LC CHEMISTRY- BONDING
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
compound
a substance that is made up of two or more different elements combined chemically together
state the "Octet Rule"
when bonding occurs, atoms tend to reach an electron arrangement with eight electrons in the outermost energy level
exceptions to octet rule
transition metals usually do not obey the octet rule
hydrogen lithium beryllium tend to achieve two electrons in the outermost energy level instead of eight
Elements in Group I of the Periodic Table..
+1 charge as they lose their 1 outermost electron
Elements in Group II of the Periodic Table..
+2 charge as they lose their 2 outermost electrons
Elements in Group III of the Periodic Table...
+3 charge as they lose their 3 outermost electrons
what are positive ions called
cations
Explain whats going on in the picture
to fulfil the octet rule sodium lost its valence electron in its outer shell. Sodium atom 2,8,1 to Sodium ion 2,8
Elements in Group VI of the Periodic Table..
-2 charge as they gain 2 electrons
Elements in Group VII of the Periodic Table..
-1 charge as they gain 1 electron
what are negative ions called
anions
describe whats going on in this picture
to fulfil the octet rule fluorine gained an electron in its outer shell. Fluorine atom 2,7 to Fluoride ion 2,8
ionic bond definition
the force of attraction between oppositely charged ions in a compound, always formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another
what do we use to show ionic bonding in a compound
dot and cross diagram
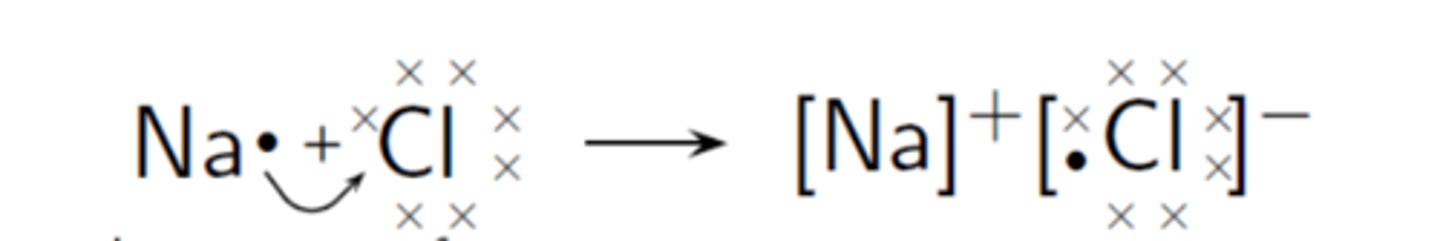
whats going on in the image here
the valence electron of na is transferring to the incomplete outer shell of cl, to fulfil octet rule
charges in a ionic compound are
always neutral
3 pieces of info on the Crystal Structure of Sodium Chloride
3d arrangement of ions called a crystal lattice
each sodium ion is surrounded by 6 chloride ions
each chloride ion is surrounded by 6 sodium ions
when writing the formula of any (transition complex etc) ionic compounds
-positive ion goes first
-find which group each of the elements are from
-work how much they lose or gain
-find lcm of the charges
-add necessary coefficients
complex ion definition
an ion made up of two or more different atoms
complex ion name: Hydroxide ion
write the....
