pennsylvania, Delaware, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island (Please Don’t Call My Room)
Name the New England colonies
Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire
Name the middle colonies
Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, Delaware
Name the Southern colonies
Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia
(South Carolina having black population majority)
Which are the more religious tolerant colonies?
PA and RI (top), Maryland, NJ, DE next
Who was the first governor of Boston (the Massachusetts colony)
John Winthrop
What was the motto did the Massachusetts colony live by? (they were to be a …)
City upon a hill
Who was the man to settle in Roanoke Island?
Sir Walter Raleigh (Raa-lee)
What is the House of Burgesses?
Elected general assembly of citizen representatives in local government
What are the Navigation Acts?
They are the rules that England made to control how colonies traded with other countries. They operated as salutary neglects (not strictly enforced)
What was the primary economy of the New England colonies?
Commerce, shipbuilding, fishing
What was the primary economy of the middle colonies?
Staple crops (wheat corn) on family farms
What was the primary economy of the southern colonies?
cash crops (indigo, tobacco, rice) reliance on slavery
What was the triangular trade?
a system of transatlantic trade that connected Europe, Africa, and the Americas
Europe to Africa: manufactured goods
Africa to Americas: slaves
Americas to Europe: raw materials
Middle Passage: brutal transatlantic voyage on which enslaved Africans were forcibly transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade
Who is the founder of Rhode Island?
Roger Williams
He was a strong advocate for the separation of church and state (state should not interfere in religious matters)
Who is Anne Hutchinson?
The female leader who was also banished from Massachusetts
She preached the idea that God communicated directly to individuals instead of through the church elders
(Also most likely she’s female)
What happened to the Roanoke Colony?
The people vanished when John White (grandfather of the 1st person born in the Americas to British parents) came to find them. It was the mystery of the Lost Colony
Who founded the first permanent English settlement, Jamestown, in North America?
The Virginia Company of London (a group of merchants) or London Company
Why did the first settlers did not survive well in Jamestown?
Undrinkable water
Disease-carrying mosquitoes
Settlers more focused on searching for gold than building houses or planting food
How did Captain John Smith, the first governor, helped salvage the Jamestown situation?
His work ethic “He that will not work shall not eat.”
What happened to the settlement after John Smith left?
The Starving Time began and many died
What was the cash crop that helped Virginia to get back on its feet?
Tobacco
Who is John Rolfe?
The first Jamestown settler to grow/export tobacco, husband of Pocahontas
What happened after the Virginia Company showed inability to protect settlers (shown by the 1622 Indian Massacre) or make enough money?
King James revoked their charter and Jamestown became a royal colony (king in charge)
Name the three types of colonies
1) joint-stock colonies (chartered)
2) Proprietary Colonies
3) Crown Colonies (royal)
Who started Connecticut?
Thomas Hooker, a minister who disagreed with John Winthrop’s leadership
Who was the charter of Maryland given to (from King Charles I)?
George Calvert, Lord Baltimore (later became a proprietary colony)
What was Maryland first meant for?
The Catholics, to be a safe place from the Protestants
What actions did Lord Baltimore carry out to protect the Catholics?
The Act of Tolerance (1649) making it illegal to persecute Christians (1654 act was revoked by Protestant-led government
Who was the last Dutch governor of New Amsterdam?
Peter Stuyvesant
How did New York end up to belong to the English?
The Dutch (who were living in New Amsterdam) were unprepared for attack from the English, surrendered
Only Stuyvesant had desire to fight the English
How was New York named?
The colony was given to the Duke of York (later King James II) as a proprietary colony
Who was the founder for Pennsylvania?
William Penn, a Quaker
How did Pennsylvania come about?
Land given to him by King Charles II for repayment of debts the king owed his father
“sylvania”=woods
What is the biggest difference between the Quakers and Puritans?
Quakers believe that there is an inner light in everyone, so they do not believe in predestination like the Puritans
Who founded Georgia?
James Oglethorpe (he got a charter from King George - namesake of the colony)
What was the reason for James Oglethorpe to found Georgia?
For poor debtors who had regained freedom to have a new start in life
What is the Great Migration of 1620?
It was the large-scale movement of people (mostly Puritans), primarily from England to New England, between 1620 and 1640 to create a perfect religious utopia (freedom, idyllic place)
John Winthrop told the Puritans that their society would be regarded as "a city upon a hill." But before that, there would always be inequalities of wealth and power, that some people would always be in positions of authority, and that others would be dependent. What did he really mean?