Formula:
charge:
OH- 1-
complex ion name: Nitrate ion
Formula:
charge:
NO3- 1-
complex ion name: Hydrogencarbonate ion
Formula:
charge:
HCO3- 1-
complex ion name: Permanganate ion
Formula:
charge:
MnO4- -1
complex ion name: Carbonate ion
Formula:
charge:
CO3^2- 2-
complex ion name: Chromate ion
Formula:
charge:
CrO4^2- 2-
complex ion name: Dichromate ion
Formula:
charge:
Cr2O7^2- 2-
complex ion name: Sulphate ion
Formula:
charge:
SO4^2- 2-
complex ion name: Sulphite ion
Formula:
charge:
SO3^2- 2-
complex ion name: Thiosulphate ion
Formula:
charge:
S2O3 2-
complex ion name: Phosphate ion
Formula:
charge:
PO4^3- 3-
complex ion name: Ammonium ion
Formula:
charge:
NH4+ 1+
where are transition metals located
d block except scandium and zinc
why are the transition metals special what properties makes them special
used as catalysts
can make different ions with different charges e.g Mn(II) (IV) (VII)
can form coloured compounds
how to name the compounds given in formula form
look at the charges and work backwards
covalent bonding definition
when bonding electrons are being shared between atoms
molecule definition
a group of atoms joined together, it is the smallest particle of an element or compound that can independently exist
valency definition
the number of atoms of hydrogen which the element will combine with (outmost shell babes)
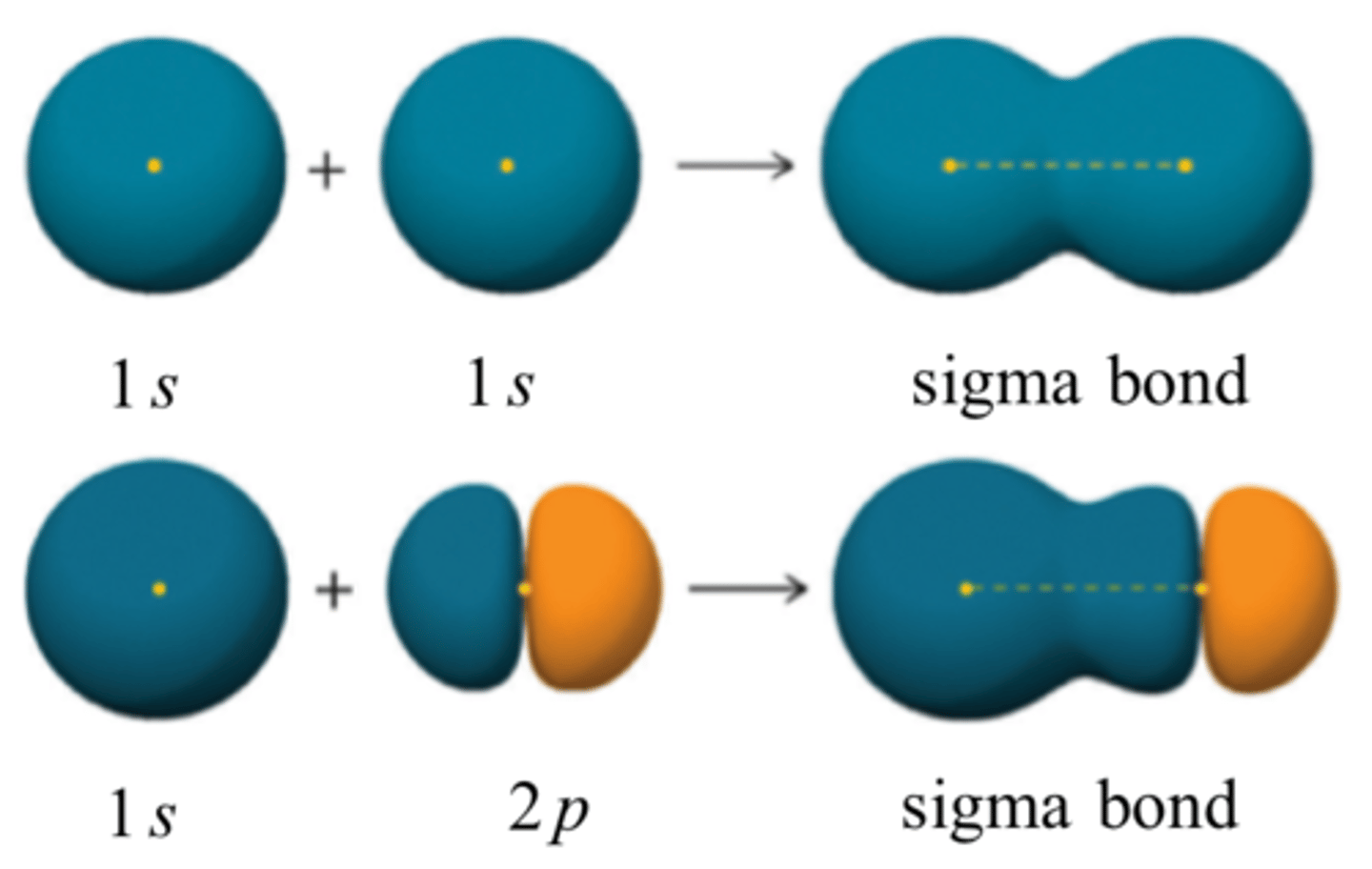
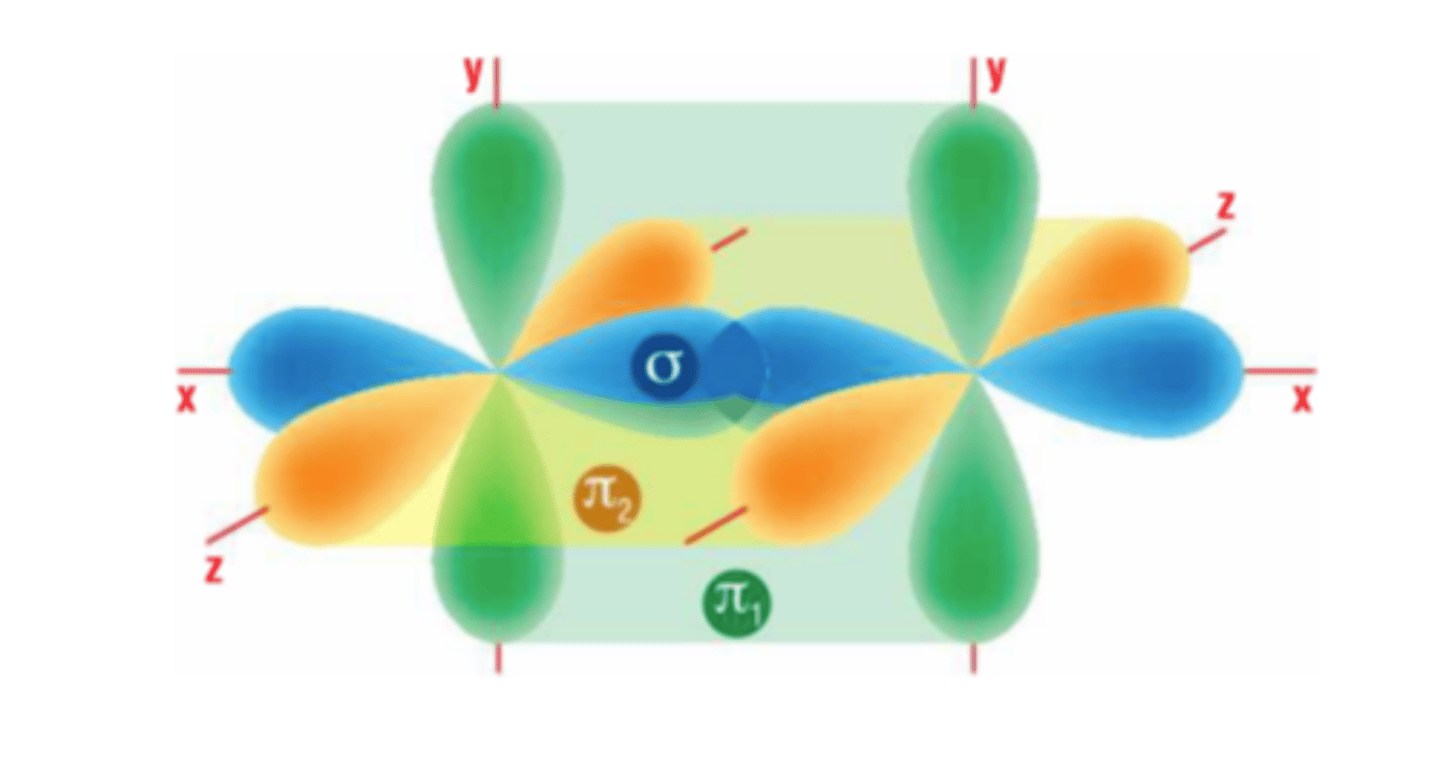
sigma bonding
head on overlap of atomic orbitals
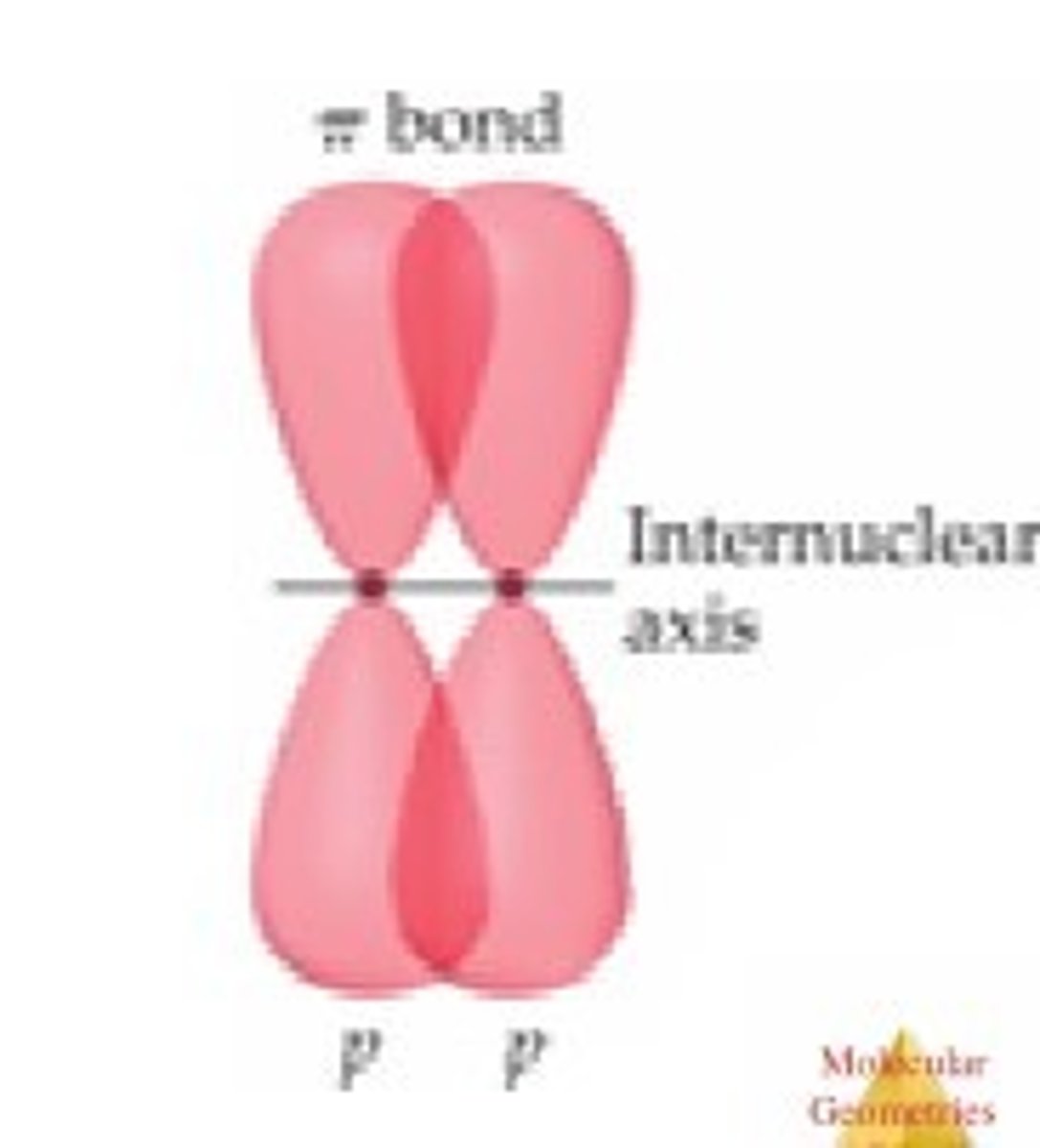
pi bonding
sideways overlap of p orbitals
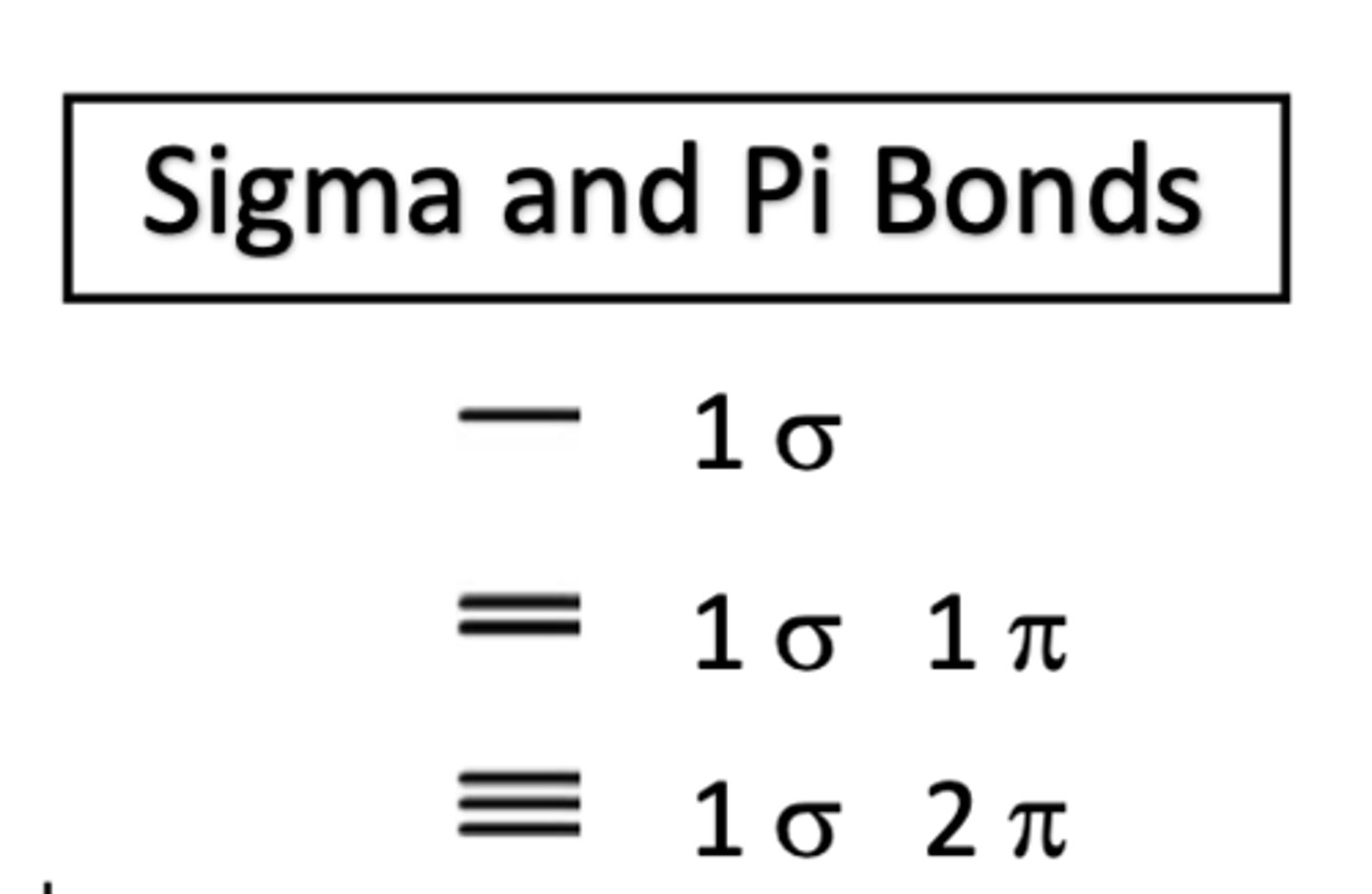
single bond
1 sigma bond
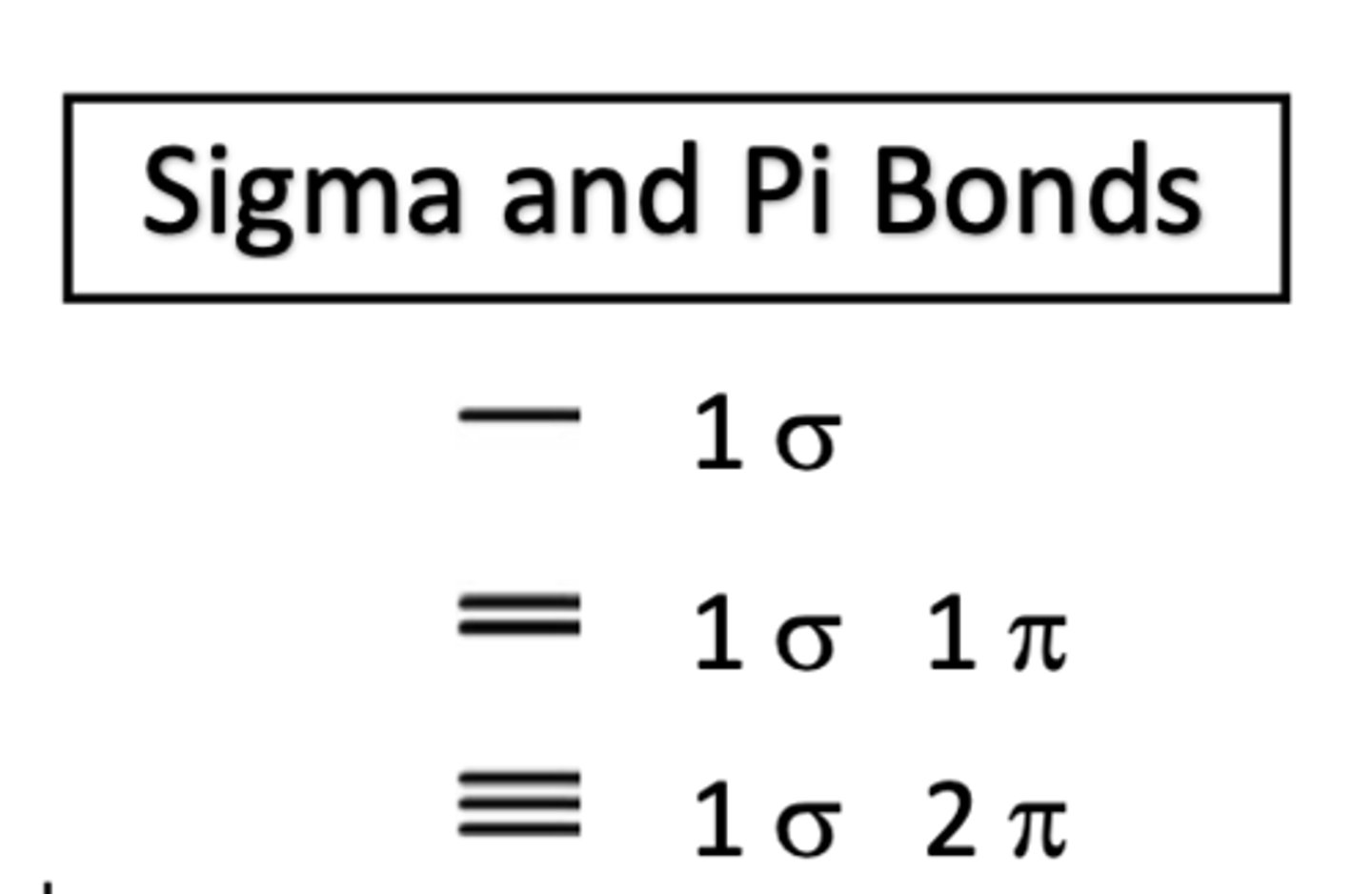
double bond
1 sigma bond 1 pi bond
triple bond
1 sigma bond and 2 pi bonds
ionic compound properties
hard and brittle
high melting and boiling point
solid at room temperature
conducts electricity when molten or dissolved in water
covalent compound properties
soft
low melting and boiling points
liquids, gases or soft solids at room temperature
do not conduct electricity
what theory do we use to predict the shapes of covalent molecules
valence shell electron pair repulsion theory
how do we carry out the theory
1 carry out dot and cross diagram of molecule in question
2 count how many bond pairs electrons are around the central atom of the molecule
3 count how many lone pairs electrons are around the central atom of the molecule
4 use number of bond and lone pair to find shape
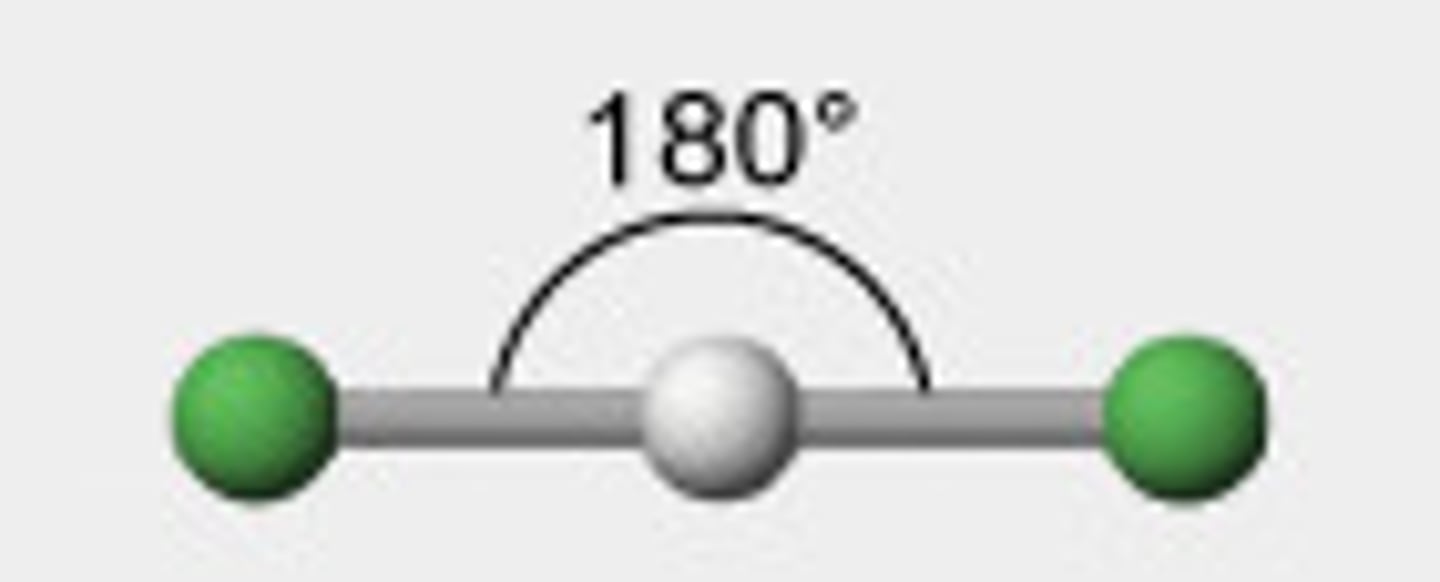
shape: linear
no. bond pairs:
no lone pairs:
bond angles:
2 0 180
shape: V shaped
no. bond pairs:
no lone pairs:
bond angles:
2 2 104.5
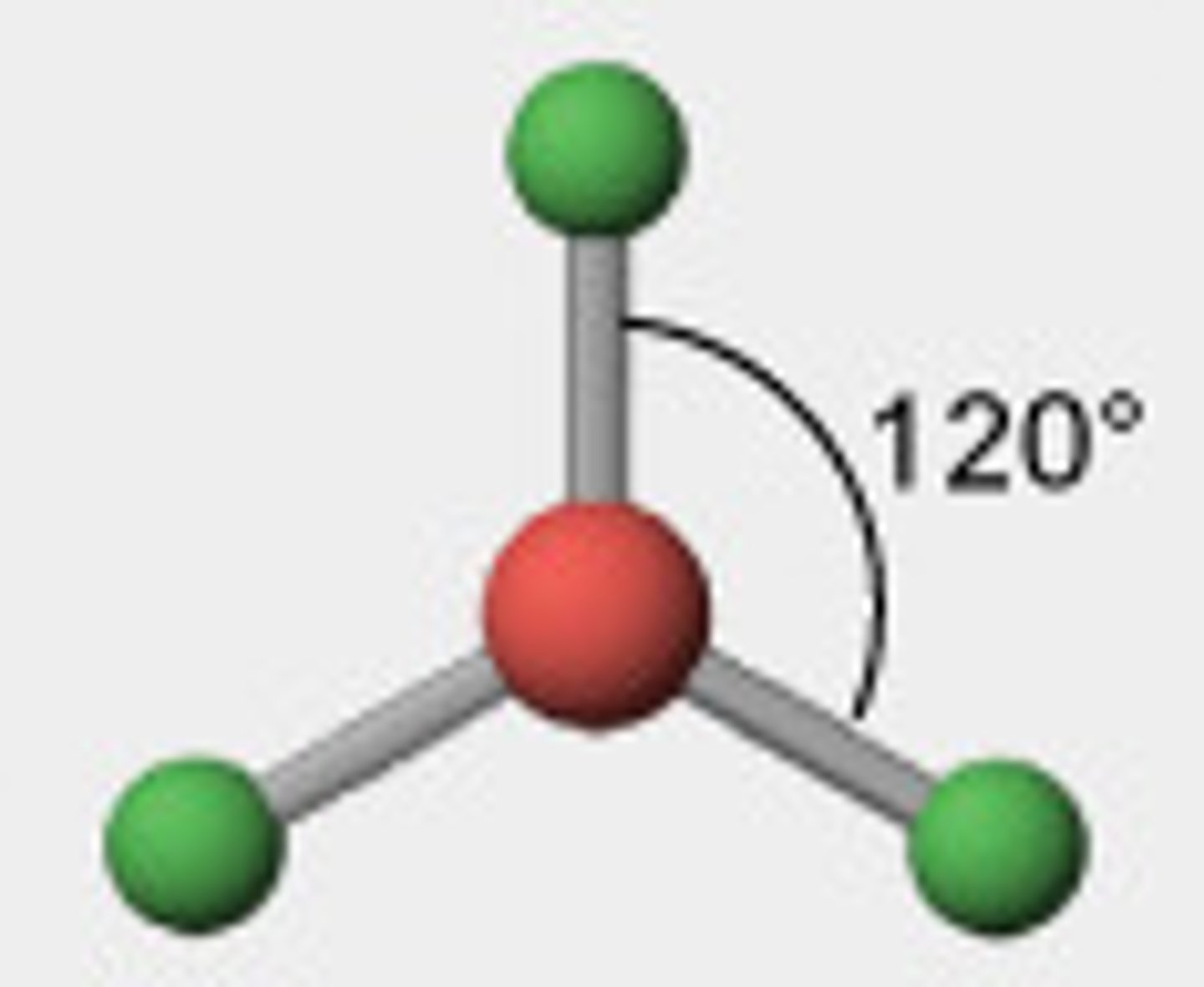
shape: Triangular
no. bond pairs:
no lone pairs:
bond angles:
3 0 120
shape: Pyramidal
no. bond pairs:
no lone pairs:
bond angles:
3 1 107
shape: Tetrahedral
no. bond pairs:
no lone pairs:
bond angles:
4 0 109.5
Electronegativity
is the relative attraction that an atom in a molecule has for the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond
non polar covalent bond
atoms in molecule all equally shared
polar covalent bond
atoms in molecule not equally shared, one end is slightly positive and the other end is slightly negative
how to find electronegative of a molecule
1 find lectronegativity of the molecule
2 use pauling scale to determine electronegaitvy
nonpolar bond on pauling scale