He meant that the Puritans should accept f the traditional belief that social order depended on a system of ranks
What is it like for white women in colonial America?
considered politically and socially unequal to their husbands
only allowed to work in “lower trades” like seamstress, or help in husband’s business
restricted in holding property and making legal contracts after marriage
Not eligible to run for political office
Not allowed to be ordained as ministers.
American Colonization Society: What did it do?
The American Colonization Society (ACS), founded in 1816, aimed to resettle free African Americans in Africa (move from America BACK to Africa)
Overall, England was able to establish successful colonies more than others in the 1700s because
they had crucial advantages over European rivals, like their navy and growing economy (cash crops)
they also live in tightly clustered communities
Many New England colonial families have these traits
a social institution that provided vocational training
a hierarchical institution in which the father represented the source of authority
a basic farming unit
a social institution that cared for the needy and the poor
(They mostly operate as a family unit rather than work “outside”)
What is the use of slave labor in Virginiain the 17th century?
It spread rapidly in the late-seventeenth century, as enslaved Africans replaced European indentured
Where did Peter Minuit “purchase” from the Algonquin?
Manhattan
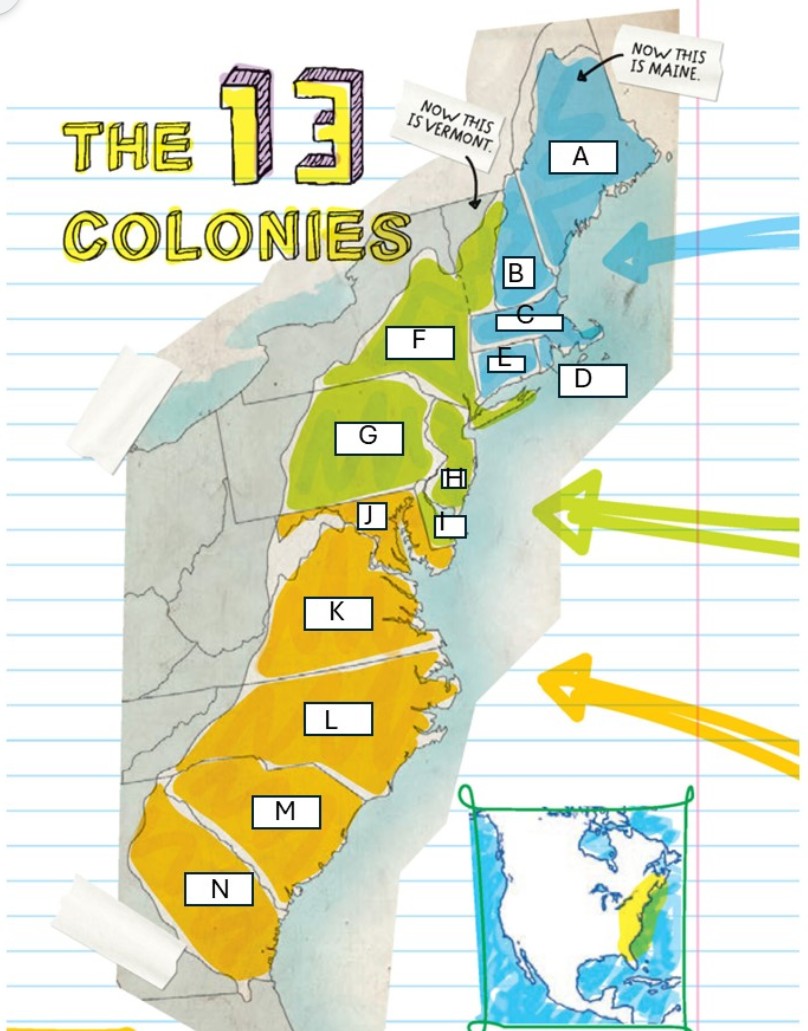
Name the colonies
A: Massachusetts (later became something else)
B: New Hampshire
C:Massachusetts (remained as MA)
D:Rhode Island
E:Connecticut
F: New York
G:Pennsylvania
H:New Jersey
I: Delaware
J:Maryland
K:Virginia
L:North Carolina
M:South Carolina
N:Georgia
King Philip’s War (1675-1676)
Indians (ended with Metacom killed) VS British
to establish English control over the Indians in New England