0.0 - 0.4
polar bond on pauling scale
0.4-1.7
ionic bond on pauling scale
> 1.7
how do we prove water is polar
water is polar, by placing a charged plastic rod near a thin stream of water (from a burette, if the rod is positively charged, the water molecules will spin so that the negative end of the water molecule is facing the rod, causing an attraction (SAY THE OPPOSITE TOO)
Intramolecular Bonding DEFINITION
bonding that takes place within a molecule e.g covalent bonding
Intermolecular Forces/Bonding definition
forces of attraction that exist between molecules
Intermolecular Forces/Bonding 3 examples order in weakest to strongest
van der waals forces
dipole-dipole forces
hydrogen bonding
van der waals forces definition
these are weak attractive forces between molecules caused by temporary dipoles
van der waals forces explaination
-in non-polar molecules the constant movement of electrons can create a slight negative charge on one side and a slight positive charge on the other, this temporary dipole can induce a similar dipole in nearby molecules, leading to attraction between them
-get stronger for bigger molecules
-the stronger the vwf on molecule higher the boiling and metal point
dipole dipole forces definition
forces of attraction between the negative pole of one polar molecule and the positive pole of another polar molecule
dipole dipole forces explaination
stronger intermolecular forces that occur between non polar molecule
the more electronegative atom in a molecule gains a partial negative charge, while the less electronegative atom gains a partial positive charge. + on one molecule is attracted to the - on nearby molecule, creating a dipole dipole attraction often shown with a dotted line
Hydrogen Bonds definition
particular types of dipole dipole attractions between molecules in which hydrogen atoms are bonded to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, hydrogen atom carries a partial positive charge and is attracted to the
electronegative atom (n, o or f) in another molecule
Hydrogen Bonds explaintion
hydrogen bonding is the strongest form of intermolecular force because of the big electronegativity
difference between the atoms
intermolecular bonding is...
much weaker than covalent bonds
how to answer exam q's with this
when given list of compounds and boiling
find which intermolecular forces they are
non-polar molecule → Van der Waals.
Polar molecule, but no H bonded to N, O, or F?→ Dipole-Dipole.
Polar molecule, with H bonded to N, O, or F? → Hydrogen Bonding.